Cyber Security-Module2 Notes
Uploaded by
twitterkatoolkitCyber Security-Module2 Notes
Uploaded by
twitterkatoolkitCyber Security
Module-II: Cyber Crime and Cyber Law
Introduction to Cybercrime
Introduction
The crime that involves and uses computer devices and Internet, is known as
cybercrime.
Cybercrime can be committed against an individual or a group; it can also be committed
against government and private organizations. It may be intended to harm someone’s
reputation, physical harm, or even mental harm.
Cybercrime can cause direct harm or indirect harm to whoever the victim is.
However, the largest threat of cybercrime is on the financial security of an individual as
well as the government.
Cybercrime causes loss of billions of USD every year.
Definition
Cybercrime is any criminal activity that involves a computer, networked device or a
network.
Cybercrime is defined as a crime in which a computer is the object of the crime or is
used as a tool to commit an offense.
Origin of Cyber Crime
At the beginning of the 1970s, criminals regularly committed crimes via telephone lines.
The perpetrators were called Phreakers and discovered that the telephone system in
America functioned on the basis of certain tones. They were going to imitate these
tones to make free calls.
John Draper was a well-known Phreaker who worked on it daily; he toured America in
his van and made use of public telephone systems to make free calls. Steve Jobs and
Steve Wozniak were inspired by this man, and even joined him. Of course they all ended
up on the right path: Steve Jobs and Wozniak founded Apple, the well-known computer
company.
One person hacked another person’s computer to find, copy or manipulate personal
data and information. The first person to be found guilty of cybercrime was Ian Murphy,
also known as Captain Zap, and that happened in the year 1981. He had hacked the
American telephone company to manipulate its internal clock, so that users could still
make free calls at peak times.
The first recorded cybercrime took place in the year 1820.
The firm spam email took place in 1978 when it was sent out over the Arpanet.
The first virus was installed on an Apple computer in 1982.
Denial of Service (DoS) attacked by ‘Mafia Boy’ on eBay, Yahoo!, Amazon and other
popular sites in 2000.
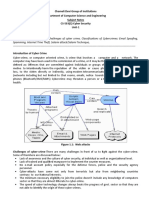
Classifications of Cybercrimes
Cybercrime against individuals
Electronic mail (E -Mail) Spoofing, Online frauds, Data hiding, Cyberstalking and
harassment, Password sniffing etc.,
Cybercrime against property
Intellectual property crimes, Credit card fraud, Internet time theft etc.,
Cybercrime against organization
Unauthorised accessing of computer, Virus attack, Industrial spying, Software
privacy etc.,
Cybercrime against society
Forgery, Cyber terrorism, Web jacking etc.,
Cybercrime against individuals
Electronic mail (E -Mail) Spoofing: It is one that appears to originate from one source but
actually has been sent from another source. For Example, Suresh send email in the
name of Ramesh to spoil the relationship with his friend. A hacker logs in to a computer
illegally, using a different identity than his own.
Online Fraud: Like lottery Frauds are letters or emails that inform the recipient that
he/she has won a prize in a lottery. To get the money the recipient has to reply with
bank details so that money can be directly transferred. They also ask for processing
/handling fee.
Data diddling: It is a attack involves altering raw data just before it is processed by a
computer and then changing it back after the processing is completed
Cyberstalking and harassment: It refer to the use of internet and / or other electronic
communication devices to stalk another person. It involves harassing an individual will
conduct repeatedly. For example, following a person, visiting his home or business
place, making phone calls, leaving written messages
Password sniffing: Password sniffers are the programs that monitor and record the
name and password of network users as they login.
Cybercrime against Property
Intellectual property crime: Intellectual property crime is committed when someone
manufactures, sells or distributes counterfeit or pirated goods, such as such as patents,
trademarks, industrial designs or literary and artistic works, for commercial gain.
Credit card Fraud: Credit card fraud increasing day by day. Millions of dollars may be
lost annually by consumers who have credit card, credit card number stolen from online
databases. Online services are frequent targets for hackers who want to access large
databases of credit card information.
Internet time theft: Such a theft occurs when an unauthorised person uses the Internet
hours paid for by another person. Basically, in Internet theft the person who get access
to someone else’s ISP user ID and password, either by hacking or by gaining access to it
by illegal means, uses it to access the Internet without the other person’s knowledge.
Cybercrime against organization
Virus attacks: A virus is a piece of code which is capable of copying itself and typically
has a detrimental effect, such as corrupting the system or destroying data. These viruses
can cause severe damage to organization data and important documents, also it can
cause companies to lose Client data, Customers, Money, Brand credibility.
Industrial Spying: Spies can get information about product finances, research and
development and marketing strategies, an activity known as industrial spying.
Software piracy: It is the theft of software through the illegally copying of genuine
programs or the copying and distribution of product intended to pass for original. Ex:
end use copying, duplication and distribution of illegally copied software, illegal
downloads from the internet etc.,
Cybercrime against society
Forgery: It means the action of forging a copy or imitation of a document, signature,
banknote, or work of art. Fake currency notes, postage and revenue stamps, marksheets
etc., can be forged using sophisticated computers, printers and scanners.
Cyberterrorism: It is terrorist activities intended to damage or disrupt vital computer
systems. It refers to unlawful attacks and threats of attacks against computers, networks
and the information stored therein.
Web Jacking: It occurs when someone forcefully takes control of a website by cracking
the password and later changing it. Thus first stage of this crime involves password
sniffing. The actual owner of the website does not have any more control over what
appears on that website.
Cybercriminals modus-operandi
Legal perspective of cyber crime
IT Act 2000 and its amendments
Organisations dealing with Cyber-crime and Cyber security in India
You might also like
- Gojek Take Home Test Assessment - Achmad RamlanNo ratings yetGojek Take Home Test Assessment - Achmad Ramlan10 pages
- Understanding Cybercrime: Phenomena, Challenges and Legal Response100% (1)Understanding Cybercrime: Phenomena, Challenges and Legal Response29 pages
- LAW-468.005 Ethics-Professionalism SalterNo ratings yetLAW-468.005 Ethics-Professionalism Salter5 pages
- Introduction to Cybercrime(Unit-1).pptx (1)No ratings yetIntroduction to Cybercrime(Unit-1).pptx (1)74 pages
- Cyber Security - CS-503 (C) - Class Notes - 1563265709No ratings yetCyber Security - CS-503 (C) - Class Notes - 156326570929 pages
- P7-Chapter 7 - Cyber Crime and Cyber SecurityNo ratings yetP7-Chapter 7 - Cyber Crime and Cyber Security112 pages
- R20-CSF-UNIT-1-INTRODUCTION TO CYBERCRIMENo ratings yetR20-CSF-UNIT-1-INTRODUCTION TO CYBERCRIME133 pages
- Cyber Crimes With Special Reference To Cyber MoneylaunderingNo ratings yetCyber Crimes With Special Reference To Cyber Moneylaundering36 pages
- Chap1 - Introduction To Cybercrime and CyberSecurityNo ratings yetChap1 - Introduction To Cybercrime and CyberSecurity44 pages
- Bca Second Semester: SUBJECT:-Cyber SecurityNo ratings yetBca Second Semester: SUBJECT:-Cyber Security51 pages
- A Guide to Cyber Safety, Internet Security and Protection for Kids, Teens, Parents and ProfessionalsFrom EverandA Guide to Cyber Safety, Internet Security and Protection for Kids, Teens, Parents and ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- 22 Point Code Review Checklist & Process GuidelinesNo ratings yet22 Point Code Review Checklist & Process Guidelines6 pages
- Steven Cooley, WCSO - Vol II - Minor RedactionNo ratings yetSteven Cooley, WCSO - Vol II - Minor Redaction25 pages
- Lecture 1 - Digital Forensics and ArtifactsNo ratings yetLecture 1 - Digital Forensics and Artifacts13 pages
- McAfee File and Removable Media Protection (FRP) 4.3.1 - Release Notes - enNo ratings yetMcAfee File and Removable Media Protection (FRP) 4.3.1 - Release Notes - en3 pages
- Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Microsoft Word: Exercise 1No ratings yetAbcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Microsoft Word: Exercise 112 pages
- Hacker Powered Security Report 2019 PDFNo ratings yetHacker Powered Security Report 2019 PDF66 pages
- The Importance of Electronics in Modern Life - Free Essay Example - EdubirdieNo ratings yetThe Importance of Electronics in Modern Life - Free Essay Example - Edubirdie3 pages
- State Bank of India: Application Form Atm Transaction DisputeNo ratings yetState Bank of India: Application Form Atm Transaction Dispute6 pages
- Brandon S. Sand Settlement Demand LetterNo ratings yetBrandon S. Sand Settlement Demand Letter5 pages
- Incident Handling During Attack On Critical Information Infrastructure Handbook PDFNo ratings yetIncident Handling During Attack On Critical Information Infrastructure Handbook PDF20 pages
- Problems: Managerial Statistics Problem Set Populations and Distributions Boston CollegeNo ratings yetProblems: Managerial Statistics Problem Set Populations and Distributions Boston College3 pages
- Understanding Cybercrime: Phenomena, Challenges and Legal ResponseUnderstanding Cybercrime: Phenomena, Challenges and Legal Response
- Cyber Security - CS-503 (C) - Class Notes - 1563265709Cyber Security - CS-503 (C) - Class Notes - 1563265709
- Cyber Crimes With Special Reference To Cyber MoneylaunderingCyber Crimes With Special Reference To Cyber Moneylaundering
- Chap1 - Introduction To Cybercrime and CyberSecurityChap1 - Introduction To Cybercrime and CyberSecurity
- A Guide to Cyber Safety, Internet Security and Protection for Kids, Teens, Parents and ProfessionalsFrom EverandA Guide to Cyber Safety, Internet Security and Protection for Kids, Teens, Parents and Professionals
- 22 Point Code Review Checklist & Process Guidelines22 Point Code Review Checklist & Process Guidelines
- McAfee File and Removable Media Protection (FRP) 4.3.1 - Release Notes - enMcAfee File and Removable Media Protection (FRP) 4.3.1 - Release Notes - en
- Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Microsoft Word: Exercise 1Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Microsoft Word: Exercise 1
- The Importance of Electronics in Modern Life - Free Essay Example - EdubirdieThe Importance of Electronics in Modern Life - Free Essay Example - Edubirdie
- State Bank of India: Application Form Atm Transaction DisputeState Bank of India: Application Form Atm Transaction Dispute
- Incident Handling During Attack On Critical Information Infrastructure Handbook PDFIncident Handling During Attack On Critical Information Infrastructure Handbook PDF
- Problems: Managerial Statistics Problem Set Populations and Distributions Boston CollegeProblems: Managerial Statistics Problem Set Populations and Distributions Boston College