Biotech 9 Part 2
Biotech 9 Part 2
Uploaded by
semalmarezCopyright:
Available Formats
Biotech 9 Part 2
Biotech 9 Part 2
Uploaded by
semalmarezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Biotech 9 Part 2
Biotech 9 Part 2
Uploaded by
semalmarezCopyright:
Available Formats
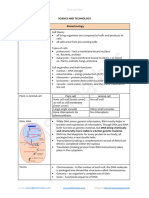
DNA TECHNOLOGY Micropipette - used to accurately and precisely transfer
volumes of liquid in the microliter range.
- use of DNA to improve quality of life
1. Gel Electrophoresis
the study and manipulation of genetic material
-device used for profiling DNA fragments based on size and
- use of DNA to answer unknown questions about life electric charge in an electric field.
specially for the treatment of disease
2. Restriction enzymes (molecular scissors)
2 types of DNA technology
- an enzyme isolated from bacteria that cuts
With recombinant DNA
- DNA molecules at specific sequences
- creates DNA hybrid or altered genes
3. DNA Ligase (genetic paste)
- DNA are isolated from two different cells and joined
together that do not normally occur - Specific type of enzyme that facilitates the joining if DNA
strands together
Without recombinant
4. Host
- Do not warrant the use of creation of recombinant DNA
- enables the multiplication of molecular sequence
- genes may only be isolated, identified, sequenced and
amplified - Prokaryotic host or Eukaryotic host
TYPES OF DNA TECHNOLOGY 5. Plasmid
* With recombinant DNA - commonly known as vectors
modify - Genetic engineering - serves as tool to clone, transter, and manipulate genes
fix - Gene and radiation therapy 6. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
medicine - Pharmacogenomics - a laboratory technique used to amplify DNA sequences
unnatural - Making of GMOs
* Without recombinant Genetic Engineering
characteristics - DNA screening - also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation
identity - DNA fingerprinting - direct organism's biotechnology
twin - Gene/human/cell cloning manipulation genes an using process of using recombinant
natural - Selective breeding - DNA (rDNA) technology to alter the genetic makeup of an
organism
COMMONLY USED TOOLS IN GENETIC ENGINEERING
Autoclave - The main purpose of this device is to sterilize
materials and media under pressure and steam. GMO vs Transgenic Organism
Centrifuge - This device is mainly used in cell culture, nucleic * GMO
acid isolation and in microbiology to separate two liquids in
emulsion form or suspended solids in liquids by the help of GMO is an organism that possesses a genetically modified
the centrifugal force. genome.
UV light - Used to view the separated fragments of DNA in * Transgenic Organism
gel electrophoresis set up.
Transgenic organism is a CMO, but carries DNA sequences or
genes received from a different organism.
Foreign DNA Process of Cloning a Gene in a Bacterial Plasmid
* GMO 1. Isolation of vector and gene-source DNA. - gene of interest
May or may not have foreign DNA 2. Insertion of DNA into the vector. - hybrid DNA
* Transgenic Organism 3. Introduction of the cloning vector into cells. -deliberation
of hybrid DNA
Have foreign DNA
4. Cloning of cells (and foreign genes). - amplification of
genes
Transgenic Organism 5. Identifying cell clones with the right gene. - field testing
- organisms that have altered genomes
- most transgenic organisms are generated in the laboratory Genetically Modified Organisms
for research purposes
British company Oxitec has created genetically modified
- genes of one species can be modified, or genes can be male mosquitoes that carry a "self limiting gene". When they
transplanted from one are released into the wild and mate with females their
offspring do not reach adulthood, so crucially do not
contribute to the spread of the Zika virus. Other researchers
Tracy the Sheep, 1997 are looking at using genetic modification to curb the spread
of malaria.
First transgenic animal to produce a recombinant protein
drug in her milk alpha Engineered to grow at twice the rate of regular salmon, it is
also believed to be the first example of a genetically
-1-antitrypsin (AAT) treatment for emphysema and cystic engineered animal bred and sold for human consumption.
fibrosis.
FLAVR SAVR tomato (1987)
Goats that Produce Important Proteins in their Milk
The FLAVR SAVR™ tomato was developed through the use of
- Goats modified to produce FDA-approved human antisense RNA to regulate the expression of the enzyme
antithrombin (ATryn), which is used to treat a rare blood polygalacturonase (PG) in ripening tomato fruit.
clotting disorder in humans. Goats have also been
genetically modified to produce spider silk, one of the Arctic Apple
strongest materials known to man, in their milk. Proposed
Browning is caused by the release of polyphenol oxidase
uses for this recombinant spider silk range from artificial
(PPO). The gene for PPO release is activated during times of
tendons to bulletproof vest.
stress (slicing, biting, throwing / By identifying the gene that
Golden Rice is responsible for PPO release, biotechnology is used to
silence that gene.
Modified rice that produces beta-carotene, the precursor to
vitamin A. Vitamin A deficiency is a public health problem for
millions of people around the world, particularly in Africa
Steps in DNA Manipulation
and Southeast Asia. Golden rice is still waiting regulatory
approval. In order to produce recombinant DNA, following are
requires:
BT Corn
* Gene of interest, which is to be cloned
These GE plants produce crystal (Cry) proteins or toxins
derived from the soil bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), * Molecular scissors, to cut out the gene of interest
hence the common name "Bt maize".
* Molecular carrier (vector), on which gene of interest could
be placed
* An expression system, on which the gene of interest along is now open. The process of joining these two pieces
with the vector is then introduced as a result of which a together using the enzyme DNA ligase is ligation. The
specific product is made resulting DNA molecule is a hybrid of two DNA molecules -
the interest molecule and the vector. In the terminology of
How to get a genes: genetics this intermixing of different DNA strands is called
recombination.
In the process of recombinant DNA technology, first of all
we'll have to get a gene which is to be cloned. There are two Hence, this new hybrid DNA molecule is also called a
ways to get the gene of interest. recombinant DNA molecule and the technology is referred
to as the recombinant DNA technology.
* To Isolate It from The Chromosome: Genes can be isolated
from the chromosomes by cutting the chromosomes on the 5. Insertion of Recombinant DNA into Host - In this step, the
flanking sites of the gene using special enzymes known as recombinant DNA is introduced into a recipient host cell
restriction endonucleases. mostly, a bacterial cell. This process is called transformation.
Bacterial cells do not accept foreign DNA easily. Therefore,
* Chemical Gene Synthesis by Messenger RNA (mRNA): If
they are treated to make them competent to accept new
the genes are small or for some reason we can't isolate from
DNA. The processes used may be thermal shock, Cat+ ion
chromosomes, they can also be synthesized chemically in
treatment, and electroporation.
the laboratory. To make a gene chemically in laboratory,
messenger RNA (mRNA) is used. We'll use the reverse Ways of Hybrid DNA deliberation
transcriptase enzyme method. Reverse transcriptase is the
enzyme which forms DNA from an RNA template in reverse * Bacteria - transformation- exposure to heat and cold to
transcription. This DNA molecule is called complementary open up and close the bacterial pores
DNA (cDNA) and is mainly associated with retro viruses.
* Plants - exposure to radiation (particle bombardment
device) exposure to Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Steps of Genetic Recombination Technology * Animals - microinjection
1. Isolation of Genetic Material - involves enzymes such as 6. Isolation of Recombinant Cells-The transformation
restriction enzymes. process generates a mixed population of transformed and
non-transformed host cells. The selection process involves
2. Restriction Enzymes Digestion - technique 'Agarose Gel filtering the transformed host cells only. For isolation of
Electrophoresis' reveals the progress of the restriction recombinant cells from non-recombinant cells, a marker
enzyme digestion - it allows separating and cutting out the gene of the plasmid vector is employed.
digested DNA fragments. The vector DNA is also processed
using the same procedure. 7. Obtaining or culturing the Foreign Gene product - When
you insert a piece of alien DNA into a cloning vector and
3. Amplification Using PCR transfer it into a bacterial cell, the alien DNA gets multiplied.
The ultimate aim is to produce a desirable protein
PCR reactions are run on thermal cyclers using the following
expression.
components:
The cells harboring cloned genes of interest are grown on a
•Template - DNA to be amplified
small scale in the laboratory. These cell cultures are used for
• Primers - small, chemically synthesized oligonucleotides extracting the desired protein using various separation
that complementary to a region of the DNA. techniques.
•Enzyme - DNA Polymerase
•Nucleolides - needed to extend the primers by the enzyme.
The cut fragments of DNA can be amplified using PCR and
then ligated with the cut vector.
4. Ligation of DNA Molecules - The purified DNA and the
vector of interest are cut with the same restriction enzyme.
This gives us the cut fragment of DNA and the cut vector that
You might also like
- Basic Principles of Hurricane Resistant HousingDocument39 pagesBasic Principles of Hurricane Resistant HousingaojacksonNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Recombinant DNA Technology (173865)Document69 pagesBasic Principles of Recombinant DNA Technology (173865)Yap Jacky80% (5)
- Summary & Study Guide - A Crack in Creation: Gene Editing and the Unthinkable Power to Control EvolutionFrom EverandSummary & Study Guide - A Crack in Creation: Gene Editing and the Unthinkable Power to Control EvolutionNo ratings yet
- PT2234 - Configuring Initial Switch Settings: Part 1: Verify The Default Switch ConfigurationDocument2 pagesPT2234 - Configuring Initial Switch Settings: Part 1: Verify The Default Switch ConfigurationmanNo ratings yet
- MAZDA Tribute - Instrukcja Obslugi (2003) ENGDocument245 pagesMAZDA Tribute - Instrukcja Obslugi (2003) ENGjszbpNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument11 pagesReviewerJaja BalicantaNo ratings yet
- DNA Genetic EngineeringDocument72 pagesDNA Genetic EngineeringEmman Matthew GregorioNo ratings yet
- Transgenic OrganismsDocument3 pagesTransgenic OrganismsGalino Julia Cristine A.No ratings yet
- Bio 3Document3 pagesBio 3CameronNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio-Q1Document5 pagesGen Bio-Q1hilaryblancelinsanganNo ratings yet
- vt59.2708-21424810576 - 1098526164484586 - 5189445820608338690 - n.pdfLESSON-1-and-2-RECOMBINANT-DNA-and-its - 8Document30 pagesvt59.2708-21424810576 - 1098526164484586 - 5189445820608338690 - n.pdfLESSON-1-and-2-RECOMBINANT-DNA-and-its - 8CameronNo ratings yet
- 2.5.9 Genetic EngineeringDocument44 pages2.5.9 Genetic EngineeringHanung PujanggaNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument3 pagesGenetic EngineeringjackybuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- 2 5 9-Genetic-EngineeringDocument42 pages2 5 9-Genetic-EngineeringsoffiahNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio-Q1Document5 pagesGen Bio-Q1hilaryblancelinsanganNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering Unit IDocument49 pagesGenetic Engineering Unit Ihabeebullakhan069No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument5 pagesGenetic EngineeringDe Juan, Angela Marie G.No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument43 pagesGenetic EngineeringGeonyzl L. AlviolaNo ratings yet
- MIC 210 Basic Molecular Biology: Dna CloningDocument46 pagesMIC 210 Basic Molecular Biology: Dna CloningDrAhmedSalimNo ratings yet
- Identification and Isolation of Gene of InterestDocument19 pagesIdentification and Isolation of Gene of InterestKhushnood FatimaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Technology: What You'll LearnDocument29 pagesGenetic Technology: What You'll LearnYadiNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 NotesDocument3 pagesGen Bio 2 NotesEmil CaridoNo ratings yet
- 07 Notes Genetic EngineeringDocument38 pages07 Notes Genetic Engineeringzymofii228No ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and Processes - OP and ASIR SeminarDocument26 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes - OP and ASIR Seminarasirmohammed2019No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument8 pagesGenetic EngineeringWynne Cassandra JoverNo ratings yet
- Micro BiotechDocument28 pagesMicro Biotechreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Rekayasa Genetik, Konsultasi Genetik Dan Terapi GeneDocument124 pagesRekayasa Genetik, Konsultasi Genetik Dan Terapi GeneRollyRiksantoNo ratings yet
- GB2 Lesson 1 and 2Document109 pagesGB2 Lesson 1 and 2mitch anne c desquitadoNo ratings yet
- BS10003 Lecture8 Genetic EngineeringDocument37 pagesBS10003 Lecture8 Genetic EngineeringUpal MazumderNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument23 pagesBiotechnology Principles and ProcessesRoshan KumarNo ratings yet
- Lec-6 Cloning & RDNA-2 & CDNADocument26 pagesLec-6 Cloning & RDNA-2 & CDNARukaiya Islam Roza 2121526649No ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering Part 3 and 4Document42 pagesGenetic Engineering Part 3 and 4KSHITIJ K GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- GB2 4. Producing GMOsDocument47 pagesGB2 4. Producing GMOsMehaela Pearl MendezNo ratings yet
- Genetic TechnologyDocument36 pagesGenetic TechnologyAnggraeni Kusuma Wardani100% (1)
- Genetic EngineeringDocument40 pagesGenetic EngineeringRalph Vincent De MesaNo ratings yet
- BME 203 - Lecture No. 18-19Document45 pagesBME 203 - Lecture No. 18-19SagorNo ratings yet
- General Biology 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 4th QuarterSandy SarajosNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering TechnologyDocument51 pagesGenetic Engineering TechnologyAzeleah Nosil VilladiegoNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Tech For UploadDocument32 pagesRecombinant DNA Tech For Uploadathishshubhan05No ratings yet
- 06-Genomics, Proteomics, and Genetic EngineeringDocument4 pages06-Genomics, Proteomics, and Genetic EngineeringBen AbellaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles & ProcessesDocument14 pagesBiotechnology Principles & ProcessesKhushi GuleriaNo ratings yet
- 1GENETICSDocument30 pages1GENETICSJhunner BuanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology)Document4 pagesGenetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology)Geo NalobNo ratings yet
- PPT DNA Recombineering TechnologyDocument22 pagesPPT DNA Recombineering TechnologyNurida FajriahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Genetic EngineeringDocument41 pagesChapter 9 Genetic EngineeringmlNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Dasar Teknik DNA RekombinanDocument39 pagesPrinsip Dasar Teknik DNA RekombinanAyu RahmaniaLestaryNo ratings yet
- 02 S T Lyst9400Document18 pages02 S T Lyst9400Anusha Rani YaramalaNo ratings yet
- 2.5.9 Genetic EngineeringDocument30 pages2.5.9 Genetic EngineeringFrancis SugueNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 ReviewerDocument11 pagesGen Bio 2 Revieweradriansobredo41No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 BiotechnologyDocument21 pagesChapter 9 BiotechnologyAtiya FalakNo ratings yet
- SHS Q2 WEEK 4 Describe the Process of Genetic EngineeringDocument44 pagesSHS Q2 WEEK 4 Describe the Process of Genetic Engineeringbernadette.pacana001No ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument3 pagesRecombinant DNABenedick CruzNo ratings yet
- Rekayasa Genetika - 1Document17 pagesRekayasa Genetika - 1Meri hardinaNo ratings yet
- Bot CC 408 (RDT)Document12 pagesBot CC 408 (RDT)Swagata GhoshNo ratings yet
- New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Revision Notes Chapter 27Document4 pagesNew Senior Secondary Mastering Biology Revision Notes Chapter 27yuu1957No ratings yet
- Analysing and ENGINEERING DNA, Genes, Cells and Organisms: (Ch. 19ish)Document29 pagesAnalysing and ENGINEERING DNA, Genes, Cells and Organisms: (Ch. 19ish)Matthew Hoang NguyenNo ratings yet
- CHEM 291 - Lecture No. 43-45Document45 pagesCHEM 291 - Lecture No. 43-45faiyaznoorshaelNo ratings yet
- Recent Trend in Cell BioDocument33 pagesRecent Trend in Cell BioJay DansNo ratings yet
- Biotech - Karuna MishraDocument81 pagesBiotech - Karuna Mishrabesthorrorshow203No ratings yet
- Genbio2 NotesDocument5 pagesGenbio2 NotesalliyahmuanaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in General Biology Ii Quarter 3, Week 1: Department of EducationDocument15 pagesActivity Sheets in General Biology Ii Quarter 3, Week 1: Department of EducationKashima KotaroNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Notes AP BiologyDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Notes AP Biologyjjj1111No ratings yet
- 2008 Teacher 20080131 2158Document24 pages2008 Teacher 20080131 2158RindoNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION MANUAL Akm 1 PDFDocument4 pagesSOLUTION MANUAL Akm 1 PDFRizka khairunnisaNo ratings yet
- LEGETHICS DIGEST (2 and 3) PDFDocument41 pagesLEGETHICS DIGEST (2 and 3) PDFPammyNo ratings yet
- Acc Ecg ChallengeDocument91 pagesAcc Ecg ChallengeMiguel LizarragaNo ratings yet
- Ali-Bondagjy v. ArtadiDocument3 pagesAli-Bondagjy v. ArtadiBananaNo ratings yet
- Performance and Characteristic Analysis of Double Gate Mosfet Over Single Gate MosfetDocument4 pagesPerformance and Characteristic Analysis of Double Gate Mosfet Over Single Gate Mosfetranvir singhNo ratings yet
- Set-I Course: PGS 505: Agricultural Research, Research Ethics and Rural DevelopmentDocument11 pagesSet-I Course: PGS 505: Agricultural Research, Research Ethics and Rural Developmentgouthami shivaswamyNo ratings yet
- Chapter III: The Revolving Door: Mexicans Welcomed In, Kicked Out, Invited Back As "Braceros", Kicked Out Again As "Wetbacks"Document34 pagesChapter III: The Revolving Door: Mexicans Welcomed In, Kicked Out, Invited Back As "Braceros", Kicked Out Again As "Wetbacks"Roy WardenNo ratings yet
- White Black Beige Simple Corporate Serifs PresentationDocument30 pagesWhite Black Beige Simple Corporate Serifs PresentationAMINTA MANZANILLANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic ConceptsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Basic ConceptsM Hussnain JavedNo ratings yet
- NLR77 TILT W Alum VanDocument1 pageNLR77 TILT W Alum Vanİåň ŞåböçöNo ratings yet
- Eco 201 F 12 SylDocument3 pagesEco 201 F 12 SylMandyWongNo ratings yet
- On TASAWWUF Ibn Ata Allah Al IskandariDocument8 pagesOn TASAWWUF Ibn Ata Allah Al IskandariNafisa ZamanNo ratings yet
- English Work PlanDocument12 pagesEnglish Work PlanIzza De LunaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Exposure of Cold Temperature On Hematological Parameters and Plasma Electrolytes of Cold Water Fish Shizothorax RichardsoniiDocument4 pagesImpact of Exposure of Cold Temperature On Hematological Parameters and Plasma Electrolytes of Cold Water Fish Shizothorax RichardsoniiBlagojaNo ratings yet
- Employee Engagement Practices in Hindustan Times: A Project Report ONDocument93 pagesEmployee Engagement Practices in Hindustan Times: A Project Report ONRakesh Sharma100% (1)
- Introduction To Tax LawDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Tax LawVijayant DalalNo ratings yet
- 2021chapter 1 MarketingDocument48 pages2021chapter 1 MarketingAptHouL AzizNo ratings yet
- Montnets RCS Introduction 20211007Document40 pagesMontnets RCS Introduction 20211007chee wyNo ratings yet
- Physics and Modeling of Microelectronic Devices: BITS PilaniDocument17 pagesPhysics and Modeling of Microelectronic Devices: BITS PilaniKrunalKapadiya1No ratings yet
- Publication 4Document4 pagesPublication 4ankitNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Triplex Slush PumpsDocument26 pagesService Manual: Triplex Slush PumpsActivos FijosNo ratings yet
- My Project SatarliteDocument33 pagesMy Project SatarlitesarjoonNo ratings yet
- Shri Sai Satcharitra in English Language (Concise or Prose Version)Document32 pagesShri Sai Satcharitra in English Language (Concise or Prose Version)saipmpatil100% (2)
- The New Normal For HealthDocument26 pagesThe New Normal For Healthkyle gerome BayotNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science N4 July 2017Document11 pagesEngineering Science N4 July 2017lilspectrex24No ratings yet
- Elements of Art PaintingDocument102 pagesElements of Art PaintingAlexandria Masangkay100% (3)
- Hospital Pharmacy Activity 6, 7Document9 pagesHospital Pharmacy Activity 6, 7Alyssa Marie Petonio BialaNo ratings yet