Income Tax Deductions List - Section 80C To 80U Deductions FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) - Tax2win
Income Tax Deductions List - Section 80C To 80U Deductions FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) - Tax2win
Uploaded by
Saidas VengurlekarCopyright:
Available Formats
Income Tax Deductions List - Section 80C To 80U Deductions FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) - Tax2win
Income Tax Deductions List - Section 80C To 80U Deductions FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) - Tax2win
Uploaded by
Saidas VengurlekarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Income Tax Deductions List - Section 80C To 80U Deductions FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) - Tax2win
Income Tax Deductions List - Section 80C To 80U Deductions FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25) - Tax2win
Uploaded by
Saidas VengurlekarCopyright:
Available Formats
Products Tools Knowledge Center Guides Pricing Contact Log In Sign Up
Maximize Your Income Tax Refund
File Your Taxes with the Experts
Start Today
Home Income Tax Income Tax Deductions Income Tax Deductions List - Section 80C to 80U Deductions FY 2023-24 (AY 2024-25)
Income Tax Deductions List:
Deductions on Section 80C,
80CCC, 80CCD & 80D - FY 2023-24
(AY 2024-25)
Updated on: 26 Jun, 2024 12:36 PM
deduction under chapter vi a, chapter vi a deductions, deductions under sec 80c to 80u,
income tax deduction list
The Income Tax Department, recognizing the significance of fostering savings and investments, has
incorporated a comprehensive set of income tax deductions under Chapter VI A of the Income Tax Act.
While deduction under 80C stands out as a widely known provision, several other deductions exist,
providing taxpayers with opportunities to strategically reduce their tax liabilities. These deductions
under section 80C to 80U serve as powerful incentives, allowing individuals to optimize their financial
planning and contribute to the nation's economic growth. In this article, we will present the 80C
deduction list as well as discuss in detail the chapter VI A deductions.
Contents
What is Income Tax Deduction under Chapter VI A of Income Tax Act?
Section 80 Deduction List - Who can Claim Income Tax Deductions?
Investments that Qualify for Deductions under Section 80C
Expenses that Qualify for Tax Deductions under Section 80C
Features of Income Tax Deduction u/s 80
FAQs on Deductions Under Sections 80C to 80U?
What is Income Tax Deduction under Chapter
VI A of Income Tax Act?
Income Tax Deduction under Chapter VIA of Income Tax Act refers to a reduction in the taxable income
of an individual or a business entity, which results in a lower tax liability. The Indian Income Tax Act
provides for various deductions under sections 80C to 80U, which can be claimed by an individual or a
business entity while calculating their taxable income.
Let us take an example of tax saving for individuals with yearly salaries up to 20 lakhs.
Tax saving calculation for yearly income-20 lakhs
Gross Salary 2,000,000
Less:
HRA 200,000
LTA 40,000
Reimbursements 24,500
Children education and hostel allowance 9,600
Standard Deduction 50,000
Professional Tax 2400
Taxable Salary Income
Less: Deductions
80C (Refer Note below) 150,000
80D 50,000
80E 22,000
Net Taxable Income 14,51,500
Tax on the above income 2,57,868
Rebate u/s 87A Not applicable
Total Tax 2,57,868
Apart from this, you can also claim these tax deductions if eligible:
Interest on home loan EMIs under Section 24b -2,00,000
Principal amount of the home loan under section 80EEA -1,50,000
National Pension Scheme (NPS) investments u/s 80CCD(1B) -50,000
Section 80 Deduction List - Who can Claim
Income Tax Deductions?
Only eligible taxpayers can claim these deductions in their income tax returns. Such eligible taxpayers
have been specified under various sections of the Act. It is pertinent to note that the taxpayers who opt
to pay tax under the new tax regime can claim only deductions under sections 80CCD(2) and 80JJAA.
Income tax deduction needs to be claimed at the time of filing your Income Tax Return, and no
separate disclosure compliances are required for claiming such deductions. The number of deductions
should be reduced from the gross income to reach the taxable amount.
Sections Income Tax Deduction for FY Eligible person Maximum
2023-24(AY 2024-25) deduction
available for
FY 2023-24(AY
2024-25)
Section Investing into very common and Individual Upto Rs
80C popular investment options like Or 1,50,000
LIC, PPF, Sukanya Samriddhi HUF
Account, Mutual Funds, FD,
child tuition fee, ULIP, etc
Section Investment in Pension Funds Individuals
80CCC
Section Atal Pension Yojana and Individuals
80CCD (1) National Pension Scheme
Contribution
Section Atal Pension Yojana and Individuals Upto Rs 50,000
80CCD(1B) National Pension
SchemeContribution (additional
deduction)
Section National Pension Individuals Amount
80CCD(2) SchemeContribution by Contributed
Employer or
14% of Basic
Salary +
Dearness
Allowance (in
case the
employer is
Government)
10% of Basic
Salary+
Dearness
Allowance(in
case of any
other employer)
- Whichever is
lower
Section Medical Insurance Premium, Individual Upto Rs
80D preventive health checkup and Or 1,00,000
Medical Expenditure HUF
Section Medical Treatment of a Individual Normal
80DD Dependent with Disability Or Disability
HUF (atleast 40% or
more but less
than 80%): Rs
75000/-
Severe
Disability
(atleast 80% or
more) : Rs
125000/-
Section Medical expenditure for Individual Senior Citizens:
80DDB treatment of Specified Diseases Or Upto Rs
HUF 1,00,000
Others: Upto
Rs 40,000
Section Interest paid on Loan taken for Individual No limit (Any
80E Higher Education amount of
interest paid on
education
loan)upto 8
assessment
years
Section Interest paid on Housing Loan Individual Upto Rs 50,000
80EE subject to some
conditions
Section Interest Paid on Housing Loan Individual Upto Rs
80EEA 1,50,000/-
subject to some
conditions
Section Interest paid on Electric Vehicle Individual Upto Rs
80EEB Loan 1,50,000
subject to some
conditions
Section Donation to specified All Assessee 100% or 50% of
80G funds/institutions. Institutions (Individual, HUF, the Donated
Company, etc) amount or
Qualifying limit,
Allowed
donation in
cash upto
Rs.2000/-
Section Income Tax Deduction for Individual Rs. 5000 per
80GG House Rent Paid month
25% of
Adjusted Total
Income
Rent paid -
10% of
Adjusted Total
Income
- whichever is
lower
Section Donation to Scientific Research All assessees 100% of the
80GGA & Rural Development except those who amount
have an income donated.
(or loss) from a Allowed
business and/or a donations in
profession cash upto
Rs.10,000/-
Section Contribution to Political Parties Companies 100% of the
80GGB amount
contributed
No deduction
available for the
contribution
made in cash
Section Individuals on contribution to Individual 100% of the
80GGC Political Parties HUF amount
AOP contributed.
BOI No deduction
Firm available for the
contribution
made in cash
Section Royalty on Patents Individuals (Indian Rs.3,00,000/-
80RRB citizen or foreign Or
citizen being Specified
resident in India) Income
- whichever is
lower
Section Royalty Income of Authors Individuals (Indian Rs.3,00,000/-
80QQB citizen or foreign Or
citizen being Specified
resident in India) Income
- whichever is
lower
Section Interest earned on Savings Individual Upto Rs
80TTA Accounts Or 10,000/-
HUF (except
senior citizen)
Section Interest Income earned on Individual (60 yrs Upto Rs
80TTB deposits(Savings/ FDs) or above) 50,000/-
Section Disabled Individuals Individuals Normal
80U Disability: Rs.
75,000/-
Severe
Disability: Rs.
1,25,000/-
If you want to know about more such tax-saving options and want to maximize your tax refund,
file your ITR with Tax2win’s tax experts and never fall prey to penalties.
Investments that Qualify for Deductions under
Section 80C
Tax saving options under Section 80C
There are several options you can choose to save tax under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. The
Income Tax deduction list include:
1. Equity Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS)
2. National Pension Scheme (NPS)
3. Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP)
4. Public Provident Fund (PPF)
5. Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY)
6. National Savings Certificate (NSC)
7. Fixed Deposit (FD)
8. Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
Please note that these benefits are available if you have chosen the “Old Tax Regime.”
Expenses that Qualify for Tax Deductions
under Section 80C
Life Insurance Premiums
Employee Provident Fund (EPF) contributions
Public Provident Fund (PPF) investments
National Savings Certificate (NSC) investments
Equity-Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS) investments
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) investments
5-Year Fixed Deposit with Banks
Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS) investments
Tuition Fees for up to two children
Home Loan Principal Repayment
Stamp Duty and Registration Charges for a Home
Features of Income Tax Deduction u/s 80
Section 80C: This section provides a deduction of up to Rs. 1.5
lakh for investments in specified instruments such as EPF, PPF,
NSC, ELSS, tax-saving fixed deposits, etc.
An income tax deduction list consisting of the investments that are eligible for deduction
under section 80 is given below -
1) Premium paid for life insurance policy Premium paid on insurance policies of self,
spouse, or child (minor or major). If you pay a premium for your parents, then you will
not be allowed to take a deduction under chapter vi a. If In the case of HUF, the
premium paid for any member. It can be either a life policy or an endowment policy.
2) Any amount invested in the Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme in the name of your
daughter or any girl child for whom you are a legal guardian.
3) Contribution to:
- Public Provident Fund
- Approved superannuation fund
- Unit-linked Insurance Plan, 1971
- Unit-linked Insurance Plan of LIC Mutual Fund
- Approved annuity plan of LIC
- Pension fund, which is set up by a mutual fund or by the administrator or the specified
company
- National Housing Bank Term Deposit Scheme, 2008
- additional account under NPS
- Senior Citizens Savings Scheme Rules, 2004
4) Subscription to:
- National Savings Certificates (VIII issues)
- units of any mutual fund or from the administrator or the specified company
- notified deposit scheme of a public sector company that provides long-term finance
for construction or purchase or construction of houses for the construction or purchase
or construction of houses for residential purposes in India or any other deposit scheme
concerned with housing accommodation or planning, improvement, or development of
cities, towns, and villages, or both.
- specified equity shares or debentures or units of mutual fund
- notified bonds issued by NABARD
5) Investment in a five-year fixed deposit (FD) of a Scheduled Bank or Post Office
6) Repayment of housing loan principal amount(including stamp duty, registration fee,
and other expenses)
7) Payment of tuition fees to any college, school, university, or other educational
institutions within India for full-time education for maximum 2 children
Check the detailed guide on section 80 C deduction.
Section 80CCC: This section provides a deduction for contributions
made to annuity plans of LIC or any other insurer for receiving
pension.
Under section 80CCC income tax deduction for the contributions made in specified pension
plans can be claimed. The tax deduction can be claimed by individuals (whether resident or
non-resident). Maximum permissible deduction under sections 80C, 80CCC, and 80CCD(1) put
together is Rs. 1,50,000
Section 80CCD(1): An income tax deduction for contributions made
by individuals to eligible NPS
The contribution made to eligible NPS account is tax-deductible up to Rs 1.5 lakhs under
section 80CCD(1). The deductions shall be restricted to the amount contributed or the below-
given percentage, whichever is less. However, this tax benefit is within the overall ceiling limits
of section 80CCE, i.e., Rs. 1,50,000. To know the computation of the exempt amount, eligibility,
and much more. Read more
Section 80CCD(1B): Additional Income tax deduction for
contributions made by individuals to eligible NPS
Section 80CCD(1B) gives you the additional tax saving benefit of up to Rs 50,000 for
contributions to the NPS account. It is over and above the limits of section 80C,i.e., It shall not
be subjected to the ceiling limit of Rs. 1,50,000. This section 80CCD has gained so much
attention as you can invest up to Rs. 2 lakh in an NPS account and claim a deduction of the full
amount, i.e., Rs. 1.50 lakh under Sec 80CCD(1) and Rs. 50,000 under Section 80CCD(1B). Click
to know more.
Section 80CCD(2): An income tax deduction for contributions by an
employer to eligible NPS
The contribution to NPS is deductible under 80CCD(1), and 80CCD(1B), and the amount
contributed by your employer towards your NPS account is also tax-deductible under section
80CCD(2). Read to know more details. The deduction amount shall be restricted to 14% of
salary(Basic salary + DA) in the case of Govt. employees and 10% in case of any other
employees.
Section 80D: Income Tax benefit for medical insurance premium
Section 80D is amongst the most popular tax-saving options. Under this tax, the benefit is
admissible for
. Medical Insurance Premiums
. Expenditure on Preventive Health Check-up
. Other Medical Expenditure
The admissible deductions under this section are as under:
In
In the
the case
case of
of an
an individual
individual
. Case I – If your self/spouse or dependent children are below 60 Years of age, then
the maximum deduction is Rs. 25,000, and if your parents are also below 60 years of
age, then the maximum deduction is Rs. 25,000. Therefore, the aggregate deduction
shall be a maximum of Rs. 50,000.
. Case II – If your self/spouse or dependent children are below 60 Years of age, then
the maximum deduction is Rs. 25,000. If parents are 60 years or above, the maximum
deduction is Rs. 50,000. Therefore, the aggregate deduction shall be a maximum of
Rs. 75,000.
. Case III – If your self/spouse or dependent children are 60 years or above, then the
maximum deduction is Rs. 50,000. If your parents are also 60 years or older, the
maximum deduction is Rs. 50,000. Therefore, the aggregate deduction shall be a
maximum of Rs. 1,00,000.
. Deduction up to Rs. 5,000 shall be allowed for payment made towards preventive
health check-ups of self, spouse, dependent children, or dependent parents made
during the previous year. However, the said deduction of Rs. 5,000 shall be within the
overall limit of Rs. 25,000 or Rs. 50,000 specified above.
In
In the
the case
case of
of HUF,
HUF,
The maximum deduction available to a HUF in respect of premium paid to insure the health of
any member of the family would be Rs. 25,000, and in case any member is a senior citizen,
then Rs. 50,000.
Notes:
Notes:
. You can also claim a deduction of upto Rs. 50,000 under section 80D even if you do
not have any health insurance policy, provided any amount is incurred towards:
- medical treatment expenditure of self, spouse, and dependent children (who is of
the age of sixty years or more and not having medical insurance cover)
- medical treatment expenditure of any parent(s) (who is of the age of sixty years or
more and not having medical insurance cover)
. Deduction where the health insurance premium is paid in lump sum: Deduction shall
be apportioned towards all the years for which the premium is paid.
Read to know further details.
Section 80DD: Income Tax Deduction for Medical Treatment of a
Dependent with Disability
Section 80DD provides an income tax benefit to the extent of Rs 75,000 (Where disability is
40% or more but less than 80%) & Rs 1,25,000 (Where there is a severe disability (disability is
80% or more), respectively. The benefit can be availed for incurring medical expenditures for a
disabled dependent relative. For diseases covered, documents required, and other
information, please refer to the detailed guide.
Section 80DDB: Income Tax Deduction for Specified Diseases
The income tax deduction under section 80DDB serves as financial help for those suffering
from a severe disease or taking care of such dependent family members. The deduction is
allowed regarding the amount paid for the medical treatment of such disease or ailment of the
specified persons. The maximum deduction is summarized hereunder:
Dependant
Dependant Maximum
Maximum limit
limit (Rs.)
(Rs.)
A senior citizen (being a resident individual) 1,00,000
Other than a senior citizen 40,000
No such deduction shall be allowed unless a prescription is obtained for such medical
treatment from a neurologist, oncologist, urologist, hematologist, immunologist, or other
specialists, as may be prescribed. Read more to know the eligibility and other qualifying
criteria.
Section 80E: Income Tax Deduction for Interest paid on Higher
Education Loan
The interest paid on higher education loans taken for self, spouse, child, or student of whom
you are a legal guardian is eligible for income tax deduction under section 80E. The tax
benefit is available for the 8 Assessment Years. i.e., The current year and the next 7 years,
without maximum limits. Read to know more.
Section 80EE: Income Tax Deduction for Home Loan
Section 80EE provides an additional deduction of up to Rs. 50,000 in respect of the interest
on a loan taken by an individual to acquire residential house property from any financial
institution. Read insights here. 80EE deduction is in addition to the deduction available under
section 24 while computing ‘income from house property’. The conditions for availing
deduction of interest are: here.
Section 80EEA: Income Tax Deduction for first time home buyers
This section is Section 80EEA, which allows an additional deduction to taxpayers for paying
interest on a home loan availed by them. While Section 24 allowed for interest exemption on
home loans up to INR 2 lakhs, this section allows an additional exemption of Rs 1.5 lakhs to
home buyers who avail of a home loan and pay interest on the loan.
Other conditions for availing deduction of interest:
Section 80EEB: Income Tax Deduction for Repayment of Electronic
Vehicle Loan
This section was introduced to promote the purchase of electric vehicles among individuals by
giving them tax relief on the interest paid on loans taken to purchase such vehicles from any
financial institution from 01/04/2019 to 31/03/2023. The limit of deduction is up to Rs 1.5 lakhs.
Section 80G: Deduction in respect of donations made to specified
funds and charitable institutions etc
. Deduction under this section is available to all types of taxpayers (individual/ firm/ LLP
or any other person).
. The deduction amount is based on the category in which the fund falls, i.e., with or
without any qualifying limit.
Where the funds are subject to a qualifying limit, the formula for calculation of
deduction = Gross Qualifying Amount - Net Qualifying Amount
. The donation should be made in any mode of payment other than cash if it exceeds
Rs. 2,000. Donations in kind are not eligible for deduction under this section.
You might also like
- HSC Eco Essay PlansDocument65 pagesHSC Eco Essay Plansbmstf9hyfmNo ratings yet
- HCL PayslipDocument1 pageHCL PayslipkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Deductions List - Deductions On Section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD and 80D - FY 2022-23 (AY 2023-24) - Tax2winDocument26 pagesIncome Tax Deductions List - Deductions On Section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD and 80D - FY 2022-23 (AY 2023-24) - Tax2winJaydeep DasadiyaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax NewDocument10 pagesIncome Tax Newmarketing.incand24No ratings yet
- Personal Income Tax Under The New Regime and Old RegimeDocument4 pagesPersonal Income Tax Under The New Regime and Old RegimeAiswarya BNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Calculator For F.Y 2020 21 A.Y 2021 22 ArthikDishaDocument8 pagesIncome Tax Calculator For F.Y 2020 21 A.Y 2021 22 ArthikDishaGeetanjali BarejaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Divyastra CH 13 Deductions From GTI RDocument22 pagesIncome Tax Divyastra CH 13 Deductions From GTI RN AparnaNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Madras: CircularDocument5 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Madras: CircularAravinthram R am18m002No ratings yet
- SalaryDocument10 pagesSalaryMaanoj K SharmaaNo ratings yet
- Net Income How To Calculate Net Income in Income TaxDocument34 pagesNet Income How To Calculate Net Income in Income TaxSeetha SenthilNo ratings yet
- Faq'S & Guidlines On Income TaxDocument50 pagesFaq'S & Guidlines On Income TaxRavikarthik GurumurthyNo ratings yet
- Taxation CLass Test 1Document6 pagesTaxation CLass Test 1ap.quatrroNo ratings yet
- DeductionsDocument81 pagesDeductionsRaju DuttaNo ratings yet
- Form 16 - BLMPB2218K - 2019-20 - Part B PDFDocument6 pagesForm 16 - BLMPB2218K - 2019-20 - Part B PDFUmair BaigNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Planner FY 2020-21Document12 pagesIncome Tax Planner FY 2020-21RedNo ratings yet
- Employee Declaration Form 1Document4 pagesEmployee Declaration Form 1rifas caNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 Shrikant Jadhav Form 16-Part B PDFDocument6 pages2021-2022 Shrikant Jadhav Form 16-Part B PDFVidya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Investment POI Guidance Notes (FY 23-24)Document33 pagesInvestment POI Guidance Notes (FY 23-24)Puneet GuptaNo ratings yet
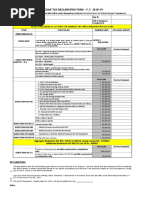
- Employee Tax Declaration - FY 22-23-DBMPDocument3 pagesEmployee Tax Declaration - FY 22-23-DBMPthetrilight2023No ratings yet
- NMIMS Global Access School For Continuing Education (NGA-SCE) Course: Taxation-Direct and Indirect Internal Assignment Applicable For June 2020 ExaminationDocument10 pagesNMIMS Global Access School For Continuing Education (NGA-SCE) Course: Taxation-Direct and Indirect Internal Assignment Applicable For June 2020 ExaminationAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- F0RM NO. 16 (See Rule 31 (1) (A) ) (Annexure-B) : (B) Tax On EmploymentDocument1 pageF0RM NO. 16 (See Rule 31 (1) (A) ) (Annexure-B) : (B) Tax On EmploymentSourabhthakral_1No ratings yet
- Rebates and Releifs Page 415 To 418Document4 pagesRebates and Releifs Page 415 To 418Nitin RajNo ratings yet
- Final Tommorow YetDocument6 pagesFinal Tommorow YetGourav BathejaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Old and New Tax Regime 04042023Document3 pagesComparison of Old and New Tax Regime 04042023VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Principles of Taxation - DeductionsDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Taxation - Deductions20047 BHAVANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- DeductionsDocument81 pagesDeductionshitesh1601kukrejaNo ratings yet
- IT Form 16 Back - WWW - Ibadi.inDocument1 pageIT Form 16 Back - WWW - Ibadi.inGOKUL HD LIVE EVENTSNo ratings yet
- Form 1614062023 173940Document3 pagesForm 1614062023 173940jrqvd9d5rnNo ratings yet
- CA FInal DT SampleDocument8 pagesCA FInal DT SampleprasannaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Calculation Worksheet: Ellucian Higher Education Systems India Private Limited Ascent PayrollDocument2 pagesIncome Tax Calculation Worksheet: Ellucian Higher Education Systems India Private Limited Ascent PayrollShiva098No ratings yet
- Deductions Available Under Chapter VI of Income TaxDocument4 pagesDeductions Available Under Chapter VI of Income TaxDeepanjali NigamNo ratings yet
- Form-16-Excel-Format-AY-2024-25Document6 pagesForm-16-Excel-Format-AY-2024-25faijalrazakhanNo ratings yet
- Train Law ActDocument231 pagesTrain Law ActKristine Japitana100% (1)
- Break Even Point For Choosing Tax RegimeDocument9 pagesBreak Even Point For Choosing Tax RegimeSivasankariNo ratings yet
- Tax Report Jan 2024Document1 pageTax Report Jan 2024yashodhan.kadam30No ratings yet
- Tax Decalaration 2023-24Document3 pagesTax Decalaration 2023-24thetrilight2023No ratings yet
- Form 1602102023 160124Document3 pagesForm 1602102023 160124isantbasnet3561No ratings yet
- Form 1617082023 112227Document2 pagesForm 1617082023 112227rinsha.sherinNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Deductions ListDocument4 pagesIncome Tax Deductions Listamitks525No ratings yet
- Income Tax Deductions and Exemptions in India 2018: MenuDocument7 pagesIncome Tax Deductions and Exemptions in India 2018: MenusandeshNo ratings yet
- Tax Laws New Syllabus Mock Test 1 by VG SirDocument20 pagesTax Laws New Syllabus Mock Test 1 by VG Sirsharmaaryan1030No ratings yet
- S Income Tax Declaration April 2016Document2 pagesS Income Tax Declaration April 2016HanumanthNo ratings yet
- Form 1615012023 135230 PDFDocument3 pagesForm 1615012023 135230 PDFSahil ThakurNo ratings yet
- New Cals Case 14Document2 pagesNew Cals Case 14Rishi ChandakNo ratings yet
- Deductions From Gross Total Income: HapterDocument20 pagesDeductions From Gross Total Income: HapterJAWED MOHAMMADNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Calculator WarikooDocument10 pagesIncome Tax Calculator Warikoomehmood.aribNo ratings yet
- Section 80CCD (1B) Deduction - About NPS Scheme & Tax BenefitsDocument7 pagesSection 80CCD (1B) Deduction - About NPS Scheme & Tax BenefitsP B ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- R.A. 10963 (TRAIN) - Income Tax ProvisionsDocument50 pagesR.A. 10963 (TRAIN) - Income Tax ProvisionsKrishtineRapisoraBolivarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Taxation Law - (Week 8)Document56 pagesPrinciples of Taxation Law - (Week 8)Snigdha RohillaNo ratings yet
- S Income Tax Declaration April 2017Document2 pagesS Income Tax Declaration April 2017HanumanthNo ratings yet
- Employee Declaration FormDocument3 pagesEmployee Declaration Formmeshakjunior13No ratings yet
- DeductionsDocument7 pagesDeductionsAnurag BishtNo ratings yet
- Decoding Indian Union Budget Finance Bil PDFDocument7 pagesDecoding Indian Union Budget Finance Bil PDFkumarNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Calculation Worksheet: Thermax LTD Ascent PayrollDocument1 pageIncome Tax Calculation Worksheet: Thermax LTD Ascent PayrollAnuragNo ratings yet
- IT Form 16 Back - WWW - Ibadi.inDocument1 pageIT Form 16 Back - WWW - Ibadi.inKATHI JAYANo ratings yet
- Summary Charts Deduction Chapter ViaDocument4 pagesSummary Charts Deduction Chapter ViaUttam Gagan18100% (1)
- TRAIN-LAWDocument49 pagesTRAIN-LAWAina AmainNo ratings yet
- Deductions From Gross Total Income: Learning OutcomesDocument86 pagesDeductions From Gross Total Income: Learning OutcomesNisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- How To Save Tax For Salary Above 20 LakhsDocument12 pagesHow To Save Tax For Salary Above 20 LakhsvijaytechskillupgradeNo ratings yet
- 1724015062-Old-Cals-Case-1Document2 pages1724015062-Old-Cals-Case-1nitikadogra207No ratings yet
- Income Tax Declaration April 2017Document2 pagesIncome Tax Declaration April 2017HanumanthNo ratings yet
- Wiley GAAP for Governments 2012: Interpretation and Application of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles for State and Local GovernmentsFrom EverandWiley GAAP for Governments 2012: Interpretation and Application of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles for State and Local GovernmentsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2Document2 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2Sharlyn Marie An Noble-BadilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document28 pagesChapter 4april020718No ratings yet
- 12th Accountancy EM Quarterly Exam 2022 Original Question Paper Tenkasi District English Medium PDF DownloadDocument4 pages12th Accountancy EM Quarterly Exam 2022 Original Question Paper Tenkasi District English Medium PDF DownloadJansi ArulNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics SummaryDocument3 pagesMacroeconomics Summaryzsarlie786No ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument42 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisM RNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5eDocument38 pagesLecture 5eShedrine ButaliNo ratings yet
- F3 - ACCA Chapter-18-1Document40 pagesF3 - ACCA Chapter-18-1Nile NguyenNo ratings yet
- Nama Nama AkunDocument26 pagesNama Nama AkunTia YuliandiniNo ratings yet
- Break Even AnalysisDocument13 pagesBreak Even Analysissuchipatel100% (2)
- Compiled Econ Objective Type From Examveda-1Document38 pagesCompiled Econ Objective Type From Examveda-1Jeziel AtaNo ratings yet
- COMPANY/FINANCE/PROFIT AND LOSS/175/Nestle IndiaDocument1 pageCOMPANY/FINANCE/PROFIT AND LOSS/175/Nestle IndiabhuvaneshkmrsNo ratings yet
- LKTT SC - 30 Jun 2020Document146 pagesLKTT SC - 30 Jun 2020adjipramNo ratings yet
- Taylor NZ CaseDocument60 pagesTaylor NZ CaseSarthak ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Nepal Budget 2076-77 (2019-20)Document38 pagesNepal Budget 2076-77 (2019-20)Menuka SiwaNo ratings yet
- Tugas AuditDocument11 pagesTugas AuditJihan Faradhilah326No ratings yet
- Research Essay Cs FinalDocument13 pagesResearch Essay Cs Finalapi-519794514No ratings yet
- Clubbing of Income Under Income Tax Act, 1961 - Section 60 To 64 - Taxguru - inDocument6 pagesClubbing of Income Under Income Tax Act, 1961 - Section 60 To 64 - Taxguru - inRISHITA RAJPUT SINGHNo ratings yet
- MODULE 9 MicroDocument7 pagesMODULE 9 MicroGladz De ChavezNo ratings yet
- Tally Chapter 3Document54 pagesTally Chapter 3bhavya gNo ratings yet
- Jat Holdings Limited: Sri LankaDocument3 pagesJat Holdings Limited: Sri Lankacpasl123No ratings yet
- Shopify Financial Worksheet Template: More Instructions On Cash Flow Management HereDocument6 pagesShopify Financial Worksheet Template: More Instructions On Cash Flow Management HereOLOMOSEDARA IFEOLUWANo ratings yet
- BE Mar 2020 Assignment SolutionDocument9 pagesBE Mar 2020 Assignment SolutionJATINNo ratings yet
- Lgu FSSDocument32 pagesLgu FSSAh MhiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Sources of Family IncomeDocument22 pagesLesson 2 Sources of Family Incomeroel mabbayad83% (6)
- Advanced FA I Course OutlineDocument4 pagesAdvanced FA I Course Outlinebekelesolomon828No ratings yet
- CH 4 - The Economic Environments Facing BusinessDocument28 pagesCH 4 - The Economic Environments Facing BusinessSamarth Dargan100% (1)
- Case Competition GuideDocument49 pagesCase Competition GuidexxNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation-FinalsDocument14 pagesIncome Taxation-FinalsTheaNo ratings yet