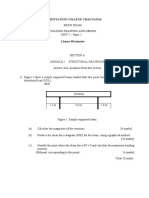
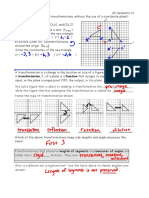
Tutorial 1 Cace
Tutorial 1 Cace
Uploaded by
nasma.nvnCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 1 Cace
Tutorial 1 Cace
Uploaded by
nasma.nvnOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 1 Cace
Tutorial 1 Cace
Uploaded by
nasma.nvnCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:
Department of Civil Engineering Roll No.:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CALICUT
Monsoon semester 2015
Tutorial I
CE 4001 COMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Duration: 1.25 h Maximum Marks: [20]
(i) Answer all questions. Answer to the question.
(ii) Indicate all intermediate steps clearly in the answers
1. The concentration of pollutant bacteria C in a decreases according to C=75𝑒 !!.!! +
20𝑒 !.!"#! Determine the time required for the bacteria for reducing the concentration to 15
using
(i) Newton Raphson method with an initial guess of t=0(4 iterations) (2)
(ii) Method of False Position with [4, 10] as the brackets (4 iterations) (2)
2. (a) Compute a real root of 2𝑥 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 + 1 using the method of Successive Approximation
starting with 𝑥! = 0, Carry out 3 iterations. (1.5)
(b) Use Aitkens ∆! process to get a more accurate solution using the above, (1.5)
(c) If the exact solution of the given equation is 0.83543, determine the Absolute error,
Relative error, Percentage error (1)
3. Solve the following system of linear algebraic equation using LU Decomposition technique
8𝑥 + 2𝑦 − 2𝑧 = −2 (5)
10𝑥 + 2𝑦 + 4𝑧 = 4
12𝑥 + 2𝑦 + 2𝑧 = 6
4. A civil engineer involved in construction requires 4800, 5800, 5700 m3 of sand, fine gravel
and coarse gravel respectively for a building project. There are three pits from which these
materials can be obtained. The composition of these pits is given below
Pit Sand % Fine gravel % Coarse gravel %
I 55 30 15
II 25 45 30
III 25 20 55
How many cubic meters must be hauled from each pit in order to meet the engineer’s
needs? Use Gauss elimination method. (4)
5. Use Gauss Seidal method to obtain the following system of equations, correct up to three
significant digits. 17𝐶! − 2𝐶! − 3𝐶! = 500
−5𝐶! + 21𝐶! − 2𝐶! = 200
−5𝐶! − 5𝐶! + 22𝐶! = 30 (3)
You might also like
- Dijkstra AlgorithmDocument2 pagesDijkstra AlgorithmKhoa NguyenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 CaceDocument1 pageTutorial 1 Cacenasma.nvnNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Geotechnical testDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Geotechnical testmbrightzuluNo ratings yet
- CEng2142 REG 2011 Test1 Examination Paper SetDocument10 pagesCEng2142 REG 2011 Test1 Examination Paper SetCaalchisaa MargaaNo ratings yet
- 15PHY201 - II Ass - Sep 2018Document2 pages15PHY201 - II Ass - Sep 2018rajeevatyNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chem p2 2nd Term 2023 - CambridgeDocument20 pagesForm 4 Chem p2 2nd Term 2023 - CambridgenokumavhaivhaiNo ratings yet
- May Jun 2023Document5 pagesMay Jun 2023pranavakharche21No ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Exam Assessment Level Full Marks Programme Pass Marks Year/ Part TimeDocument1 pageDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Exam Assessment Level Full Marks Programme Pass Marks Year/ Part Timesujit kcNo ratings yet
- Induction Civil EngineeringDocument105 pagesInduction Civil EngineeringKosygin LeishangthemNo ratings yet
- M.E (2017 April 2019Document484 pagesM.E (2017 April 2019Sachin KadlagNo ratings yet
- ME 2008 PaperDocument949 pagesME 2008 PaperPRAMOD KESHAV KOLASENo ratings yet
- BMS College of Engineering, Bengaluru-560019Document3 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bengaluru-560019ahmadNo ratings yet
- Entrance - Exam MSC - CEM 2013 BatchDocument3 pagesEntrance - Exam MSC - CEM 2013 BatchezzNo ratings yet
- TIE6111201508 Design, Analysis and Control of Manufacturing SystemsDocument5 pagesTIE6111201508 Design, Analysis and Control of Manufacturing Systemstafara mundereNo ratings yet
- Ecn 1100 Worksheet #2Document3 pagesEcn 1100 Worksheet #2Suraj SomaiNo ratings yet
- Mnipur Teqnikel Yunibrsiti: Manipur Technical UniversityDocument105 pagesMnipur Teqnikel Yunibrsiti: Manipur Technical UniversityKosygin LeishangthemNo ratings yet
- 13-07-2024 SR - Super60 Nucleus&Sterling-bt Jee-Main Rptm-01 Key & Sol'sDocument13 pages13-07-2024 SR - Super60 Nucleus&Sterling-bt Jee-Main Rptm-01 Key & Sol'ssanju.e.onlineNo ratings yet
- M.E (2017 Pattern) 288 PDFDocument386 pagesM.E (2017 Pattern) 288 PDFkanchan khadeNo ratings yet
- GRADE X CHEM PRACTICE WORKSHEETDocument25 pagesGRADE X CHEM PRACTICE WORKSHEETanaghaa.shrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term QuestionsDocument3 pagesMid-Term QuestionsNorris wongNo ratings yet
- TEST 2 NUMECDocument5 pagesTEST 2 NUMECamirul aminnNo ratings yet
- Final Exam BFC24203 PDFDocument7 pagesFinal Exam BFC24203 PDFzsNo ratings yet
- DIPLOMA Second Sem Syllabus (Core Branches)Document113 pagesDIPLOMA Second Sem Syllabus (Core Branches)ranjith kumarNo ratings yet
- Jec Cie 1 7th SemDocument4 pagesJec Cie 1 7th SemNaheed SaikiaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Scheme Syllabus AEDocument60 pages2nd Year Scheme Syllabus AEHareesha N GNo ratings yet
- Al-Azhar Polytechnic College: Quantity Surveying - IDocument4 pagesAl-Azhar Polytechnic College: Quantity Surveying - Ianishsukumar000gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Overheads FinalDocument12 pagesOverheads FinalSanskar VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Oct 2018Document487 pagesOct 2018udayNo ratings yet
- Pert, Surve, Steel, Waterresources, Som SoluDocument18 pagesPert, Surve, Steel, Waterresources, Som Solunagapuri bharathchandraNo ratings yet
- TCW3204201505 Irrigation Systems DesignDocument6 pagesTCW3204201505 Irrigation Systems DesignNyashah FelixNo ratings yet
- Third Term Exam-Wps Office-5Document5 pagesThird Term Exam-Wps Office-5Shonekan KhadijahNo ratings yet
- FTS-28 - Paper-2 - JEE Advanced-2020 - Solution PDFDocument9 pagesFTS-28 - Paper-2 - JEE Advanced-2020 - Solution PDFVIKRAM SINGHNo ratings yet
- REGRESSION AND CORRELATION ANALYSIS - AssignmentDocument2 pagesREGRESSION AND CORRELATION ANALYSIS - AssignmentFilbert SimonNo ratings yet
- Cse 215 - Engineering Drawing IiiDocument3 pagesCse 215 - Engineering Drawing IiiWol Monydeng BolditNo ratings yet
- SY BTech IT SEM III ODD Jan - 2023Document19 pagesSY BTech IT SEM III ODD Jan - 2023savitakate1No ratings yet
- BE10-R3 July 08Document4 pagesBE10-R3 July 08Sougata ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- 8.solution - Project 2-Circular MeasureDocument10 pages8.solution - Project 2-Circular MeasurekedaitakafulbsnNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2015 P2Document20 pagesCSEC Physics June 2015 P2Is IbrahimNo ratings yet
- CPT3701 Major Test 1Document4 pagesCPT3701 Major Test 1unisamodules5No ratings yet
- TIE6111201412 Design, Analysis and Control of Manufacturing SystemsDocument5 pagesTIE6111201412 Design, Analysis and Control of Manufacturing Systemstafara mundereNo ratings yet
- 1155 CE F242 20230524105854 Mid Semester Question PaperDocument2 pages1155 CE F242 20230524105854 Mid Semester Question Paperf20211718No ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument24 pagesLab ManualASHVINI GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- CHT206 - KQB KtuQbankDocument9 pagesCHT206 - KQB KtuQbankYuxin CasioNo ratings yet
- BUILDING MOCK BMED Unit 2 - Paper 2Document7 pagesBUILDING MOCK BMED Unit 2 - Paper 2Kareem AliNo ratings yet
- 2018 2019 (Online)Document5 pages2018 2019 (Online)samia.asha3636No ratings yet
- Pe3-Stage 9 Chemistry - P6Document5 pagesPe3-Stage 9 Chemistry - P6Puja DhawanNo ratings yet
- WS4 Decimal FractionsDocument2 pagesWS4 Decimal FractionsABDUL RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/33Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/33Alya Defa AnindaNo ratings yet
- Csvtu Syllabus Be Mining 5 SemDocument12 pagesCsvtu Syllabus Be Mining 5 Semvirendra behraNo ratings yet
- Mix DesignDocument74 pagesMix DesignKarthikeyan m.karthiNo ratings yet
- 0620/62/F/M/16 © Ucles 2016Document5 pages0620/62/F/M/16 © Ucles 2016aaryavaminNo ratings yet
- SCM-210 Assignment 2 Student VersionDocument5 pagesSCM-210 Assignment 2 Student VersionEvelyn PattNo ratings yet
- Imt 15Document8 pagesImt 15remembersameerNo ratings yet
- M.E (2013 Pattern) PDFDocument557 pagesM.E (2013 Pattern) PDFVarsha KumariNo ratings yet
- M.E (2013 Pattern) PDFDocument557 pagesM.E (2013 Pattern) PDFVarsha KumariNo ratings yet
- M.E (2013 Pattern) PDFDocument557 pagesM.E (2013 Pattern) PDFVarsha KumariNo ratings yet
- M.E (2013 Pattern) PDFDocument557 pagesM.E (2013 Pattern) PDFVarsha KumariNo ratings yet
- M.E (2013 Pattern) PDFDocument557 pagesM.E (2013 Pattern) PDFVarsha KumariNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A Complete Guide to M.C.Q (Class-10, Mathematics): CBSE MCQ Series, #1From EverandA Complete Guide to M.C.Q (Class-10, Mathematics): CBSE MCQ Series, #1No ratings yet
- Sin X TaylorDocument64 pagesSin X TaylorAlex TanNo ratings yet
- Princípio de Babinet 1Document3 pagesPrincípio de Babinet 1josh16kalebNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2023Document2 pagesAssignment 2023princenarib16No ratings yet
- Model Predictive ControlDocument55 pagesModel Predictive ControlMuhammad Faiz Fudzaili100% (2)
- GEC410 Lecture Note IIDocument23 pagesGEC410 Lecture Note IInelsonNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 - Aim 12 10HDocument7 pagesMod 1 - Aim 12 10HShubham TelrandheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1& 2 Control System Concepts and Review of Laplace TransformDocument7 pagesChapter 1& 2 Control System Concepts and Review of Laplace TransformFasika TegegnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19Document52 pagesLecture 19Axel Coronado PopperNo ratings yet
- B.tech. (Mechanical Engineering) W.E.F. Admitted Batch (2012-13)Document94 pagesB.tech. (Mechanical Engineering) W.E.F. Admitted Batch (2012-13)Kodanda RamaraoNo ratings yet
- Inner Product Spaces: Unit - IiDocument28 pagesInner Product Spaces: Unit - IiShubham PhadtareNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Document1 pageFormula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Roberto DiscutidoNo ratings yet
- Integration and Summation: Edward JinDocument33 pagesIntegration and Summation: Edward JinAkash HedaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Background of Beam DeflectionDocument3 pagesTheoretical Background of Beam DeflectionSharmaine Gomez FalcisNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument35 pagesFinalshekhawatmahaveerNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods QB 11148S51B 12148S51BDocument10 pagesNumerical Methods QB 11148S51B 12148S51BvenkiatNo ratings yet
- Backpropagation in Matrix NotationDocument8 pagesBackpropagation in Matrix NotationEkta GavasNo ratings yet
- Num DiffDocument7 pagesNum DiffMohsan HasanNo ratings yet
- Equation: William W. LarryDocument18 pagesEquation: William W. LarrysumathyNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems.60 Q.PDocument9 pagesSignals and Systems.60 Q.Prubiniravichandran100% (1)
- Operation ResearchDocument2 pagesOperation ResearchShraddhanjali SahooNo ratings yet
- Quiz-2 PARTBDocument4 pagesQuiz-2 PARTBkunal chaturvediNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph'S College, Devagiri, Calicut (Autonomous) : Total Credits: 80Document50 pagesSt. Joseph'S College, Devagiri, Calicut (Autonomous) : Total Credits: 80Franklin GeorgeNo ratings yet
- K-Means and PCADocument69 pagesK-Means and PCAvdjohnNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Curriculum - Courses OnlyDocument146 pagesCivil Engineering Curriculum - Courses OnlyJoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Final Exam 2016Document4 pagesSolutions Final Exam 2016ayadmanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument20 pagesQuadratic Equationkartikgujjar541No ratings yet
- Gauss's Law & Potential: Flux of An Electric FieldDocument13 pagesGauss's Law & Potential: Flux of An Electric FieldgopalNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions MCQ and Answers On Numerical Methods PDFDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions MCQ and Answers On Numerical Methods PDF2003ahisNo ratings yet
- 1117 1 M-Ary Signals PART 1Document11 pages1117 1 M-Ary Signals PART 1PARKSANGWOOKNo ratings yet