Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes Mellitus
Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes Mellitus
Uploaded by
Pong's Teodoro SalvadorCopyright:
Available Formats
Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes Mellitus
Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes Mellitus
Uploaded by
Pong's Teodoro SalvadorCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes Mellitus
Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes Mellitus
Uploaded by
Pong's Teodoro SalvadorCopyright:
Available Formats
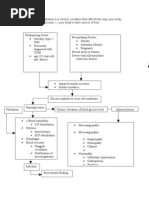
PREDISPOSING FACTOR AGE: 80 yrs.
Old Family History of DIABETES Hereditary
PRECIPITATING FACTORS DIET: eating foods rich in sugar, carbs, and fats LIFESTYLE: smoking, drinking alcohol Compliance: no maintenance of meds. for DM
Exhaustion of beta cells occurs
Altered pancreatic insulin production Decreased insulin production Decreased absorption of glucose by the cells Glucose is unable to enter the cells Glucose remains in the blood stream Increased serum glucose level
HYPERGLYCEMIA (304 mg/dl, 13.2 mg/dl)
Sluggish flow of blood Impaired delivery of blood components Inadequate inflammatory response Microorganism would enter the body at any route
Serum osmolarity
Blood viscosity
Tissue perfusion of kidney
Impaired removal of waste Failure to initiate erythropoietin
Osmotic pressure in blood H20 from cell towards the blood
Glucose concentration in urine Reabsorption of glucose in renal tubule
Glucose intake of cells ATP production Energy for normal cells functions Cells starvation occurs Stimulation of the hunger mechanism Hunger occurs
POLYPHAGIA
Blood flow to the organs and extremities Tissue perfusion in nerves Nerve hypoxia Segmental demyelization Nerve damaged Excessive glucose is converted into SORBITOL w/c accumulate in nerves Sorbitol impairs motor nerve conduction
Impaired removal of waste from blood Glucose level exceeds renal threshold Impaired renal Fnx Permeability of the renal cell wall Filtration of macro cells & particles
Stimulation of the bone marrow fails RBC production decreased
Dehydration Stimulation of osmoreceptors thirst
Osmotic pressure H20 reabsorption Urine output
Infection occurs
WBC (14.4), eusinophils (7%)
POLYDIPSIA RBC (4.5) POLYURIA
Fatigue
Inadequate nutritional support
Poor wound healing
Paresthesia, numbness
Decreased PR (60 bpm)
Sugar+2, protein+2, blood+5, RBC >100/hpf
DIABETES MELLITUS
Pathophysiology of BPH
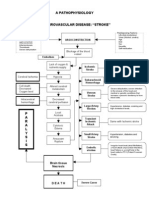
Thickening of the cardiac blood vessels wall Plaque formation begins
Occlusion of the blood vessels occurs
Blockage of blood flow
Myocardial ischemia occurs Decreased myocardial O2 supply
+ TROPONIN T ST-T abnormality
Half of the bundle of his loss its function Left fascicular block occurs
Increased cellular hypoxia
Mild left axis deviation
Increased lactic acid production release of metabolites Altered cell membrane functions
CHEST PAIN
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (ACS)
Ineffective right ventricular contractility
Reduced right ventricular pumping ability
Decreased cardiac output
Backflow of blood into the right atrium and peripheral circulation
Shifting of fluids into interstitial spaces
Grade 2 edema @ lower extremities
SINUS BRADYCARDIA
DOB, fatigue, with rales upon auscultation
Ineffective left ventricular contractility
Reduced left ventricular pumping ability
Decreased cardiac output
Backflow of blood into the left atrium and lungs
Pulmonary congestion
Pulmonary edema
HEART FAILURE
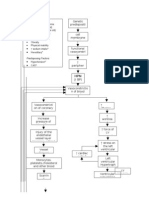
PREDISPOSING FACTORS AGE: 80 yrs. Old FAMILY HISTORY OF BPH NORMAL BODY CHANGES
PRECIPITATING FACTORS SMOKING WITH DM, HF, AND MI
As mans age increased prostate gland increased Androgen Testosterone Dihydrosterone Binds to nuclear androgen receptors
Deterioration of the blood vessel in the prostate Blood flow becomes abnormal and 02 supply impaired
Signals growth factors
Stimulation of cell growth
HYPERPLASIA
Encroaches upon the bladder neck occurs
Increased size of prostate
Reduced ability to funnel in response to micturition
Overwhelms the detrusor muscles ability to ensure effective bladder evacuation by micturition
UTI (1-2 PUS CELLS), HEMATURIA
Obstruction occurs
Increase urethral resistance
LUTS
Dribbling of urine
Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
Increased daytime voiding frequency
POLYURIA
URGENCY
NOCTURIA
BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA
You might also like
- Concept Map Worksheet Mary Richards Heart Failure Jasgou1752Document3 pagesConcept Map Worksheet Mary Richards Heart Failure Jasgou1752Jasmyn Rose100% (1)
- Nephrotic Syndrome PathophysiologyDocument1 pageNephrotic Syndrome PathophysiologyKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ap Psychology Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesAp Psychology Multiple Choice Questionsapi-319829528No ratings yet
- Aphasia Treatment Goals and Targets-1Document16 pagesAphasia Treatment Goals and Targets-1Emily UlaNo ratings yet
- Pahtophysiology of EsrdDocument5 pagesPahtophysiology of EsrdCarl JardelezaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Aan 202 CourseworkDocument17 pagesAan 202 CourseworkCris GalendezNo ratings yet
- Metabolic EncephalopathyDocument26 pagesMetabolic Encephalopathywirdahaja100% (3)
- SY 2020-2021 Learning Area Week Grade Date Section Quarter Class Adviser Subject TeacherDocument4 pagesSY 2020-2021 Learning Area Week Grade Date Section Quarter Class Adviser Subject TeacherJanel Flores0% (1)
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument11 pagesPa Tho PhysiologyJonathan CuaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyDocument16 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyDale LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Micro and Macrovascular Complications of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathogenesis of Micro and Macrovascular Complications of DiabetesFrancesca LiNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument69 pagesLiver CirrhosisAhmed Alboun75% (4)
- Renal Case Study Final1Document41 pagesRenal Case Study Final1api-202881815100% (1)
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- DM Case StudyDocument21 pagesDM Case StudyBern TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus - Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument21 pagesDiabetes Mellitus - Diabetic KetoacidosisJamil Lorca100% (5)
- Liver Cirrhosis LectureDocument83 pagesLiver Cirrhosis LectureSheila Regina Tiza100% (1)
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PathoDocument2 pagesDiabetes Pathodrewcel100% (1)
- HCVDDocument5 pagesHCVDkhrizaleehNo ratings yet
- DkaDocument29 pagesDkaShadowSpectre0No ratings yet
- Liver Case StudyDocument6 pagesLiver Case StudyGhulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AnginaDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of AnginaPhilip SimanganNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection FractionDocument19 pagesHeart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fractioncosmin balanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewDocument5 pagesChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewAnonymous uziTjed5j100% (1)
- Chronic Heart FailureDocument222 pagesChronic Heart FailureGustavo Meneo100% (1)
- Presentation Liver CirrhosisDocument26 pagesPresentation Liver CirrhosisFaye Dominique Roxas PalmaresNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease Secondary To Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument84 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Secondary To Type 2 Diabetes Mellituswar5No ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument37 pagesChronic Renal Failuredorkiebaby100% (10)
- Stroke and Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument14 pagesStroke and Cerebrovascular DiseaseMarwan M.No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument10 pagesAnemiaBia Payawal100% (2)
- Cerebral HemorrhageDocument10 pagesCerebral HemorrhageJayd Lorenz Vicente ChuanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument52 pagesPredisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSaad MotawéaNo ratings yet
- A Review: Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease PatientsDocument13 pagesA Review: Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease Patientsscience worldNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocument3 pagesSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument79 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentKathy B. AbuanNo ratings yet
- Case Study PPT Patho NLNGDocument36 pagesCase Study PPT Patho NLNGKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyAileen Grace RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology HPN CvaDocument1 pagePathophysiology HPN Cvatresdos09No ratings yet
- CAD PathoDocument3 pagesCAD PathoMark Anthony YabresNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument16 pagesHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseTintin Ponciano100% (1)
- MNT For Liver DiseaseDocument44 pagesMNT For Liver Diseasemedikasudirman118100% (4)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument33 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasesexiiimammaNo ratings yet
- Acute Liver Failure in Adults: Etiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument14 pagesAcute Liver Failure in Adults: Etiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnosis - UpToDateIatros GarciniNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultDocument11 pagesSepsis Is The Consequence of A Dysregulated Inflammatory Response To An Infectious InsultShrests SinhaNo ratings yet
- Case Study NSTEMIDocument35 pagesCase Study NSTEMInikaaraaaNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Hepatitis: Ekaterine Labadze MDDocument18 pagesAlcoholic Hepatitis: Ekaterine Labadze MDsushant jainNo ratings yet
- 25 Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument35 pages25 Cardiovascular DiseaseBramantyo NugrosNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology ErDocument3 pagesPathophysiology ErAlexa A. AldayNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument12 pagesCellulitisAlma Bertos-Agub100% (1)
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument28 pagesCongestive Heart Failuresarguss1480% (5)
- Case Presentation On Chronic Kidney Disease1Document18 pagesCase Presentation On Chronic Kidney Disease1d100% (1)
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypocalcemia, (Low Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDiabetic Ketoacidosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pancytopenia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPancytopenia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Congenital Heart Disease: Eisenmenger’s Syndrome - A Global PerspectiveFrom EverandPulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Congenital Heart Disease: Eisenmenger’s Syndrome - A Global PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVasculitis Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Data/Cues Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Implementation RationaleDocument6 pagesData/Cues Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Implementation RationalePong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Primary ComplexDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Primary ComplexPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Primary ComplexDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Primary ComplexPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- STI College of Nursing Sta. Cruz, Laguna College of Nursing: Submitted To: Mrs. Aurea Celino, RN Clinical InstructorDocument41 pagesSTI College of Nursing Sta. Cruz, Laguna College of Nursing: Submitted To: Mrs. Aurea Celino, RN Clinical InstructorPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Preterm PathoDocument1 pagePreterm PathoPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure - PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCongestive Heart Failure - PathophysiologyPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Primary ComplexDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Primary ComplexPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Broncho PneumoniaDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Broncho PneumoniaPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Basic Occupational Safety and Health: Prepared By: Engr. Orik Niko SantosDocument79 pagesBasic Occupational Safety and Health: Prepared By: Engr. Orik Niko SantosNICE ONE100% (1)
- Abnormal Psychology Mock Boards - WIth AnswersDocument47 pagesAbnormal Psychology Mock Boards - WIth AnswersEunicaSelrabNo ratings yet
- Role PlayDocument8 pagesRole Playmjtan730No ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in - Lesson Plan Avaids Nursing EducationDocument9 pagesFdocuments - in - Lesson Plan Avaids Nursing Educationjuliya ShNo ratings yet
- ComEngpdf MergedDocument29 pagesComEngpdf MergedSujan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Market Access For Pharmaceuticals 1st Edition Mondher Toumi (Editor) Download PDFDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Market Access For Pharmaceuticals 1st Edition Mondher Toumi (Editor) Download PDFchayladanchi100% (3)
- Program of The: Online Conference &Document39 pagesProgram of The: Online Conference &Iulian ApostuNo ratings yet
- Modul.eng.Practice.new Sts'.Sep.2024Document31 pagesModul.eng.Practice.new Sts'.Sep.2024KiplyNo ratings yet
- Unit-2: Rural Development Programmes: Prepared By: Ankur Sachdeva Assistant Professor, MEDocument36 pagesUnit-2: Rural Development Programmes: Prepared By: Ankur Sachdeva Assistant Professor, MEAnupriyaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and The Entrepreneurial Mind-Set: Hisrich Peters ShepherdDocument19 pagesEntrepreneurship and The Entrepreneurial Mind-Set: Hisrich Peters ShepherdAwab HamidNo ratings yet
- ASD in PregnancyDocument15 pagesASD in PregnancyAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- FDA-3537 Stat Sec Ext 01-04-23Document10 pagesFDA-3537 Stat Sec Ext 01-04-23Erick BellidoNo ratings yet
- La Grange Issues With 30 S. La Grange RoadDocument61 pagesLa Grange Issues With 30 S. La Grange RoadDavid GiulianiNo ratings yet
- Research Presentation BasherDanielaDocument13 pagesResearch Presentation BasherDanielaJerome PomentoNo ratings yet
- Infinite Jest in BriefDocument49 pagesInfinite Jest in Briefwilliamsmith1404No ratings yet
- Stasha Andrews-Teacher-Pdp-2019-End of YearDocument5 pagesStasha Andrews-Teacher-Pdp-2019-End of Yearapi-424238197No ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Inflammation and Distension of The Colon.Document2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Inflammation and Distension of The Colon.JULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- NMT 04209 - Basic Pharmacology-1Document126 pagesNMT 04209 - Basic Pharmacology-1Rubeni VENANSI chisiNo ratings yet
- CHN 2Document14 pagesCHN 2Aira PayadNo ratings yet
- Sample Protest Art WriteupDocument2 pagesSample Protest Art Writeupapi-266674779No ratings yet
- CV Buti Azfiani AzhaliDocument3 pagesCV Buti Azfiani AzhaliRANO KURNIADINo ratings yet
- En Stomach Cancer Guide For PatientsDocument51 pagesEn Stomach Cancer Guide For Patientsmanuaf2000No ratings yet
- UG LR-09 Critical ReasoningDocument25 pagesUG LR-09 Critical ReasoningdextuNo ratings yet
- Chuck Sipes Super SeminarDocument47 pagesChuck Sipes Super SeminarWarhammer13100% (9)
- Thesis On Veterinary HospitalDocument8 pagesThesis On Veterinary Hospitalbk156rhq100% (2)
- Full Option Yoga Free eBookDocument35 pagesFull Option Yoga Free eBooklauraparejaextremeraNo ratings yet
- Body Image BrochureDocument2 pagesBody Image Brochureden_a100% (1)