IP06 Sol S2A E Web
IP06 Sol S2A E Web
Uploaded by
pakfan1130Copyright:
Available Formats
IP06 Sol S2A E Web
IP06 Sol S2A E Web
Uploaded by
pakfan1130Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
IP06 Sol S2A E Web
IP06 Sol S2A E Web
Uploaded by
pakfan1130Copyright:
Available Formats
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
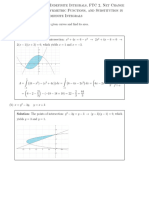
1. 2 x + y = 6
x 0 1 2
y 6 4 2
x + 4 y = −4
x 0 2 4
y −1 −1.5 −2
1A
From the figure, the two straight lines intersect at
(4, −2).
∴ The solution is x = 4 , y = −2 . 1A
(2)
2. x = 3 y
x 0 3 6
y 0 1 2
2x + y = 7
x 0 1 2
y 7 5 3
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 1
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
1A
From the figure, the two straight lines intersect at
(3, 1).
∴ The solution is x = 3 , y = 1. 1A
(2)
3. 3x + 2 y = 10
x 0 2 4
y 5 2 −1
2 x − 5 y = −12
x −1 1.5 4
y 2 3 4
1A
From the figure, the two straight lines intersect at
(1.4, 2.9) (cor. to 1 d.p.).
∴ The solution is x = 1.4 , y = 2.9 . 1A
(2)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 2
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
3 x − y = 1............................. (1)
4.
5 x − y = −1.......................... (2)
From (1), y = 3 x − 1............... (3)
Substitute (3) into (2),
5 x − (3 x − 1) = −1 1M
5 x − 3x + 1 = −1
2 x = −2
x = −1
Substitute x = −1 into (3),
y = 3(−1) − 1
= −4
∴ The solution is x = −1, y = −4 . 1A
(2)
x − 4 y = 2 ........................... (1)
5.
3 x − 2 y = 16 ........................ (2)
From (1), x = 4 y + 2 ..............(3)
Substitute (3) into (2),
3(4 y + 2) − 2 y = 16 1M
12 y + 6 − 2 y = 16
10 y = 10
y =1
Substitute y = 1 into (3),
x = 4(1) + 2
=6
∴ The solution is x = 6 , y = 1. 1A
(2)
2 y + 7 x = −15 .....................(1)
6.
−4 x − 3 y = 3 ....................... (2)
−7 x − 15
From (1), y = ......... (3)
2
Substitute (3) into (2),
−7 x − 15
−4 x − 3 =3 1M
2
−7 x − 15
2(−4 x) − 2 3 = 2(3)
2
−8 x + 21x + 45 = 6
13 x = −39
x = −3
Substitute x = −3 into (3),
−7(−3) − 15
y=
2
=3
∴ The solution is x = −3, y = 3. 1A
(2)
x + 4 y = 7 ...............................(1)
7.
3 x − y = 8 ............................... (2)
(1) × 3: 3 x + 12 y = 21................ (3)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 3
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
(3) − (2): (3x + 12 y ) − (3x − y ) = 21 − 8 1M
3x + 12 y − 3 x + y = 13
13 y = 13
y =1
Substitute y = 1 into (1),
x + 4(1) = 7
x=3
∴ The solution is x = 3 , y = 1. 1A
(2)
2 x − 3 y = 4 ............................. (1)
8.
4 x − 2 y = 8 ............................. (2)
(1) × 2: 4 x − 6 y = 8 ................... (3)
(2) − (3): (4 x − 2 y ) − (4 x − 6 y ) = 8 − 8 1M
4x − 2 y − 4x + 6 y = 0
4y = 0
y=0
Substitute y = 0 into (1),
2 x − 3(0) = 4
2x = 4
x=2
∴ The solution is x = 2 , y = 0 . 1A
(2)
3 x + 8 y = −18 ........................ (1)
9.
−2 y + 5 x = −7 ........................ (2)
(2) × 4: −8 y + 20 x = −28 .......... (3)
(1) + (3): (3 x + 8 y ) + (−8 y + 20 x) = −18 + (−28) 1M
3 x + 8 y − 8 y + 20 x = −46
23x = −46
x = −2
Substitute x = −2 into (1),
3(−2) + 8 y = −18
8 y = −12
3
y=−
2
3
∴ The solution is x = −2, y = − . 1A
2
(2)
10. (a) 2 x = ( x + 10°) + 40° (ext. ∠ of ) 1M
2 x = x + 50°
x = 50° 1A
(b) AC = BC (given)
∴ ∠BAC = x + 33° (base ∠s, isos. )
In ABC,
( x + 33°) + ( x + 33°) = 5 x (ext. ∠ of ) 1M
2 x + 66° = 5 x
3x = 66°
x = 22° 1A
(4)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 4
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
11. (a) 5 x + 72° + 160° + 78° + 100° = (5 − 2) × 180°
(∠ sum of polygon) 1M
5 x + 410° = 540°
5 x = 130°
x = 26° 1A
(b) x + 4 x + 32° + 90° + 133° + 90° = (6 − 2) × 180°
(∠ sum of polygon) 1M
5 x + 345° = 720°
5 x = 375°
x = 75° 1A
(4)
12. (a) x + 2 x + 131° + 61° = 360° (sum of ext. ∠s of polygon) 1M
3 x + 192° = 360°
3 x = 168°
x = 56° 1A
(b) 4 x + (3 x + 2°) + 90° + 25° + 75° + 70° = 360°
(sum of ext. ∠s of polygon) 1M
7 x + 262° = 360°
7 x = 98°
x = 14° 1A
(4)
13. (a) DEF ~ XYZ (given)
DE DF
∴ = (corr. sides, ~ s) 1M
XY XZ
x 3
= 1M
4 6
x=2 1A
(b) LMN ~ IJK (given)
∴ ∠M = ∠J (corr. ∠s, ~ s) 1M
= 60°
∠N = ∠K (corr. ∠s, ~ s)
=x
In LMN,
∠L + ∠M + ∠N = 180° (∠ sum of ) 1M
52° + 60° + x = 180°
x = 68° 1A
(6)
14. (a) Substitute x = 4 into the equation,
3y + 7 = 4 1M
3 y = −3
y = −1
∴ The y-coordinate of A is −1. 1A
(b) Substitute x = 1 and y = 2 into the equation,
L.H.S. = 3(2) + 7 1M
= 13
R.H.S. = 1
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 5
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ (1, 2) does not satisfy the equation.
i.e. (1, 2) does not lie on the graph of 3 y + 7 = x . 1A
(4)
15. (a) Size of each interior angle
= 180° − 15° (adj. ∠s on st. line) 1M
= 165° 1A
(b) Let n be the number of sides of the regular polygon.
360°
= 15° (sum of ext. ∠s of polygon) 1M
n
n = 24
∴ The number of sides of the regular polygon
is 24. 1A
(4)
16. Let x g and y g be the weights of a cupcake and a piece of
cheesecake respectively.
Accordingly,
5 x + 4 y = 900......................(1)
3 x + 8 y = 1 240....................(2) 1M
(1) × 2: 10 x + 8 y = 1 800........(3) 1M
(3) − (2): (10 x + 8 y ) − (3x + 8 y ) = 1 800 − 1 240 1M
10 x + 8 y − 3x − 8 y = 560
7 x = 560
x = 80
∴ The weight of a cupcake is 80 g. 1A
(4)
17. Let x and y be the original numbers of stamps owned by
Luke and Zoe respectively.
Accordingly,
x + y = 33 ........... (1)
1 1M
x + 3 = 2 y .......... (2)
1
(1) − (2): ( x + y ) − ( x + 3) = 33 −y 1M
2
1
x + y − x − 3 = 33 − y
2
3y
= 36
2
y = 24
Substitute y = 24 into (1),
x + 24 = 33
x=9
∴ The original number of stamps owned by Luke
is 9 and the original number of stamps owned
by Zoe is 24. 1A + 1A
(4)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 6
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
18. Let x and y be the numbers of apples and pears Kary
bought respectively.
Accordingly,
6 x + 4.5 y = 90...............(1)
x = 3 y ............................(2) 1M
Substitute (2) into (1),
6(3 y ) + 4.5 y = 90 1M
22.5 y = 90
y=4
Substitute y = 4 into (2),
x = 3(4)
= 12
∴ Total number of fruits Kary bought
= 12 + 4 1M
= 16 1A
(4)
5 x − y = 11........................(1)
19.
2 y − 3 x = 7 x − 22..............(2)
From (1), y = 5 x − 11..........(3)
Substitute (3) into (2),
2(5 x − 11) − 3 x = 7 x − 22 1M
10 x − 22 − 3 x = 7 x − 22
7 x − 22 = 7 x − 22
0=0
∴ The equations have infinitely many solutions. 1A
(2)
x 2 y 19
− = ..................................... (1)
20. 2 5 10
3
( x + 3) = 8 − y ................................ (2)
2
x 2y 19
(1) × 10: × 10 − × 10 = × 10
2 5 10
5 x − 4 y = 19 ............. (3)
From (2), 3( x + 3) = 2(8 − y )
3 x + 9 = 16 − 2 y
3 x + 2 y = 7 .......................... (4)
(4) × 2: 6 x + 4 y = 14 ............................. (5)
(3) + (5): (5 x − 4 y ) + (6 x + 4 y ) = 19 + 14 1M
5 x − 4 y + 6 x + 4 y = 33
11x = 33
x=3
Substitute x = 3 into (4),
3(3) + 2 y = 7
2 y = −2
y = −1
∴ The solution is x = 3 , y = −1 . 1A
(2)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 7
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
21. Rewrite the simultaneous equations as follows:
4 − x y +1
2 + 3 = 8 .................................. (1)
3 y − 4 − 3 x = 8 .................................... (2)
4
4− x y +1
(1) × 6: ×6+ × 6 = 8× 6
2 3
3(4 − x) + 2( y + 1) = 48
12 − 3 x + 2 y + 2 = 48
2 y − 3 x = 34 ........... (3)
4 − 3x
(2) × 4: 3 y × 4 − × 4 = 8× 4
4
12 y − (4 − 3 x) = 32
12 y − 4 + 3 x = 32
12 y + 3 x = 36 .............. (4)
(3) + (4): (2 y − 3 x) + (12 y + 3 x) = 34 + 36 1M
2 y − 3x + 12 y + 3 x = 70
14 y = 70
y=5
Substitute y = 5 into (4),
12(5) + 3x = 36
3x = −24
x = −8
∴ The solution is x = −8, y = 5. 1A
(2)
3 x = −2( y + 2) ........... (1)
22. (a)
x = y − 3 .................... (2)
Substitute (2) into (1),
3( y − 3) = −2( y + 2) 1M
3 y − 9 = −2 y − 4
5y = 5
y =1
Substitute y = 1 into (2),
x =1− 3
= −2
∴ The solution is x = −2, y = 1. 1A
(b) Let x = a + 1 and y = b − 3 . 1M
3 x = −2( y + 2)
The simultaneous equations can be
x = y − 3
3(a + 1) = −2(b − 1)
written as .
a + 1 = b − 6
From the result of (a),
x = −2
a + 1 = −2
a = −3
y =1
b −3 =1
b=4
∴ The solution is a = −3, b = 4 . 1A
(4)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 8
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
23. ABC ~ PQR (given)
∴ ∠A = ∠P (corr. ∠s, ~ s)
x + y = 70°
∠B = ∠Q (corr. ∠s, ~ s)
y + 20° = 2 x
2 x − y = 20°
x + y = 70° .................(1)
∴ 1M
2 x − y = 20° ...............(2)
(1) + (2): ( x + y ) + (2 x − y ) = 70° + 20° 1M
3 x = 90°
x = 30° 1A
Substitute x = 30° into (1),
30° + y = 70°
y = 40° 1A
(4)
24. Each interior angle of a regular pentagon
(5 − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon)
5
= 108°
4 x + 3 y = 108°..................(1)
∴ 1M
2 x + 4 y + 4° = 108° ..........(2)
(2) × 2: 4 x + 8 y + 8° = 216°
4 x + 8 y = 208° .......(3)
(3) − (1): (4 x + 8 y ) − (4 x + 3 y ) = 208° − 108° 1M
5 y = 100°
y = 20° 1A
Substitute y = 20° into (1),
4 x + 3(20°) = 108°
4 x + 60° = 108°
4 x = 48°
x = 12° 1A
(4)
25. Let n be the number of sides of the regular polygon.
∴ Each exterior angle
360°
= (sum of ext. ∠s of polygon) 1M
n
Each interior angle
(n − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon) 1M
n
360° (n − 2) × 180°
∴ 7 = 1M
n n
2 520° = 180°n − 360°
2 880° = 180°n
n = 16
∴ The number of sides of the regular polygon is 16. 1A
(4)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 9
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
26. (a) In CBA and ABD,
∠BAC = ∠BDA (given)
∠ABC = ∠DBA (common ∠)
∠ACB = 180° − ∠BAC − ∠ABC (∠ sum of ) 1M
= 180° − ∠BDA − ∠DBA (proved)
= ∠DAB (∠ sum of )
∴ CBA ~ ABD (A.A.A.) 1
(b) CBA ~ ABD (proved)
CB BA
∴ = (corr. sides, ~ s) 1M
AB BD
8 12
= 1M
12 8 + CD
64 + 8CD = 144
8CD = 80
CD = 10 1A
(5)
27. (a) Sum of interior angles of a regular 12-sided polygon
= (12 − 2) × 180° (∠ sum of polygon) 1M
= 1 800°
∴ Size of each interior angle = 1 800° ÷ 12 1M
= 150° 1A
(b) PQ = QR
∴ ∠RPQ = ∠PRQ (base ∠s, isos. ) 1M
In PQR,
∠RPQ + ∠PRQ + ∠PQR = 180° (∠ sum of ) 1M
2∠PRQ + 150° = 180°
2∠PRQ = 30°
∠PRQ = 15° 1A
(6)
28. Let x and y be the original numbers of jelly beans Stanley
and Timothy has respectively.
Accordingly,
x = 7 y .......................(1)
x − 54 = y + 54..........(2) 1M
Substitute (1) into (2),
7 y − 54 = y + 54 1M
6 y = 108
y = 18
Substitute y = 18 into (1),
x = 7(18)
= 126
∴ Number of jelly beans they have in total
= 126 + 18 1M
= 144 1A
(4)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 10
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
29. Let x and y be the numbers of bottles of juice and others
respectively.
Accordingly,
x + y = 255.....................(1)
x = y (1 − 30%)...............(2) 1M
Substitute (2) into (1),
y (1 − 30%) + y = 255 1M
0.7 y + y = 255
1.7 y = 255
y = 150
Substitute y = 150 into (1),
x + 150 = 255
x = 105
∴ Required difference = 150 − 105 1M
= 45 1A
(4)
30. Let x and y be the numbers of boys and girls respectively.
Accordingly,
x + y = 298 ....................... (1)
3 1M
5 x + 18 = y ...................... (2)
(1) × (3): 3 x + 3 y = 894 ...... (3)
(2) × 5: 3 x + 90 = 5 y .......... (4)
(3) − (4): (3 x + 3 y ) − (3 x + 90) = 894 − 5 y 1M
3 x + 3 y − 3 x − 90 = 894 − 5 y
8 y = 984
y = 123
∴ There are 123 girls in the Christmas party. 1A
(3)
31. Let $x and $y be the original prices of a lemon tart and a
cup of coffee respectively.
Accordingly,
x + y = 67 ................................................ (1) 1M
x(1 + 15%) + y (1 − 8%) = 67 + 2 ...............(2)
From (1), x = 67 − y .................................. (3)
Substitute (3) into (2),
(67 − y ) × (1 + 15%) + y (1 − 8%) = 67 + 2 1M
1.15(67 − y ) + 0.92 y = 69
77.05 − 1.15 y + 0.92 y = 69
−0.23 y = −8.05
y = 35
Substitute y = 35 into (3),
x = 67 − 35
= 32
∴ The original price of a lemon tart is $32 and the
original price of a cup of coffee is $35. 1A + 1A
(4)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 11
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
32. Let m be the number of stickers owned by Paul.
Accordingly,
n:m = 7:4
n 7
=
m 4
4n = 7 m ........................... (1)
1M
n − 9 = m + 9 ....................... (2)
From (2), m = n − 18 ...........(3)
Substitute (3) into (1),
4n = 7(n − 18) 1M
4n = 7 n − 126
126 = 3n
n = 42 1A
(3)
33. (a) Let a and b be the original numbers of $2 coins and $5
coins respectively.
Accordingly,
a :b = 2:3
a 2
=
b 3
2b
a= ........................... (1)
3
(a − 3) : (b + 3) = 3 : 7
a −3 3
= 1M
b+3 7
7(a − 3) = 3(b + 3)
7 a − 21 = 3b + 9
7 a − 3b = 30 ............(2)
Substitute (1) into (2),
2b
7 − 3b = 30 1M
3
2b
3 7 − 3(3b) = 3(30)
3
14b − 9b = 90
5b = 90
b = 18
Substitute b = 18 into (1),
2(18)
a=
3
= 12
∴ The original number of $2 coins is 12 and
the original number of $5 coins is 18. 1A + 1A
(b) Original amount of money : New amount of money
= $(2 × 12 + 5 × 18) : $ [2 × (12 − 3) + 5 × (18 + 3)] 1M
= $114 : $123
$114 $123
= :
$3 $3
= 38 : 41 1A
(6)
34. (a) ABC ≅ AED (given)
∴ AC = AD (corr. sides, ≅ s) 1M
∴ ∠ADC = ∠ACD (base ∠s, isos. ) 1M
= 70°
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 12
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
In ACD,
∠ACD + ∠CAD + ∠ADC = 180° (∠ sum of ) 1M
70° + (112° − 2 x) + 70° = 180°
2 x = 72°
x = 36° 1A
(b) Each interior angle of a regular pentagon
(5 − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon) 1M
5
= 108°
∠BCD = 36° + 70°
= 106°
≠ 108° 1M
∴ ABCDE is not a regular pentagon. 1A
(7)
35. (a) In APQ and ACB,
∠PAQ = ∠CAB (common ∠)
∠AQP = ∠ABC (given)
∠APQ = 180° − ∠PAQ − ∠AQP (∠ sum of ) 2M
= 180° − ∠CAB − ∠ABC (proved)
= ∠ACB (∠ sum of )
∴ △ APQ ~ ACB (A.A.A.) 1
(b) △ APQ ~ ACB (proved)
AQ PQ
∴ = (corr. sides, ~ s) 1M
AB CB
4 cm 3 cm
= 1M
5 cm + PB 6 cm
4 cm 1
=
5 cm + PB 2
5 cm + PB = 8 cm
PB = 3 cm 1A
(c) In PBC and PQC,
PB = PQ = 3 cm
PC = PC (common side)
∠PQC + 90° = 180° (adj. ∠s on st. line) 1M
∠PQC = 90°
= ∠PBC
∴ PBC ≅ PQC (R.H.S.) 1
(8)
36. (a) In ABC and DEF,
AB = DE
BC = EF 1M
∠ABC = ∠DEF
∴ ABC ≅ DEF (S.A.S.) 1
(b) In ACD and DFA,
ABC ≅ DEF (proved)
∴ AC = DF (corr. sides, ≅ s) 1M
CD = FA
AD = DA (common side)
∴ ACD ≅ DFA (S.S.S.) 1
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 13
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
(c) Each interior angle of a regular hexagon
(6 − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon) 1M
6
= 120°
∴ ∠ABC = ∠BCD = 120°
BA = BC
∴ ∠BAC = ∠BCA (base ∠s, isos. ) 1M
In ABC,
∠ABC + ∠BAC + ∠BCA = 180° (∠ sum of )
120° + 2∠BCA = 180°
2∠BCA = 60°
∠BCA = 30°
∠ACD = ∠BCD − ∠BCA
= 120° − 30°
= 90° 1A
∴ AC ⊥ CD
∴ The claim is agreed. 1A
(8)
37. (a) Each interior angle of a regular pentagon
(5 − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon) 1M
5
= 108°
∴ ∠PQR = 108°
∠TQP = 180° − 108° (adj. ∠s on st. line)
= 72° 1A
(b) Each interior angle of a regular octagon
(8 − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon) 1M
8
= 135° 1A
∴ ∠DEF = ∠EFG = ∠FGT = 135°
∠QRS = ∠RSE = 108°
In hexagon EFGTRS,
∠GTR + 108° + 108° + 135° + 135° + 135° = (6 − 2) × 180°
(∠ sum of polygon) 1M
∠GTR + 621° = 720°
∠GTR = 99° 1A
∠GTQ + ∠TQP = 99° + 72°
= 171°
≠ 180° 1M
∴ GH and PQ are not parallel to each other. 1A
(8)
38. Extend the straight lines in the figure such that the graphs of the two
equations intersect.
From the figure, the two straight lines intersect at (3, 1).
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 14
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
∴ The solution is x = 3 , y = 1 .
∴ The answer is B.
39. A. Substitute x = 8 and y = −3 into x = − 8 ,
L.H.S. = 8
R.H.S. = −8
L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ (8, −3) does not satisfy the equation x = −8.
i.e. (8, −3) does not satisfy the simultaneous equations
x = −8
2 x − y = 13 .
B. Substitute x = 8 and y = −3 into x − 5 y = −7 ,
L.H.S. = 8 − 5(−3)
= 23
R.H.S. = −7
L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ (8, −3) does not satisfy the equation x − 5 y = −7 .
i.e. (8, −3) does not satisfy the simultaneous equations
y = −3
x − 5 y = −7 .
C. Substitute x = 8 and y = −3 into x − 2 y = 2 ,
L.H.S. = 8 − 2(−3)
= 14
R.H.S. = 2
L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ (8, −3) does not satisfy the equation x − 2 y = 2 .
i.e. (8, −3) does not satisfy the simultaneous equations
x + y = 5
x − 2 y = 2 .
D. Substitute x = 8 and y = −3 into x − y = 11,
L.H.S. = 8 − (−3)
= 11
R.H.S. = 11
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Substitute x = 8 and y = −3 into 2 x + 3 y = 7 ,
L.H.S. = 2(8) + 3(−3)
=7
R.H.S. = 7
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ (8, −3) satisfies the equations x − y = 11 and 2 x + 3 y = 7 .
x − y = 11
i.e. (8, −3) satisfies the simultaneous equations .
2 x + 3 y = 7
∴ The answer is D.
40. Rewrite the simultaneous equations as follows:
6 x + 7 y = 45....................(1)
3 x + 11 y = 45...................(2)
(2) × 2: 6 x + 22 y = 90 ....... (3)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 15
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
(3) − (1): (6 x + 22 y ) − (6 x + 7 y ) = 90 − 45
6 x + 22 y − 6 x − 7 y = 45
15 y = 45
y =3
∴ The answer is A.
41. The answer is D.
42. Reflex ∠BCD = 360° − c (∠s at a pt.)
Reflex ∠AED = 360° − e (∠s at a pt.)
a + b + Reflex ∠ BCD
+ d + Reflex ∠AED = (5 − 2) × 180° (∠ sum of polygon)
a + b + (360° − c ) + d + (360° − e) = 540°
a + b − c + d − e + 720° = 540°
a + b + d = c + e − 180°
∴ The answer is B.
43. In regular pentagon ABCDE,
(5 − 2) × 180°
each interior angle = (∠ sum of polygon)
5
= 108°
In quadrilateral CDFG,
p + r + t + v = (4 − 2) × 180° (∠ sum of polygon)
= 360°
∴ p + q + r + s + t + u + v = ( p + r + t + v) + ( q + s + u )
= 360° + 3 × 108°
= 684°
∴ The answer is A.
44. In ABE and ADC,
AB 10 2
= =
AD 8 + 7 3
AE 8 2
= =
AC 10 + 2 3
AB AE
∴ =
AD AC
∠EAB = ∠CAD (common ∠)
∴ ABE ~ ADC (ratio of 2 sides, inc. ∠)
AB BE
∴ = (corr. sides, ~ s)
AD DC
2 x
=
3 18
x = 12
∴ The answer is C.
45. In ABC and CDE,
∠ABC = ∠CDE (given)
∠BAC + ∠ABC = ∠ACD (ext. ∠ of )
∠BAC + ∠ABC = ∠ACE + ∠DCE
∠BAC + ∠ABC = ∠ABC + ∠DCE (given)
∠BAC = ∠DCE
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 16
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
∠ACB = 180° − ∠ABC − ∠BAC (∠ sum of )
= 180° − ∠CDE − ∠DCE (proved)
= ∠CED (∠ sum of )
∴ ABC ~ CDE (A.A.A.)
DE CD
∴ = (corr. sides, ~ s)
BC AB
DE 12
=
6 18
DE = 4
∠ABC = ∠ADB (given)
∴ AD = AB (sides opp. equal ∠s)
= 18
AE = AD − DE
= 18 − 4
= 14
∴ The answer is C.
46. Let $x and $y be the selling prices of a bag A and a bag B respectively.
Accordingly,
2 x + 3 y = 3 030 ................................. (1)
3 x + 2 y = 2 970 ................................. (2)
(1) × 2: 4 x + 6 y = 6 060 ....................... (3)
(2) × 3: 9 x + 6 y = 8 910 ........................(4)
(4) − (3): (9 x + 6 y ) − (4 x + 6 y ) = 8 910 − 6 060
9 x + 6 y − 4 x − 6 y = 2 850
5 x = 2 850
x = 570
∴ The selling price of a bag A is $570.
∴ The answer is C.
x + 2 y = 3 ....................... (1)
47.
2 x + 4 y = 5 ..................... (2)
(1) × 2: 2 x + 4 y = 6 ........... (3)
(3) − (2): (2 x + 4 y ) − (2 x + 4 y ) = 6 − 5
0 =1
∴ The equations have no solutions.
∴ The answer is D.
48. Each interior angle of a regular n-sided polygon
(n − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon)
n
Each exterior angle of a regular n-sided polygon
360°
= (sum of ext. ∠s of polygon)
n
(n − 2) × 180° 360°
∴ = 4×
n n
180°n − 360° = 1 440°
180°n = 1 800°
n = 10
∴ I is not true.
(10 − 2) × 180°
Each interior angle of the polygon =
10
= 144°
∴ II is true.
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 17
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
360°
Each exterior angle of the polygon =
10
= 36°
∴ III is true.
∴ The answer is C.
49. I. Each interior angle of a regular pentagon
(5 − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon)
5
= 108°
Each interior angle of a regular 10-sided polygon
(10 − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon)
10
= 144°
∴ I is not correct.
II. Each exterior angle of a regular pentagon
= 180° − 108° (adj. ∠s on st. line)
= 72°
Each exterior angle of a regular 10-sided polygon
= 180° − 144° (adj. ∠s on st. line)
= 36°
∴ II is correct.
∴ The answer is B.
50. In ABC and CDE,
AB = CD
BC = DE
∠ABC = ∠CDE
∴ ABC ≅ CDE (S.A.S.)
∴ I is true.
AF = EF
∴ AEF is an isosceles triangle.
∴ II is true.
Similarly,
ABC ≅ EFA (S.A.S.)
∴ AC = EA (corr. sides, ≅ s)
ABC ≅ CDE (proved)
∴ AC = CE (corr. sides, ≅ s)
∴ AC = EA = CE
∴ ACE is an equilateral triangle.
∴ III is true.
∴ The answer is D.
51. ABC is an equilateral triangle.
∴ ∠EBF = ∠FCD = 60°
In BEF and CFD,
∠EBF = ∠FCD
∠EBF + ∠BEF = ∠EFC (ext. ∠ of )
∠EBF + ∠BEF = ∠EFD + ∠CFD
60° + ∠BEF = 60° + ∠CFD
∠BEF = ∠CFD
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 18
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
∠BFE = 180° − ∠EBF − ∠BEF (∠ sum of )
= 180° − ∠FCD − ∠CFD
= ∠CDF (∠ sum of )
∴ BEF ~ CFD (A.A.A.)
∴ The answer is D.
52. Each interior angle of a regular pentagon
(5 − 2) × 180°
= (∠ sum of polygon)
5
= 108°
AB = CB
∴ ∠BCA = ∠BAC (base ∠s, isos. )
In ABC,
∠BCA + ∠BAC + ∠ABC = 180° (∠ sum of )
2 ∠BAC + 108° = 180°
2 ∠BAC = 72°
∠BAC = 36°
Similarly,
∠ABE = ∠AEB = ∠DCE = ∠DEC = ∠BCA = 36°
∴ ∠CEF = ∠AED − ∠AEB − ∠DEC
= 108° − 36° − 36°
= 36°
∠FCE = ∠BCD − ∠BCA − ∠DCE
= 108° − 36° − 36°
= 36°
In ABF and CEF,
∠ABF = ∠CEF (proved)
∠FAB = ∠FCE (proved)
∠AFB = ∠CFE (vert. opp. ∠s)
∴ ABF ~ CEF (A.A.A.)
∴ I is true.
In BCF and FEA,
∠CBF = ∠ABC − ∠ABE
= 108° − 36°
= 72°
∠EFA = ∠ABF + ∠FAB (ext. ∠ of )
= 36° + 36°
= 72°
∴ ∠CBF = ∠EFA
∠ABF = ∠BAF (proved)
∴ BF = FA (sides opp. equal ∠s)
∠BFC = ∠ABF + ∠FAB (ext. ∠ of )
= 36° + 36°
= 72°
∠FAE = ∠BAE − ∠BAF
= 108° − 36°
= 72°
∴ ∠BFC = ∠FAE
∴ BCF ≅ FEA (A.S.A.)
∴ II is true.
In CFE and CDE,
∠FCE = ∠DCE (proved)
CE = CE (common side)
∠FEC = ∠DEC (proved)
∴ CFE ≅ CDE (A.S.A.)
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 19
New Effective Learning Mathematics S2A
Integrated Practice VI Solution Guide
∴ III is true.
∴ The answer is D.
53. x + x + y + x + 80° = 360° (sum of ext. ∠s of polygon)
3 x + y = 280° ............................ (1)
(180° − 70° − 80°) + (180° − x) = y + y (ext. ∠ of )
210° − x = 2 y
x + 2 y = 210° ......... (2)
(1) × 2: 6 x + 2 y = 560° ................................. (3)
(3) − (2): (6 x + 2 y ) − ( x + 2 y ) = 560° − 210°
5 x = 350°
x = 70°
Substitute x = 70° into (1),
3(70°) + y = 280°
y = 70°
∴ The answer is A.
54. In AFE and CFB,
∠AFE = ∠CFB (vert. opp. ∠s)
∠FAE = ∠FCB (alt. ∠s, AD // BC)
∠FEA = ∠FBC (alt. ∠s, AD // BC)
∴ AFE ~ CFB (A.A.A.)
AF AE
∴ = (corr. sides, ~ s)
CF CB
AE
=
AD
1
AD
= 3
AD
1
=
3
∴ AF : FC = 1: 3
∴ The answer is B.
© 2021 Chung Tai Educational Press Limited |
© 2021 Marshall Cavendish Education (a member of Times Publishing Limited) 20
You might also like
- 01 - Pulse Neutron Neutron (PNN) Tool - Logging For PorosityDocument9 pages01 - Pulse Neutron Neutron (PNN) Tool - Logging For PorosityDaniel UmañaNo ratings yet
- More About Equations: y X y XDocument56 pagesMore About Equations: y X y XWinnie SitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Simultaneous EquationsDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Simultaneous Equationsbrenwong@ymail.comNo ratings yet
- Algebra IX QP BoardsDocument4 pagesAlgebra IX QP BoardsGyaani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Board 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Matrices Ex 2.3Document10 pagesMaharashtra Board 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Matrices Ex 2.3rohitNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1candychongNo ratings yet
- SimultaneousDocument27 pagesSimultaneousLatchmi DeviNo ratings yet
- SAT ACT EquationsDocument18 pagesSAT ACT EquationsYb Andik Adi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- X y y XDocument33 pagesX y y XMiki LeongNo ratings yet
- QMI1500 Solutions Ass 02 2022Document19 pagesQMI1500 Solutions Ass 02 2022Mike NdunaNo ratings yet
- In Problems 31-36, Change Each Rational Number To A Decimal by Performing Long DivisionDocument3 pagesIn Problems 31-36, Change Each Rational Number To A Decimal by Performing Long DivisionNovaSoniaChuaNo ratings yet
- Solutions 8Document9 pagesSolutions 8Ashish SitareNo ratings yet
- Week 20 - Intersection of The LineDocument26 pagesWeek 20 - Intersection of The LineJeff LacasandileNo ratings yet
- MAT111 by Prof IloriDocument168 pagesMAT111 by Prof IloriFáróminíyì Mathefaro SimeonNo ratings yet
- Sat10e SSM 12Document109 pagesSat10e SSM 12Anonymous d6dZvmNo ratings yet
- Be Mechanical-Engineering Semester-4 2018 December Applied-mathematics-IV-cbcgs (1)Document16 pagesBe Mechanical-Engineering Semester-4 2018 December Applied-mathematics-IV-cbcgs (1)ujwalshetty24No ratings yet
- StudenttextDocument17 pagesStudenttextapi-195130729No ratings yet
- Math p1 Eng MemoDocument14 pagesMath p1 Eng Memoelson mandlate100% (1)
- Ncert Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3 3Document15 pagesNcert Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3 3amritarawat331985No ratings yet
- FDocument15 pagesFJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONSDocument5 pagesLesson 10 - SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONSHerrera, Mark NathanielNo ratings yet
- Equations and InequalitiesDocument21 pagesEquations and InequalitiesLeonard AbellaNo ratings yet
- JEE-MAIN-MATHS MODULE-1(Solution)Document17 pagesJEE-MAIN-MATHS MODULE-1(Solution)emogirlslovewineNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q1 W7 LASDocument21 pagesMath8 Q1 W7 LASdonita jane pacudanNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving:: SolutionDocument5 pagesProblem Solving:: SolutionRoschelle MiguelNo ratings yet
- 10STA 101-Test 1 Solution - 14 Sept 2018Document4 pages10STA 101-Test 1 Solution - 14 Sept 2018fanejennifer431No ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Mathematics: Midterm Exam AnswerDocument3 pagesPre-Calculus Mathematics: Midterm Exam AnswerFernandoNo ratings yet
- Sia3e SSM 03Document106 pagesSia3e SSM 03brianNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous EquationsDocument9 pagesSimultaneous Equationsfombati415No ratings yet
- 2020 Nw Grade 12 Assignment Term 1 Memo2020Document13 pages2020 Nw Grade 12 Assignment Term 1 Memo2020Lerato bunnyNo ratings yet
- 1700 Worksheet 5 SolutionsDocument7 pages1700 Worksheet 5 Solutionsm.amin.obohatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Methods 1/2 - Chapter 18 Applications of Differentiation of PolynomialsDocument70 pagesCambridge Methods 1/2 - Chapter 18 Applications of Differentiation of PolynomialsEsther CheungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Solutions of EquationsDocument16 pagesChapter 3 Solutions of Equations123owisNo ratings yet
- MAV Exam 1 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMAV Exam 1 SolutionsPradeep MahawattaNo ratings yet
- 23 Algebraic Manipulation: Student TextDocument17 pages23 Algebraic Manipulation: Student TextCharlotte BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Miscellaneous ProblemsDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Miscellaneous ProblemsAngel HilasacaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Algebra: 8 Grade Mathematics Summary Notes Vo.1Document3 pagesChapter 2: Algebra: 8 Grade Mathematics Summary Notes Vo.1Ak 47No ratings yet
- DeterminantDocument6 pagesDeterminantr55088299No ratings yet
- MAV Exam 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesMAV Exam 1 SolutionsPradeep MahawattaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1 Solutions 1Document2 pages2022 Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1 Solutions 1martin juNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 3 - AnswerDocument4 pagesExercise No 3 - AnswerRabiahNo ratings yet
- 334 RationexDocument8 pages334 RationexLouis GuyNo ratings yet
- Balik Aral (Algebra)Document17 pagesBalik Aral (Algebra)Mj DimapilisNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument19 pagesQuadratic EquationsLoh Chee WeiNo ratings yet
- Answers Are You Ready For CalculusDocument6 pagesAnswers Are You Ready For CalculusKevin HsiehNo ratings yet
- Tumi Math Lesson Note - 044246Document4 pagesTumi Math Lesson Note - 044246solomon celestineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 ExponentDocument8 pagesLecture 7 Exponentrahman241abdurNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 MergedDocument18 pages1 2 3 MergedMohammed MohsinNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Mandatory ExerciseDocument23 pagesPolynomials Mandatory Exercisehemal mitreshNo ratings yet
- Problem 1Document3 pagesProblem 1Carlo KaramNo ratings yet
- 2018 Additional Mathematics PamphletDocument127 pages2018 Additional Mathematics PamphletJacklim NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- 2.monomials and PolynomialsDocument6 pages2.monomials and PolynomialsMohamed AlyNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Systems With Three VariablesDocument8 pages4.4 Systems With Three Variablesvictorymornah017No ratings yet
- 2.quadratic EquationsDocument17 pages2.quadratic EquationsHarith HanifNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions and InequalitiesRevisedDocument57 pagesQuadratic Functions and InequalitiesRevisedShawn100% (1)
- Ass Dca2101Document10 pagesAss Dca2101tera baapNo ratings yet
- 5Document10 pages5Cheryl ChongNo ratings yet
- 101 Copy3Document4 pages101 Copy3job.kh.11.11No ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- ALGEBRA SIMPLIFIED EQUATIONS WORKBOOK WITH ANSWERS: Linear Equations, Quadratic Equations, Systems of EquationsFrom EverandALGEBRA SIMPLIFIED EQUATIONS WORKBOOK WITH ANSWERS: Linear Equations, Quadratic Equations, Systems of EquationsNo ratings yet
- F2 Term 2 Exam 1819 QPDocument8 pagesF2 Term 2 Exam 1819 QPpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B12E SolDocument3 pagesCS1B12E Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B11B SolDocument2 pagesCS1B11B Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B11C SolDocument3 pagesCS1B11C Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS2A01A SolDocument3 pagesCS2A01A Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- ExtraDrill 1E05A BQDocument2 pagesExtraDrill 1E05A BQpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B09B SolDocument5 pagesCS1B09B Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B11A SolDocument3 pagesCS1B11A Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B10C SolDocument6 pagesCS1B10C Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B08D SolDocument3 pagesCS1B08D Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B10A SolDocument4 pagesCS1B10A Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B10B SolDocument6 pagesCS1B10B Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B09A SolDocument5 pagesCS1B09A Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1B09C SolDocument4 pagesCS1B09C Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1A04A SolDocument2 pagesCS1A04A Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- CS1A03D SolDocument2 pagesCS1A03D Solpakfan1130No ratings yet
- Extra Drill 1A: Challenging QuestionsDocument4 pagesExtra Drill 1A: Challenging Questionspakfan1130No ratings yet
- IP07 Sol S2B E WebDocument18 pagesIP07 Sol S2B E Webpakfan1130No ratings yet
- IP02 Sol S1A E WebDocument10 pagesIP02 Sol S1A E Webpakfan1130No ratings yet
- Book 1 CanswerDocument81 pagesBook 1 Canswerpakfan1130No ratings yet
- Integrated Practice IIDocument13 pagesIntegrated Practice IIpakfan1130No ratings yet
- Integrated Practice VDocument12 pagesIntegrated Practice Vpakfan1130No ratings yet
- Integrated Practice IIIDocument14 pagesIntegrated Practice IIIpakfan1130No ratings yet
- Exam Elect 2B - English Test & Exam PapersDocument44 pagesExam Elect 2B - English Test & Exam Paperspakfan1130No ratings yet
- John Hawthorne's Knowledge and LotteriesDocument6 pagesJohn Hawthorne's Knowledge and LotteriesÖmer OsmanoğluNo ratings yet
- Permutation & Combinations: Hints & Solutions To Assignment Problems (Subjective)Document18 pagesPermutation & Combinations: Hints & Solutions To Assignment Problems (Subjective)zaid khanNo ratings yet
- Class 7 (2023 - 2024) 2Document1 pageClass 7 (2023 - 2024) 2MishkaNo ratings yet
- Maguga Dam, Swaziland Consultants: Maguga Dam Joint Ventures. Design Engineer: Pieter LouwDocument2 pagesMaguga Dam, Swaziland Consultants: Maguga Dam Joint Ventures. Design Engineer: Pieter LouwUmberto DizNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1-4 Conceptual QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapters 1-4 Conceptual QuestionsdsowmNo ratings yet
- DLL - Simple InterestDocument4 pagesDLL - Simple InterestAL JoHn S. TY100% (1)
- Competitive NewDocument11 pagesCompetitive NewmeenketanNo ratings yet
- RRB Alp CBT 1 Previous Year Question Paper 15667Document54 pagesRRB Alp CBT 1 Previous Year Question Paper 15667kusalmitra2No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6. Right Triangel and TRIGONOMETRY PDFDocument57 pagesCHAPTER 6. Right Triangel and TRIGONOMETRY PDFginikuNo ratings yet
- Full Download Quantum Computing by Practice Python Programming in The Cloud With Qiskit and IBM Q 2nd Edition Silva PDFDocument73 pagesFull Download Quantum Computing by Practice Python Programming in The Cloud With Qiskit and IBM Q 2nd Edition Silva PDFshafamohaen3100% (1)
- MAIN Hall: (No Photocopy) If You Are Missing Either Item, You Won'T Be AdmittedDocument1 pageMAIN Hall: (No Photocopy) If You Are Missing Either Item, You Won'T Be AdmittedKaixuan KhooNo ratings yet
- Computational Techniques in Civil Engineering IOE BCE Past Questions CollectionDocument32 pagesComputational Techniques in Civil Engineering IOE BCE Past Questions CollectionFlush BinNo ratings yet
- Module 4 A CentroidDocument64 pagesModule 4 A CentroidKazi Afroz AlamNo ratings yet
- Python For Data ScienceDocument22 pagesPython For Data ScienceMohit MalghadeNo ratings yet
- Parabola Test 1Document12 pagesParabola Test 1bodhi20041No ratings yet
- Physics Aptitude MCQs (DICC)Document179 pagesPhysics Aptitude MCQs (DICC)Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Edward John Specht, Harold Trainer Jones, Keith G. Calkins, Donald H. Rhoads Euclidean Geometry and Its SubgeometriesDocument537 pagesEdward John Specht, Harold Trainer Jones, Keith G. Calkins, Donald H. Rhoads Euclidean Geometry and Its SubgeometriesJoão JúniorNo ratings yet
- First Year First SemesterDocument15 pagesFirst Year First SemesterAditya GainNo ratings yet
- AU-2014 6557 Practically Dynamo - Marcello SgambelluriDocument73 pagesAU-2014 6557 Practically Dynamo - Marcello SgambelluriAutodesk University100% (1)
- Log Periodic Dipole Array: Baluis, Kathleen Anne Rose Poda, Joy Grace Villanueva, CarmelaDocument33 pagesLog Periodic Dipole Array: Baluis, Kathleen Anne Rose Poda, Joy Grace Villanueva, Carmelacamming soonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Complex Kind: Week 7Document9 pagesAnalysis of A Complex Kind: Week 7Bindeshwar YadavNo ratings yet
- Oriole News: "If You Don't Go To Oriole, Well, You Don't Go To Oriole"Document4 pagesOriole News: "If You Don't Go To Oriole, Well, You Don't Go To Oriole"api-26267532No ratings yet
- Trigonometry - ProvingDocument2 pagesTrigonometry - Provingrairaicute100% (13)
- Lecture No.1 - Control SystemsDocument41 pagesLecture No.1 - Control SystemsCH MOHAMMAD ATTIR KHAYYAMNo ratings yet
- Use of Statistics in EpidemiologyDocument30 pagesUse of Statistics in Epidemiologysmaran2meNo ratings yet
- Internship Report in Accounting FieldDocument25 pagesInternship Report in Accounting Field桐桐No ratings yet
- IEEE Standard: Test Procedure For AntennasDocument31 pagesIEEE Standard: Test Procedure For AntennasCharlaine Bufi PanchoNo ratings yet
- MC Lab - EXP3Document4 pagesMC Lab - EXP3Mohammad SamheelNo ratings yet
- Tema 2: Edgeworth's Exchange TheoryDocument21 pagesTema 2: Edgeworth's Exchange TheoryAllan SantizoNo ratings yet