Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Jntu - Uandistar.org)
Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Jntu - Uandistar.org)
Uploaded by
apadmaja.eeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Jntu - Uandistar.org)
Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Jntu - Uandistar.org)
Uploaded by
apadmaja.eeeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Jntu - Uandistar.org)
Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Jntu - Uandistar.org)
Uploaded by
apadmaja.eeeCopyright:
Available Formats
for more :- jntu.uandistar.
org
Code No: R21013 R10 SET - 1
II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov – 2012
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
(Com. to CE, ME, CHEM, PE, AME, MM)
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75
All Questions carry Equal Marks
Note: Answer any FIVE Questions, not exceeding Three Questions from any one part
PART-A
1. a) State and explain Ohms law and its limitation
b) Two resistances of 50Ω and 40Ω respectively are connected in parallel. A third resistance
of 10Ω is connected in series with the combination and a D.C supply of 220 V is applied to the
ends of the completed circuit. Calculate the current in each resistance.
2. With a neat sketch explain the main parts of the DC machine and state the material of which
each part is made and their function
3. a)From the fundamentals, derive the expression for the EMF equation of a single phase
transformer.
b) A transformer has a primary winding of 600 turns and a secondary turns of 300. When the
load current on the secondary is 50A at 0.85 p.f lagging, the primary current is 25A at 0.707
lagging. Determine the no load current of the transformer and the phase angle with respect to
the voltage.
4. a) Explain the slip-torque characteristics of three phase induction motor
b) Find the no-load phase and line voltage of a star-connected 3-phase, 6-pole alternator which
runs at 1200 rpm, having flux per pole of 0.1 wb sinusoidally distributed. Its stator has 54 slots
having double layer winding. Each coil has 8 turns and the coil is chorded by 1 slot.
PART-B
5. a) Explain the working of P-N junction diode
b) What is a rectifier? Discuss the operation of half wave rectifier with a neat circuit diagram.
6. a) Explain the concept of feedback amplifier
b) If a transistor with α = 0.96 and emitter to base resistance 80Ω is placed in common emitter
configuration, find the gains of Ai, Av, and AP?
7. a) What are the various types of induction heating?
b) Explain Dielectric Heating with a neat diagram.
8. Explain the following with neat diagram
i) LVDT ii) Thermistors
1 of 1
Our New Site for Tutorials on different technologies : www.tutsdaddy.com
for more :- jntu.uandistar.org
Code No: R21013 R10 SET --22
SET
II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov – 2012
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
(Com. to CE, ME, CHEM, PE, AME, MM)
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75
All Questions carry Equal Marks
Note: Answer any FIVE Questions, not exceeding Three Questions from any one part
PART-A
1. a) state and explain Kirchoffs laws
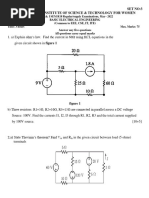
b) In the circuit shown in below figure, find the current in the each resistance.
2. Compare DC generator and DC motor with respect to principle of operation of mention the
application of each machine
3. a) Explain the principle of operation of transformer
b) In a 25 kVA, 2000/200V, 50Hz single phase transformer, the iron and full load copper losses
are 350 and 400 W respectively. Calculate the efficiency at unity power factor on full load and
half load.
4. a) Explain the principle of operation of alternator
b) A 3-phase induction motor has 2 poles and is connected to 400V, 50Hz, supply. Calculate
the actual rotor speed and rotor frequency when the slip is 4%.
PART-B
5. a)Draw and explain the equivalent circuit of the P-N junction diode
b) An a.c. voltage of peak value 20V is connected in series with a silicon diode and load
resistance of 500Ω. If the forward resistance of diode is 10Ω, find the following:
i) peak current through diode ii) peak output voltage
What will be these values if the diode is assumed to be ideal?
6. a)Explain the V-I characteristics of common emitter configuration
b) Explain the static characteristics of the SCR?
7. Explain the dielectric heating with necessary diagrams? List out its merits and give some
applications.
8. Explain the working principle of the following with neat diagrams
a) Strain gauge b) Piezo-electric transistors
1 of 1
Our New Site for Tutorials on different technologies : www.tutsdaddy.com
for more :- jntu.uandistar.org
Code No: R21013 R10 SET --33
SET
II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov – 2012
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
(Com. to CE, ME, CHEM, PE, AME, MM)
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75
All Questions carry Equal Marks
Note: Answer any FIVE Questions, not exceeding Three Questions from any one part
PART-A
1. A Wheatstone bridge consists of AB = 4Ω, BC=3Ω, CD=6Ω and DA=5Ω. A 10V cell is
connected between B and D and a galvanometer of 8Ω is connected between A and C. Find the
current through the galvanometer.
2. a) Derive the emf equation of a DC generator
b) A 4-pole DC motor is fed at 400V and takes an armature current of 35A. The resistance of
the armature circuit is 0.2Ω. The armature winding is wave connected with 800 conductors and
useful flux per pole is 0.023 Wb. Calculate the speed of the motor.
3. a) What are the different losses occurring in a transformer on load? and what are the tests
required for finding these losses.
b) Short-circuit test is conducted on a 5kVA, 400V/100 V single phase transformer with 100
V winding shorted. The input voltage at full load current is 40 V. The wattmeter, on the
input reads 250 W. Find the power factor for which regulation at full load is zero.
1 of 2
Our New Site for Tutorials on different technologies : www.tutsdaddy.com
for more :- jntu.uandistar.org
Code No: R21013 R10 SET - 3
4. a) Explain the regulation of alternator by synchronous impedance method
b) A 3-phase induction motor is wound for 4 poles and is supplied from 50 Hz systems.
Calculate (i) the synchronous speed, (ii) the speed of the motor when slip is 4% and (iii) the
rotor current frequency when the motor runs at 600 r.p.m.
PART-B
5. a) Explain the forward current, peak inverse voltage and reverse current in a P-N junction
diode
b) Compare half wave and full wave rectifiers and their output voltage waveforms
6. a) Explain the V-I characteristics of SCR?
b) A transistor is operated at a forward current of 2µA and with the collector open circuited .
Calculate the junction voltages Vc and Ve the collector to emitter voltage Vce assuming,
IC0=2µA , IE0=1.6µA, αn=0.98.
7. a) What are the various core type induction furnaces? Explain one of them.
b) Discuss the industrial applications of dielectric heating.
8. a) Explain the working of CRO with neat diagram.
b) Explain the working of digital multimeter.
2 of 2
Our New Site for Tutorials on different technologies : www.tutsdaddy.com
for more :- jntu.uandistar.org
Code No: R21013 R10 SET - 4
II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov – 2012
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
(Com. to CE, ME, CHEM, PE, AME, MM)
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75
All Questions carry Equal Marks
Note: Answer any FIVE Questions, not exceeding Three Questions from any one part
PART-A
1. a) Three equal resistances of value R ohms are connected in a delta fashion. This is to be
replaced by an equivalent star connected resistance R1, R2 and R3. What are the values of R1,
R2 and R3 in terms of R.
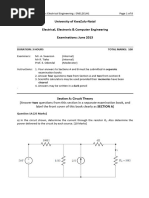
b) By applying Kirchhoff’s law, find the current through all the elements in the circuit as
shown in the figure?
2. a) What is DC generator and explain the basic principle of operation of a DC generator?
b) Derive the torque equation of a DC motor.
3. a) State and prove the condition for maximum efficiency of a transformer?
b) In a 25KVA, 2000/200V transformer the constant and variable losses are 350 W and 400 W
respectively calculate the efficiency on u.p.f at i) Full load and ii) Half full load.
4. a) Explain the principle of operation of alternator
b) A 6-pole, 3-phase, 50 Hz induction motor is running at full-load with a slip of 4%. The rotor
is star-connected and its resistance and standstill reactance are 0.25 Ω and 1.5 Ω per phase.
The e.m.f. between slip rings is 100 V. Find the rotor current per phase and p.f., assuming
the slip rings are short-circuited.
PART-B
5. a) With a neat circuit diagram, explain the operation of centre tap full wave rectifier
b) The applied input a.c. power to a half-wave rectifier is 100 watts. The d.c. output power
obtained is 40 watts. i) What is the rectifier efficiency? ii) What happens to remaining 60
watts?
6. a) Compare the characteristics of transistor amplifiers in the three configurations?
b) Explain the necessary conditions for oscillators
7. a) Explain the generation of ultrasonic’s and mention the applications
b) Explain the principle of induction heating.
8. a) Draw the schematic diagram of a CRO and explain its principle of working
b) Explain the working of a thermocouples.
1 of 1
Our New Site for Tutorials on different technologies : www.tutsdaddy.com
You might also like
- DT 2-Wire SystemDocument16 pagesDT 2-Wire SystemkperenNo ratings yet
- Harsen ChargerDocument1 pageHarsen ChargerCarlos AguiarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Divices and CircuitsDocument4 pagesElectronic Divices and CircuitssrihariNo ratings yet
- BEET101 Basic Electrical Engg.-1Document2 pagesBEET101 Basic Electrical Engg.-1mr.prashant.cseNo ratings yet
- NR 320204 HIgh Voltge EngineeringDocument4 pagesNR 320204 HIgh Voltge EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- NR-220402-Electrical TechnologyDocument8 pagesNR-220402-Electrical TechnologytemesgenNo ratings yet
- BEET 101 Basic Electrical Engineering BACK PAPER-mergedDocument28 pagesBEET 101 Basic Electrical Engineering BACK PAPER-mergednekovax2524No ratings yet
- bt21R0718 p1 18 11 09rahulDocument30 pagesbt21R0718 p1 18 11 09rahulAnonymous nTxB1EPvNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument4 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 Electronic Devices and CircuitsUr's Lovely NagNo ratings yet
- R07aec13 - Electrical TechnologyDocument5 pagesR07aec13 - Electrical TechnologymdabdulhaqNo ratings yet
- -Template- KEE-101T (SET-C)Document4 pages-Template- KEE-101T (SET-C)rifilos171No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument6 pagesElectrical and Electronics EngineeringsrihariNo ratings yet
- BEE Model Papers-2Document3 pagesBEE Model Papers-2Kumara SwamyNo ratings yet
- Power System - IDocument8 pagesPower System - Isatya_vanapalli3422No ratings yet
- FEE Model 2Document2 pagesFEE Model 2amangamingofficial2020No ratings yet
- BEE-C412: B. Tech. Semester Iv Examination, 2021Document5 pagesBEE-C412: B. Tech. Semester Iv Examination, 2021NamanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Analysis - IDocument12 pagesElectrical Circuit Analysis - IEmerson NuSaNo ratings yet
- BE - First Year - Electrical Engg - 13 JULY 2021Document3 pagesBE - First Year - Electrical Engg - 13 JULY 202121bit026No ratings yet
- Last 6 Year Question PapersDocument17 pagesLast 6 Year Question Papersalvinkerketta2No ratings yet
- NR 220205 Electro Mechanics IIDocument8 pagesNR 220205 Electro Mechanics IISrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Rr-10205-Edc Apr 2003Document8 pagesRr-10205-Edc Apr 2003mpssassygirlNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument4 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electronic Devices and CircuitsViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- NR 220402 Electrical TechnologyDocument8 pagesNR 220402 Electrical TechnologySrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- BEE Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesBEE Important QuestionsBilal Ahmed100% (10)
- BEE Model Papers-3Document3 pagesBEE Model Papers-3Kumara SwamyNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument30 pagesJntuworld: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringRajeev BujjiNo ratings yet
- 75339-BTech-BTEE-101-18-Basic-electrical-engineeri_250113_052701Document3 pages75339-BTech-BTEE-101-18-Basic-electrical-engineeri_250113_052701pulsar200123456No ratings yet
- Bee - 2023 JulyDocument3 pagesBee - 2023 Julyeshanpadhiar3No ratings yet
- 2021 22 Even 1Document28 pages2021 22 Even 1sarojkuldeepkumar181No ratings yet
- QB KEE101T ElectricalDocument15 pagesQB KEE101T Electricalplantforest16No ratings yet
- r05211002 Electrical TechnologyDocument7 pagesr05211002 Electrical TechnologySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Electrical and Electronic MeasurementDocument4 pagesSample Question Paper Electrical and Electronic MeasurementDeeo Dhadiwal0% (1)
- 9A02504 Power ElectronicsDocument4 pages9A02504 Power ElectronicsMohan Krishna100% (1)
- Manipal Institute of Technology: Reg. NoDocument2 pagesManipal Institute of Technology: Reg. Nodreamivory29No ratings yet
- 9d557ac92719be387d81e6d1f97bf832Document2 pages9d557ac92719be387d81e6d1f97bf832vaseemramNo ratings yet
- BEE MODEL QUESTION PAPERs March 2023 (R22)Document17 pagesBEE MODEL QUESTION PAPERs March 2023 (R22)Kumara Swamy100% (1)
- Btech 1 Sem Basic Electrical Engineering Ree 101 2018 19Document2 pagesBtech 1 Sem Basic Electrical Engineering Ree 101 2018 19Shrey SharmaNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-I PDFDocument4 pagesPower Systems-I PDFpadmajasivaNo ratings yet
- ENEL2ELH1 2013ElectricalEngineeringDocument8 pagesENEL2ELH1 2013ElectricalEngineeringsameehawahab85No ratings yet
- Fy Bee Suk Qb Nep2.0Document3 pagesFy Bee Suk Qb Nep2.0aratipatil3478No ratings yet
- Final Put 2023Document3 pagesFinal Put 2023Akash AnandNo ratings yet
- Et Prsolutions08Document8 pagesEt Prsolutions08BajiNo ratings yet
- NR 310204 Power ElectronicsDocument8 pagesNR 310204 Power ElectronicsSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Electronic Devices Circuits2Document1 pageElectronic Devices Circuits2Shaik BawajanNo ratings yet
- Mws Gen Ode TXT Runge4thDocument2 pagesMws Gen Ode TXT Runge4thArshad SaifiNo ratings yet
- Btech Sem 1 and 2 Btee 101 18Document2 pagesBtech Sem 1 and 2 Btee 101 18mehakkaurcheemaNo ratings yet
- Set No: 1 R10Document4 pagesSet No: 1 R10Viswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Set No.1: Code No.V3109/R07Document8 pagesSet No.1: Code No.V3109/R07Ashish AtriNo ratings yet
- Firstranker: Ii B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations May - 2013 Electrical TechnologyDocument4 pagesFirstranker: Ii B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations May - 2013 Electrical Technologyteodoro berouNo ratings yet
- BEE Question Bank With AnswersDocument11 pagesBEE Question Bank With AnswersSyed UmarNo ratings yet
- EE PYQ (Mid + End)Document35 pagesEE PYQ (Mid + End)Shalini KashyapNo ratings yet
- EIR2C4 - End SemDocument3 pagesEIR2C4 - End SemPravendra KushwahaNo ratings yet
- May 2012Document8 pagesMay 2012satya_vanapalli3422No ratings yet
- 22212-Fundamentals-of-Electrical-Engineering-sample-question-paperDocument5 pages22212-Fundamentals-of-Electrical-Engineering-sample-question-paperkartikmenase26No ratings yet
- Nr-220101-Applied ElectronicsDocument4 pagesNr-220101-Applied ElectronicsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Rr220402 Electrical TechnologyDocument8 pagesRr220402 Electrical TechnologySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Rr310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesRr310202 Electrical MeasurementsSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR09 Set No. 2Samiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Basic Elect. Iind Sessional Avinash 01-4-2015Document2 pagesBasic Elect. Iind Sessional Avinash 01-4-2015Avinash ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsFrom EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovNo ratings yet
- Controlmaster Cm10, Cm30 and Cm50: Universal Process Controllers, 1/8, 1/4 and 1/2 DinDocument92 pagesControlmaster Cm10, Cm30 and Cm50: Universal Process Controllers, 1/8, 1/4 and 1/2 DinDavesh JadonNo ratings yet
- Sony KDL 40HX800 ManualDocument24 pagesSony KDL 40HX800 ManualRipu Simiyu100% (1)
- Sohag Sir Part ADocument26 pagesSohag Sir Part ATA MI MNo ratings yet
- Datasheet CR35iADocument1 pageDatasheet CR35iAsantiagoNo ratings yet
- Topswitch: Designing Multiple Output Flyback Power Supplies WithDocument24 pagesTopswitch: Designing Multiple Output Flyback Power Supplies WithDinh TucNo ratings yet
- Secret Codes For Nokia PhonesDocument2 pagesSecret Codes For Nokia Phonesradu1508100% (1)
- Ihm Exor PDFDocument4 pagesIhm Exor PDFMário Sérgio OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Basic Manual: VHF Air Band TransceiversDocument24 pagesBasic Manual: VHF Air Band TransceiversOjeda O GerardNo ratings yet
- Plasma TV Service ManualDocument14 pagesPlasma TV Service ManualGerman BookNo ratings yet
- MC34063ADocument8 pagesMC34063ADiego MontaltoNo ratings yet
- PL2303TA USB To Serial Bridge Controller Product Datasheet: Document Revision: 1.1.0 Document Release: February 21, 2012Document25 pagesPL2303TA USB To Serial Bridge Controller Product Datasheet: Document Revision: 1.1.0 Document Release: February 21, 2012Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- DC Servo Motor Control System: User ManualDocument35 pagesDC Servo Motor Control System: User ManualBayeNo ratings yet
- Use Arduino As AVR ProgrammerDocument8 pagesUse Arduino As AVR ProgrammerHrvojeNo ratings yet
- AssignDocument5 pagesAssignShourya TayalNo ratings yet
- E - Press Release - INCJ - RenesasDocument3 pagesE - Press Release - INCJ - RenesasafdgtdsghfNo ratings yet
- Cisco ATT DigitalLife CSDocument6 pagesCisco ATT DigitalLife CSUpendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Zapi H2 Traction ControllerDocument5 pagesZapi H2 Traction ControllerHartanto DwiNo ratings yet
- SA-78-EDocument4 pagesSA-78-EFgidalevichNo ratings yet
- 2008-11 HUB The Computer Paper ToDocument40 pages2008-11 HUB The Computer Paper TothecomputerpaperNo ratings yet
- Hands On Relay School: Test Set SelectionDocument27 pagesHands On Relay School: Test Set SelectionVictor SampaNo ratings yet
- 06 Speed Control of Induction MotorDocument3 pages06 Speed Control of Induction MotorAbdljelil NesruNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Improvement of Single Phase Ac Voltage Controller Employing Extinction Angle ControlDocument6 pagesPower Factor Improvement of Single Phase Ac Voltage Controller Employing Extinction Angle Controlapi-27465568100% (2)
- Robonet Eng V2Document12 pagesRobonet Eng V2EstebanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics (EE 5 Semester) Unit 3: ChoppersDocument23 pagesPower Electronics (EE 5 Semester) Unit 3: ChoppersDadaNo ratings yet
- ) Star Topology. Each Device in Star Topology Has A Dedicated Point-To-Point Link ToDocument1 page) Star Topology. Each Device in Star Topology Has A Dedicated Point-To-Point Link Toswapnil nanvareNo ratings yet
- Lglite + Load Board: Fundamentals of Fault DetectionDocument14 pagesLglite + Load Board: Fundamentals of Fault DetectionVijayakumar SNo ratings yet
- 1A Chapter 7Document32 pages1A Chapter 7Kb KabzaNo ratings yet
- Reflector AntennasDocument20 pagesReflector AntennaslvsaruNo ratings yet