Subject Matter Content Is An Integration of Cognitive, Skill and Affective Elements
Subject Matter Content Is An Integration of Cognitive, Skill and Affective Elements
Uploaded by
Selenai SelenaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Subject Matter Content Is An Integration of Cognitive, Skill and Affective Elements
Subject Matter Content Is An Integration of Cognitive, Skill and Affective Elements
Uploaded by
Selenai SelenaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Subject Matter Content Is An Integration of Cognitive, Skill and Affective Elements
Subject Matter Content Is An Integration of Cognitive, Skill and Affective Elements
Uploaded by
Selenai SelenaiCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
Subject matter
content is an
integration of
cognitive, skill
and affective
elements.
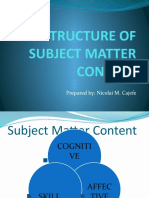
Must contain the three domains:
Cognitive
Affective
Skills
INTEGRATED
Structure
of the
Subject
Matter
Content
COGNITIVE
Fact- an idea that can be verified.
Concept- a categorization of events, places, people, ideas.
Principle- relationship between and among facts and concepts.
Hypotheses- educated guesses about relationship(principles).
Theories- set of facts, concepts, and principles that describe the possible
underlying unobservable mechanisms that regulate human learning,
development, and behavior. They explain why these principles are true.
Personal Theories- acquiring general beliefs about how the world operates
Laws- firmly established, thoroughly tested principle or theory.
Thinking skills are the skills that are beyond recall as well as
comprehension. These skills are concerned with the application of what
was being learned such like having a problem solving in real life situation.
It also includes synthesis, evaluation as well as critical and creative
thinking.
The Manipulative Skills are those skills that are dominantly skill-oriented
such like computer manipulation, physical education and many else. A
gross motor skill involving the use of the hands to control the movement
of other objects.
In Physical Education, these are the skills developed while using an implement.
These may include: receiving; e.g., catching, collecting: retaining; e.g., dribbling,
carrying, bouncing, trapping: sending; e.g., throwing, kicking, striking.
Thinking Skills
There were two different
forms of thinking or ability in
play here:
Divergent
Convergent
Convergent vs. Divergent
Divergent thinking
Divergent thinking is the type of thinking we do when
solving an abstract or new problem that has many
possible answers, solutions, or outcomes. It is a process
of creating many unique solutions in order to solve a
problem. It is spontaneous and free-flowing.
Here the student's skill is in broadly creative
elaboration of ideas prompted by a stimulus, and is
more suited to artistic pursuits and study in the
humanities.
Divergent thinking is generally associated with the humanities
and fine arts
EXAMPLE:
When you write a poem or story you have an endless supply of possible
characters, words to use, and themes or events that might happen, so this
creative process requires divergent thinking.
Convergent thinking
Convergent thinking is the type of thinking we do
when solving a well-defined, straightforward, correct
answer to a problem. Convergent thinking is used
when there is a simple, correct answer to a question
Many tests that are used in schools, such as multiple choice
tests, spelling tests, math quizzes, and standardized tests, are
measures of convergent thinking.
Applying logical steps in order to determine what is the
single best solution.
Convergent thinking is generally associated with math and
science
For example, what's the capital of England? The answer is London.
If you knew the answer, you used convergent thinking. Creativity is
not relevant to convergent thinking because you don't have to be
creative to know the answer to this problem; all you have to do is
come up with the stated, factual answer.
You might also like
- Structure of Subject Matter Content Principles of TeachingDocument34 pagesStructure of Subject Matter Content Principles of TeachinganalizaNo ratings yet
- Subject MatterDocument26 pagesSubject MatterShauneNo ratings yet
- Habits of Mind Sem 2Document27 pagesHabits of Mind Sem 2Nakanjala PetrusNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Cognition (Thinking and Intelligence) : - Thought and The BrainDocument61 pagesUnit 5: Cognition (Thinking and Intelligence) : - Thought and The BrainPuna Ram GhimireNo ratings yet
- BSU 343 Module 1Document25 pagesBSU 343 Module 1Rituparna DasNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Subject Matter ContentDocument30 pagesThe Structure of Subject Matter ContentBC Eimor100% (1)
- Understanding The Process of Learning M.Ed.Document40 pagesUnderstanding The Process of Learning M.Ed.arunNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Thinking and Problem SolvingDocument75 pagesUnit 6 - Thinking and Problem SolvingSujan BistaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Problem Solving in The Information Age: Lesson 1 - New Learning Skills 2Document8 pagesIntroduction To Problem Solving in The Information Age: Lesson 1 - New Learning Skills 2hayleykhoNo ratings yet
- Chp7 Notes ThinkingDocument15 pagesChp7 Notes Thinkingdasmanami09100% (1)
- Selection and Organization of Content DalimbangDocument18 pagesSelection and Organization of Content DalimbangLag Lag Alberca100% (1)
- Cagu I Sem Unit 3 FinalDocument37 pagesCagu I Sem Unit 3 FinalAravindNo ratings yet
- 3learning Mt-Kog-Konstruct-1Document24 pages3learning Mt-Kog-Konstruct-1Ma RiaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Subject Matter ContentDocument49 pagesThe Structure of Subject Matter ContentNicolai M. Cajefe100% (6)
- EDU 302 Quiz 4Document17 pagesEDU 302 Quiz 4Irfan KashmiriNo ratings yet
- Module 4 & 5Document23 pagesModule 4 & 5shravan AbrahamNo ratings yet
- BA Sem II Cognitive Psychology SLM-Module 3Document15 pagesBA Sem II Cognitive Psychology SLM-Module 3GPRNo ratings yet
- Concept and Inquiry-Based TeachingDocument34 pagesConcept and Inquiry-Based TeachingHibajene MweembaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching - Part 2Document25 pagesPrinciples of Teaching - Part 2Jomar M. TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Principle of TeachingDocument19 pagesPrinciple of TeachingRicca Piadozo VelasquezNo ratings yet
- notesDocument13 pagesnotesl233045No ratings yet
- (Finals) Educ-Psych ReviewerDocument11 pages(Finals) Educ-Psych ReviewerTrisha Lavainne SuatNo ratings yet
- Applying Learning Theories To Healthcare PracticeDocument47 pagesApplying Learning Theories To Healthcare PracticeDylan VallartaNo ratings yet
- Teaching StrategiesDocument12 pagesTeaching Strategieszandra capioNo ratings yet
- Thinking and ReasoningDocument6 pagesThinking and ReasoningAreeba asgharNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document25 pagesUnit 7Noshaba SharifNo ratings yet
- Mundeshwari College For Teacher EducationDocument18 pagesMundeshwari College For Teacher EducationCvam RebornNo ratings yet
- Reflection MetacognitionDocument4 pagesReflection Metacognitionapi-188661956100% (1)
- LEARNING THEORIESDocument14 pagesLEARNING THEORIESeswariNo ratings yet
- Selection and Organization of Content: "There Are Dull Teachers, Dull Textbooks, Dull Films, But No Dull Subjects."Document10 pagesSelection and Organization of Content: "There Are Dull Teachers, Dull Textbooks, Dull Films, But No Dull Subjects."FallenPrince HoumanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Reflective Writing and Critical Thinking, Educational PlatformDocument44 pagesUnit 1 Reflective Writing and Critical Thinking, Educational PlatformUmarNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving and CreativityDocument22 pagesProblem Solving and CreativityMuhammad NadimNo ratings yet
- 6 Thinking (Compatibility Mode)Document21 pages6 Thinking (Compatibility Mode)BhargavNo ratings yet
- Make Notes of Special and Important Points Regarding Definition of Critical Thinking As A Subject of Study and An Action To Learn in The Skills.Document11 pagesMake Notes of Special and Important Points Regarding Definition of Critical Thinking As A Subject of Study and An Action To Learn in The Skills.chanchal shahiNo ratings yet
- Intelligence: Citation: Huitt, W. (2002) - Intelligence. Educational University. Retrieved (Date), FromDocument35 pagesIntelligence: Citation: Huitt, W. (2002) - Intelligence. Educational University. Retrieved (Date), FromMuhammad PulunganNo ratings yet
- Learning To Think by Atxu Amann (Formated by JArgota)Document9 pagesLearning To Think by Atxu Amann (Formated by JArgota)jargotaNo ratings yet
- Higher Order ThinkingDocument15 pagesHigher Order ThinkingDelikanliXNo ratings yet
- Thinking chap 8Document23 pagesThinking chap 8Angelika ManchandaNo ratings yet
- 1.intelligence SfsDocument162 pages1.intelligence Sfspcmwalebhaiya592No ratings yet
- Psychology IntelligenceDocument14 pagesPsychology Intelligenceadilakm2000No ratings yet
- Complex Cognitive Process PDFDocument33 pagesComplex Cognitive Process PDFfatin marliaNo ratings yet
- Psychology From Science To Practice: Cognition and IntelligenceDocument19 pagesPsychology From Science To Practice: Cognition and IntelligenceThalia SandersNo ratings yet
- 16 Habits of MindDocument51 pages16 Habits of Mind26csvishuNo ratings yet
- ThinkingDocument32 pagesThinkingMalaika Noor 1277-FSS/BSPSY/F19No ratings yet
- NOTES CHAP 8Document7 pagesNOTES CHAP 8Angelika ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Teaching 2Document38 pagesPrinciple of Teaching 2Ronelio Marabante80% (5)
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4Blessie Kaye AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Reasoning and Problem SolvingDocument77 pagesUnit 5 - Reasoning and Problem SolvingAnanta ChaliseNo ratings yet
- Selection and Organization of ContentDocument65 pagesSelection and Organization of ContentRuss TyNo ratings yet
- UNIT III - Lesson 2 Selection and Organization of ContentDocument5 pagesUNIT III - Lesson 2 Selection and Organization of Contentextra accountNo ratings yet
- Thinking Like A ResearcherDocument43 pagesThinking Like A Researcherdavid juddNo ratings yet
- Chp7 Notes ThinkingDocument14 pagesChp7 Notes Thinkingdasmanami09No ratings yet
- CH 8 Thinking - PDF NotesDocument10 pagesCH 8 Thinking - PDF Notesmahima.thakkarNo ratings yet
- Developing HIgher Order Thinking SkillsDocument27 pagesDeveloping HIgher Order Thinking SkillsMichael E. EcobenNo ratings yet
- Content and Pedagogy in Teaching Mathematics and Current Issues and Trends in Teaching MathematicsDocument91 pagesContent and Pedagogy in Teaching Mathematics and Current Issues and Trends in Teaching MathematicsErma OradaNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Cognitive Processes (Constructivism, Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument9 pagesLesson: Cognitive Processes (Constructivism, Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational ObjectiveslisaNo ratings yet
- Complex Cognitive ProcessesDocument5 pagesComplex Cognitive ProcessesVarian M.No ratings yet
- Cognitive PsyhchologyDocument51 pagesCognitive Psyhchologylew zhee piangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 33 Age of ExplorationDocument13 pagesChapter 33 Age of ExplorationSelenai Selenai100% (2)
- Teaching ProfessionDocument19 pagesTeaching ProfessionSelenai SelenaiNo ratings yet
- Constitution of The Republic of The PhilippinesDocument16 pagesConstitution of The Republic of The PhilippinesSelenai SelenaiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Validity For Teachers Activity: What Is Content-Related Validity?Document6 pagesUnderstanding Validity For Teachers Activity: What Is Content-Related Validity?Selenai SelenaiNo ratings yet
- Criterion-Related Validity: Prepared By: Group 3Document8 pagesCriterion-Related Validity: Prepared By: Group 3Selenai SelenaiNo ratings yet
- Ped 121Document171 pagesPed 121Selenai SelenaiNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Thesis On DamDocument36 pagesPresentation - Thesis On DamRavi Sharma BhandariNo ratings yet
- Influence of Karl Marx On Modern LiteratureDocument4 pagesInfluence of Karl Marx On Modern LiteratureSumaira Malik100% (1)
- 2021 054LTc IQ V1.0 2021.11.19Document53 pages2021 054LTc IQ V1.0 2021.11.19amr ADELNo ratings yet
- UPPCL Technician Grade 2 Trainee Electrical Syllabus PDFDocument24 pagesUPPCL Technician Grade 2 Trainee Electrical Syllabus PDFAnonymous RhWeE3NNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Breach and The CISG - A Unique Treatment or Failed Experiment? Bruno ZellerDocument12 pagesFundamental Breach and The CISG - A Unique Treatment or Failed Experiment? Bruno ZellerGuillermo C. DurelliNo ratings yet
- Time (T) Sales (In PHP) Forecast Time (T) Sales (In PHP) ForecastDocument10 pagesTime (T) Sales (In PHP) Forecast Time (T) Sales (In PHP) ForecastPrecy CaseroNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 4th Quarter 7-9th WeekDocument9 pagesGrade 7 4th Quarter 7-9th WeekCipriano BayotlangNo ratings yet
- Guesstimate Techniques - HCGDocument58 pagesGuesstimate Techniques - HCGR JNo ratings yet
- Common Rhetorical Strategies & Frameworks Used in Visual ArgumentsDocument1 pageCommon Rhetorical Strategies & Frameworks Used in Visual ArgumentsChilekasi AdeleNo ratings yet
- Ip Project File-12th ClassDocument59 pagesIp Project File-12th ClassSaurabh Sharma40% (5)
- G8 Graphing and Solving Linear Inequality in Two VariablesDocument18 pagesG8 Graphing and Solving Linear Inequality in Two VariablesMontealto Loren MaeNo ratings yet
- Christopher Et Al. 2018Document10 pagesChristopher Et Al. 2018Chaturyya 028No ratings yet
- Kirim-1-Getaran KristalDocument20 pagesKirim-1-Getaran Kristalanton febriyantoNo ratings yet
- Ebook Dashboards PDFDocument30 pagesEbook Dashboards PDFRonNo ratings yet
- MSH COP MineSurveyDocument28 pagesMSH COP MineSurveyPrince KumarNo ratings yet
- VIM Quick Reference CardDocument2 pagesVIM Quick Reference CardJames MillerNo ratings yet
- Mtle ScoresDocument3 pagesMtle Scoresapi-296788592No ratings yet
- Creativity For StudentDocument3 pagesCreativity For StudentElianna MelnikNo ratings yet
- Ib History Thesis StatementsDocument5 pagesIb History Thesis Statementsafbtmznam100% (2)
- Structural Design Criteria-March 2008Document14 pagesStructural Design Criteria-March 2008mtaha82No ratings yet
- Cronbach's AlphaDocument4 pagesCronbach's AlphaRobert RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 117BH - Ceramic Science and Technology PDFDocument8 pages117BH - Ceramic Science and Technology PDFvenkiscribd444No ratings yet
- Conversion Tables: 12.1 Metric To English Conductor SizeDocument16 pagesConversion Tables: 12.1 Metric To English Conductor SizeGerardo Muñoz UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Compass - 2014 - Smuts - Normative Reasons For Love Part IDocument11 pagesPhilosophy Compass - 2014 - Smuts - Normative Reasons For Love Part IyoungNo ratings yet
- Review Test - English - Grade X - Chapter 2Document4 pagesReview Test - English - Grade X - Chapter 2Harini PahlawatiningsihNo ratings yet
- Ringi System of Japanese Management Paper Published IJMH G0055041715Document2 pagesRingi System of Japanese Management Paper Published IJMH G0055041715lalsagiNo ratings yet
- The Slow Frog An Intraday Trading Strategy: A Rules Based Intra-Day Trading Strategy (Ver 1.0)Document17 pagesThe Slow Frog An Intraday Trading Strategy: A Rules Based Intra-Day Trading Strategy (Ver 1.0)ticman123100% (1)
- ErdasDocument770 pagesErdascikdlaNo ratings yet
- Sap MagDocument6 pagesSap MagakunooNo ratings yet
- 1.3 of Strategies, Deliberate and EmergentDocument16 pages1.3 of Strategies, Deliberate and Emergentsuhasinidx2024No ratings yet