0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 viewsPandas Cheat Sheet
Pandas Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Ananda SaikiaThe document provides information about data analysis and visualization using Pandas. It covers topics like loading and exporting data, data wrangling operations, merging and aggregating data, and creating basic visualizations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Pandas Cheat Sheet
Pandas Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Ananda Saikia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views2 pagesThe document provides information about data analysis and visualization using Pandas. It covers topics like loading and exporting data, data wrangling operations, merging and aggregating data, and creating basic visualizations.
Original Title
pandas-cheat-sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document provides information about data analysis and visualization using Pandas. It covers topics like loading and exporting data, data wrangling operations, merging and aggregating data, and creating basic visualizations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views2 pagesPandas Cheat Sheet
Pandas Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Ananda SaikiaThe document provides information about data analysis and visualization using Pandas. It covers topics like loading and exporting data, data wrangling operations, merging and aggregating data, and creating basic visualizations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
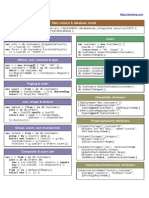
Data export Set tick marks:
labels = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'] Pandas
cheat sheet
Data as NumPy array: positions = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0]
df.values plt.xticks(positions, labels)
plt.yticks(positions, labels)
Save data as CSV file:
df.to_csv('output.csv', sep=",") Select area to plot: All of the following code examples refer to this table:
plt.axis([0.0, 2.5, 0.0, 10.0])
Format a data frame as tabular string: # [from x, to x, from y, to y] df=
df.to_string() col1 col2
Label diagram and axes:
Convert a data frame to a dictionary: plt.title('Correlation') A 1 4
df.to_dict() plt.xlabel('Nunstück')
plt.ylabel('Slotermeyer') B 2 5
Save a data frame as an Excel table:
df.to_excel('output.xlsx') Save most recent diagram: C 3 6
plt.savefig('plot.png')
(requires package xlwt) plt.savefig('plot.png', dpi=300)
plt.savefig('plot.svg') Getting started
Visualization Import pandas:
import pandas as pd
Import matplotlib:
import pylab as plt Create a series:
s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['A', 'B', 'C'],
Start a new diagram: name='col1')
plt.figure()
Create a data frame:
Scatter plot: data = [[1, 4], [2, 5], [3, 6]]
df.plot.scatter('col1', 'col2', style='ro') index = ['A', 'B', 'C']
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=index,
Bar plot: columns=['col1', 'col2'])
df.plot.bar(x='col1', y='col2', width=0.7)
Load a data frame:
Area plot: df = pd.read_csv('filename.csv',
df.plot.area(stacked=True, alpha=1.0) sep=',',
names=['col1', 'col2'],
Box-and-whisker plot: index_col=0,
df.plot.box() encoding='utf-8',
Text by Kristian Rother, Thomas Lotze (CC-BY-SA 4.0) nrows=3)
Histogram over one column:
df['col1'].plot.hist(bins=3) https://www.cusy.io/de/seminare
Selecting rows and columns
Histogram over all columns:
df.plot.hist(bins=3, alpha=0.5) Select single column:
df['col1']
Select multiple columns: Merge multiple data frames horizontally: Count unique values:
df[['col1', 'col2']] df3 = pd.DataFrame([[1, 7], [8, 9]], df['col1'].value_counts()
index=['B', 'D'],
Show first n rows: columns=['col1', 'col3']) Summarize descriptive statistics:
df.head(2) df.describe()
Only merge complete rows (INNER JOIN):
Show last n rows: df.merge(df3)
df.tail(2) Hierarchical indexing
Left column stays complete (LEFT OUTER JOIN):
Select rows by index values: df.merge(df3, how='left') Create hierarchical index:
df.loc['A'] df.stack()
df.loc[['A', 'B']] Right column stays complete (RIGHT OUTER JOIN):
df.merge(df3, how='right') Dissolve hierarchical index:
Select rows by position: df.unstack()
df.loc[1] Preserve all values (OUTER JOIN):
df.loc[1:] df.merge(df3, how='outer')
Aggregation
Merge rows by index:
Data wrangling df.merge(df3, left_index=True, right_index=True) Create group object:
g = df.groupby('col1')
Filter by value: Fill NaN values:
df[df['col1'] > 1] df.fillna(0.0) Iterate over groups:
for i, group in g:
Sort by columns: Apply your own function: print(i, group)
df.sort_values(['col2', 'col2'], ascending=[False, True]) def func(x): return 2**x
df.apply(func) Aggregate groups:
Identify duplicate rows: g.sum()
df.duplicated() g.prod()
Arithmetics and statistics g.mean()
Identify unique rows: g.std()
df['col1'].unique() Add to all values: g.describe()
df + 10
Swap rows and columns: Select columns from groups:
df = df.transpose() Sum over columns: g['col2'].sum()
df.sum() g[['col2', 'col3']].sum()
Remove a column:
del df['col2'] Cumulative sum over columns: Transform values:
df.cumsum() import math
Clone a data frame: g.transform(math.log)
clone = df.copy() Mean over columns:
df.mean() Apply a list function on each group:
Connect multiple data frames vertically: def strsum(group):
df2 = df + 10 Standard devieation over columns: return ''.join([str(x) for x in group.values])
pd.concat([df, df2]) df.std() g['col2'].apply(strsum)
You might also like
- ChatGPT Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesChatGPT Cheat SheetAt Rial100% (27)
- HANA Performance AnalysisDocument130 pagesHANA Performance Analysissunil.h.v14112100% (1)
- How To Upload and Download Files Programmatically To Azure Blob Storage UsingDocument17 pagesHow To Upload and Download Files Programmatically To Azure Blob Storage UsingJuan CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Codecademy SQLDocument11 pagesCodecademy SQLapi-362845526No ratings yet
- Customized Text Search in ACCE Using IBM® Content Search ServiceDocument35 pagesCustomized Text Search in ACCE Using IBM® Content Search Serviceeliseu.drummondNo ratings yet
- ,Document1 page,Aid FatušićNo ratings yet
- Python Seaborn Tutorial - Jupyter NotebookDocument19 pagesPython Seaborn Tutorial - Jupyter NotebookAnil MalikNo ratings yet
- Python Web Server With FlaskDocument11 pagesPython Web Server With Flaskyash kumarNo ratings yet
- Acceleo User GuideDocument56 pagesAcceleo User GuiderrefusnikNo ratings yet
- Data Science Course ContentDocument8 pagesData Science Course ContentQshore online trainingNo ratings yet
- R Cheat Sheet 3 PDFDocument2 pagesR Cheat Sheet 3 PDFapakuniNo ratings yet
- Python PresentationDocument71 pagesPython Presentationhariskoh100% (1)
- Pyspark IQ FREE GuideDocument57 pagesPyspark IQ FREE GuideRISHABH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Arrays & StringsDocument76 pagesArrays & StringsVipul KaliaNo ratings yet
- Day 1 S2Document24 pagesDay 1 S2Shailaja UdtewarNo ratings yet
- MySQL AssignmentDocument4 pagesMySQL AssignmentsumitNo ratings yet
- XMLDocument90 pagesXMLrahulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Visualization in PythonDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Data Visualization in PythonudayNo ratings yet
- List Comprehension in PythonDocument8 pagesList Comprehension in PythonAhsan NaeemNo ratings yet
- Array and String-StudentsDocument33 pagesArray and String-StudentsCarlos Vicente E. TorralbaNo ratings yet
- 14-Lesson Cloudera HiveDocument9 pages14-Lesson Cloudera Hiveadchy7No ratings yet
- Python For Non-Programmers - 1-1Document19 pagesPython For Non-Programmers - 1-1Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Resume - SujanGyawali - Full Stack Python DeveloperDocument3 pagesResume - SujanGyawali - Full Stack Python Developerjethalal.gujaratiNo ratings yet
- Tuple Data Structure PDFDocument8 pagesTuple Data Structure PDFRajendra BuchadeNo ratings yet
- Pandas: ImportDocument13 pagesPandas: Importhello100% (1)
- Maya PythonDocument10 pagesMaya PythonRiya GowarikarNo ratings yet
- Summary of Python Commands PyProg 1819aDocument16 pagesSummary of Python Commands PyProg 1819afitNo ratings yet
- Advanced PythonDocument204 pagesAdvanced PythonpkpshantibiharNo ratings yet
- Figure Style and Scale: Darkgrid Whitegrid Dark White Ticks DarkgridDocument15 pagesFigure Style and Scale: Darkgrid Whitegrid Dark White Ticks DarkgridmaaottoniNo ratings yet
- Bad IdeasDocument69 pagesBad IdeasArmin RonacherNo ratings yet
- 250+ TOP MCQs On SQL Queries and Answers - QuizDocument1 page250+ TOP MCQs On SQL Queries and Answers - QuizSanjib Biswas (193014012)No ratings yet
- Columbia Seaborn TutorialDocument12 pagesColumbia Seaborn TutorialPatri ZioNo ratings yet
- Set 1 - Fundamental Questions Date: - 13/05/2020 Version: - 1.0 Total: - 50 QuestionsDocument51 pagesSet 1 - Fundamental Questions Date: - 13/05/2020 Version: - 1.0 Total: - 50 QuestionsNARASIMHA CHARYNo ratings yet
- Fourth Semester General Course Paper: Microprocessors Architecture and ProgrammingDocument79 pagesFourth Semester General Course Paper: Microprocessors Architecture and ProgrammingSANAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- DWV Unit1Document102 pagesDWV Unit1Ujwal mudhirajNo ratings yet
- C Cheatsheet CodeWithHarry PDFDocument11 pagesC Cheatsheet CodeWithHarry PDFRace VinDieselNo ratings yet
- Resume PDFDocument1 pageResume PDFtestmailforbughuntingNo ratings yet
- Python Decorators PDFDocument6 pagesPython Decorators PDFRajendra BuchadeNo ratings yet
- Model Field Reference Django Documentation DjangoDocument20 pagesModel Field Reference Django Documentation DjangoMusa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Automation Cheat Sheet 2.0Document6 pagesAutomation Cheat Sheet 2.0Ananda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Python FunctionDocument22 pagesPython Functionelezear repilNo ratings yet
- Groovy in ActionDocument18 pagesGroovy in Actionapi-3997953No ratings yet
- Python Interview UsecasesDocument33 pagesPython Interview UsecasesAkash NawinNo ratings yet
- Datastage Transformer FunctionsDocument71 pagesDatastage Transformer FunctionsAnonymousHPNo ratings yet
- Python TutorialsDocument205 pagesPython TutorialsdineshkumarenggNo ratings yet
- Python RegexDocument8 pagesPython RegexUtkarsh PathakNo ratings yet
- Web Scraping Cheat Sheet 2.0Document3 pagesWeb Scraping Cheat Sheet 2.0Ananda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Fds Unit - IIIDocument58 pagesFds Unit - IIIjai geraNo ratings yet
- Pandas Total NotesDocument66 pagesPandas Total Notespranav gohadNo ratings yet
- Python MicrosoftDocument16 pagesPython Microsoftnak bambNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Dirty Data With Pandas & Python - DevelopIntelligence Blog PDFDocument8 pagesCleaning Dirty Data With Pandas & Python - DevelopIntelligence Blog PDFaravindcj3600No ratings yet
- Hive SuccinctlyDocument114 pagesHive SuccinctlymayboyhanNo ratings yet
- Python (Advanced)Document84 pagesPython (Advanced)Sabyasachi MoitraNo ratings yet
- Fourth Semester Core Course Paper: Microprocessors Architecture and ProgrammingDocument44 pagesFourth Semester Core Course Paper: Microprocessors Architecture and ProgrammingSANAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Programming Using PythonDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Programming Using PythontiyajainNo ratings yet
- Modeling With UML: SolutionsDocument6 pagesModeling With UML: SolutionsPrathiba EzhilarasuNo ratings yet
- Scala CheatsheetDocument2 pagesScala CheatsheetlilliputNo ratings yet
- Python - ArraysDocument13 pagesPython - ArraysQuan ZhouNo ratings yet
- PostgreSQL Cheat Sheet - Hackr - IoDocument90 pagesPostgreSQL Cheat Sheet - Hackr - Ioampm tamzilNo ratings yet
- Prompt Engineering TutorialDocument217 pagesPrompt Engineering TutorialAnanda Saikia100% (1)
- Automation Cheat Sheet 2.0Document6 pagesAutomation Cheat Sheet 2.0Ananda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Python For Beginners Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPython For Beginners Cheat SheetAnanda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Git Cheat Sheet: Presented by Tower - The Best Git Client For Mac and WindowsDocument2 pagesGit Cheat Sheet: Presented by Tower - The Best Git Client For Mac and WindowsMomarNo ratings yet
- Web Scraping Cheat Sheet 2.0Document3 pagesWeb Scraping Cheat Sheet 2.0Ananda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- React Native GuideDocument31 pagesReact Native GuideAnanda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Hands-On Workshop On LinkedIn & Github - GDSCAKUDocument5 pagesHands-On Workshop On LinkedIn & Github - GDSCAKUAnanda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Python3 Lesson 03Document20 pagesPython3 Lesson 03Ananda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- 8 DFA MinimizationDocument23 pages8 DFA MinimizationAnanda SaikiaNo ratings yet
- ABAP Data Dictionary: Field Domain + Data ElementDocument9 pagesABAP Data Dictionary: Field Domain + Data ElementSHIVANo ratings yet
- Advance Database Chapter 1-1Document76 pagesAdvance Database Chapter 1-1Riyad TamamNo ratings yet
- ABAP Performance Tips - Contributor Corner (Read-Only) - Community WikiDocument3 pagesABAP Performance Tips - Contributor Corner (Read-Only) - Community WikiArun Varshney (MULAYAM)No ratings yet
- 1 SQLDocument45 pages1 SQLdev1xcNo ratings yet
- Firebird 2.1 ReleaseNotesDocument172 pagesFirebird 2.1 ReleaseNotescgarciaglNo ratings yet
- Accenture SQL Blended LearningDocument6 pagesAccenture SQL Blended LearningTriveniNo ratings yet
- Exam Topics 1Z0-082Document12 pagesExam Topics 1Z0-082HARIPUSHP SHARMANo ratings yet
- 1Z0 061 Q - A Demo Troytec PDFDocument7 pages1Z0 061 Q - A Demo Troytec PDFUdayanNo ratings yet
- 1Document123 pages1zayazssNo ratings yet
- An Inactive Version of The Repository Object Must Exist. A Transport LayerDocument10 pagesAn Inactive Version of The Repository Object Must Exist. A Transport LayerAkhil VermaNo ratings yet
- Oracle CTSDocument62 pagesOracle CTSRambabu Murakonda0% (1)
- Advanced SQL ConceptsDocument55 pagesAdvanced SQL ConceptsJAYNo ratings yet
- PLSQL For AllDocument154 pagesPLSQL For AllKamineni Kalyan Pavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Other Relevant Roadmaps: Postgresql Roadmap Backend Developer RoadmapDocument1 pageOther Relevant Roadmaps: Postgresql Roadmap Backend Developer RoadmapVăn MinhNo ratings yet
- MSBI and T-SQL Technical Ques & AnsDocument128 pagesMSBI and T-SQL Technical Ques & AnsGanesh singh N100% (1)
- Top 200 Data Engineer Interview Question PDFDocument482 pagesTop 200 Data Engineer Interview Question PDFSurbhi Mantri100% (2)
- About ThisDocument89 pagesAbout ThisSaiKiran TanikantiNo ratings yet
- Database AssignmentDocument65 pagesDatabase AssignmentRAHUL CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Linq Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesLinq Cheat SheetPedro CachacoNo ratings yet
- Object Query Language Reference: StarterDocument7 pagesObject Query Language Reference: StarterAnh Dũng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Joins in Tableau 19Document12 pagesJoins in Tableau 19Giri RajNo ratings yet
- Part 5 - Joining Tables - Inner JoinDocument17 pagesPart 5 - Joining Tables - Inner JoinchiNo ratings yet
- Oracle JoinsDocument8 pagesOracle JoinsMohammad Aminul Islam TalukderNo ratings yet
- Oracle Interview Questions and Answers PDF 1Document12 pagesOracle Interview Questions and Answers PDF 1Harsh ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- Use Features of Enhanced Open SQLDocument8 pagesUse Features of Enhanced Open SQLEsther VizarroNo ratings yet
- DBMS QueDocument16 pagesDBMS QueVishalNo ratings yet
- D49996GC10Document2 pagesD49996GC10Benjamin Sabornido TomasNo ratings yet
- Informatica Interview Questions On Filter TransformationDocument11 pagesInformatica Interview Questions On Filter TransformationRadha100% (1)