10 Isroset Ijsrcse 09124
10 Isroset Ijsrcse 09124
Uploaded by
Md Sazzad HossenCopyright:
Available Formats
10 Isroset Ijsrcse 09124
10 Isroset Ijsrcse 09124
Uploaded by
Md Sazzad HossenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
10 Isroset Ijsrcse 09124
10 Isroset Ijsrcse 09124
Uploaded by
Md Sazzad HossenCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Scientific Research in
Computer Science and Engineering
Vol.11, Issue.5, pp.88-92, October 2023
E-ISSN: 2320-7639
Available online at: www.isroset.org
Research Paper
Integrated Management of Patient Health Records with Smart Card and
Its Benefits
Patel Karika Digesh1
1
Computer Engineering, L.D. College of Engineering, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India
Author’s Mail Id: karikapatel@gmail.com
Received: 18/Aug/2023; Accepted: 20/Sept/2023; Published: 31/Oct/2023
Abstract—The healthcare system is facing critical issues with the effective and efficient storage and retention of patient health
records. As information technology is gradually becoming more important nowadays, its use in health records has become
crucial. The challenge of present documentation in electronic health records (EHRs) is that there is not enough documentation to
demonstrate the quality and necessity of care. Common errors in using the EHRs were found to be more like scattered and
discrete data without integration, which ultimately were not usable. Smart cards may be utilized for integrated health records and
to simplify the prescription process, facilitate the delivery of care, and improve the standard of care given. Smart cards are
portable integrated devices with data storage and data processing capabilities. The research paper focuses on how smart card
technology can be applied to an essential and vital sector of healthcare. The system uses smartcards for personal identification
and transfer of health data and provides data communication. In addition to personal information, general health information
about the patient is also loaded onto the patient’s smart card. Healthcare providers use smart cards to access data about patients.
Electronic health records with smart card usage enhance the integrated approach and have several advantages over paper records
such as improving the accuracy, and quality of patient care, and reducing cost, efficiency, and productivity.
Keywords—Patient, Integrated, Smart card, patient health record (PHR), RFID, OTP, Cloud, Electronic Health Record (EHR),
Accessibility, Availability, Security, Cloud storage.
1. Introduction Today’s world is undergoing globalization with digitalization
and witnessing technological advancement in big data
Medical records are the document that describes all details management. Paper data is going to obsolete due to lack of
about the patient’s history, clinical findings, diagnostic test efficiently and timely retrieval of the data. It is of paramount
results, pre and postoperative care, patient progress, and importance to manage patient health data in an efficient way.
medication. If the details are collected and preserved Concurrent issues in patient healthcare records drive the
accurately, it will help the doctor treat the patient research.
appropriately. Despite the awareness of the benefits of
maintaining a proper health record, the current healthcare 2. Rational Behind the Research
system of many developing countries is still in its initial More often printed documents preserved as health records are
stages. Medical records are one of the most important aspects difficult to systematize. Healthcare practices paper medical
on which practically historic details can be fetched and records in storage. These paper records require more space
accessed promptly. and are prone to environmental disasters, paper records also
A smart card is in use in daily life applications are discussed tend to deteriorate over time. Moreover, printed documents
below: The most commonly used smart cards for domestic are endangered from breaking in, and getting misplaced from
purposes are DTH (Direct to Home) cards. These cards storage. Many times, healthcare professionals maintain only a
provide authorized access to information received from single photocopy of a paper health document, if a particular
satellites. The information received by these cards gets documentation is lost it is irretrievable. Hence, the smart card
encrypted and decrypted within it. seeks to develop a solution that not only safeguards patient
information but also streamlines administrative operations
A SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card given by cellular and enhances overall healthcare delivery. As healthcare
operators to their subscribers is an example of a smart card. institutions throughout the world continue to digitize, the
Smart cards are very handy as a tool for financial transactions significance of such research in ensuring the integrity and
both in traditional as well as web-based applications. security of patient health records becomes apparent.
© 2023 IJSRCSE All Rights Reserved 88
Int. J. Sci. Res. in Computer Science and Engineering Vol.11, Issue.5, Oct 2023
3. Research Methodology Efforts are needed to improve (1) PHR data quality through
patient-centred user interface design and standardized patient-
The research is exploratory type using secondary data of generated data guidelines, (2) data integrity through
prevailing research outcomes. consolidation of various types and sources, (3) PHR
The secondary data used comprises of reference books and functionality through application of new data analytics
research published in journals. methods, and (4) metrics to evaluate clinical outcomes
associated with automated PHR system use, and costs
4. Literature Review associated with PHR data storage and analytics. [9]
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are real time digital According to Bodake et al. (2012) A smart card, typically a
version of patient records. An Electronic Health Record type of chip card, is a plastic card that contains an embedded
(EHR) is a comprehensive report of an individual’s overall computer chip– either a memory or microprocessor type–that
health. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) help track patient’s stores and transacts data. This data is usually associated with
clinical progress, facilitate improved health care decisions and either value, information, or both and is stored and processed
provide evidence-based care. [1] within the card's chip. Systems that are enhanced with smart
Any healthcare system must include information on a very cards are in use today throughout several key applications,
regular basis. This is due to the fact that information is useful including healthcare, banking, entertainment, and
for making decisions, formulating policies, conducting transportation. [10]
research, as well as for administrative and medical purposes.
The research advises the following strategies for managing Today there is a growing number of smart card and smart
information flow in the context: token manufacturers around the world, and there are already
dozens, perhaps hundreds, of different smart card and token
Deploying electronic healthcare systems and developing
interfaces and interface protocols. While there may be a need
human capacity in the healthcare industry.
for specialized cards or tokens in certain access control
Providing policies that facilitate the implementation of e-
systems, extensive use of smart cards in everyday activities
health systems; Providing a unified standard for health depends on the interoperability of cards and card reader/writer
information exchange. devices produced by different companies. The current efforts
Integrating private healthcare organizations with of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
Government owned healthcare organizations.[2] and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) may
yield standards for contact-type smart cards (and their
The RFID based Universal transaction system offers a simple corresponding reader/writers) which will help steer the smart
and efficient alternative to modern transaction systems. The card industry toward interoperability.
system is easy to build and deploy. Though the initial setup
cost would be high the maintenance cost would be negligible. In the case of user data access, proper security controls and
As soon as the tag comes in the vicinity, it is identified by the restrictions must also be implemented around the application,
reader, thus it is very fast in identification. [3] database, and environments that house the electronic data.
The use of paper as a means of recording health data in most Smart cards can be effective in supporting numerous
healthcare facilities and organizations has led to an extensive organizational programs in the country such as SIM card
paper trail and most organizations have developed interest in registration, voters card registration, healthcare applications
shifting from paper-based health records to electronic health and many more, with or without a unique identifier. [11]
records.[4]
The research of Singh et al. (2017) came up with smart card
Effectively managing an electronic health record requires a that served as identification, library, canteen, shops, and
multidisciplinary team including telecommunication, online storage card. They made use of bar-coded smart cards.
instrumentation, and computer science to enable the exchange These have the advantage of being cheaper than other types of
of medical data across wider geographic regions.[5] cards. They identified advantages of multi-application cards
The common issues that need to be addressed in electronic as reduction in card issuance and administrative costs. The
medical record systems are privacy, security, and convenience of carrying a single card that serves several
confidentiality [6] purposes is also an advantage. [12]
It is highly recommended that an efficient encryption scheme This review revealed that the current quality of the
that can easily be applied by both the healthcare professionals documentation in EHRs remains a challenge, with insufficient
and the patients be applied on the latest EHR records. [7] documentation to substantiate the quality and necessity of
care. Common errors in using the EHRs (Electronic Health
Some examples of RFID techniques include the storage of Records) were found in both chiropractic and other healthcare
data within RFID tags and imposing restrictions for accessing practitioners. These errors were more often a result of
RFID tags. These techniques have improved privacy and problems with software misuse or abuse, budgetary
security through restrictions allowing only authorized constraints, insufficient training, or carry-forward errors from
individuals to access the information.[8] manual methods. Electronic health records training continued
© 2023 IJSRCSE All Rights Reserved 89
Int. J. Sci. Res. in Computer Science and Engineering Vol.11, Issue.5, Oct 2023
financial incentives, appropriate implementation processes, coordinated health service process. Using the smart health
and utilization of available software features may decrease card patient data, doctor’s prescription, and patient’s present,
documentation errors.[13] and former health history are accessible. When an infant is
born a record is formed with details like blood group,
The evolution of PHRs as described in this study might not vaccination dates, complications involved, allergies, and other
necessarily reflect the state of the practice. More research is important details. This card plays a crucial role during
therefore needed to extract and evaluate PHR scope and the unexpected incidents like accidents and reduces child traffic
functionalities of the various PHR systems available in problems. The cloud computed system enrolled within helps
practice. Also, as mentioned above, this study focused on US to secure the data of patients and prevent data intrusion.
studies, thereby limiting the scope of our analysis. Research Hence, it reveals that an appropriate record system for health
comparing PHR systems in the United States with those used records is required.
in other countries would help improve future data uses.[14]
It has shown that, although it is in constant technological The research is aimed at developing such a method using
evolution, the smart card is now well established in the field. smart cards for patient health records with an integrated
In addition to the fare collection function, smart card systems approach.
can be useful for providing data to both planners and
researchers. This continuously flowing data on passenger 6. Workflow and Methodology
behaviour can serve to enhance the strategic, tactical, and
operational performance of transit.[15] The basic workflow diagram of a smart card is as below.
The service will ensure the health insurance for the potential
card-holding patient. Through this model, it will be possible
to differentiate the patient’s healthcare information that can
only be accessed by the Government healthcare services and
by the other registered private organizations as well. It will
also protect the corruption from different bodies of health care
sectors. However, the implementation of this proposed project
needs huge efforts. Our research result shows that the
successful implementation of this project depends on several
issues such as financial arrangement, mass awareness,
voluntary participation of healthcare-related people, etc. In
return, the benefit of this project is long-term and wide on the
national health care system. Implementation of the system as
well as identifying its pros and cons has been left as open
research for future work.[16]
The patient’s smart card is filled with general health
information. Over the distributed object protocol, encryption
keys and digital signature keys stored on the system’s smart
cards are utilized to exchange secure and authorized data
between clients and database servers.[17]
5. Importance of the research
It is evident from the literature review that patient health
records are of due importance and the current record system is
having issues and is not sufficiently preserving and retaining
records securely. Electronic Health Records allow structured
medical data to be shared easily among authorized healthcare
providers so as to improve the overall quality of the
healthcare services delivered to the patients. The use of
electronic health data enables users to have wider thinking
and allows healthcare providers to network effectively.
The health care system is one of the critical issues for
developing countries and thus information technology is Figure 1. Workflow diagram of smart card
becoming progressively more important nowadays. The
deployment of smart health cards simplifies the prescription Smart card working process:
process, improves the standard of care given, and facilitates Step-1: A smart card is inserted into the card reader which
electronic healthcare records management through a reads the information from the smart card.
© 2023 IJSRCSE All Rights Reserved 90
Int. J. Sci. Res. in Computer Science and Engineering Vol.11, Issue.5, Oct 2023
Step-2: After the card reader reads information from the card assigned to the system to upload the documents of newly
it passes the information to the payment system or registered users. Admin will check the user’s ID to verify the
authentication system. new user and the mobile number.
Smart cards can be utilized to completely digitalize the For security, the mobile number will be linked to an RFID
tracking and situating of physical records and archives, card for a 2-factor authentication system. It will send OTP
including approving access, recording (One Time Password) including some numerical or alphabets.
registration/registration, and all related detailing. Digitization This OTP is only valid for a short time for security. After the
with complete precision implies that the collaboration of user’s registration and identity verification, the admin will
individuals utilizing the records is no longer an issue. In the provide an RFID card to the new user.
event, if that smart card comes extremely close to an RFID
reader, its report will be caught. Radio Frequency Then for the documents upload procedure, Admin will log
Identification (RFID – Radio Frequency Identification) is the into the system. Then user is required to scan the RFID card
most recent and most developed technique programmed and enter OTP from the registered mobile number into the
information assortment innovation, increasing wide system. After OTP gets verified, the admin will check and
acknowledgment as individuals comprehend and utilize this verify the original documents provided by the new user. After
innovation. The primary components of a smart card (RFID verification of documents, the admin will scan it and
framework) are basically a transponder (tag), a reader, documents will get converted into jpg format. For the
correspondence organizations, and host PCs. In a RFID document’s security, these uploaded documents will be
(Radio Frequency Identification) framework there are two encrypted. These encrypted documents will be stored in the
sorts of reception apparatuses: one is in the tag while the other database. In this system, users can download personal
is associated with the reader. The data stream during the smart documents from the system using the RFID card. Admin can
card (from straightforward tag to the host application) starts also check all registered user’s activities such login/log out
with have overseen Reader and issues orders. The reader and and further processes.
tag impart utilizing a radiofrequency (RF) signal. The reader
produces a transporter signal on demand from the host 8. Results and Discussion
application and sends it out from the reader reception
apparatus. This signal hits the label which gets and adjusts it Table-1-Attributes required in process.
and reflects the regulated sign. The reader catches modified Process Attribute
signals and sends them to the reader which converts the signal Register Identification code
into digital. The digitized information is shipped off the host Verification password
application. For the authentication system, a 2-step Edit/Update RFID
authentication procedure that prevents unauthorized access to Storage Cloud
documents through a smart card. RFID is an innovation,
which recognizes an object or individual naturally by utilizing
radio waves through a RFID's unique number. RFID can be
utilized in the management of health records of patients.
The bar code consists of wide and narrow bars which
represent each character. Barcodes can be read through a
barcode scanner which uses a photosensor that converts
barcodes into electrical signals as it scans through the
barcode. The relative width of bars and spaces is measured
and scanned through a scanner which is then converted into
regular characters. These characters are then used to uniquely
identify a card to a system. Every bar code starts and ends
with a special start and end character. With the help of this bar Figure-2 Integrated Outcome
code the reader can detect whether the card is being scanned
forward or backward. Some barcodes also provide error The proposed scheme require registration for the purpose of
checking by providing a checksum character just before the record of valid user and afterwards on verification feedback is
stop character. Patient information along with a unique taken from registration details for authentication and
barcode will be stored in the system with the help of a verification. User can enter data, edit data, read data with the
database or file structure. In the case of file structures, various help of RFID tag. The proposed scheme can cloud as storage
technologies such as length indicators or delimiters can be and anywhere across the globe data can be fetched and
used. accessed. Security of data is ensured as access is password
protected.
7. Proposed sequence of process It is evident from the methodology adopted for the schema of
integrated approach of managing patient vital health record
First thing, when a new user wants to use the system, the user using smartcard offers data availability, accessibility, and
is required to carry out registration on the system. Admin is
© 2023 IJSRCSE All Rights Reserved 91
Int. J. Sci. Res. in Computer Science and Engineering Vol.11, Issue.5, Oct 2023
security in all. The system ensures the confidentiality, International Journal of Scientific Research in Multidisciplinary
integrity, and availability of patient information through a Studies Vol.9, Issue.5, pp.14-21, May 2023.
[3] Farida Attar , Amina Bhatkar, S Hasan Haider , Tahir Abbas
series of well-defined processes and security measures.
Kadiwala, “RFID Based Universal Transaction System”,
International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science
9. Conclusion and Engineering Vol.8, Issue.2, pp.52-54, April-2020.
[4] Carey DJ, Fetterolf SN, Davis FD, Faucett WA, Kirchner HL,
The results and outcomes of usage overcomes lack of routine Mirshahi U, Murray MF, Smelser DT, Gerhard GS, Ledbetter DH.,
“The Geisinger MyCode community health initiative: an electronic
method of maintaining health records of patient like difficulty health record-linked biobank for precision medicine research.” Genet
in access, lack of reliability and security, and most Med. pp.18(9):906-3, Sep-2016.
importantly prompt retrieval of the data across the globe with [5] Kiah ML, Zaidan BB, Zaidan AA, Nabi M, Ibraheem R. , “MIRASS:
world wide web and cloud storage. medical informatics research activity support system using
To conclude, the integrated management of patient health information mashup network Journal of Medical Systems Volume 38
Issue 4, pp.1–15, April 2014.
records with a smart card system presents a robust and secure
[6] Alanazi HO, Zaidan AA, Zaidan BB, Kiah ML, Al-Bakri SH.
solution for handling sensitive healthcare data efficiently. “Meeting the security requirements of electronic medical records in
the ERA of high-speed computing.” J Med Syst.pp.39(1):165, Jan-
10. Future Scope of the Study 2015. [7] Ismail Keshta, Ammar Odeh, “Security and privacy of
electronic health records: Concerns and challenges”, Egyptian
Informatics Journal, Volume 22, Issue 2, pp. 177-183, ISSN 1110-
The research can be further extended by adding algorithms 8665,2021.
and utilizing AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning [8] Jannetti MC. (2014), “Safeguarding patient information in electronic
algorithms for data analytics and predictive modelling to health records.” AORN Journal;100(3): pp. C7–C8, 2014.
improve patient care and treatment outcomes. Moreover, the [9] Bouayad L, Ialynytchev A, Padmanabhan B. “Patient Health Record
use of blockchain for decentralized and tamper-proof health Systems Scope and Functionalities: Literature Review and Future
Directions.” J Med Internet Res. 15; pp. 19(11): e388, Nov-2017.
record management can further enhance data security and [10] Bodake, A., Baviskar, V., Bodake, A., Bhoite, S., and Kulkarni, N. J.
integrity. (2012), “Multipurpose Smartcard System.”, International
Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Engineering &
11. Recommendations Technology (IJARCET), 1(9).pp. 175-178, 2012.
[11] Martha E. Haykin Robert B. J. Warnar, “Smart Card Technology:
New Methods for Computer Access Control”, Computer Science and
The research recommends the use of smart card for managing Technology; NIST Special Publication pp.500-157, 1988.
health record of patients which are plethora of important for [12] Singh, A., Chopra, A., Imran, M., and Singh, R. (2017), “Designing
their lives. The research outcome and Implementation of Smart Card Technology for the Students of
Higher Education.”, International Journal of Computer Science and
Data Availability Mobile Computing IJCSMC, 6, pp. 144-149.,2017.
[13] Taylor DN. “A literature review of electronic health records in
The data of this research would be made available through an
chiropractic practice: common challenges and solutions.” J Chiropr
online repository including ISROSET. Humanit 1;24(1): pp.31–40, Dec-2017.
Conflict of Interest There is not any conflict of interest in [14] Bouayad L, Ialynytchev A, Padmanabhan B. “Patient Health Record
this research work. Systems Scope and Functionalities: Literature Review and Future
Directions.” J Med Internet Res. 15; pp.19(11): e388, Nov-2017.
Funding Source [15] Pelletier, M.-P., Trépanier, M. & Morency, C. (2011). “Smart card
data use in public transit: A literature review.” Transportation
This work was supported by the conference and published Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 19, pp.557—568, 2011.
research paper references. [16] Ayan Patel, Kansara P., Marvania M., Shah A. (2019), “Patient
Smart Card”; IJSART -Volume5 Issue1, pp.5-7, January-2019.
Authors’ Contributions [17] K. W. Ashan Pivithuru, A. Srinivasan, A. Wijeratnam, I. Nassar,
This research focuses on the proposed Frameworks to be S. S. Chandrasiri and P. K. Suriyaa Kumari, "E-patient Card: An
used to manage challenges of managing patient health record Integrated Electronic Health Recording System for Patient," 2021
3rd International Conference on Advancements in Computing
in healthcare sector. The researcher has revied relevant (ICAC), Colombo, Sri Lanka, pp.395-400, 2021.
literature for the proposed research work and obtained the
outcomes with the help of proposed framework. AUTHOR’S PROFILE
Patel Karika Digesh is a Research
Acknowledgements Scholar and studying in the Final year of
The researcher would like to sincerely acknowledge the Bachelor of Engineering in Computer
guidance of Ayan Patel and Digesh patel for accomplishment Engineering at L.D. College of
of the research work. Engineering, Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Her
research interests include application of
References Computer science and engineering for the
benefit of the society in a constructive
[1] Manisha Wadhwa “Electronic Health Records in India”, ICT India manner. Research area of interest include Artificial
Working Paper #25 CSD Working Paper Series, pp.1-23, March Intelligence and machine learning, algorithms, and
2020.
[2] Attahiru Saminu, “A Paradigm for Efficient Security of Information
complexity.
System Control in Healthcare Organizations in Nigeria”,
© 2023 IJSRCSE All Rights Reserved 92
Submit your manuscripts at
www.isroset.org
email: support@isroset.org
Call for Papers:
Authors are cordially invited to submit their original research papers, based on theoretical or experimental works for
publication in the journal.
All submissions:
- must be original
- must be previously unpublished research results
- must be experimental or theoretical
- must be in the journal's prescribed Word template
- and will be peer-reviewed
- may not be considered for publication elsewhere at any time during the review period
You might also like
- Smart Card 2Document47 pagesSmart Card 2Msambili NdagaNo ratings yet
- JPNR 2022 S03 063Document4 pagesJPNR 2022 S03 063Md Sazzad HossenNo ratings yet
- 2006 CMPB PDFDocument47 pages2006 CMPB PDFDhanashreeNo ratings yet
- Smart Card For Health Care SystemDocument6 pagesSmart Card For Health Care SystemSurendra Kumar TaraiNo ratings yet
- Smart Cards Applications in The Healthcare SystemDocument8 pagesSmart Cards Applications in The Healthcare SystemJournal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems (JMEDS)No ratings yet
- Name:: Mohammad Khamis BalochiDocument7 pagesName:: Mohammad Khamis BalochiNaveed Akhtar BalochNo ratings yet
- Ria 37.02 22Document15 pagesRia 37.02 22rajivfr144No ratings yet
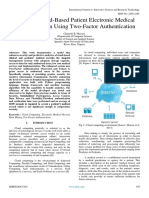
- A Secure Cloud-Based Patient Electronic Medical Records System Using Two-Factor AuthenticationDocument6 pagesA Secure Cloud-Based Patient Electronic Medical Records System Using Two-Factor AuthenticationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Security and Privacy-Preserving Challenges of E-Health Solutions in Cloud ComputingDocument22 pagesSecurity and Privacy-Preserving Challenges of E-Health Solutions in Cloud ComputingfardzlyNo ratings yet
- Ijet V3i6p2Document6 pagesIjet V3i6p2International Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Machine-Learning Approach For Predicting Harmful Diseases Using Big Data and IoT A ReviewDocument6 pagesMachine-Learning Approach For Predicting Harmful Diseases Using Big Data and IoT A ReviewIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Bhanu Prathap ProjectDocument6 pagesBhanu Prathap ProjectZoran GacovskiNo ratings yet
- The Implementation of The Electronic Healthcare RecordDocument1 pageThe Implementation of The Electronic Healthcare RecordN WNo ratings yet
- Medicine Dispenser Using RFIDDocument8 pagesMedicine Dispenser Using RFIDIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering in HealthcareDocument5 pagesSoftware Engineering in HealthcareIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Smart Cards and Healthcare Providers: in This FAQDocument12 pagesSmart Cards and Healthcare Providers: in This FAQBlasi puuaboyNo ratings yet
- A Blockchain Framework To Secure Personal Health RDocument19 pagesA Blockchain Framework To Secure Personal Health RpersonneNo ratings yet
- Health CNN-SMO: To Secure and Enhance The Medical Healthcare System by Using Convolution Neural NetworkDocument4 pagesHealth CNN-SMO: To Secure and Enhance The Medical Healthcare System by Using Convolution Neural NetworkInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- BN2021 4028761Document9 pagesBN2021 4028761Manoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Proposed System Using Iot and Gis To Generate Electronic Medical RecordsDocument11 pagesProposed System Using Iot and Gis To Generate Electronic Medical Recordsindex PubNo ratings yet
- AmirLatif2020 Article ARemixIDESmartContract-basedFrDocument24 pagesAmirLatif2020 Article ARemixIDESmartContract-basedFrDivya KandpalNo ratings yet
- Blockchain-Based Secure Healthcare Application For Diabetic-Cardio Disease Prediction in Fog Computing PDFDocument15 pagesBlockchain-Based Secure Healthcare Application For Diabetic-Cardio Disease Prediction in Fog Computing PDFBhuvana SenthilkumarNo ratings yet
- MR 221022163025Document8 pagesMR 221022163025pearl ikebuakuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials JournalDocument10 pagesAdvanced Materials Journalmounikad.openventioNo ratings yet
- Run Your Health Profile - A Digital Health Profile To Store Personal Health HistoryDocument8 pagesRun Your Health Profile - A Digital Health Profile To Store Personal Health HistoryIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Report Black BookDocument48 pagesReport Black BookShraddha SinghNo ratings yet
- WSN 180 (2023) 82-93Document12 pagesWSN 180 (2023) 82-93john carl cuerpoNo ratings yet
- An RFID-based System For Emergency Health Care ServicesDocument4 pagesAn RFID-based System For Emergency Health Care ServicesgingeevimalNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument28 pagesBusiness PlanNirajan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery: Applications, Techniques, Challenges and Process Models in HealthcareDocument7 pagesData Mining and Knowledge Discovery: Applications, Techniques, Challenges and Process Models in Healthcareraj1o1oNo ratings yet
- Efficient and Secure Communication Architecture For E-Health SystemDocument9 pagesEfficient and Secure Communication Architecture For E-Health SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- 1.+amrik IJISAE 1Document14 pages1.+amrik IJISAE 1karthick avNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document12 pagesAssignment 1Smarika ShresthaNo ratings yet
- E - Health CardDocument6 pagesE - Health CardIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- A Review On Emerging Smart Technological Innovations in Healthcare Sector For Increasing Patient's Medication AdherenceDocument7 pagesA Review On Emerging Smart Technological Innovations in Healthcare Sector For Increasing Patient's Medication AdherenceEdi Berani BermimpiNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Two-Stage Classification Model For The Prediction of Heart Disease Using Iomt and Artificial IntelligenceDocument19 pagesSensors: Two-Stage Classification Model For The Prediction of Heart Disease Using Iomt and Artificial Intelligencemailshruthi001No ratings yet
- Patient Record TrackingDocument85 pagesPatient Record TrackingMajestyNo ratings yet
- 19DCS148Document5 pages19DCS148waxape9612No ratings yet
- Combining Blockchain and Iot For Decentralized Healthcare Data ManagementDocument16 pagesCombining Blockchain and Iot For Decentralized Healthcare Data ManagementJames MorenoNo ratings yet
- Privacy - by - Design 10.1007/s12394 010 0055 XDocument8 pagesPrivacy - by - Design 10.1007/s12394 010 0055 XscribrrrrNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Online Hospital Management Information SystemDocument10 pagesDesign and Development of Online Hospital Management Information SystemRula ShakrahNo ratings yet
- Iot Edge (Fog) - 2Document11 pagesIot Edge (Fog) - 2Rakesh PotlaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Interoperability in HealthcareDocument4 pagesImportance of Interoperability in HealthcareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Iot Based Smart Healthcare Kit: March 2016Document7 pagesIot Based Smart Healthcare Kit: March 2016Gajalakshmi AshokNo ratings yet
- SR22626222432 PDFDocument5 pagesSR22626222432 PDFMr.Jitender Chaurasia (SU System Administrator)No ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Survey of The Internet of Things IDocument20 pagesA Comprehensive Survey of The Internet of Things Imisericordemassoma371No ratings yet
- IoT Application in HealthcareDocument9 pagesIoT Application in HealthcareDimas AtmojoNo ratings yet
- Security and Privacy Issues in Healthcare Information SystemDocument5 pagesSecurity and Privacy Issues in Healthcare Information SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Kiourtis2019 Article StructurallyMappingHealthcareDDocument13 pagesKiourtis2019 Article StructurallyMappingHealthcareDNidhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Monitoring System For Remote AreasDocument7 pagesHealthcare Monitoring System For Remote AreasIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Personal Health Record Cloud Platform Using Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based EncryptionDocument8 pagesImplementing A Personal Health Record Cloud Platform Using Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based EncryptionAyeni AyomideNo ratings yet
- Decision Tree Based Health Prediction SystemDocument8 pagesDecision Tree Based Health Prediction SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document15 pagesJurnal 1Eka Ratna SariNo ratings yet
- Medinform 2022 7 E39145Document7 pagesMedinform 2022 7 E39145Hanako KoyanagiNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0045790622002440 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S0045790622002440 MainNeha NehaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain-Based Secure Healthcare For Cardio Disease Prediction of ArrhythmiaDocument9 pagesBlockchain-Based Secure Healthcare For Cardio Disease Prediction of ArrhythmiaIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: A Panacea For Healthcare Cloud-Based Data Security and Privacy?Document7 pagesBlockchain: A Panacea For Healthcare Cloud-Based Data Security and Privacy?omarNo ratings yet
- Author'S Copy Author'S CopyDocument5 pagesAuthor'S Copy Author'S Copyziafat shehzadNo ratings yet
- DichDocument4 pagesDichngocphh.35No ratings yet
- Machine Learning and AI for Healthcare: Big Data for Improved Health OutcomesFrom EverandMachine Learning and AI for Healthcare: Big Data for Improved Health OutcomesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)