Module 2 Unifying Themes in The Study
Module 2 Unifying Themes in The Study
Uploaded by
Angela NuquiCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2 Unifying Themes in The Study
Module 2 Unifying Themes in The Study
Uploaded by
Angela NuquiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Module 2 Unifying Themes in The Study
Module 2 Unifying Themes in The Study
Uploaded by
Angela NuquiCopyright:
Available Formats
Quarter 2 – Module 2: Unifying Themes in the Study of Life
After going through this module, you are expected to:
1. name the unifying themes in the study of life;
2. describe the unifying themes illustrated;
3. explain the connection among living things and their interaction with the
environment;
4. give details on how these themes serve as the foundation in the study of
biology.
5. value life by taking good care of all beings, human, plants and animals.
Earth is the home of organisms including animals, plants and
microorganisms. They are found in the different parts of the planet. The
ecosystems-the biological communities- include living organisms (biotic
factors) like animals, plants, insects and bacteria (interacting to its
environment), as well as the non-living components (abiotic factors) like the
rock, soil, water and sunlight. Non-living things are classified as inanimate
objects that may influence, alter or impact the life of biotic factors. These
abiotic factors are essential to biotic factors in various ways. The field of
science that deals with the study of life is the Life Science or Biology. It
involves different disciplines. These disciplines are connected to one another,
through which biologist termed as unifying themes. This module emphasizes
these unifying themes that serve as the bases of the study of Life Science.
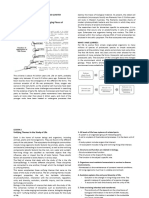
The ten unifying themes include: emergent properties, the cell, the heritable
information, structure or function, interaction with the environment,
regulation, unity and diversity, evolution, scientific inquiry, and the science,
technology and society. More so, this module explores how organisms
interact with one another and its environment.
The unifying theme connects the different subdisciplines that make biology
as a science. In addition to, the living organisms differ from non-living
organisms in various aspects. What are these shared properties (of living
organisms) that make something “alive”?
All levels of life have systems of related parts.
- A system is an organized group of interacting parts.
- A cell is a system of chemicals and processes. It is the basic unit of life.
- A body system includes organs that interact.
- An ecosystem includes living and non-living things that interact.
Structure and function are related in biology.
- Structure determines function.
- The structure is the shape of the object.
- The function is the object’s specific role.
Organisms must maintain homeostasis to survive in diverse environments.
- Homeostasis is the maintenance of constant internal conditions.
- All living organisms must live in a stable environment.
Evolution explains the unity and diversity of life.
- Evolution is the change in living things over time. The genetic makeup of a
population of a species changes.
- It accounts for both the diversity and the unity of life.
Traits are being inherited and transferred.
- The continuity of life depends on the inheritance of biological
information in the form of DNA molecules.
- The genetic information is encoded in the nucleotide sequences of the DNA
(Deoxyribonucleic acid).
Organisms reproduce.
- It is necessary part of living; process of making more of one’s own kind.
Organisms are interdependent with one another.
- Organisms have evolved to live and interact with other organisms.
- Ecology deals with the interactions of living organisms with one another
and their environment.
Organisms acquire and process energy.
- Living organisms use a source of energy for their metabolic activities.
- Some living organisms capture the light energy and convert it into
chemical energy in food.
- Some living organisms use chemical energy stored in molecules obtained
from food.
In addition to the properties mentioned, the two additional unifying themes
in the study of life include the scientific inquiry and science, technology and
society.
Scientific Inquiry
- The process of science includes observation-based discovery and the
testing of explanations through the hypothetic-deductive.
- Scientific credibility depends on the repeatability of observation and
experiments.
Science, Technology and Society
- Many technologies are goal-oriented applications of science.
- The relationships of science and technology to society are now more crucial
to understand than ever before.
You might also like
- Ed & Lorraine Warren - Demonologistas - Gerald BrittleDocument166 pagesEd & Lorraine Warren - Demonologistas - Gerald BrittleErivelton Menezes69% (13)
- 0654 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2019)Document159 pages0654 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2019)Vibhor Pandey67% (3)
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Living AnimalDocument43 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Living AnimalLouella Artates67% (3)
- Earth is the home of organismsDocument2 pagesEarth is the home of organismsLiam GonzalesNo ratings yet
- EL Q2 02 - Unifying themes in the Study of LifeDocument14 pagesEL Q2 02 - Unifying themes in the Study of LifeHyper ZedNo ratings yet
- Earth Scie 22Document26 pagesEarth Scie 22HayaradjNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Handouts q2Document5 pagesEarth & Life Handouts q2Ariel Barredo CogayNo ratings yet
- ELSQ2 L2Document8 pagesELSQ2 L2Pinky Jean BruaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Wk3 New FileDocument81 pagesQ2 Wk3 New FilegianpeleciamagdamitNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument5 pagesLesson 2 - Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeMelvin CarranzaNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 Module-2 Unifying-ThemesDocument12 pagesELS Q2 Module-2 Unifying-ThemesmalvargillianeNo ratings yet
- Life Science l1 3 HoDocument4 pagesLife Science l1 3 HonucupyhiaztineNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Lesson 2 - Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument16 pagesEarth and Life Science Lesson 2 - Unifying Themes in The Study of Lifejhondee lagramaNo ratings yet
- M2 Introduction To BiologyDocument7 pagesM2 Introduction To BiologyArnel Portas JrNo ratings yet
- SMILE L.P Q2 EARTH AND LIFE SCI WK 2Document4 pagesSMILE L.P Q2 EARTH AND LIFE SCI WK 2Angelie Espartero Araneta LobitañaNo ratings yet
- SLM No. 1 Bio Study of LifeDocument16 pagesSLM No. 1 Bio Study of LifeAshley Nicole SabsilicaNo ratings yet
- What Is Biology?Document5 pagesWhat Is Biology?VidGe MasaquelNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument2 pagesUnifying Themes in The Study of Lifefranzfsalvacion15No ratings yet
- Energy for lifeDocument11 pagesEnergy for lifeMicah DionNo ratings yet
- Activity sheet-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesActivity sheet-WPS Officerosemarie45casasNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in Earth and Life ScienceDocument23 pagesActivity Sheet in Earth and Life ScienceRODEL AZARES0% (1)
- Welcome To Biochemistry ClassDocument14 pagesWelcome To Biochemistry Classleexie2821No ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Biology (GE111)Document8 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Biology (GE111)Nathaniel Victor BalerNo ratings yet
- Second NotesDocument2 pagesSecond Notesedrianpana580No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument4 pagesGeneral BiologyKasai KristineNo ratings yet
- ELS - Q2 - Module 2 - Unifying Themes in The Study of Life - v2Document12 pagesELS - Q2 - Module 2 - Unifying Themes in The Study of Life - v2ELEZAR PEDERENo ratings yet
- CertainlyDocument7 pagesCertainlyseeratytNo ratings yet
- PNUS2101 week 1 and 2Document6 pagesPNUS2101 week 1 and 2Ryan KarlNo ratings yet
- UnifyingDocument19 pagesUnifyingjefprilcangkeNo ratings yet
- 01 The Living WorldDocument16 pages01 The Living Worldjocoge4337No ratings yet
- Q2 EALS Week2 Unifying ThemesDocument20 pagesQ2 EALS Week2 Unifying ThemesjayemlorenzoNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Introduction To Biology AutosavedDocument19 pagesLab 1 Introduction To Biology Autosavedhazharomar958No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter NotesDocument716 pagesBiology Chapter NotesjyothibsNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Fundamentals of Biology ModuleDocument66 pagesBIO 101 Fundamentals of Biology ModuleCathleen AndalNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument15 pagesMidterm ReviewerlowdicakesNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument3 pagesBiology Noteselaykar141No ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Exploring LifeDocument10 pagesChapter 01 - Exploring LifeIndu MuruganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biology Exploring LifeDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Biology Exploring Lifemzunl25476No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Science of LIfeDocument33 pagesChapter 1 The Science of LIfeNur-aine HajijulNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologyLara Loraine Norbe VicenteNo ratings yet
- Enviscie 1 LectureDocument23 pagesEnviscie 1 LectureRikatokariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Exploring Life Overview: Biology's Most Exciting EraDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Exploring Life Overview: Biology's Most Exciting EraKrizziane Ivy CuajotorNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Scienceۦۦ ۦۦ ۦۦ ۦۦNo ratings yet
- General Biology IntroDocument45 pagesGeneral Biology IntroAnna kris DulfoNo ratings yet
- Define BiologyDocument11 pagesDefine BiologyPatricia PaezNo ratings yet
- Bot 101 Lecture 1Document4 pagesBot 101 Lecture 1tdirk342No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Biological ScienceDocument7 pagesLesson 2 Biological Sciencerainevincent08No ratings yet
- Module 2Document16 pagesModule 2Melorie MutiaNo ratings yet
- Overview: Biology's Most Exciting Era: Chapter 1 Exploring LifeDocument9 pagesOverview: Biology's Most Exciting Era: Chapter 1 Exploring LifeDhara PatelNo ratings yet
- Learning-Module-for-Modern-BiologyDocument76 pagesLearning-Module-for-Modern-Biologysofiyang2000No ratings yet
- Zoology NotesDocument42 pagesZoology NotesNolour de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BiologyPamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Lecture1Document107 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Lecture1Mary Jane M. MorenoNo ratings yet
- Local Media2210703659562817356Document41 pagesLocal Media2210703659562817356Regie MorialNo ratings yet
- Biology 111 Revised Notes 2021Document39 pagesBiology 111 Revised Notes 2021jeplee107No ratings yet
- LP Q1. Science11 w1Document6 pagesLP Q1. Science11 w1Christy BetitaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture Generan Biology PartDocument5 pages2nd Lecture Generan Biology Partyr44grf94kNo ratings yet
- Ken (Portfolio)Document18 pagesKen (Portfolio)CRING TVNo ratings yet
- 1001 Biol Part 1Document56 pages1001 Biol Part 1Hamdy AlyNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument98 pagesBotanyMikhail Landicho100% (1)
- Branches of BiologyDocument12 pagesBranches of BiologyAdriene Mikaela OrzalNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 Benefits of Genetically Modified OrganismsDocument3 pagesMODULE 5 Benefits of Genetically Modified OrganismsAngela NuquiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 GENETIC ENGINEERINGDocument2 pagesModule 4 GENETIC ENGINEERINGAngela NuquiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document4 pagesLecture 1Angela NuquiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document1 pageLesson 4Angela NuquiNo ratings yet
- 2Q Lecture1Document2 pages2Q Lecture1Angela NuquiNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: 2 Semester - Module 4Document20 pagesGeneral Biology 2: 2 Semester - Module 4Almira IbbaNo ratings yet
- 90 Days NEETDocument4 pages90 Days NEETvarunazimNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering GuideDocument71 pagesBiochemical Engineering GuideJeremiah AdeolaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY Module PDFDocument245 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY Module PDFKim Gyeoljong100% (1)
- Unit Plan 1 Earth ScienceDocument9 pagesUnit Plan 1 Earth SciencejessaNo ratings yet
- PCA 2EGB Science PhenomenalDocument9 pagesPCA 2EGB Science PhenomenalMARJORIE CONRADE CRESPONo ratings yet
- P2 2013-10-03 Why Extremophiles Bode Well For Life Beyond Earth - Louisa PrestonDocument1 pageP2 2013-10-03 Why Extremophiles Bode Well For Life Beyond Earth - Louisa PrestonliNo ratings yet
- 00 (Existence - 051608Document200 pages00 (Existence - 051608Aakash Chand100% (1)
- BSC (P) - 2022-II-IV-VI Sem (CBCS) 2019-2020-07-04-2022Document10 pagesBSC (P) - 2022-II-IV-VI Sem (CBCS) 2019-2020-07-04-2022Ruchi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Levashov, Nicolai - The Final Appeal To Mankind - 1Document127 pagesLevashov, Nicolai - The Final Appeal To Mankind - 1vidra1709100% (1)
- Earth Science Q1 Module 1Document18 pagesEarth Science Q1 Module 1JamRey VlogsNo ratings yet
- Q2 Earth and Life Module 10Document25 pagesQ2 Earth and Life Module 10Jomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Permaculture Design LecturesDocument63 pagesPermaculture Design LecturesMaria ZaharievaNo ratings yet
- SHS - HUMSS - Intro To Philo - Week16Day1-3Document3 pagesSHS - HUMSS - Intro To Philo - Week16Day1-3Jaime Curag Jr.No ratings yet
- Sample Science Lesson PlanDocument33 pagesSample Science Lesson Planapi-317770553No ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCES SAGs 2023 (Updated Oct 2022)Document66 pagesLIFE SCIENCES SAGs 2023 (Updated Oct 2022)ntwenhlet706No ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument32 pagesBiology NotesTaylor BonnetNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in FinlandDocument43 pagesTeaching Science in FinlandMinh NguyetNo ratings yet
- Teacher: GURO AKO Science Teaching Dates/Time: QuarterDocument15 pagesTeacher: GURO AKO Science Teaching Dates/Time: QuarterGEORGE ANN CARDINONo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 AnswersDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 AnswerskalebNo ratings yet
- Reviewer BiologyDocument25 pagesReviewer Biologyyumi timtimNo ratings yet
- Program of Inquiry: Term One Term Two Term Three Term FourDocument5 pagesProgram of Inquiry: Term One Term Two Term Three Term FourDipaliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.6 Biology Careers in The Twenty-First Century: Living and InteractingDocument2 pagesLesson 1.6 Biology Careers in The Twenty-First Century: Living and InteractingAlexa Mae TinongaNo ratings yet
- 1.3. E01 TSW 1.3.Document4 pages1.3. E01 TSW 1.3.CarmenNo ratings yet
- Imat Topic List by SectionDocument1 pageImat Topic List by Sectionlara germirNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Guro Ako Science Teaching Dates/Time: Quarter:: Value Integration: Caring For The EnvironmentDocument6 pagesTeacher: Guro Ako Science Teaching Dates/Time: Quarter:: Value Integration: Caring For The EnvironmentDiana Marie Vidallon Aman100% (1)
- Earthdayyear 1Document11 pagesEarthdayyear 1api-250695989No ratings yet