0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 viewsOxy Cad
Oxy Cad
Uploaded by
rlinaoThis document discusses coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. Coronary artery disease occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked, limiting blood flow to the heart and potentially causing chest pain or a heart attack. Risk factors include family history, age, gender, hypertension, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and physical inactivity. A heart attack occurs when an area of the heart muscle dies due to lack of oxygen from a blockage of blood flow. Symptoms include chest pain and potential complications are addressed through medications, surgery, monitoring, and lifestyle changes to manage risk factors and prevent future events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Oxy Cad
Oxy Cad
Uploaded by
rlinao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views21 pagesThis document discusses coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. Coronary artery disease occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked, limiting blood flow to the heart and potentially causing chest pain or a heart attack. Risk factors include family history, age, gender, hypertension, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and physical inactivity. A heart attack occurs when an area of the heart muscle dies due to lack of oxygen from a blockage of blood flow. Symptoms include chest pain and potential complications are addressed through medications, surgery, monitoring, and lifestyle changes to manage risk factors and prevent future events.
Original Description:
Oxygenation
Original Title
oxy-cad
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document discusses coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. Coronary artery disease occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked, limiting blood flow to the heart and potentially causing chest pain or a heart attack. Risk factors include family history, age, gender, hypertension, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and physical inactivity. A heart attack occurs when an area of the heart muscle dies due to lack of oxygen from a blockage of blood flow. Symptoms include chest pain and potential complications are addressed through medications, surgery, monitoring, and lifestyle changes to manage risk factors and prevent future events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views21 pagesOxy Cad
Oxy Cad
Uploaded by
rlinaoThis document discusses coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. Coronary artery disease occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked, limiting blood flow to the heart and potentially causing chest pain or a heart attack. Risk factors include family history, age, gender, hypertension, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and physical inactivity. A heart attack occurs when an area of the heart muscle dies due to lack of oxygen from a blockage of blood flow. Symptoms include chest pain and potential complications are addressed through medications, surgery, monitoring, and lifestyle changes to manage risk factors and prevent future events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
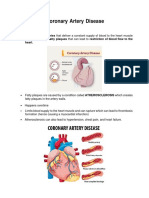
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
The disorder of the coronary arteries that
disrupts bld supply to the myocardium.
Permanent disruption of bld flow causes
myocardial dysfxn, including sudden death.
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTOR PROFILE
family hx of heart dse
sex Males: 35-55yrs
- Females: > 50 yrs or p menopause
hpn
smoking
overwt or obesity
elevated serum level of lipids & fats
DM
physical inactivity; sedentary lifestyle
stress
for women < 50 yrs: use of estrogen & smoking
ATHEROSCLEROSIS the basic underlying dse
affecting coronary lumen size, is marked by
changes in the intimal lining of the arteries.
- obstructions of more than 75% of the
lumen of one or more of the three coronary
arteries inc. the risk of death.
ANGINA PECTORIS chest pain
- used to describe pain as a symptom of
myocardial ischemia w/c is the result of an
imbalance bet myocardial O2 supply & demand.
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION development of
ischemia & necrosis of myocardial tissue. It results
from the sudden decrease in coronary perfusion
or an increase in myocardial O2 demand w/o
adequate coronary perfusion
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Waxy cholesterol plaque
- Pearly grey mounds of tissue
Deposit in the inner lining of the arteries
Rough surface
Attract platelet & fibrin
Narrowing & less vessel wall surface
Prevent absorption of
nutrients by vessel wall
Vessel wall weakens
Distension of the vessel
wall
aneurysm
Depress
adjacent
tissues
rupture
hemorrhage
Blocking of vessel
amt of bld the different
parts of the heart
Myocardial ischemia
Angina
pectoris
Sudden
cardiac death
Myocardial
infarction
Area of
concern
Stable angina
pectoris
Variant
(Prinzmetals)
angina
Unstable angina
pectoris
Myocardial
infarction
Chest
Pain
quality
Aching, sharp,
tingling or
burning
Similar to
stable angina
Similar to
stable angina
Crushing,
squeezing,sta
bbing,
oppressive or
as if a heavy
obj sitting on
the chest
location
&
radiation
Substernal w/
radiation to L
shoulder, down
the inner
aspect of L or
both arms;
neck, jaw, &
scapula
Similar to
stable angina
Similar to
stable angina
Retrosternal
& L precordial
radiating
down L arm &
to the neck,
jaws, teeth,
epigastric
area, & back
Area of
concern
Stable angina
pectoris
Variant
(Prinzmetals)
angina
Unstable
angina
pectoris
Myocardial
infarction
Precipitating
factors
Exercise or
activity that
myocardial
O2 demand
Onset at rest;
pain is cyclic,
often occuring
during sleep
Pain may be
brought on w/
less than
usual
exertion; may
occur at rest
May occur at
reat or during
exercise
Duration &
alleviating
factors
3-15 mins;
relieved by
rest, stopping
pain-inducing
activies,
nitroglycerine
SL
Pain
intensifies
quickly, tends
to last longer
than angina &
subsides w/
exercise
Prolonged &
not ususally
as quickly
relieved by
rest or taking
nitroglycerine
Continuous,
lasting more
than 30 mins,
unrelieved by
rest, position
change or
taking
nitroglycerine
Diagnosis
ECG
Cardiac enzymes
CBC, ESR
lipid levels
Exercise Stress Test
Cardiac catherterization & angiography
Cardiac profile
Cardiac
enzyme
Normal value with Acute Myocardial Infarction
onset peak Duration
Troponin I 0 ng/ml
(> 1.5 ng/ml is dx
for MI)
3.5 7 hrs 4 6 days
CPK 96 140 IU/L (F)
38 174 IU/L (M)
4 6 hrs 12 - 24 hrs 3 -4 days
CPK MB 0 24 48 hrs 12 24 hrs 2 3 days
SGOT 6 18 IU/L (F)
7 21 IU/L (M)
12 18 hrs 24 48 hrs 3 -4 days
LDH 70 180 mg/dl 24 48 hrs 3 6 days 7 10
days
Other associated manifestations
anxiety
dyspnea
nausea & vomiting
cold clammy skin
epifastric pain
low grade fever
leucocytosis
ECG changes
- injury: elevated ST
- ischemia: inverted T wave
- infarction: significant or
deep Q wave
Management
medications
- vasodilators
- antihyperlipidemic agents
- streptokinase
- antiplatelet agent (aspirin)
- diperidamole
surgery
- CABG (Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting)
- PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal
Coronary Angioplasty)
general mgt
- CV monitoring: arrhythmias, heart failure, extension of
MI, cardiogenic shock, ventricular muscle rupture
- ECG
- IABP (Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump)
- admission to CCU
- Diet: Acute phase NPO or clear liquids progressing
to 1500 cal, soft, low salt; no caffeine; small
frequent feedings
Discharge diet reduced saturated fats, cholesterol,
Na restriction, limit total caloric consumption to
maintain IBW
- oxygenation
Angina Pectoris
1. Stop activity. Rest
2. Nitroglycerine SL
3. Pearls of Amyl nitrate
4. Whiskey or brandy
5. Beta-blockers
6. Ca channel blockers
Myocardial infarction
1. Reduce pain & promote
comfort Morphine SO4; O2;
semifowlers
2. Maintain adequate bld
circulation
3. CBR
4. Diet
5. Facilitate fecal elimination
6. Promote adequate sexual
expression
7. Encourage gradual return to
usual activities
NSG MGT
You might also like
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Document55 pagesIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)rameshbmc100% (8)
- Cardiac Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesCardiac Lecture NotesKateNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndromes-PresentationDocument86 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromes-Presentationpatange jayaprakash rahul100% (4)
- HypertensionDocument34 pagesHypertensionmalikman83% (6)
- Partograph ExercisesDocument2 pagesPartograph Exercisesrlinao100% (1)
- Yearbook 2021Document123 pagesYearbook 2021rlinaoNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Renal CancerDocument5 pagesA Case Study On Renal CancerrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Partograph ExercisesDocument2 pagesPartograph Exercisesrlinao50% (2)
- Pdhpe Sports Medicine HSC NotesDocument18 pagesPdhpe Sports Medicine HSC Notesamacqueen12325% (4)
- C9 BookletDocument28 pagesC9 BookletAmol DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Super Size Me Film ReportDocument7 pagesSuper Size Me Film ReportKatharine NervaNo ratings yet
- Ncmb+312+Lec Coronary+Artery+Diseases+Document46 pagesNcmb+312+Lec Coronary+Artery+Diseases+esbercinio8528valNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart Disease (Ihd)Document29 pagesIschaemic Heart Disease (Ihd)Brian MulengaNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart Disease: DR Haider Baqai Assistant Professor of Medicine Rawalpindi Medical CollegeDocument104 pagesIschaemic Heart Disease: DR Haider Baqai Assistant Professor of Medicine Rawalpindi Medical CollegeputriluftiNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart Disorders-2Document111 pagesCoronary Heart Disorders-2shiklemeNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris 2Document47 pagesAngina Pectoris 2inyanji.barasaNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument34 pagesCardiovascularRianna LarezaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesMyocardial InfarctionLetecia MooreNo ratings yet
- MF3 - Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument28 pagesMF3 - Ischemic Heart DiseaseAnnbe BarteNo ratings yet
- ANOM Lapsus PresentationDocument36 pagesANOM Lapsus PresentationPetrus TjiangNo ratings yet
- Huson CadDocument52 pagesHuson CadHusson GhalyaNo ratings yet
- Osce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesOsce Notes - Myocardial InfarctionmmmalcampoNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Care of Client With IMA: Alfrina HanyDocument42 pagesThe Nursing Care of Client With IMA: Alfrina HanyVio Alveolita PrimayaniNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: - Mercy Grace DucusinDocument17 pagesMyocardial Infarction: - Mercy Grace DucusinMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Assessment & Cardiac DisordersDocument57 pagesCardiovascular Assessment & Cardiac DisordersgtsantosNo ratings yet
- MIT Lecture CardioDocument161 pagesMIT Lecture Cardioramish.riazNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (Acs)Document48 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome (Acs)LJie ChanNo ratings yet
- Stemi Extensive Anterior LBH 24 Hour Onset Killip IDocument35 pagesStemi Extensive Anterior LBH 24 Hour Onset Killip IIta MaghfirahNo ratings yet
- 2013 103 Notes 7Document18 pages2013 103 Notes 7clarheenaNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document105 pagesCase 2Ritz CelsoNo ratings yet
- Cad, MiDocument23 pagesCad, MiSandeep ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Presentor: John Hommer E. Dy M.D. Moderator: Joy Marchadesch M.DDocument57 pagesPresentor: John Hommer E. Dy M.D. Moderator: Joy Marchadesch M.DJohn Hommer DyNo ratings yet
- Acute Chest PainDocument45 pagesAcute Chest PainJonathan DavidNo ratings yet
- Masalah PD Sist KardiovaskulerDocument78 pagesMasalah PD Sist KardiovaskulergunawanNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument16 pagesAngina Pectorisashutoshtiwari6172No ratings yet
- Lapkas PP (STEMI)Document68 pagesLapkas PP (STEMI)KurbulNo ratings yet
- Ischaemic Heart Disease (DR Asfaw T)Document44 pagesIschaemic Heart Disease (DR Asfaw T)Rebira WorkinehNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Lec DisordersDocument5 pagesCardiovascular Lec DisordersmagnacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- MedHOCC 13.5.2023 CardioDocument111 pagesMedHOCC 13.5.2023 Cardiofarith nasirNo ratings yet
- Acute Biologic CrisisDocument142 pagesAcute Biologic CrisisAngel VallejoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Heart DiseasesDocument54 pagesChronic Heart DiseasesHazel Roda EstorqueNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction. BPTDocument62 pagesMyocardial Infarction. BPTAanchal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3 Ischemic Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)Document24 pages3 Ischemic Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)Loai Mohammed IssaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4e Internal MedicineDocument19 pagesChapter 4e Internal MedicinepodmmgfNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseEms MagneticoNo ratings yet
- Stemi Extensive Anterior Onset 12 Hours Killip 2Document30 pagesStemi Extensive Anterior Onset 12 Hours Killip 2Nurul Rezki Fitriani AzisNo ratings yet
- Stemi Extensive Anterior Onset 12 Hours Killip 2Document30 pagesStemi Extensive Anterior Onset 12 Hours Killip 2dhinialfiandariNo ratings yet
- Cardiology NotesDocument72 pagesCardiology Notesnu.bombinaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 pagesMyocardial InfarctionAly PinpinNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris / Myocardial IschemiaDocument33 pagesAngina Pectoris / Myocardial IschemiaChrissia Laine MiloNo ratings yet
- 2 - Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument42 pages2 - Ischemic Heart Diseasesamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Emergency PDFDocument62 pagesCardiac Emergency PDFJose Paul RaderNo ratings yet
- 14. CADDocument32 pages14. CADMj MontalbanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disorders HandoutDocument14 pagesCardiac Disorders HandoutRizielle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Care and Management of The Client With Cardiac Alterations: Presented By: Jessaly Joyce SiosonDocument38 pagesCare and Management of The Client With Cardiac Alterations: Presented By: Jessaly Joyce SiosonJoyce SiosonNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument63 pagesIschemic Heart DiseasesagdaabdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart Disease 3Document47 pagesCoronary Heart Disease 3Silvia RNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Review II: Ana H. Corona, MSN, FNP-C Nursing Instructor October 2007Document79 pagesCardiovascular Review II: Ana H. Corona, MSN, FNP-C Nursing Instructor October 2007leesteph78No ratings yet
- Cardio PPT Module 5Document45 pagesCardio PPT Module 5ʕ•ᴥ•ʔNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus Kardio CHF Ec CADDocument35 pagesLaporan Kasus Kardio CHF Ec CADpun212No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disorders LectureDocument18 pagesCardiovascular Disorders LectureCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- Manajement Acut Coronary Syndroma (Acs) : Lalu Aries FahroziDocument77 pagesManajement Acut Coronary Syndroma (Acs) : Lalu Aries FahroziJanuar MardaniNo ratings yet
- Unstable Angina PectorisDocument24 pagesUnstable Angina PectorisAkbar IskandarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument27 pagesCardiovascular DiseaseKyrajane EsguerraNo ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesNo ratings yet
- Mitral Valve Regurgitation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMitral Valve Regurgitation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- CHN NCP Format, by Araceli Maglaya (4 Edition Vs 5 Edition)Document1 pageCHN NCP Format, by Araceli Maglaya (4 Edition Vs 5 Edition)rlinaoNo ratings yet
- Gawang Pilipino: Ang JeepneyDocument1 pageGawang Pilipino: Ang JeepneyrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Barthel IndexDocument4 pagesBarthel IndexrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Effects of Labor and Delivery ProcessDocument3 pagesAcute Pain Related To Effects of Labor and Delivery ProcessrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment - Rle (Simulation)Document10 pagesHealth Assessment - Rle (Simulation)rlinaoNo ratings yet
- Case ScenariosDocument1 pageCase ScenariosrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument12 pagesTherapeutic CommunicationrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Roy Cresencio R. Linao JR., RN, MNDocument4 pagesRoy Cresencio R. Linao JR., RN, MNrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Day - 2 - Date - Se P T e Mber 2 6, 2 0 2 0 Area - Shift - 7 A M - 3 P M Clinical Instructor: S I R Roy L I N AoDocument4 pagesDay - 2 - Date - Se P T e Mber 2 6, 2 0 2 0 Area - Shift - 7 A M - 3 P M Clinical Instructor: S I R Roy L I N AorlinaoNo ratings yet
- WIPO CoursesDocument2 pagesWIPO CoursesrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Sample Evaluative ToolDocument5 pagesSample Evaluative ToolrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Digital FundraisingDocument9 pagesDigital FundraisingrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Spinal Traction QuizDocument3 pagesSpinal Traction QuizrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentation Rubrik 2015Document10 pagesOral Presentation Rubrik 2015rlinaoNo ratings yet
- Nurse'S Prayer: Florence Nightingale'S PledgeDocument1 pageNurse'S Prayer: Florence Nightingale'S Pledgerlinao100% (1)
- Barthels and KatzDocument13 pagesBarthels and KatzrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Geria Test Questions For MoodleDocument15 pagesGeria Test Questions For MoodlerlinaoNo ratings yet
- "Interpersonal Relations Theory" "Interpersonal Relations Theory"Document3 pages"Interpersonal Relations Theory" "Interpersonal Relations Theory"rlinaoNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundations in NursingDocument13 pagesTheoretical Foundations in NursingrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument36 pagesAnatomical PositionsrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Eu StressDocument1 pageEu StressrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Authority To Sell - Real EstateDocument1 pageAuthority To Sell - Real EstaterlinaoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Body CompositionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Body CompositionPasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)Document2 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility (CSR)Giu AragãoNo ratings yet
- How To Live ForeverDocument12 pagesHow To Live ForeverPham ThinhNo ratings yet
- Abdominal CavityDocument21 pagesAbdominal Cavitymoneth gerarmanNo ratings yet
- Home Slim Thick Fitmas Week 6 PDFDocument84 pagesHome Slim Thick Fitmas Week 6 PDFjennaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Question BankDocument17 pagesNutrition Question BankSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Expert Paper Final DraftDocument5 pagesExpert Paper Final Draftapi-540442849No ratings yet
- 12 Health Benefits of CoffeeDocument2 pages12 Health Benefits of CoffeeJamey SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Metabolic FinishersDocument30 pagesMetabolic FinisherselsozoNo ratings yet
- Keto After 50 Book CDocument94 pagesKeto After 50 Book Ckinyua benjaminNo ratings yet
- Components of Physical FitnessDocument29 pagesComponents of Physical FitnessEdrian EspedillonNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Case Study 1Document5 pagesGroup 6 Case Study 1api-380169571No ratings yet
- Review of LiteratureDocument54 pagesReview of LiteratureShweta YaragattiNo ratings yet
- Stronglifts 5x5 Spreadsheet TrackerDocument10 pagesStronglifts 5x5 Spreadsheet Trackercanjaysfan89No ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For The Critically IllDocument11 pagesMedical Nutrition Therapy For The Critically IllPutri DeskantariNo ratings yet
- Fuel For PerformanceDocument8 pagesFuel For PerformanceRasell de LunaNo ratings yet
- First Summative Test in Mapeh 6 Q1Document3 pagesFirst Summative Test in Mapeh 6 Q1Sharmaine RamirezNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document4 pagesTest 1smiedt ancuta0% (1)
- Ingredients: o o o o o o o oDocument11 pagesIngredients: o o o o o o o osupergirl131No ratings yet
- Fat-Shaming Criticism EssayDocument7 pagesFat-Shaming Criticism Essayapi-272186926No ratings yet
- BULIMIADocument15 pagesBULIMIAMohamedYosefNo ratings yet
- Sopanam E Magazine Issue 12Document30 pagesSopanam E Magazine Issue 12vbkuwaitNo ratings yet
- Matveyev About The Consrtuction of Training PDFDocument6 pagesMatveyev About The Consrtuction of Training PDFZachary LeeNo ratings yet
- Dapnia TestDocument16 pagesDapnia TestleshakaloshaNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument8 pagesPractical ResearchRomar CambaNo ratings yet
- Unseen Passage ReadingDocument3 pagesUnseen Passage ReadingAdeebunissa BegumNo ratings yet
- Mini AbdominoplastyDocument4 pagesMini AbdominoplastyAhmad Arbi Anindito100% (1)