Chapter 4 SB Answers
Chapter 4 SB Answers
Uploaded by
FaathimathCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4 SB Answers
Chapter 4 SB Answers
Uploaded by
FaathimathCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4 SB Answers
Chapter 4 SB Answers
Uploaded by
FaathimathCopyright:
Available Formats
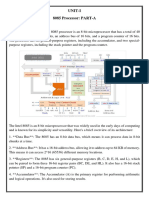
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science
Chapter 4 Student Book Answers
4.1 What you should already know
1 a) monitor, keyboard, mouse, hard disk drive or solid state drive, microprocessor
b) Tablet or phone
has a smaller screen
has a virtual or small keyboard
uses cellular network instead of WiFi connectivity
requires different type of operating system
uses instant messaging rather than emailing
is fully portable … usually have it with you.
2
processor speed
size of screen
screen resolution
ease of operation
is OS easy to use/interface easy to use
what Apps are available
type of I/O ports
battery life
3 USB, HDMI, VGA, lightning connector (mobile phones) are the most common
4
much faster performance (has increased by about 50% each year)
faster clock speeds
greater reliability
smaller components allowing more components on the motherboard (for example)
transistor dimensions have reduced by 30% every two years which results in doubling
transistor density; electric fields must also be kept constant therefore a reduction of supply
voltage from 12 V (in 1970) to 0.05 V (in 2018)
in reality, reduction has been nearer 10% than 30% which has contributed to a slowdown in
recent performance increases
(Refer to website https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.05215.pdf for further information if this is to form a
project)
Activity 4A
1 a) i) CIR – stores the current instructions being executed.
ii) MAR – stores the address of the memory location which is about to be accessed.
iii) PC – stores the address of the next instruction to be executed.
b) i) N = negative flag; set to 1 if result of calculation is negative
C = carry flag; set to 1 if there is a carry bit following a calculation
V = overflow flag; set to 1 if there is an overflow bit following a calculation
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 1
© Helen Williams and David Watson 2020
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
ii) two positive numbers added together give a negative result:
01110001
01011110 N 1
𝟏1001111
when two bytes are added together an arithmetic carry bit is generated from the most
significant bit position:
(Note: the carry bit is used for unsigned integers)
10000110
11001011 C 1
𝟏01010001
overflow occurs when 7 bits are used for the binary number and the 8th bit is a sign
bit; if +127 is the largest integer which can be stored then a sum > 127 will cause
overflow:
01110001
01011110 V 1
𝟏1001111
2 a) address bus, data bus, control bus
b)
Address bus
carries addresses to memory controller, thus identifying memory location which is to be
read or written to
bus is unidirectional between CPU and memory thus preventing an address being carried
back to the CPU.
Data bus
bidirectional bus which carries data (address, instruction or numerical value) throughout
the processor
data can be carried from CPU to memory (and vice versa) and to/from input/output
devices.
Control bus
bidirectional bus which transmits signals from the control unit to other components of the
computer
this includes clock signals used to synchronise all operations.
c)
In general, a higher clock speed increases the performance of a computer.
Using a wider address bus and data bus allows a larger range of memory locations to be
directly accessed or allows a larger word size to be handled by the computer.
Both of the above speed up computer operations.
However, it is not a simple matter of just increasing clock speed since …
… If the processor doesn’t use wider buses (etc.), increasing the clock speed alone could
lead to problems such as overheating and non-synchronisation of operations.
Risk of overclocking can occur.
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 2
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
4 a) Fetch-execute cycle
is the basic operational process of a computer system
is the process whereby computer fetches (retrieves) a program instruction from memory
and determines what the instruction ‘means’
once decoded, the instruction is executed
makes use of buses and addresses to carry out the various functions/operations.
b) MAR [PC] (contents of PC copied into MAR)
PC [PC] + 1 (PC is incremented by 1)
MDR [[MAR]] (data stored at address shown in MAR is copied into MDR)
CIR [MDR] (contents of MDR copied into CIR)
5 fetches, immediate access store (IAS), program counter (PC), MAR, address bus, MDR, decoded,
executed, control signals, control bus, ALU, accumulator
4.2 What you should already know
1 a) Assembly language and machine code
b) Machine code
c) Writing instructions in binary is time consuming and can be error prone as codes need to be
exact and binary numbers are not easy to remember. Testing can only be done by executing
the code.
2 Examples include, Intel Pentium and X86, AMD and X86, ARM and A32 or A64 or T32
3 Examples include, Intel i7 and X86, Qualcomm Octo (ARM) and A64
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 3
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
Activity 4B
1 a) i) 200
ii) 300
(iii) 50
b) i) CMP #5
ii) JPE 100
2 a)
Label Address
nomore 106
Number1 109
Number2 110
Number3 111
Number4 112
total 113
b)
CIR Opcode Operand ACC total 113
100 LDD number1 30 0
101 SUB number2 -10 0
102 ADD number3 10 0
103 CMP #10 10 0
104 JPE nomore 10 0
106 STO total 10 10
107 END 10 10
c) Subtracts number2 from number1, then add number3. Only add number4 if the result of
the first calculation is not equal to 10. Store the answer in total
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 4
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
3 a)
Label Opcode Operand Comment
LDM #0 Load 0 into ACC
STO counter Store 0 in counter
LDR #0 Set IX to 0
loop: LDX array Load the element of the array indexed by IX into ACC
OUT Output the ASCII character
INC IX Add 1 to the contents of IX
LDD counter Load counter into ACC
INC ACC Add 1 to ACC
STO counter Store result in counter
CMP #4 Compare with 4
JPN loop If ACC not equal to 4 then return to start of loop
END
array: #67 Array of 4 ASCII characters
#79
#68
#69
counter: counter for loop
b)
Label Address
loop 103
array 113
counter 117
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 5
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
c)
CIR Opcode Operand ACC IX counter Output
100 LDM #0 0
101 STO counter 0
102 LDR #0 0 0 0
103 LDX array 67 0 0
104 OUT 67 0 0 C
105 INC IX 67 1 0
106 LDD counter 0 1 0
107 INC ACC 1 1 0
108 STO counter 1 1 1
109 CMP #4 1 1 1
110 JPN loop 1 1 1
103 LDX array 79 1 1
104 OUT 79 1 1 O
105 INC IX 79 2 1
106 LDD counter 1 2 1
107 INC ACC 2 2 1
108 STO counter 2 2 2
109 CMP #4 2 2 2
110 JPN loop 2 2 2
103 LDX array 68 2 2
104 OUT 68 2 2 D
105 INC IX 68 3 2
106 LDD counter 2 3 2
107 INC ACC 3 3 2
108 STO counter 3 3 3
109 CMP #4 3 3 3
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 6
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
110 JPN loop 3 3 3
103 LDX array 69 3 3
104 OUT 69 3 3 E
105 INC IX 69 4 3
106 LDD counter 3 4 3
107 INC ACC 4 4 3
108 STO counter 4 4 4
109 CMP #4 4 4 4
110 JPN loop 4 4 4
111 END counter 2 2 2
Activity 4C
1 a) i) B10010000
ii) B00000000
b) i) OR #B1000
ii) XOR #B1
2 a) Arithmetic shifts preserve the sign bit of the number and logical shifts always fill with zeros.
b) No bits are lost during a shift, bits shifted out of one end of the register are introduced at the
other end of the register, for example an 8-bit register containing the binary value 10101111
shifted left cyclically 3 places would become 01111101.
c) Shift left logical 3.
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 7
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
End of chapter questions
1 a)
Stage Order
Instruction is copied from the MDR and is placed in the CIR 3
Instruction is executed 6
Instruction is decoded 5
Address contained in PC is copied to the MAR 1
Value in PC is incremented by 1 4
Instruction is copied from memory location in MAR and placed in MDR 2
b) i) Width of the data bus and address bus
determines number of bits that can be simultaneously transferred
hence wider bus improves processing speed as fewer transfers are needed
double bus width = 2 × data transferred per clock pulse.
ii) Clock speed
determines number of cycles computer can execute per second
increasing clock speed increases number of operations per unit time
limited by heat generated by higher clock speeds.
iii) Dual or quad core
each CPU contains 2 cores or 4 cores
CPU with 2 or 4 processors in the same integrated circuit; each processor has its own
cache and controller
single computing component with 2/4 independent processing units (cores) which can
read and execute program instructions
this gives processor double or four times the processing power of a single core
processor
however, this isn’t the case in reality since the CPU needs to communicate with each
core which reduces overall performance
software frequently can’t take advantage of 2 or 4 core processors again reducing
potential overall performance.
c) Dangers are overheating and risk of going out of synchronisation causing errors and potential
computer ‘crash’ due to instructions no longer correctly synchronized.
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 8
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
2 a HDMI
allows output (audio and visual) from a computer to be connected to HDMI-enabled
monitor/tv
supports high definition and enhanced signals
it is a digital system which can support high definition televisions which require more data
and at a faster data transfer rate
can also protect against piracy by using authentication protocols
supports a refresh rate of 120 Hz.
VGA
supports 640×480 resolution with refresh rate of 60 Hz
analogue system which makes it easier to split the signals between more than one device.
USB
allows computers to communicate with peripherals
uses 4-wire shielded cables
devices are automatically detected when plugged into computer USB port
serial data transmission
industry standard to connect devices to a computer.
b Interrupts
data sent to printer buffer from computer
contents of buffer sent to printer and document starts to be printed
processor carries on with other tasks while printing continues in background
if printer runs out of paper, runs out of ink, paper jam (etc.) then it sends out an interrupt
signal
if interrupt sent out, message is displayed on computer screen requesting user to resolve
issue
once all the data from the buffer is printed, printer sends an interrupt signal to the processor
requesting more data
depending on its priority, interrupt is serviced
once interrupt is serviced, more data is sent to the printer buffer and the above stages are
repeated until all 1000 pages are printed out.
3 a i) ii) PC – stores address of next instruction to be executed
MDR – stores data in transit between memory and other registers
CIR – stores current instruction being executed
MAR – stores address of memory location which is about to be accessed
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 9
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
4 Logical shift – bits shifted out of the register are replaced with zeros, for example an 8-bit
register containing the binary value 10101111 shifted left logically 3 places would become
01111000
Arithmetic shift – the sign of the number is preserved, for example an 8-bit register containing
the binary value 10101111 shifted right arithmetically 3 places would become 11110101.
Arithmetic shifts can be used for multiplication or division by powers of two.
Cyclic shift – no bits are lost during a shift, bits shifted out of one end of the register are
introduced at the other end of the register, for example an 8-bit register containing the binary
value 10101111 shifted left cyclically 3 places would become 01111101
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 10
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science Answers
5
a) i) monitoring system
ii) there is no ‘control’ taking place
b) Pressure …If intruder steps on sensor, Infra-red …If beam cut by intruder
c) i) SENSORS COUNT VALUE ACC
B00001010 0 1 B00001010
B00000000
1
2 2
B00001010
B00000010
0
1 1
2
4 4
B00001010
B00000000
4
8 8
B00001010
B00001000
1
2 2
8
c) ii) #1
c) iii) CMP #8 instruction
CMP #128
Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science 11
© Helen Williams and David Watson/Hodder & Stoughton Ltd
You might also like
- In New SampleDocument9 pagesIn New Samplearun neupaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SB AnswersDocument11 pagesChapter 4 SB Answers송준혁67% (3)
- Sample Final Exam EECS388 - Fall 2020Document19 pagesSample Final Exam EECS388 - Fall 2020Jeren ChenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 AnswersDocument10 pagesChapter 6 AnswersJohn HoltNo ratings yet
- Inf2c Cs 201112Document9 pagesInf2c Cs 201112davidcorreobasura1No ratings yet
- IICT - FinalPaper-Final VersionDocument14 pagesIICT - FinalPaper-Final VersionUsman Mohyud Din ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- MidTerm Exam Fall2013 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMidTerm Exam Fall2013 SolutionsA ANo ratings yet
- Computer Science MS2023 - 1-Edited - 101823Document18 pagesComputer Science MS2023 - 1-Edited - 101823Brightwell kasuNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Organization - I-Mid-Sem: Btech3 SemesterDocument3 pagesComputer Architecture and Organization - I-Mid-Sem: Btech3 SemesterDutta Computer AcademyNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers (Answers Are in Bold)Document11 pagesQuestions and Answers (Answers Are in Bold)Louie ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1Document10 pages1Siddhesh Pawar 1433No ratings yet
- CompNet Exam en WS2021Document10 pagesCompNet Exam en WS2021Herman Deulieu NoubissieNo ratings yet
- CS211 ExamDocument10 pagesCS211 ExamTetzNo ratings yet
- CSEC Info Tech 1993-2003 SolutionsDocument68 pagesCSEC Info Tech 1993-2003 SolutionsVernon WhiteNo ratings yet
- Networks Question PaperDocument3 pagesNetworks Question PaperragulNo ratings yet
- Axes - Placement Sample Question Papers: Micro ProcessorDocument7 pagesAxes - Placement Sample Question Papers: Micro ProcessorNagaValliNo ratings yet
- Inf2c Cs 201314Document10 pagesInf2c Cs 201314davidcorreobasura1No ratings yet
- Important ?Document16 pagesImportant ?ruhipravin352No ratings yet
- Semester Two Examinations - Summer 2007: Microprocessor Engineering 16-7210Document5 pagesSemester Two Examinations - Summer 2007: Microprocessor Engineering 16-7210amit panvekarNo ratings yet
- Coa Test 2Document6 pagesCoa Test 29111roshanNo ratings yet
- Department of Eee: Special Course Exam Iot Based AutomationDocument6 pagesDepartment of Eee: Special Course Exam Iot Based AutomationsathyatnNo ratings yet
- NPCIL Question PaperDocument2 pagesNPCIL Question Paperअभिषेक कुमार उपाध्यायNo ratings yet
- CS438 Midterm SolDocument6 pagesCS438 Midterm SolDavide SlanziNo ratings yet
- IT233 Final RevisionDocument22 pagesIT233 Final RevisionOmar EloueljiNo ratings yet
- CLAT3_Set D_answerkeyDocument5 pagesCLAT3_Set D_answerkeypw5908No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam1 - 2020-2021 - Model AnswerDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam1 - 2020-2021 - Model AnswerKhaled HeshamNo ratings yet
- F Computer Architecture and Organization CSE205 F1-2Document4 pagesF Computer Architecture and Organization CSE205 F1-2Akash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Past PapersDocument7 pagesPast Papersdavidcorreobasura1No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Information and Communication Technology Past Paper 2020 3rd Term Test Western ProvinceDocument25 pagesGrade 11 Information and Communication Technology Past Paper 2020 3rd Term Test Western ProvincemenulatworkNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument7 pagesMicroprocessorEjay BildanNo ratings yet
- The University of Auckland: Total 100Document17 pagesThe University of Auckland: Total 100orhanaliuNo ratings yet
- 1029uf CS ABC Com-OrgDocument8 pages1029uf CS ABC Com-OrgnimitrajanNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer ArchitectureDocument8 pagesWhat Is Computer Architectureamutha dNo ratings yet
- Practice Final SolnDocument17 pagesPractice Final SolnJimmie J MshumbusiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Homework - Chapter Review Multiple Choice Questions (Pgs. 78 - 81)Document3 pagesChapter 3 Homework - Chapter Review Multiple Choice Questions (Pgs. 78 - 81)JimmyNo ratings yet
- 2021 - CC - ASSIGN - 8weeks CourseDocument34 pages2021 - CC - ASSIGN - 8weeks CoursesaiNo ratings yet
- Coa - Sample Mcqs - 24-25Document19 pagesCoa - Sample Mcqs - 24-25jaiaakash205No ratings yet
- Cycle-I: Computer Communication Networks Lab Manual (18TE63), 2020-2021Document77 pagesCycle-I: Computer Communication Networks Lab Manual (18TE63), 2020-2021SHANTANU B SNo ratings yet
- Se, All Branches. C A - oDocument2 pagesSe, All Branches. C A - oanuragnair377No ratings yet
- MCS-012 J-16Document7 pagesMCS-012 J-16ps34778jNo ratings yet
- The University of Auckland: Second Semester, 2014 Campus: CityDocument22 pagesThe University of Auckland: Second Semester, 2014 Campus: CityorhanaliuNo ratings yet
- Assignments CSE211Document4 pagesAssignments CSE211Raghav JhanjeeNo ratings yet
- Final Sup ExamDocument10 pagesFinal Sup ExamtesfuNo ratings yet
- 2629acomputer ArchitectureDocument15 pages2629acomputer ArchitectureSiddhant Jain SethNo ratings yet
- Answer:A & EDocument13 pagesAnswer:A & EkingmibNo ratings yet
- Fabbc9: Convert Hexadecimal To BinaryDocument11 pagesFabbc9: Convert Hexadecimal To BinaryShan NavasNo ratings yet
- 2012S IP QuestionDocument57 pages2012S IP QuestionBenjie R. SAMONTENo ratings yet
- Grade 11 ICT 1st Term Test Paper 2020 English Medium - North Western ProvinceDocument15 pagesGrade 11 ICT 1st Term Test Paper 2020 English Medium - North Western Provincehenuue1No ratings yet
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument23 pagesComputer Organization and ArchitectureVinay DesaiNo ratings yet
- CLAT3_Set BDocument3 pagesCLAT3_Set Bpw5908No ratings yet
- CLAT3_Set B_answerkeyDocument7 pagesCLAT3_Set B_answerkeypw5908No ratings yet
- Answer Key - Set BDocument5 pagesAnswer Key - Set Bdu vigneshNo ratings yet
- 12 January 2011Document9 pages12 January 2011shaniahNo ratings yet
- MCS-012 J-20Document8 pagesMCS-012 J-20ps34778jNo ratings yet
- MCS 012june2020Document8 pagesMCS 012june2020kk2760057No ratings yet
- Test Paper Computer OrganizationDocument5 pagesTest Paper Computer Organizationsun00No ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur: Mid-Spring Semester 2021-22Document4 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur: Mid-Spring Semester 2021-22Utkarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science National Tsing Hua University CS4100 Computer ArchitectureDocument3 pagesDepartment of Computer Science National Tsing Hua University CS4100 Computer Architecture謝明浩No ratings yet
- Ec8691 MPMC MCQDocument50 pagesEc8691 MPMC MCQNithin JoelNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Notes PDFDocument101 pagesMicroprocessor Notes PDFSuyash Sanjay SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiments ManualDocument30 pagesLaboratory Experiments ManualEr Satpal Singh DhillonNo ratings yet
- DLCOunit 3Document49 pagesDLCOunit 3satyaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Computer Organization and BASIC Programming Subject Code: Comp-214Document14 pagesSubject: Computer Organization and BASIC Programming Subject Code: Comp-214Muhammad Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- FMM Unit-1Document28 pagesFMM Unit-1CS ENo ratings yet
- Running Machines: Arm Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesRunning Machines: Arm Multiple ChoicePoojaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMINGDocument122 pagesChapter 3 ASSEMBLY LANGUAGE PROGRAMMINGWann Fariera100% (1)
- EE-222 Microprocessor Systems: DE-41 (EE) Syn CDocument112 pagesEE-222 Microprocessor Systems: DE-41 (EE) Syn COsama IkramNo ratings yet
- Lab 521Document8 pagesLab 521Shashitharan PonnambalanNo ratings yet
- Machine Code For BeginnersDocument27 pagesMachine Code For BeginnerscooliowarNo ratings yet
- Memory: Computer OrganizationDocument28 pagesMemory: Computer OrganizationAteeqAftabNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of 32 Bit MicroprocessorsDocument13 pagesComparative Study of 32 Bit MicroprocessorsRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document44 pagesModule 2Anitha T G RajNo ratings yet
- Main ReportDocument46 pagesMain Reportkrish4allindians100% (3)
- I Am Intel 8086Document8 pagesI Am Intel 8086AB ESPORTSNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument212 pagesMicroprocessorraji30No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part 1Document31 pagesChapter 2 Part 1jeffNo ratings yet
- Cache SolutionsDocument6 pagesCache SolutionsKannan KaruppiahNo ratings yet
- Cse-Vii-Advanced Computer Architectures (10cs74) - SolutionDocument111 pagesCse-Vii-Advanced Computer Architectures (10cs74) - SolutionShinu100% (1)
- Prelim ExamDocument2 pagesPrelim ExamKaecee WongNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1vijaya saraswathi jayakumarNo ratings yet
- Log BookDocument8 pagesLog BookKISHAAN RAO A/L SUBRAMANIAM STUDENTNo ratings yet
- 8086 Assembly 1Document33 pages8086 Assembly 1mr.kamarNo ratings yet
- Starting MSX Assembly Part 1Document3 pagesStarting MSX Assembly Part 1OrlandoUtreraNo ratings yet
- Sex Book UrduDocument18 pagesSex Book Urdusaqib razaNo ratings yet
- 1000+ Microprocessor 8085,8086 MCQDocument164 pages1000+ Microprocessor 8085,8086 MCQSurajAnand48% (29)
- Microprocessor 8086Document14 pagesMicroprocessor 8086vshlvvkNo ratings yet
- Tcs Mpi Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesTcs Mpi Interview QuestionsChintha VenuNo ratings yet