Experiment # - 1
Experiment # - 1
Uploaded by
Ahmad ALzaabiCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment # - 1
Experiment # - 1
Uploaded by
Ahmad ALzaabiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Experiment # - 1
Experiment # - 1
Uploaded by
Ahmad ALzaabiCopyright:
Available Formats
76302354.
doc
American University of Sharjah College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering
ELE 371L Electric Machines and Power Systems Lab Objectives: To learn the measurements techniques on the three phase power system. To understand phase sequence. To understand three phase balanced operation. To understand voltage and current in the three-phase system. To under stand the real and reactive power in three-phase power system. Experiment #1 Introduction to Three Phase Power System Fall 2011
Equipment:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Description Three phase power supply Phase angle meter Three phase resistive load Three phase inductive load Three phase capacitive load Three phase ammeter Multimeter Three phase Watt/VAR meter Three phase Squirrel-cage induction motor
Table 1
Module No. EMS 8821 EMS 8451 EMS 8311 EMS 8321 EMS 8331 EMS 8425 EMS8446 EMS 8221
Quantity 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Discussion: Three phase circuits are in the majority of cases they are symmetrical and have identical impedances each branch. Each branch can be treated exactly as single phase circuit due to balance system. Therefore voltage, current and power relationships for three phase circuits can be determined using the same rules and methods developed for single phase circuits. In balanced three phase circuits the magnitude of either the voltage or the current are equals in each phase while each phase will be displaced by 120o from each other phase. |EA| = |EB| = |EC| and |IA| = |IB| = |IC|
76302354.doc
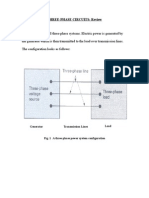
The three phase circuits can be connected in either Wye or Delta configration
Figure 1. (a) Three phase Wye configuration (b) Three phase Delta configuration
For Wye circuits: Eline = 3 Ephase and I line = Iphase For Delta connection: Eline = Ephase and I line = 3 Iphase The total active power supplied to a balanced three phase load is: PT = 3 x P phase = 3 (Ephase x Iphase x cos ) The total reactive power supplied to a balanced three phase load is: QT = 3 x Q phase = 3 (Ephase x Iphase x sin ) The total apparent power can be found by using the following formula: ST = 3 (Ephase x Iphase ) = PT + QT The phase sequence of the voltages or currents of three phase circuit is the order in which they follow each other. Positive sequence (ABC): In this configuration phase A leads phase B by 120 degree and phase B leads phase C by 120 degree.
Negative sequence (ACB): In this configuration phase A leads phase C by 120 degree and phase C leads phase B by 120 degree.
Procedure:
2
76302354.doc
Note:- Turn by turn each fellow of group must involve in connection 1. Turn on the three-phase power supply (EMS 8821) and adjust the voltage on the terminal 4-5-6 to 220 phase voltage, using on board voltmeter. Using the onboard voltmeter, measure the three lines to neutral voltages (terminal 4, 5 & 6 are defined as phases A, B & C). Quantity VAN VBN VCN VAB VBC VCA Value Units
Ist partner start connection other two require to help and monitor
Table 2
Q1) Does your data indicate the expected relationship between line-to-line and line-to-neutral voltage magnitudes? 2. Using A-phase line-to-neutral voltage as reference, determine the phase B & C line-to-neutral phase angle with the phase angle meter (EMS8451). The connection diagram is shown below for the measuring B phase.
4 5 6 N
O O O O
O 1 O 2
3 O 4 O 8451
8821
Figure 2
Quantity
AN BN CN
Value
Units
Table 3
Q2) Is the source operating with positive or negative phase sequence? 3. Using the phase angle meter (EMS8451), determine the phase angle of all the line-to-lineO voltages. Record your data and construct a phasor diagram 4 indicating all six-source voltages. Connection diagram for measuring the 5 O phase angle of the AB line-to-line voltage is shown below.
6 O 3
N O 8821
76302354.doc
O 1 O 2
3 O 4 O 8451
Figure 3
Quantity
AB BC CA
Value
Units
Table 4
Q3a)Does your phasor diagram look like as you expect? State why or why not Q3b)Is the source balanced or unbalanced? Give reason for your response. 4. Connect the three-phase power source (EMS8821) to the three phase resistive load (EMS 8311). The load should be Y-connected with a phase to neutral resistance of 685.7 . Place the three-phase ammeter (EMS 8425), using the 1.5 A setting, in series with the load. Measure and record the three line current magnitudes (three load current magnitudes are the same in the Y-connected case). Also measure and record the neutral current, using ammeter. Quantity IA IB IC IN
Table 5
Value
Units
Q4) Is the load balanced? State the reason for your answer.
5.
Using the resistive load bank (EMS 8311) create a -connected (each R = 685.7). Insert the ammeter in the circuit to measure the line currents. Are the loads equilant? Insert the ammeter to measure the load currents.
Quantity IA (line current) IB IC IAB (Load current)
Value
Units
76302354.doc
IBC ICA
Table 6
Q5) Do the currents obey the expected relationships?
6. 2nd partner start connection other two require to help and monitor
Connect the three-phase watt/VAR meter (EMS 8446) and ammeter (EMS 8425) between the source and a Y-connected load with each phase consisting of a 685.7 resistance in series with a j685.7 inductive reactance (EMS 8321). Measure and record the real and reactive power absorbed by the load and the three line current magnitudes. Quantity P3 Q3 IA IB IC
Table 7
Value W VAR
Units
Q6a) Compute and record the equivalent Y-connected impedance of the load based on the measured quantities.
ZY = -----------------------------------+ J-------------------------------------
Q6b) Using the known voltage and load impedance, compute the three phase complex power absorbed by the load. Q6c) Compare your computed result with the measured results (calculate the error percentage).
7.
Replace the inductive reactance with the three-phase capacitive load (EMS 8331) bank at -j685.7 . Measure and record the real and reactive power absorbed by the load and line current magnitudes. Quantity P3 Q3 IA IB IC
Table 8
Value W VAR
Units
Q7a) Compute and record the equivalent Y-connected impedance of the load based on the measured quantities.
ZY = -----------------------------------+ J-------------------------------------
5
76302354.doc
Q7b) Using the known voltage and load impedance, compute the three phase complex power absorbed by the load. Q7c) Compare your computed result with the measured one (calculate the error percentage).
8. 3rd partner start connection other two require to help and monitor
Replace the load with Y-connected load in which all three phases contain a series combination of 685.7 resistances, a j685.7 inductive reactance and a -j685.7 capacitive reactance. Record the real and reactive powers absorbed by the load. Remove the capacitance and record the real and reactive powers absorbed by the load. With capacitive load. Quantity P3 Q3 Value W VAR
Table 9
Units
Q8a) Explain the results for the reactive power. Without capacitive load. Quantity P3 Q3 Value W VAR
Table 10
Units
Q8b) Explain the change in the reactive power. 9. Replace the load with the three-phase squirrel-cage induction motor (EMS 8221) with no mechanical load. Record the real and reactive power delivered to the motor. Quantity P3 Q3
Table 11
Value W VAR
Units
Q9) Compute the power factor of the motor.
Note:- Your conclusion must reflect all the measurements and data.
You might also like
- Electrical Transformers and Rotating Machines 4th Edition Herman Test Bank DownloadDocument3 pagesElectrical Transformers and Rotating Machines 4th Edition Herman Test Bank DownloadViola Forsberg100% (23)
- Lab E1 RLC Circuit 1Document11 pagesLab E1 RLC Circuit 1Ching Wai Yong100% (2)
- AC Circuits 2Document16 pagesAC Circuits 2Delmark Dionisio Lusterio100% (2)
- Method Statement For Testing & Commissioning of Disabled Toilet Alarm DTA SystemDocument3 pagesMethod Statement For Testing & Commissioning of Disabled Toilet Alarm DTA Systemvin ssNo ratings yet
- 3-Rational Numbers (Practice Questions)Document6 pages3-Rational Numbers (Practice Questions)Abdulkasim AkhmedovNo ratings yet
- Lab # 11Document4 pagesLab # 11Dadu DaduNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 3-Phase MeasurementDocument10 pagesExperiment 2 3-Phase MeasurementSaraha AloNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Balanced SystemDocument5 pagesThree Phase Balanced SystemShin QuinnNo ratings yet
- Three PhaseDocument16 pagesThree Phaseeseose0701100% (3)
- ESO203A Lab Manual 2015Document47 pagesESO203A Lab Manual 2015Apoorva KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase PowerDocument6 pages3 Phase PowerRonieboy Baliber CairoNo ratings yet
- ELEC331 Lab Experiment#1Document16 pagesELEC331 Lab Experiment#1DavidNo ratings yet
- CAP Componentes SimetricasDocument40 pagesCAP Componentes Simetricasccprado1No ratings yet
- L3-BEKG2433-Three Phase Part 2 PDFDocument9 pagesL3-BEKG2433-Three Phase Part 2 PDFVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EE336 - Spring 2022 Exp 1Document8 pagesLab Manual EE336 - Spring 2022 Exp 1absNo ratings yet
- Power Sys. Analysis PDFDocument40 pagesPower Sys. Analysis PDFIrfan QureshiNo ratings yet
- 3.8 Power in Three-Phase AC Circuits: Per-Phase Powers in (A) A Delta-Connected Load and (B) A Star-Connected LoadDocument16 pages3.8 Power in Three-Phase AC Circuits: Per-Phase Powers in (A) A Delta-Connected Load and (B) A Star-Connected LoadBaquiran John Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- EE423 Fault Analysis NotesDocument26 pagesEE423 Fault Analysis NotesadnanNo ratings yet
- Iec Lab Report 3Document12 pagesIec Lab Report 3mahrabhasanchowdhury1No ratings yet
- Lab 07Document1 pageLab 07anon_785510711No ratings yet
- PITFINALDocument64 pagesPITFINALSandra WendamNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document53 pagesUnit 5sujith100% (1)
- Lab Sheets IM2-EEL1196 Tri2 1314Document11 pagesLab Sheets IM2-EEL1196 Tri2 1314RumeshNo ratings yet
- IEC - Lab Exp 3Document12 pagesIEC - Lab Exp 3sazidmohsin456No ratings yet
- ECEN 2633 Chapter 11Document6 pagesECEN 2633 Chapter 11Akira ZamudioNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase CircuitDocument35 pages3 Phase CircuitDavies amadiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualDocument152 pagesElectrical Machines Lab ManualMazoon ButtNo ratings yet
- Lab 08Document9 pagesLab 08mohsin awanNo ratings yet
- Lab 08Document7 pagesLab 08mohsin awanNo ratings yet
- PN2 06Document4 pagesPN2 06twinvbooksNo ratings yet
- Lab7 EnaDocument10 pagesLab7 EnaLaiba ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Sequence Impedances of An AlternatorDocument8 pagesSequence Impedances of An AlternatorBhanuNo ratings yet
- Three PhaseDocument19 pagesThree Phasemilinda deshappriyaNo ratings yet
- Under Voltage Unbalance Using Circle: Analysis of Induction Motor The Diagram MethodDocument6 pagesUnder Voltage Unbalance Using Circle: Analysis of Induction Motor The Diagram MethodHershal RockksNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 PTDDocument5 pagesLab 5 PTDelen19111036 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Volume 64 Issue 6 1945 (Doi 10.1109/EE.1945.6441080) Clarke, Edith - Impedances Seen by Relays During Power Swings With and Without FaultsDocument13 pagesElectrical Engineering Volume 64 Issue 6 1945 (Doi 10.1109/EE.1945.6441080) Clarke, Edith - Impedances Seen by Relays During Power Swings With and Without FaultsAnonymous m65TTcfOTNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Circuits (3 HRS)Document57 pagesThree Phase Circuits (3 HRS)Vongai ChimbundeNo ratings yet
- Load Flow Solution For Unbalanced Radial Power Distribution Using Monte Carlo SimulationDocument7 pagesLoad Flow Solution For Unbalanced Radial Power Distribution Using Monte Carlo SimulationnpfhNo ratings yet
- ET Tutorial Sheet 3Document4 pagesET Tutorial Sheet 3Nick FuryNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument7 pagesResearch PaperAjmal FarooqNo ratings yet
- 1: The Power CMMT: DC No. IeeDocument6 pages1: The Power CMMT: DC No. IeeMadhavender Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- PEE3 Lec 5 WattmeterDocument31 pagesPEE3 Lec 5 Wattmeteraubrey terencioNo ratings yet
- Network Theory Question BankDocument14 pagesNetwork Theory Question BankHarishReddyNo ratings yet
- AEP LAB 3 FinalDocument11 pagesAEP LAB 3 FinalSilas Sailas EndjalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3: Marwadi University Bachelor of Technology Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 3: Marwadi University Bachelor of Technology Department of Electrical Engineeringbapah97958No ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument40 pagesPower System AnalysisAkhtarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Varun TandonNo ratings yet
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Experiment No Name of The ExperimentDocument2 pagesIslamic University of Technology (Iut) : Course: Experiment No Name of The ExperimentshiamNo ratings yet
- IEEE Distribution Test FeedersDocument11 pagesIEEE Distribution Test FeedersAdriano Almeida100% (2)
- University of The East - Caloocan College of Engineering: Series and Parallel Circuits Experiment No. 2Document12 pagesUniversity of The East - Caloocan College of Engineering: Series and Parallel Circuits Experiment No. 2Jabber Reyes AmborNo ratings yet
- ELEC4100 Complete NotesDocument150 pagesELEC4100 Complete NotesShittyUsername2013No ratings yet
- Grupo1gg132 Laboratorio9 MR - JMDocument8 pagesGrupo1gg132 Laboratorio9 MR - JMJean Carlo Méndez SantamaríaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Three Phase Systems v3Document43 pagesModule 8 Three Phase Systems v3Pao CastillonNo ratings yet
- PHS213 Note - LMSDocument10 pagesPHS213 Note - LMSnizzychristian15No ratings yet
- Two Wattmeter MethodDocument11 pagesTwo Wattmeter MethodSARITHA SNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- OSNightDocument195 pagesOSNightRia KimNo ratings yet
- CV JaquelineDocument5 pagesCV JaquelineZulkarnain Febri Wicaksono, S.H.No ratings yet
- Hitec ServiceDocument7 pagesHitec ServiceAnonymous uEt1sNhU7l100% (1)
- Handout - The Fun They Had - Class IX - 2022-23 (1994)Document3 pagesHandout - The Fun They Had - Class IX - 2022-23 (1994)ASNNo ratings yet
- 7 Soliton PDFDocument8 pages7 Soliton PDFAnonymous K9F6Z7LwuNo ratings yet
- Sordane Stories - Plane Shift - Preview CreaturesDocument4 pagesSordane Stories - Plane Shift - Preview Creaturescacciaaltesoroadri12No ratings yet
- GCSE Media Studies Close Study Products Booklet v1.0Document35 pagesGCSE Media Studies Close Study Products Booklet v1.0HH-MEDIANo ratings yet
- 7mm MauserDocument16 pages7mm MauserJohn Anderson100% (3)
- Bio Refineries in Europe PDFDocument8 pagesBio Refineries in Europe PDFNikhil VermaNo ratings yet
- Ambitious Words To Describe The WeatherDocument2 pagesAmbitious Words To Describe The WeatherNessma AbdelfatahNo ratings yet
- Intralox (Eng)Document37 pagesIntralox (Eng)Angel David Osorio RiveroNo ratings yet
- ODI Loading MetaData and Data Into Planning and EssbaseDocument41 pagesODI Loading MetaData and Data Into Planning and Essbasesaikiran100% (1)
- Enviroline 124 Application GuidelineDocument12 pagesEnviroline 124 Application GuidelineAhmed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Digital Meter: RAASM's Digital MetersDocument13 pagesDigital Meter: RAASM's Digital MeterskupatNo ratings yet
- CompetitorsDocument3 pagesCompetitorsTeam ProspeNo ratings yet
- Francisco Orlich BolmarcichDocument2 pagesFrancisco Orlich BolmarcichХристинаГулеваNo ratings yet
- Module 11 2017Document19 pagesModule 11 2017Shabin P KNo ratings yet
- Advanced Photoshop - Issue 136, 2015Document100 pagesAdvanced Photoshop - Issue 136, 2015Raquel AntolínNo ratings yet
- Zoho Interview Questions and Answers: Vikram SinghDocument20 pagesZoho Interview Questions and Answers: Vikram SinghpoornimaepyNo ratings yet
- AUBF SemenDocument7 pagesAUBF SemenRichelyn Grace B. VenusNo ratings yet
- Free Weights PlanDocument1 pageFree Weights PlansokrisbaNo ratings yet
- 2 1 1 A CentroidsDocument5 pages2 1 1 A Centroidsapi-3060280660% (1)
- Datasheet 16070 Pillow Block Bearing Pedestal Type UCP - enDocument2 pagesDatasheet 16070 Pillow Block Bearing Pedestal Type UCP - enIslam MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Deviation and VariationDocument3 pagesDeviation and Variationjaber hasan talalNo ratings yet
- Easa Fcl-Compliant Pilot Log: The StandardDocument12 pagesEasa Fcl-Compliant Pilot Log: The StandardEm GomezNo ratings yet
- Exlime 1946 MSDSDocument2 pagesExlime 1946 MSDSMurtaza SherwaniNo ratings yet
- Olap-Operations in RDocument18 pagesOlap-Operations in RMcnylNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia - WikipediaDocument50 pagesWikipedia - WikipediaAKNo ratings yet