QuestionBankGeographyCass 10CH1
QuestionBankGeographyCass 10CH1
Uploaded by
Viveha Priya Jayamani 66Copyright:
Available Formats
QuestionBankGeographyCass 10CH1
QuestionBankGeographyCass 10CH1
Uploaded by
Viveha Priya Jayamani 66Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
QuestionBankGeographyCass 10CH1
QuestionBankGeographyCass 10CH1
Uploaded by
Viveha Priya Jayamani 66Copyright:
Available Formats
QUESTION BANK
CLASS – 10
RESOURCES AND DEVELOPMENT( CH-I GEOGRAPHY)
I MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
1. Black soil is composed of extremely :
a) rocky material b)clayey material c)sandy material
2. Arid soil’s colour changes from:
a) red to brown b)yellow to red c)brown to yellow
3. Soils are not classified on the basis of :
a) regions b)age c)colour
4. The process of transformation of things available in our environment involves an interdependent
relationship between i)nature ii)technology iii) institutions
a) I and ii b)ii and iii c)I, ii and iii
5. Widely spread strategy for judicious use of resources is
a)development of resources b)management of resources c)planning of resources
6. Maximum of waste land is covered by :
a)Saline and alkaline land b)wind eroded land c)water eroded land
ANSWERS: 1.B,2.A,3.A,4.C,5.C,6.C
II DEFINITIONS:
1. Resources:- Everything in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided it is
technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable is termed as resource
2. Sustainable development:- It means that development should take place without damaging the
environment and development in the present should not compromise the needs of the future development.
3. Resource planning:- It is a widely accepted strategy for the judicious use of resources. For eg Arunachal
Pradesh is rich in water resources but lacks in infrastructural development, so planning is required to
develop infrastructure facilities.
4. Conservation of resources:- It is defined as the management of resources by the humans which aims at
satisfying the aims of the present generations as aspirations of the future generations.
5. Net sown area:- Area sown once in a year is known as net sown area.
6. Gross sown area:- Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus the net sown area is known as gross
sown area
7. Land degradation:- It is the continuous use of land over long period of time without taking appropriate
measures to conserve and manage it.
8. Bad land:- Land unsuitable for agriculture mainly due to soil erosion. For eg. Chambal ravines in
Madhyapradesh.
III. ANSWER IN SHORT AND LONG:-
1. “Resources are a function of human activities.” Justify the statement.
Mere presence of resources as free gifts of nature does not make them resources .Human beings are
essential components of resources because they transform material available in our environment into
resources. The utility of resources depends on the stage of cultural development of man and the tools and
technology used by him.
2. Distinguish between the following:-
a)Potential and Developed resources
Potential resources- Resources which are found in a region but have not been utilised.eg: Gujarat and
Rajasthan have a lot of potential for the development of wind and solar energy , but so far they have not
been developed fully.
Developed resources- Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined
for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and level of their feasibility. Eg: water
resources used for hydel power generation or irrigation purposes
b)Stock and Reserves
Stock: Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but man does not have
the appropriate technology to access them are included among stock, eg. Water is a compound of two
inflammable gases ; hydrogen and oxygen which can be used as a rich source of energy. But we do not have
the required technical knowhow to use them for this purpose.
Reserves are the subset of the stock which can be put into use with the help of existing technical know-how
but their full use has been postponed for meeting the future needs, eg. Forest reserves, iron ore reserves
etc.
c)Bangar and Khadar
Bangar: It is old alluvial soil with higher concentration of kankar nodules. It is coarser and is found in the old
river terraces.
Khadar: It is new alluvial soil which has more fine particles. It is more fertile than bngar and is found in flood
plains.
3. Write measures to solve the problems of land degradation.
1. Afforestation
2. Management to control over grazing
3. Planting of shelter belts of plants
4. Stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes
5. Control of mining activities
6. Proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment.
7. Avoid over irrigation especially in dry areas.
8. Avoid over use of pesticides and fertilisers.
4. Expain three types of soil erosion.
1. Gully erosion: The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels called gullies.
They make the land unfit for cultivation. Such lands are called bad lands.
2. Sheet erosion : sometimes water flows as a sheet down a slope. In this case top layer if the soil is
washed away.
3. Wind erosion: Wind blows off loose and dry soil.
5. Write four methods of soil conservation.
1. Contour ploughing: By ploughing along the contour lines water will not run down the slopes.
2. Terrace cultivation: Steps can be cut on the slopes to restrict erosion.
3. Strip cropping: Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grasses are left to grow between the
crops. This breaks the force of the wind.
4. Planting of shelter belts: The planting of trees in rows to create shelter also breaks the force of the wind
and restricts soil
6. Why is resource planning necessary?
Planning is necessary for proper and judicious utilisation of resources.
Reasons of resource planning:
1. Resource availability is not the same in all parts of the country
2. Resources especially non renewable resources need extra care as they cannot be renewed.
3. There is acute shortage or deficiency of some resources.
4. Resource planning helps in proper utilisation of resources by reducing wastage. It takes care of future
needs may sustain the environment.
7. Explain three stages of resource planning.
The three stages of resource planning are as follows:
1. Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying ,
mapping and finding the qualitative and quantitative measurement of the resources.
2. Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for
implementing resource development plans.
3. Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
8. List the problems which resulted due to indiscriminate use of resources by man.
1. It has resulted in depletion of many resources.
2. Accumulation of resources in few hands which inturn divided the society in two segments into haves and
have-nots and rich and poor.
3. It has led to the global ecological crisis like global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental
degradation etc.
9. Explain the concept of resource conservation as voiced by Gandhiji.
Gandhiji voiced his concern about resource conservation in these words: “There is enough fo r
everybody’s need and not for anybody’s greed.”He placed the greedy and selfish individuals as the root
cause for resource depletion at the global level. He was against ’mass production ‘ and wanted to replace it
with ‘production by the masses.’
10. Write characteristics of laterite soil. Give reasons for their colour and why are they called laterite?
1.They are highly leached soils.
2. They develop in areas of heavy rainfall and high temperature.
3. They have low ‘humus’ content, because most of the micro-organisms get destroyed due to high
temperature.
4. These soils can be cultivated with adequate doses of manures and fertilisers.
These soils develop a reddish colour due to diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks.
It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form. The word laterite has been derived from the Latin
word later which means brick.
Since their colour is red and resembles brick colour these soils are called laterite soil.
You might also like
- Practice Questions Chap Geography 1Document2 pagesPractice Questions Chap Geography 1ajabgajab.edNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Resources and Development BoardPrep SolutionDocument10 pagesClass 10th Resources and Development BoardPrep SolutionABISHUA HANOK LALNo ratings yet
- Resource and DevelopmentDocument26 pagesResource and DevelopmentthinkiitNo ratings yet
- GeoDocument28 pagesGeoSakshi GoelNo ratings yet
- Gidb5856658 - Resource and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGidb5856658 - Resource and DevelopmentSprihi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Geo. CH 1 - Resource and Development NotesDocument13 pagesClass 10 Geo. CH 1 - Resource and Development Notessadhna yadav100% (3)
- Grade 10 Ch. 1 Geo.Document9 pagesGrade 10 Ch. 1 Geo.punian344No ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument32 pagesResources and DevelopmentSwastiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 CH.1 Geography NotesDocument6 pagesClass 10 CH.1 Geography NotesNisha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development Shobhit NirwanDocument13 pagesResources and Development Shobhit NirwanRadhika Ramesh100% (1)
- Resourcesanddevelopment 120608213338 Phpapp02Document27 pagesResourcesanddevelopment 120608213338 Phpapp02Manjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesResources and Developmentspecialiam541No ratings yet
- Resource and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesResource and Developmentroxgokul302No ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesResources and DevelopmentGITA DEVINo ratings yet
- Resource and Development PyqDocument13 pagesResource and Development PyqopopNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development: by Adarsh - NJDocument27 pagesResources and Development: by Adarsh - NJAnkur ChopraNo ratings yet
- GG 10 CH1Document3 pagesGG 10 CH1satwik1244No ratings yet
- Geography Notes For Class: X (Social Science) : Chapter 1: Resources and Development Remember These PointsDocument4 pagesGeography Notes For Class: X (Social Science) : Chapter 1: Resources and Development Remember These PointsAkshit SethiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentRBSNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesResources and Developmentpujal dabasNo ratings yet
- Original 1587566839 Resource and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesOriginal 1587566839 Resource and DevelopmentS KannanNo ratings yet
- Classification of ResourcesDocument11 pagesClassification of ResourcesbasilNo ratings yet
- Geography Ch-1 Cbse P PDocument5 pagesGeography Ch-1 Cbse P Pez1onggaNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development AssignmentDocument6 pagesResources and Development AssignmentBhavya AhujaNo ratings yet
- 01-Resource and Development (Part-01)Document5 pages01-Resource and Development (Part-01)Archit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10 CH-1 GEOGRAPHY Question-AnswersDocument4 pagesCLASS 10 CH-1 GEOGRAPHY Question-AnswersDoonites DelhiNo ratings yet
- Resource and Development ExercisesDocument18 pagesResource and Development Exercisesshahidaiqubal786No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 GeographyDocument6 pagesChapter 1 GeographyTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Geography Class 10Document56 pagesGeography Class 10niwanshi1No ratings yet
- MergDocument308 pagesMergAjay VaidNo ratings yet
- Class X Notes of All ChaptersDocument17 pagesClass X Notes of All Chapterssomilgoel2023No ratings yet
- Classification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyDocument18 pagesClassification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyMANISH JOSHINo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 1 3Document7 pagesUntitled Document 1 3Himesh kushwahaNo ratings yet
- 10 Geo ch-1 Resources & DevelopemntDocument7 pages10 Geo ch-1 Resources & DevelopemntViji VNo ratings yet
- Notes Class X Geography Resources Question AnswerDocument9 pagesNotes Class X Geography Resources Question AnswerAarush BindalNo ratings yet
- Our Resources (Land and Soil)Document10 pagesOur Resources (Land and Soil)Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Geography 1Document3 pagesGeography 1jeevarajapandian1982No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Resources and Development: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science GeographyDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - Resources and Development: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science GeographyscedhuNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesCBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentEKLABAY SONINo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Geography CH 01 Class XDocument25 pagesImportant Questions For Geography CH 01 Class Xavinashjaidev1202No ratings yet
- Studentinfo HomeworkDocument3 pagesStudentinfo Homeworkxtremeib13No ratings yet
- Extra Questions - Resources and Development - Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesExtra Questions - Resources and Development - Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Downloadbatsmen2007No ratings yet
- Resource Planning Geography CHP 1Document4 pagesResource Planning Geography CHP 1charan dheepNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development (Geo)Document5 pagesResources and Development (Geo)kumarshivam58156No ratings yet
- Geo ch-1 Class 10Document9 pagesGeo ch-1 Class 10nayshajain63No ratings yet
- Geography 1 Class X Assignment (2020-21)Document6 pagesGeography 1 Class X Assignment (2020-21)Binode SarkarNo ratings yet
- 10th Geography 21-22 - RemovedDocument24 pages10th Geography 21-22 - Removedrathermusaib800No ratings yet
- X Geography NotesDocument6 pagesX Geography Notesharendrakumar6219No ratings yet
- Geography Les 1 With AnsDocument10 pagesGeography Les 1 With AnsMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- GSEB Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Natural ResourcesDocument20 pagesGSEB Solutions Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Natural ResourcesKriti Shah100% (1)
- 8 - Geography Ch2Document4 pages8 - Geography Ch2SufianNo ratings yet
- Notes On Resource and Development STD-10 (2024)Document11 pagesNotes On Resource and Development STD-10 (2024)chaitanyabharate1No ratings yet
- Resources and Development Key NotesDocument5 pagesResources and Development Key NotesAditi PrassunNo ratings yet
- Cbse 10 Geography L1 IMPsDocument10 pagesCbse 10 Geography L1 IMPsidk113806No ratings yet
- CLASS 10 Notes - Resources & Development - WatermarkDocument12 pagesCLASS 10 Notes - Resources & Development - Watermarksuryanshsaxena064No ratings yet
- Geo PDFDocument21 pagesGeo PDFSoviya Varatharajan08No ratings yet
- Class 8-Ch-1 - Resources PDFDocument4 pagesClass 8-Ch-1 - Resources PDFSaghana SaravanakarthikNo ratings yet
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 1: Functions and ServicesFrom EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 1: Functions and ServicesJacques BerthelinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Brownfield Regeneration: Cleanup, Design, and Reuse of Derelict LandFrom EverandPrinciples of Brownfield Regeneration: Cleanup, Design, and Reuse of Derelict LandNo ratings yet
- Lecture-9 Transmission ImpairmentDocument15 pagesLecture-9 Transmission ImpairmentRIMSHANo ratings yet
- EDOC-Circuit Breaker Schematic DiagramDocument5 pagesEDOC-Circuit Breaker Schematic DiagramEl Comedor BenedictNo ratings yet
- Tork Submersible Stainless Steel PumpsDocument52 pagesTork Submersible Stainless Steel PumpsMOUSTAPHA DIALLONo ratings yet
- New Holland LS160 - LS170 Workshop ManualDocument41 pagesNew Holland LS160 - LS170 Workshop ManualFaris MohamedNo ratings yet
- Actuators in IotDocument14 pagesActuators in IotkrishchitraveniNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Revamp Webinar For DownloadDocument37 pagesAmmonia Revamp Webinar For Downloadtatoo1No ratings yet
- 07.09..2020 - Intrinsic Carrier ConcentrationDocument14 pages07.09..2020 - Intrinsic Carrier ConcentrationSri Mangai Nathan100% (1)
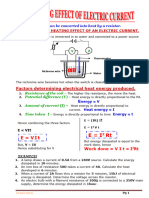
- Heating Effect of Electric CurrentDocument2 pagesHeating Effect of Electric Currentsalmansaid030No ratings yet
- Sibre BuffersDocument20 pagesSibre BuffersRajat MallickNo ratings yet
- AG & GULF PLATTS 17 April 2024 FULLDocument31 pagesAG & GULF PLATTS 17 April 2024 FULLliuheng1012No ratings yet
- Greystone Gas Range Instruction Manual Model CF FS60 07 11 2022 - 0Document32 pagesGreystone Gas Range Instruction Manual Model CF FS60 07 11 2022 - 0Christopher MillerNo ratings yet
- HPC High Pressure CompressorDocument9 pagesHPC High Pressure CompressorAbrahan BaezaNo ratings yet
- G59 Embedded Generator Regulations: Combined Heat and Power UnitsDocument10 pagesG59 Embedded Generator Regulations: Combined Heat and Power UnitsCletus GonsalvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesChapter Two Literature ReviewMcLeo AliriNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Review MCQDocument34 pagesLast Minute Review MCQIB Experts for 7on7 Pvt. Ltd.No ratings yet
- Role of Public Authority and Private Sector in Was..Document6 pagesRole of Public Authority and Private Sector in Was..prajuthejonidhi1001No ratings yet
- 13 Soal-PptlDocument7 pages13 Soal-Pptlmohamed orifNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Engineering - Lecture 2Document26 pagesCorrosion Engineering - Lecture 2Ali A AlRazzakNo ratings yet
- Bu 3 - MechanicalDocument7 pagesBu 3 - MechanicalSharmaine Danica MarceloNo ratings yet
- Doosan PDFDocument5 pagesDoosan PDFjeremih alhegnNo ratings yet
- Us11179715-Inorganic Ion - Exchanger For Selective Extraction of LithiumDocument11 pagesUs11179715-Inorganic Ion - Exchanger For Selective Extraction of LithiumDiego RossoNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Superconductor (Final)Document36 pagesUnit-4 Superconductor (Final)ShivaranjanNo ratings yet
- LP MDV Aprilie 2022Document4 pagesLP MDV Aprilie 2022Alexandru ChirilaNo ratings yet
- Perkins Engine ServiceDocument98 pagesPerkins Engine ServiceHaftom TekluNo ratings yet
- 6060 Tank Pumps Drive ControllerDocument25 pages6060 Tank Pumps Drive ControllerEdison Pfoccori BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Capacitive OEM Pressure Sensor: Typical ApplicationsDocument2 pagesCeramic Capacitive OEM Pressure Sensor: Typical ApplicationsedilbertoNo ratings yet
- MCCB WiNbreakDocument20 pagesMCCB WiNbreakhemant kumarNo ratings yet
- SIMULINKDocument5 pagesSIMULINKshresth.gupta.ug22No ratings yet
- STC-TrD-11 - Safety Precautions and Electrified SectionsDocument239 pagesSTC-TrD-11 - Safety Precautions and Electrified SectionsSuresh MeenaNo ratings yet
- APPLICATIONS of NUCLEAR FUSION in VARIOUS INDUSTRIESDocument5 pagesAPPLICATIONS of NUCLEAR FUSION in VARIOUS INDUSTRIESSHIELA HIDALGONo ratings yet