MS-01 (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)
MS-01 (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)
Uploaded by
reynanciakathCopyright:
Available Formats
MS-01 (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)
MS-01 (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)
Uploaded by
reynanciakathOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
MS-01 (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)
MS-01 (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)
Uploaded by
reynanciakathCopyright:
Available Formats
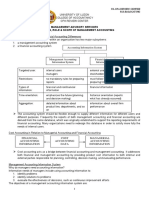
ReSA - THE REVIEW SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTANCY
CPA Review Batch 47 May 2024 CPA Licensure Examination
MS-01
MANAGEMENT SERVICES Aljon Lee Elirie Arañas Kenneth Manuel
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING VS. FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING – the use of accounting information by the company managers to make rational
economic decisions in performing its function of planning, organizing and controlling
business operations.
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
1. User of information Primarily for external users Exclusively for internal users
2. Source of information Internal data Internal data and external sources
3. Purpose of information Financial reporting and compliance Management decision-making
4. Guiding principles Accounting standards (e.g., PFRS) Management wants and needs
5. Type of information Mostly financial or monetary in nature Financial and non-financial
6. Time orientation Mainly historical Future-oriented using past, present data
7. Emphasis of reports Reliability - precision, verifiability Relevance – timeliness, materiality
8. Amount of details Aggregated and simplified Detailed and extensive
9. Focus of information Business as a whole Mainly on business segments
10. Frequency of reports Periodic (annually, quarterly) Whenever needed
11. Legal requirement Mandatory for publicly listed entities Optional on the part of management
12. Unifying model Assets = Liabilities + Equity No unifying model or equation
COST ACCOUNTING, while a separate discipline, is a subset of both management and financial accounting.
Managers are usually responsible for making decisions based on these basic MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS:
deciding on company goals and objectives and figures out how to achieve them.
PLANNING
(Associated terms: Road Mapping; Goal Setting)
deciding on how to use company resources to put plans into action.
ORGANIZING
(Associated terms: Directing & Motivating; Staffing & Subordinating)
deciding on what corrective actions to do should there be any difference between
CONTROLLING actual results and planned results
(Associated terms: Monitoring; Feedback Mechanism)
Decision-making is an inherent function of management since all management functions require a certain
level of decision-making; this makes management accounting information useful in all stages of management.
CONTROLLER – the chief management accounting executive that is primarily responsible for carrying out the
management control function. The task of a controller includes, among others, financial
reporting, cost and management accounting, accounting information system, financial analysis,
special studies.
is the authority to give orders (e.g., VP-operations over operations manager)
LINE function exercises direct downward authority over line departments
NOTE: line managers are directly involved in achieving company objectives.
is the authority to advise but not to command others
STAFF function is commonly exercised laterally or upward in an organization
NOTE: staff managers provide support via assistance or advice to other managers.
The controller primarily exercises a staff function as the controller’s office gives advice and assistance to other
departments and to whole organization; however, the controller has a line authority over subordinates within
the accounting department where the controller normally serves as the head or overall manager.
CONTROLLER vs. TREASURER
To avoid incompatible duties being assigned to a single officer, a controller (recording function) must not hold
at the same time the position of a treasurer (custody function). Consider the following distinction:
Planning and control Financial Reporting Evaluating and consulting Tax
CONTROLLER
administration Government reporting Protection of assets Economic appraisal
Provision of capital Investor relations Short-term financing Banking and custody
TREASURER
Credit and collections Investments Insurance
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT – concerns the duties of the financial manager, who is responsible for making
significant corporate investment and financing decisions.
GOAL OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Modern managerial finance theory works under the premise that the primary goal of the firm is to maximize
shareholders’ wealth, rather than just to maximize profit. The financial manager acts in the shareholders’ best
interests by making decisions that maximize the market value of the company stocks (i.e., wealth creation).
Page 1 of 4 0915-2303213 resacpareview@gmail.com
ReSA – THE REVIEW SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTANCY
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING vs. FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT MS-01
ROLE OF FINANCIAL MANAGERS
The role of a financial manager may include financial analysis and planning, investment decisions,
financing and capital structure decisions, management of financial resources and risk management. No single
person is tasked for all the responsibilities of a financial manager. These tasks are dispersed throughout the
firm. In large firms, financial responsibilities are usually carried out by the treasurer and/or the controller
while the chief financial officer (CFO) usually oversees their work.
BASIC PRINCIPLES IN FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Most techniques and tools in finance are based on the following fundamental principles:
Risk-return trade-off: a company does not take additional risks unless it expects to be compensated
with additional returns.
Time value of money: a peso received today is worth more than a peso received in the future.
Cash – not profit – is king.
Incremental cash flows: it is only what changes that counts.
Tax consideration: virtually all financial decisions are influenced by the effect of taxes.
Ethical behavior – doing the right thing – is always relevant.
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
(Sources: CMA/CIA/RPCPA/AICPA/Various test banks)
1. The main purpose of management accounting is to
a. Assess past performance c. Help managers make decisions
b. Project future transactions d. Help investors & creditors make decisions
2. The person most likely to use management accounting information is a(n)
a. Governmental taxing authority
b. Assembly department supervisor
c. Banker evaluating a credit application
d. Shareholder evaluating a stock investment
3. The person most likely to use only financial accounting information is a
a. Current shareholder c. Factory shift supervisor
b. Department manager d. Vice president of operations
4. Management accounting is similar to financial accounting in that
a. Both focus on the whole business rather business segments
b. Both classify reported information in the same way
c. Both are concerned with financial information only
d. Both deal with economic events
5. Determine the TRUE statement about managerial accounting.
a. It complies with GAAP to produce financial reports for external users
b. It tends to summarize information with precision more often than financial accounting
c. Reports are often based on estimates and are seldom useful for everything other than the
purpose for which they are prepared
d. It specifically covers various cost accumulation procedures such as job order costing,
process costing, standard costing, backflush costing and activity-based costing (ABC)
6. Which is the most accurate statement?
a. Financial accounting is a subset of cost accounting
b. Management accounting is a subset of cost accounting
c. Cost accounting is a subset of both management & financial accounting
d. Management accounting is a subset of both cost and financial accounting
7. Decision-making is required in which of the following management function(s)?
a. Planning c. Planning and organizing
b. Planning and control d. Planning, organizing and control
8. “Budgets” and “performance reports” respectively correspond to these management functions.
a. Planning and controlling c. Controlling and planning
b. Planning and organizing d. Organizing and controlling
9. The management control process contains the following four sequential steps, including
A) Measuring actual performance
B) Establishing standards of performance
C) Implementing a program of corrective action
D) Comparing actual performance with standards
What is the proper sequence of these activities?
a. A, B, C, D c. B, A, C, D
b. A, B, D, C d. B, A, D, C
Page 2 of 4 0915-2303213 resacpareview@gmail.com
ReSA – THE REVIEW SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTANCY
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING vs. FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT MS-01
10. The controller primarily occupies a
a. Line position
b. Staff position
c. Non-supervisory rank-and-file position
d. Position with very little influence in management decision-making
11. A staff position
a. Is superior in authority to a line position
b. Is not essential in a business organization
c. Relates directly to the carrying out of the basic objectives of the organization
d. Is supportive in nature, providing service and assistance to other parts of the organization
12. Which of the following statements is FALSE concerning line and staff functions?
a. Both line and staff functions are depicted on the organizational chart.
b. Line functions are directly related to the basic objectives of an organization.
c. Staff managers always have authorities over persons occupying line functions.
d. Line units or departments tend to have more employees than staff units or departments.
13. Which of the following is most likely a LINE position?
a. VP for Research of a conglomerate firm
b. Store manager of a retail convenience outlet
c. Chief financial officer of a merchandising company
d. Human resources manager for an educational institution
14. CONTROLLERS are usually not concerned with
a. Government reporting
b. Tax administration
c. Investor relations
d. Data processing
15. TREASURERS are usually not concerned with
a. Tax planning
b. Short-term financing
c. Cash custody and banking
d. Credit extension and collection of bad debts
16. The controller’s responsibilities are primarily (I) ___ in nature, while the treasurer’s responsibilities are
primarily related to (II) ____.
a. (I) Operational (II) Financial management
b. (I) Financial management (II) Accounting
c. (I) Accounting (II) Financial management
d. (I) Financial management (II) Operations
17. Which of the following is not a function of financial management?
a. Financing
b. Internal control
c. Capital budgeting
d. Risk management
18. The primary goal of financial management is to:
a. To minimize risks
b. To maximize profit
c. To maximize returns
d. To maximize shareholders' wealth
19. Profit maximization is not the primary goal of financial management because it does not take into
consideration the following:
a. Risk and EPS
b. Risk and cash flow
c. Cash flow and EPS
d. EPS and stock prices
20. The long-run objective of financial management is to:
a. Maximize market share
b. Maximize earnings per share
c. Maximize return on investment
d. Maximize the value of the firm’s common stock
Page 3 of 4 0915-2303213 resacpareview@gmail.com
ReSA – THE REVIEW SCHOOL OF ACCOUNTANCY
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING vs. FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT MS-01
MANAGEMENT SERVICES (MS)
• The word “advisory” is dropped from the subject title: MAS → MS
• One of the six CPA board exam subjects (other subjects: AUD, TAX, RFBT, FAR & AFAR)
• Projected CPALE Date & Time: 26 May 2024, Sunday, 8 AM – 11 AM
• Number of items: 70 multiple-choice questions (MCQs), mixture of theories and problems
• Topics covered based on latest version of the CPALE Syllabus for MS:
Part I – MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING (40 items)
✓ Cost Concepts and Behavior
✓ Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
✓ Standard Costing & Variance Analysis
✓ Variable Costing vs. Absorption Costing
✓ Financial Planning & Budgets
✓ Responsibility Accounting & Transfer Pricing
✓ Balanced Scorecard
✓ Relevant Costing
Part II – FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT (25 items)
✓ Financial Statement Analysis
✓ Working Capital Management
✓ Capital Budgeting
✓ Risks & Leverage
✓ Capital Structure & Long-Term Financing Decision
✓ Financial Markets
Part III – ECONOMICS (5 items)
✓ Macroeconomics
✓ Microeconomics
• Omitted topics (not covered in CPALE anymore): Management Consultancy, Project
Feasibility Study, Activity-Based Management, Strategic Cost Management, PERT-CPM.
• Most topics in MS are also covered in the US CMA Exam. Consider the following coverage
of the US CMA Exam:
CMA Part 1 – Financial Planning, Performance, and Analytics
(3 hours for 100 MCQs and 1 hour for the Essay portion)
✓ External Financial Reporting Decisions (15%)
✓ Planning, Budgeting & Forecasting (20%)
✓ Performance Management (20%)
✓ Cost Management (15%)
✓ Internal Controls (15%)
✓ Technology and Analytics (15%)
CMA Part 2 – Strategic Financial Management
(3 hours for 100 MCQs and 1 hour for the Essay portion)
✓ Financial Statement Analysis (20%)
✓ Corporate Finance (20%)
✓ Decision Analysis (25%)
✓ Risk Management (10%)
✓ Investment Decisions (10%)
✓ Professional Ethics (15%)
Page 4 of 4 0915-2303213 resacpareview@gmail.com
You might also like
- Resa MAS-01: Management Accounting - Financial Management: - T R S A100% (1)Resa MAS-01: Management Accounting - Financial Management: - T R S A4 pages
- Primarily For External Users Exclusively For Internal Users100% (1)Primarily For External Users Exclusively For Internal Users3 pages
- Must The Contractor Submit His Interim Payment Claims Before The Superintending Officer Certifies For Payment?No ratings yetMust The Contractor Submit His Interim Payment Claims Before The Superintending Officer Certifies For Payment?8 pages
- MS-A (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)No ratings yetMS-A (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)4 pages
- Management Advisory Services Objectives, Role & Scope of Management AccountingNo ratings yetManagement Advisory Services Objectives, Role & Scope of Management Accounting8 pages
- Chapter 1 (ManAcc) Overview of Management AccountingNo ratings yetChapter 1 (ManAcc) Overview of Management Accounting34 pages
- 1 - Objectives, Role and Scope of Management Accounting100% (2)1 - Objectives, Role and Scope of Management Accounting11 pages
- 01 Fundamentals of Managerial Accounting and Ethical StandardsNo ratings yet01 Fundamentals of Managerial Accounting and Ethical Standards10 pages
- Chapter I: Management and The Nature of Management AccountingNo ratings yetChapter I: Management and The Nature of Management Accounting11 pages
- Managerial Accounting: Mon Raval Sevilla, CPANo ratings yetManagerial Accounting: Mon Raval Sevilla, CPA27 pages
- 1.1 Intro To SCM and Management AccountingNo ratings yet1.1 Intro To SCM and Management Accounting6 pages
- Management Accounting and Accounting Information System Learning ObjectivesNo ratings yetManagement Accounting and Accounting Information System Learning Objectives11 pages
- Chapter 2 The Professional Environment of Cost ManagementNo ratings yetChapter 2 The Professional Environment of Cost Management20 pages
- Mas by Cabrera Chapter 1 Management Accounting An OverviewNo ratings yetMas by Cabrera Chapter 1 Management Accounting An Overview18 pages
- Cost & Mgt. Acct - I, Lecture Note - Chapter 1 & 2No ratings yetCost & Mgt. Acct - I, Lecture Note - Chapter 1 & 235 pages
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Cost and Management AccountingNo ratings yetChapter 1 Introduction To Cost and Management Accounting6 pages
- Expert Financial Analysis: Strategies for Professional SuccessFrom EverandExpert Financial Analysis: Strategies for Professional SuccessNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessNo ratings yet
- HAVAS Red Redefining Purpose October 2024No ratings yetHAVAS Red Redefining Purpose October 202418 pages
- Sample Questions MCQS 2020 GROUP II Business LawNo ratings yetSample Questions MCQS 2020 GROUP II Business Law18 pages
- 2024-02-29 - Elitheni Coal (Pty) LTD - Status ReportNo ratings yet2024-02-29 - Elitheni Coal (Pty) LTD - Status Report2 pages
- Materials Management - 1 - Dr. VP - 2017-18No ratings yetMaterials Management - 1 - Dr. VP - 2017-1833 pages
- Literature Review On Feasibility Study o PDFNo ratings yetLiterature Review On Feasibility Study o PDF4 pages
- BSBMGT517 Manage Operational Plan Task 1 QFC1912463100% (2)BSBMGT517 Manage Operational Plan Task 1 QFC191246314 pages
- Tata Communications Ticketing Portal User Manual - Release 9APR17 - v1.0No ratings yetTata Communications Ticketing Portal User Manual - Release 9APR17 - v1.029 pages
- Piata de Legume-Fructe 2015-2022 - Prezentare RezumativaNo ratings yetPiata de Legume-Fructe 2015-2022 - Prezentare Rezumativa5 pages
- Maths EM Half Yearly Exam 2022 Original Question Paper Kallakurichi District English Medium PDF DownloadNo ratings yetMaths EM Half Yearly Exam 2022 Original Question Paper Kallakurichi District English Medium PDF Download2 pages
- Exposure Draft of ICSI Guidance On Diligence Report On Governance For BanksNo ratings yetExposure Draft of ICSI Guidance On Diligence Report On Governance For Banks95 pages
- 330 Langalibalele Street, Pietermaritzburg, 3201 Directorate: Human Resource Management Services Recruitment and SelectionNo ratings yet330 Langalibalele Street, Pietermaritzburg, 3201 Directorate: Human Resource Management Services Recruitment and Selection5 pages
- Quiz For Finals With Answers and SolutionsNo ratings yetQuiz For Finals With Answers and Solutions6 pages
- Resa MAS-01: Management Accounting - Financial Management: - T R S AResa MAS-01: Management Accounting - Financial Management: - T R S A
- Primarily For External Users Exclusively For Internal UsersPrimarily For External Users Exclusively For Internal Users
- Must The Contractor Submit His Interim Payment Claims Before The Superintending Officer Certifies For Payment?Must The Contractor Submit His Interim Payment Claims Before The Superintending Officer Certifies For Payment?
- MS-A (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)MS-A (Management Accounting vs. Financial Management)
- Management Advisory Services Objectives, Role & Scope of Management AccountingManagement Advisory Services Objectives, Role & Scope of Management Accounting
- Chapter 1 (ManAcc) Overview of Management AccountingChapter 1 (ManAcc) Overview of Management Accounting
- 1 - Objectives, Role and Scope of Management Accounting1 - Objectives, Role and Scope of Management Accounting
- 01 Fundamentals of Managerial Accounting and Ethical Standards01 Fundamentals of Managerial Accounting and Ethical Standards
- Chapter I: Management and The Nature of Management AccountingChapter I: Management and The Nature of Management Accounting
- Management Accounting and Accounting Information System Learning ObjectivesManagement Accounting and Accounting Information System Learning Objectives
- Chapter 2 The Professional Environment of Cost ManagementChapter 2 The Professional Environment of Cost Management
- Mas by Cabrera Chapter 1 Management Accounting An OverviewMas by Cabrera Chapter 1 Management Accounting An Overview
- Cost & Mgt. Acct - I, Lecture Note - Chapter 1 & 2Cost & Mgt. Acct - I, Lecture Note - Chapter 1 & 2
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Cost and Management AccountingChapter 1 Introduction To Cost and Management Accounting
- Dummy Finance Guide for Nonfinancial ManagersFrom EverandDummy Finance Guide for Nonfinancial Managers
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to success
- Expert Financial Analysis: Strategies for Professional SuccessFrom EverandExpert Financial Analysis: Strategies for Professional Success
- Financial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your Business
- Corporate Governance, Finance and Operations ManagementFrom EverandCorporate Governance, Finance and Operations Management
- 2024-02-29 - Elitheni Coal (Pty) LTD - Status Report2024-02-29 - Elitheni Coal (Pty) LTD - Status Report
- BSBMGT517 Manage Operational Plan Task 1 QFC1912463BSBMGT517 Manage Operational Plan Task 1 QFC1912463
- Tata Communications Ticketing Portal User Manual - Release 9APR17 - v1.0Tata Communications Ticketing Portal User Manual - Release 9APR17 - v1.0
- Piata de Legume-Fructe 2015-2022 - Prezentare RezumativaPiata de Legume-Fructe 2015-2022 - Prezentare Rezumativa
- Maths EM Half Yearly Exam 2022 Original Question Paper Kallakurichi District English Medium PDF DownloadMaths EM Half Yearly Exam 2022 Original Question Paper Kallakurichi District English Medium PDF Download
- Exposure Draft of ICSI Guidance On Diligence Report On Governance For BanksExposure Draft of ICSI Guidance On Diligence Report On Governance For Banks
- 330 Langalibalele Street, Pietermaritzburg, 3201 Directorate: Human Resource Management Services Recruitment and Selection330 Langalibalele Street, Pietermaritzburg, 3201 Directorate: Human Resource Management Services Recruitment and Selection