100%(4)100% found this document useful (4 votes)
Immunity
Immunity
Uploaded by
leena abbasThere are two main types of white blood cells - phagocytes and lymphocytes. Phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils ingest and destroy foreign pathogens. Lymphocytes include B cells and T cells which help activate immune responses. Memory B cells allow for a faster secondary immune response against previously encountered pathogens. Vaccinations work by artificially stimulating active immunity through exposure to antigens without causing disease.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
Immunity
Immunity
Uploaded by
leena abbas100%(4)100% found this document useful (4 votes)
There are two main types of white blood cells - phagocytes and lymphocytes. Phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils ingest and destroy foreign pathogens. Lymphocytes include B cells and T cells which help activate immune responses. Memory B cells allow for a faster secondary immune response against previously encountered pathogens. Vaccinations work by artificially stimulating active immunity through exposure to antigens without causing disease.
Original Description:
Immunity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
There are two main types of white blood cells - phagocytes and lymphocytes. Phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils ingest and destroy foreign pathogens. Lymphocytes include B cells and T cells which help activate immune responses. Memory B cells allow for a faster secondary immune response against previously encountered pathogens. Vaccinations work by artificially stimulating active immunity through exposure to antigens without causing disease.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
100%(4)100% found this document useful (4 votes)
Immunity
Immunity
Uploaded by
leena abbasThere are two main types of white blood cells - phagocytes and lymphocytes. Phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils ingest and destroy foreign pathogens. Lymphocytes include B cells and T cells which help activate immune responses. Memory B cells allow for a faster secondary immune response against previously encountered pathogens. Vaccinations work by artificially stimulating active immunity through exposure to antigens without causing disease.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1/ 14
Immunity
Cells of the immune system
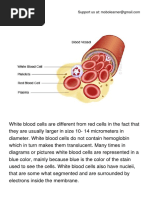
Phagocytes are originated from the bone marrow.
There are two types: Macrophages and Neutrophils.
Macrophages: Travel in the blood as monocytes,
then leave the blood to settle in body organs as
macrophages to remove any foreign.
Neutrophils: travel in the blood and leave the blood
through the walls of the capillaries. They destroy
pathogens by phagocytosis. The neutrophil engulfs
the pathogen and traps it within the phagocytic
vacuole by endocytosis. Digestive enzymes secreted
by lysosomes into the phagocytic vacuole to destroy
the pathogen.
Lymphocytes
There are two types of lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes and T-
lymphocytes.
T-lymphocytes: origin is the bone marrow where they leave
and mature in the thymus producing T cell receptors in cell
surface membrane. They leave the thymus and circulate in
the blood. T cells are activated when they encounter an
antigen. There are two types of T-lymphocytes:
Helper t cells. release hormone cytokines that: stimulate b
cells to divide into plasma cells and memory cells or
stimulate macrophages to carry out phagocytosis vigorously
or stimulate killer t cells to divide and differentiate.
Killer t cells. Recognize the antigens and attach themselves
to surfaces of infected cells, secreting toxic substances and
destroying the infected cell.
B-lymphocytes: origin is the bone
marrow, and remain there till they mature
and produce antibody receptors. B cells
divides into Plasma cells and memory
cells.
Plasma cells produce antibodies that are
secreted into the blood that combine to
antigens.
Memory cells divide rapidly into plasma
cells if the same antigen is introduced
into the body in secondary response.
Immune response
It is the complex series of responses
of the body to the entry of a foreign
antigen, it involves the activity of
lymphocytes and phagocytes. An
immune response is stimulated if a
non-self substance is recognized as
foreign. It is not stimulated in the
case of self substance because it is
not recognized as foreign as the body
has already produced it.
The significance of white blood cell count in humans with infectious diseases
and leukemia
The number of neutrophils in the blood increases
during bacterial infections and whenever tissues
become inflamed and die.
The number of lymphocytes in the blood
increases in viral infections and in TB.
Leukemia is the cancer of the stem cells that
divide to form differentiated white blood cells.
The cancer results in uncontrolled cell division of
these stem cells which fill up the bone marrow
and flow into the blood and into the lymphatic
system.
There are two types of leukemia: Myeloid
leukemia and Lymphoblastic leukemia.
The role of memory cells in long term
immunity
During primary response, the concentration on
antibodies are low because there are very few B cells
that are specific to the antigen.
The secondary response is faster because there is
many memory cells which divide and differentiate
into plasma cells, more antibodies are produced.
Question: Why if someone catches measles once he
is unlikely to catch it twice but the common cold can
be catched many times in a lifetime?
Answer: Measles has only on strain of virus and each
time it infects the body there is a fast secondary
response. While in the case of common cold there are
many different strains of the viruses each having
different antigen.
Autoimmune disease
The immune system sometimes fails to distinguish between self and
non-self.
The immune system attacks one or more self antigens usually
proteins.
The t cells have t cell receptors that are complementary to self
antigens.
This starts an attack between antibodies and killer t cells against parts
of the body.
An example is Myasthenia gravis, is an autoimmune disease between
nerve cells and skeletal muscle cells. Basically what happens is that
helper t cells in muscle tissue stimulate production of b cells that
divide into plasma cells that secrete antibodies, these antibodies bind
to the receptor proteins on cell surface membrane of muscle cell.
Which in normal case a cell signaling molecule binds to the protein
allowing sodium ions to move through the membranes, this results in
muscle contraction. Since in MG this does not take place, the muscle
tissue starts to break and one of the symptoms is muscle weakness.
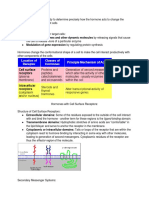
Antibodies
Variable region: Antigen binding site, to
bind to antigen.
Hinge region: gives flexibility in binding
to antigen.
Heavy polypeptide chain: binds to
phagocytes.
Disulphide bonds: to link chains
together
Light and heavy chains: form variable
region
Monoclonal Antibodies
Problem: B cells that divide by mitosis do not
produce antibodies. Plasma Cells that secrete
antibodies do not divide.
Solution:
Plasma cells producing a particular antibody fuse
with cancer cells(divide uncontrollably by
mitosis).
The resulting cell made by this fusion is known
as a hybridoma cell.
The hybridoma cells divide by mitosis and
secrete mitosis.
Use of monoclonal antibodies in diagnosis
of diseases and treatment of diseases
In diagnosis: locate the position of blood
clots in person having deep vein
thrombosis.
Locate cancer cells
Used to identify the exact strain of a virus
or bacterium that is causing an infection
Blood typing and Tissue typing
In treatment: modifying immune
responses. The monoclonal antibodies
have to humanized after taken from a
Explain how vaccination can control
disease
A vaccination is a preparation containing
antigens which is used to stimulate an
immune response artificially. Effective
vaccines are the ones that contain live
microorganisms, because they can
replicate inside the body while the less
effective ones are the ones that contain
dead viruses or bacteria.
Active and passive
immunity
Active: immunity developed after
contacting pathogens in the body.
Passive: immunity provided by
antibodies provided from outside the
body.
Natural: immunity gained by being
infected or receiving antibodies from
the mother.
Artificial: immunity gained by
vaccination or injecting antibodies.
Why vaccination programmes only
eradicated small pox?
The variola virus was stable.
Made from a live vaccine. Very
effective
The vaccine could be kept at high
temperatures for long.
Infected people were easy to identify
The virus did not infect animals
You might also like
- Presentation ON Fibrous Dysplasia: Made by Dr. Waqas Iqbal MDS in Oral PathologyNo ratings yetPresentation ON Fibrous Dysplasia: Made by Dr. Waqas Iqbal MDS in Oral Pathology47 pages
- MHC & Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Presented byNo ratings yetMHC & Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Presented by25 pages
- Primary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi SinghNo ratings yetPrimary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi Singh50 pages
- Specific Host Defenses: The Immune ResponseNo ratings yetSpecific Host Defenses: The Immune Response54 pages
- (6P) Basic Concepts in Immunity and Inflammation100% (1)(6P) Basic Concepts in Immunity and Inflammation6 pages
- Cell Cycle: SPEAKER-Dr - Ayesha.Juhi Coordinator-Dr - Ravindra.P.NNo ratings yetCell Cycle: SPEAKER-Dr - Ayesha.Juhi Coordinator-Dr - Ravindra.P.N38 pages
- Cells: USC Messed Up The Following QuestionsNo ratings yetCells: USC Messed Up The Following Questions119 pages
- Transplantation Immunology: MEDT 21 - Immunology and SerologyNo ratings yetTransplantation Immunology: MEDT 21 - Immunology and Serology47 pages
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFNo ratings yetSummary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDF8 pages
- Immunity To Microbe: Sakinah Nur Fadillah Coneta WulandariNo ratings yetImmunity To Microbe: Sakinah Nur Fadillah Coneta Wulandari34 pages
- Pathology of Bone and Soft Tissue-LectureNo ratings yetPathology of Bone and Soft Tissue-Lecture52 pages
- The Sickle Cell Allele and Malaria IgcseNo ratings yetThe Sickle Cell Allele and Malaria Igcse11 pages
- Chromosomes: Magdalena F. Natividad, PHD Dean, School of Medical Lab Science Feu-Nrmf100% (1)Chromosomes: Magdalena F. Natividad, PHD Dean, School of Medical Lab Science Feu-Nrmf24 pages
- Monoclonal Antibody Therapy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNo ratings yetMonoclonal Antibody Therapy - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia9 pages
- Submitted by Aiswarya V 1St MSC Zoology Roll Number 3301No ratings yetSubmitted by Aiswarya V 1St MSC Zoology Roll Number 330132 pages
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 04/15/2022 Haweni A. 1No ratings yetSexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 04/15/2022 Haweni A. 157 pages
- Pathophysiology of Typhoid Fever and Acute Gastroenteritis100% (5)Pathophysiology of Typhoid Fever and Acute Gastroenteritis3 pages
- PHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 05No ratings yetPHE Complete Immunisation Schedule Jun2020 052 pages
- Chronic Hepatitis B: Advances in Treatment: Department ofNo ratings yetChronic Hepatitis B: Advances in Treatment: Department of10 pages
- Package Insert - Varivax (Refrigerator)No ratings yetPackage Insert - Varivax (Refrigerator)14 pages
- Senthil Vaccination Certificate - R1740702No ratings yetSenthil Vaccination Certificate - R17407021 page
- Technical Specification - Dengue Test KitsNo ratings yetTechnical Specification - Dengue Test Kits2 pages
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic InfectionsNo ratings yetLaboratory Diagnosis of Parasitic Infections23 pages
- Oppenheim J.J., Feldmann M. - Introduction To The Role of Cytokines in Innate Host Defense and Adaptive Immunity (2000) PDFNo ratings yetOppenheim J.J., Feldmann M. - Introduction To The Role of Cytokines in Innate Host Defense and Adaptive Immunity (2000) PDF18 pages
- Presentation ON Fibrous Dysplasia: Made by Dr. Waqas Iqbal MDS in Oral PathologyPresentation ON Fibrous Dysplasia: Made by Dr. Waqas Iqbal MDS in Oral Pathology
- Primary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi SinghPrimary and Secondary Lymphoid Organs - Aditi Singh
- Cell Cycle: SPEAKER-Dr - Ayesha.Juhi Coordinator-Dr - Ravindra.P.NCell Cycle: SPEAKER-Dr - Ayesha.Juhi Coordinator-Dr - Ravindra.P.N
- Transplantation Immunology: MEDT 21 - Immunology and SerologyTransplantation Immunology: MEDT 21 - Immunology and Serology
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFSummary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDF
- Immunity To Microbe: Sakinah Nur Fadillah Coneta WulandariImmunity To Microbe: Sakinah Nur Fadillah Coneta Wulandari
- Chromosomes: Magdalena F. Natividad, PHD Dean, School of Medical Lab Science Feu-NrmfChromosomes: Magdalena F. Natividad, PHD Dean, School of Medical Lab Science Feu-Nrmf
- Monoclonal Antibody Therapy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMonoclonal Antibody Therapy - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
- Submitted by Aiswarya V 1St MSC Zoology Roll Number 3301Submitted by Aiswarya V 1St MSC Zoology Roll Number 3301
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 04/15/2022 Haweni A. 1Sexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 04/15/2022 Haweni A. 1
- Pathophysiology of Typhoid Fever and Acute GastroenteritisPathophysiology of Typhoid Fever and Acute Gastroenteritis
- Chronic Hepatitis B: Advances in Treatment: Department ofChronic Hepatitis B: Advances in Treatment: Department of
- Oppenheim J.J., Feldmann M. - Introduction To The Role of Cytokines in Innate Host Defense and Adaptive Immunity (2000) PDFOppenheim J.J., Feldmann M. - Introduction To The Role of Cytokines in Innate Host Defense and Adaptive Immunity (2000) PDF