0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsBiochem Quizz
Biochem Quizz
Uploaded by
kogliyirijames0The document contains a 20 question biological science tutorial quiz about amino acids. It tests knowledge about the properties of different amino acids, including which ones contain nonpolar groups, have a negative charge at pH 7, and are essential vs non-essential. The questions cover topics like isoelectric points, peptide bond formation, and absorption of UV light.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Biochem Quizz
Biochem Quizz
Uploaded by
kogliyirijames00 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views6 pagesThe document contains a 20 question biological science tutorial quiz about amino acids. It tests knowledge about the properties of different amino acids, including which ones contain nonpolar groups, have a negative charge at pH 7, and are essential vs non-essential. The questions cover topics like isoelectric points, peptide bond formation, and absorption of UV light.
Original Description:
Try questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document contains a 20 question biological science tutorial quiz about amino acids. It tests knowledge about the properties of different amino acids, including which ones contain nonpolar groups, have a negative charge at pH 7, and are essential vs non-essential. The questions cover topics like isoelectric points, peptide bond formation, and absorption of UV light.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views6 pagesBiochem Quizz
Biochem Quizz
Uploaded by
kogliyirijames0The document contains a 20 question biological science tutorial quiz about amino acids. It tests knowledge about the properties of different amino acids, including which ones contain nonpolar groups, have a negative charge at pH 7, and are essential vs non-essential. The questions cover topics like isoelectric points, peptide bond formation, and absorption of UV light.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE TUTORIAL QUIZ
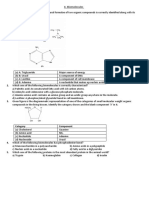
1. Identify the amino acids containing nonpolar, aliphatic
R groups.
a) Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan
b) Glycine, alanine, leucine
c) Lysine, arginine, histidine
d) Serine, threonine, cysteine
2. The two amino acids having R groups with a negative
net charge at pH 7.0 are ___________ a) Aspartate and
glutamate
b) Arginine and histidine
c) Cysteine and methionine
d) Proline and valine
3. If pK1 = 2.34 and pK2 = 9.60, then the isoelectric point
pI is?
a) 5.87
b) 5.97
c) 3.67
d) 11.94
4. Which of the following is a true statement?
a) Tryptophan and tyrosine are significantly more
polar than phenylalanine
b) Leucine is commonly used as an ingredient in the
buffers of SDS page
c) Aspartate is an essential amino acid
d) Lysine is a non-essential amino acid
5. Which among the following is a non-essential amino
acid?
a) Serine
b) Threonine
c) Lysine
d) Histidine
6. Which of the following is an essential amino acid?
a) Cysteine
b) Asparagine
c) Glutamine
d) Phenylalanine
7. Which of the following is an imino acid?
a) Alanine
b) Glycine
c) Proline
d) Serine
8. Which among the following is both glucogenic and
ketogenic?
a) Isoleucine
b) Leucine
c) Lysine
d) Histidine
9. Number of chiral centers in isoleucine is?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
10. The simplest amino acid is …………………………
a)glycine
b) alanine
c) asparagine
d) tyrosine
11. During the formation of the peptide bond which of
the following takes place?
a) Hydroxyl group is lost from its carboxyl group of one
amino acid and a hydrogen atom is lost from its
amino group of another amino acid
b) Hydrogen atom is lost from its carboxyl group of one
amino acid and a hydroxyl group is lost from its
amino group of another amino acid
c) Hydroxyl group is lost from its carboxyl group of one
amino acid and a hydroxyl group is lost from its
amino group of another amino acid
d) Hydrogen atom is lost from its carboxyl group of one
amino acid and a hydrogen atom is lost from its
amino group of another amino acid
12. A tripeptide has _________
a) 3 amino acids and 1 peptide bond
b) 3 amino acids and 2 peptide bonds
c) 3 amino acids and 3 peptide bonds
d) 3 amino acids and 4 peptide bonds
13. Which part of the amino acid gives it uniqueness?
a) Amino group
b) Carboxyl group
c) Side chain
d) None of the mentioned
14. What are the following is not a factor responsible
for the denaturation of proteins? a) pH change
b) Organic solvents
c) Heat
d) Charge
15. Which pair of amino acids absorbs the most UV
light at 280 nm? a) Thr & His.
b) Trp & Tyr.
c) Cys & Asp.
d) Phe & Pro.
e) None of the above
16. When the amino acid alanine (the R-group is: -
CH3) is added to a solution with a pH of 7.3,
alanine becomes:
a) a cation.
b) nonpolar.
c) a zwitterion.
d) an isotope.
e) an anion
17. The isoelectric point of an amino acid is defined as
a) the pH where the molecule carries no net electric
charge.
b) the pH where the carboxyl group is uncharged.
c) the pH where the amino group is uncharged.
d) the pH of maximum electrolytic mobility.
e) -log10(pKi + pKj)
18. Which of the following is true in case of an amino
acid that yields acetoacetyl CoA during the catabolism
of its carbon skeleton?
a) It’s glycogenic in nature
b) It’s ketogenic in nature
c) It’s an essential amino acid
d) It can be either glucogenic or ketogenic in nature
19. Which of the following are sulfur containing amino
acids?
a) Cysteine and methionine
b) Methionine and threonine
c) Cysteine and threonine
d) Cysteine and serine
20. Out of the following, amino acids with hydroxyl
groups are-
a) Serine and alanine
b) Alanine and Valine
c) Serine and threonine
d) Valine and Isoleucine
You might also like
- Biochemistry Questions and AnswersDocument28 pagesBiochemistry Questions and AnswersAgaba Moris Bogoya75% (4)
- Load ChartDocument4 pagesLoad ChartVishnu Menon100% (6)
- Biochemistry 8th Edition by Berg Tymoczko Gatto and Stryer ISBN Test BankDocument12 pagesBiochemistry 8th Edition by Berg Tymoczko Gatto and Stryer ISBN Test Bankdoris100% (41)
- Peterbilt PlanDocument33 pagesPeterbilt PlanDominique Voirin75% (4)
- Grief CounselingDocument24 pagesGrief CounselingDocStevens100% (8)
- Amino Acid MCQ With AnswersDocument4 pagesAmino Acid MCQ With AnswersPrince AsanteNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 (Amino Acids) PDFDocument11 pagesSheet 1 (Amino Acids) PDFShailendra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Quiz_Amino AcidsDocument7 pagesQuiz_Amino Acidschiducnguyen5No ratings yet
- Practice Questions - ProteinsDocument3 pagesPractice Questions - ProteinsalandoailanieNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument9 pagesBiochemistryjosphat mukukaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PEARSONDocument7 pagesBiomolecules PEARSONSujata UpadhyeNo ratings yet
- The Peptide Alanyiglutamylgleylalanyt Leucine HasDocument6 pagesThe Peptide Alanyiglutamylgleylalanyt Leucine Hasmohamed arifNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids:: B SC Semester-VI Unit-Iii Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins & Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesAmino Acids:: B SC Semester-VI Unit-Iii Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins & Nucleic AcidsHarsh KavirajwarNo ratings yet
- Protein ChemistryDocument4 pagesProtein ChemistryPooja TalmaleNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems (Chapter 3)Document15 pagesPractice Problems (Chapter 3)nooneisme840No ratings yet
- Ch03 QuizDocument6 pagesCh03 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- 3 QuizDocument14 pages3 Quizdhwlgo701No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Test BankDocument20 pagesChapter 5 Test BankRod De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- TEST # 38 KEYDocument7 pagesTEST # 38 KEYcixim18884No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Exam - MLS - PhaDocument8 pagesBiochemistry Exam - MLS - PhaChristine AyambaNo ratings yet
- E) CatabolismDocument6 pagesE) Catabolism11. Gia HuyNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument22 pagesAmino Acidskarli geethanjaliNo ratings yet
- Ch03 QuizDocument7 pagesCh03 QuizcatlovesfoodNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank CH 3pdfDocument17 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry Test Bank CH 3pdfMcLovin LUNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Proteins MCQ Flashcards - QuizletDocument9 pagesAmino Acids and Proteins MCQ Flashcards - QuizletAina AdesolaNo ratings yet
- 100 Level Revision Chm 102Document8 pages100 Level Revision Chm 102ezegbudochiamaka18No ratings yet
- Chapter+5 19+McKee+Suggested+ProblemsDocument30 pagesChapter+5 19+McKee+Suggested+ProblemsShivam PatelNo ratings yet
- 26c71 MCQ On Amino Acid MetabolismDocument7 pages26c71 MCQ On Amino Acid MetabolismPrince AsanteNo ratings yet
- DOC-20241005-WA0001.Document10 pagesDOC-20241005-WA0001.38.hetviyogeshsoniNo ratings yet
- Oc Amino Acids Peptides and ProteinsDocument11 pagesOc Amino Acids Peptides and ProteinsNhung Lý NgọcNo ratings yet
- Test 24,25Document6 pagesTest 24,25youssefbaioumy571972No ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 7th EditionDocument12 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 7th EditionJessica BarriosNo ratings yet
- Biochem Sample Test-2-2016-AnswersDocument6 pagesBiochem Sample Test-2-2016-Answerssuperfr3shmNo ratings yet
- DR - Moaaz Wahdan 2023/24 BiochemistryDocument16 pagesDR - Moaaz Wahdan 2023/24 Biochemistrymuhamedkaml2004No ratings yet
- 考古1 protein LinDocument9 pages考古1 protein LinRR JNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3r13641028No ratings yet
- Foundation Chemistry - Practice Questions On Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesFoundation Chemistry - Practice Questions On Organic ChemistryTkNo ratings yet
- Bio PsDocument27 pagesBio PsYelleNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 4 BioDocument9 pagesTutorial Chapter 4 BioZunnurain AmniNo ratings yet
- Fundamental PrinciplesDocument4 pagesFundamental PrinciplesNadeem HassanNo ratings yet
- Bİochem 5Document79 pagesBİochem 5john doeNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSTIC EXAM IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesDIAGNOSTIC EXAM IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRYMANUEL, BUSTY P.No ratings yet
- Exam 1 BCH 3023Document12 pagesExam 1 BCH 3023cwodNo ratings yet
- Exam On Proteins & Enzymes and Lipids: I. Multiple Choice. Submit All Your Answers To Google Classroom in PDF FormatDocument7 pagesExam On Proteins & Enzymes and Lipids: I. Multiple Choice. Submit All Your Answers To Google Classroom in PDF Formatsylv ackermanNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 S 13Document10 pagesExam 1 S 13Asad Javed MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Gpat 2016Document15 pagesGpat 2016Nilanjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Exam1 S14Document33 pagesExam1 S14Asad Javed MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Testbank Dr. Baya Education G11, G12Document209 pagesOrganic Chemistry Testbank Dr. Baya Education G11, G12مطبعة الأقصي100% (1)
- Hydrocarbon Practice Paper-3Document4 pagesHydrocarbon Practice Paper-3sandysrilakshmiNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Chemistry 2022Document4 pagesSample Test Chemistry 2022Hussein AlwaalyNo ratings yet
- Bchm3300 P2 MCDocument11 pagesBchm3300 P2 MCDaphne HernaezNo ratings yet
- BioChem Final Study GuideDocument9 pagesBioChem Final Study Guidenick420springerNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules DPP 1Document4 pagesBiomolecules DPP 1ssnehasish481No ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalDocument12 pagesBiochemistry FinalAhmed Hamarneh100% (1)
- Edited - Chapter 6 Test BankDocument18 pagesEdited - Chapter 6 Test BankRod De Guzman100% (1)
- Bio MoleculesDocument8 pagesBio MoleculesPrasad YarraNo ratings yet
- Biochemestry MCQs From Proteins 1Document4 pagesBiochemestry MCQs From Proteins 1mazharalikhan146No ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 ch9 Class 11Document4 pagesWorksheet 9 ch9 Class 11akilapaul17682No ratings yet
- Microbiology An Introduction 11th Edition Tortora Test Bank DownloadDocument987 pagesMicrobiology An Introduction 11th Edition Tortora Test Bank DownloadMarge Norton0% (1)
- M.SC - Biochemistry - 2015Document18 pagesM.SC - Biochemistry - 2015jdas30753No ratings yet
- 2017 2018 Dis Org (TR) 1 Komite Soru8 DuzeltilmisDocument10 pages2017 2018 Dis Org (TR) 1 Komite Soru8 DuzeltilmisTiba MohammedNo ratings yet
- DSR Analizer Ver.16Document5 pagesDSR Analizer Ver.16Anoop GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Arts q1Document29 pagesModule 2 Arts q1Jaypee CancejoNo ratings yet
- Pes CV PDFDocument1 pagePes CV PDFkamaleshupadhyay388No ratings yet
- (Slimcrm) Mẫu Báo Cáo Dự Án Cuối CùngDocument11 pages(Slimcrm) Mẫu Báo Cáo Dự Án Cuối Cùngtrinhnhan889No ratings yet
- Your Guide To The NJBCT 2014Document4 pagesYour Guide To The NJBCT 2014mgstibraniNo ratings yet
- Murid Darjah 2-6 Tahun 2023Document22 pagesMurid Darjah 2-6 Tahun 2023CHE WAN SITI MARIAM BINTI CHE WAN OTHMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Prepositions in DiscourseDocument42 pagesPrepositions in DiscourseClarissa AyresNo ratings yet
- France Write UpDocument6 pagesFrance Write Upapi-239969991No ratings yet
- ScriptDocument4 pagesScriptTrương KhánhNo ratings yet
- PW-3 Part Design For Ultrasonic Welding (Single PGS) HRDocument8 pagesPW-3 Part Design For Ultrasonic Welding (Single PGS) HRhjgajjarNo ratings yet
- By-Prateek Bebortha Regn No-1727524 Class-1MBA-HDocument18 pagesBy-Prateek Bebortha Regn No-1727524 Class-1MBA-Hprateek beborthaNo ratings yet
- Eapp Fourth Quarter ExaminationDocument6 pagesEapp Fourth Quarter ExaminationROSLYN MACEDANo ratings yet
- Vitalis PNI SDS 051018Document5 pagesVitalis PNI SDS 051018hellowyellow09No ratings yet
- Yonex Arcsaber Badminton RacketDocument2 pagesYonex Arcsaber Badminton RacketgjnhgfhghgNo ratings yet
- Roadseal: Product SpecificationDocument2 pagesRoadseal: Product SpecificationSaran Kl100% (1)
- Ncdeevpb 11Document9 pagesNcdeevpb 11mjpawarrailNo ratings yet
- TobaccoDocument6 pagesTobaccoapi-239797851No ratings yet
- Test 1Document12 pagesTest 1Thoa LeNo ratings yet
- (OA) I BSc. (CS&IT) Syllabus-4-6Document3 pages(OA) I BSc. (CS&IT) Syllabus-4-6K.MarijothiNo ratings yet
- Jeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitDocument27 pagesJeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitTweed3ANo ratings yet
- Chap 06Document62 pagesChap 06api-26090714No ratings yet
- Design and Semantics of Form and Movement - 2008 ProceedingsDocument100 pagesDesign and Semantics of Form and Movement - 2008 ProceedingsDesigner Marcio Dupont100% (8)
- Strategic Capacity ManagementDocument50 pagesStrategic Capacity ManagementHarsh JaswalNo ratings yet
- CSC100MIDTERM ReviewerDocument13 pagesCSC100MIDTERM ReviewerPrincess Noelyn TubilNo ratings yet
- LCI 1100SpecSheetDocument11 pagesLCI 1100SpecSheetandy131078No ratings yet
- MehotrassDocument26 pagesMehotrassshiwani sharmaNo ratings yet
- VirtuesDocument26 pagesVirtuesapi-379914050% (2)