0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 viewsTrimebutine: Drug Delivery Systems Ii
Trimebutine: Drug Delivery Systems Ii
Uploaded by
merve yamanTrimebutine is a spasmolytic agent used to treat irritable bowel syndrome and other gastrointestinal motility disorders. It exists as both a white to off-white powder and as the maleate salt trimebutine maleate. Trimebutine regulates intestinal and colonic motility by targeting ion conductance involved in gastrointestinal motility through various mechanisms including inhibiting calcium and potassium currents. It can both stimulate and inhibit spontaneous contractions in the gastrointestinal tract depending on its concentration. Common side effects include dry mouth and gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, while overdosage is treated with gastric lavage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Trimebutine: Drug Delivery Systems Ii
Trimebutine: Drug Delivery Systems Ii
Uploaded by
merve yaman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views12 pagesTrimebutine is a spasmolytic agent used to treat irritable bowel syndrome and other gastrointestinal motility disorders. It exists as both a white to off-white powder and as the maleate salt trimebutine maleate. Trimebutine regulates intestinal and colonic motility by targeting ion conductance involved in gastrointestinal motility through various mechanisms including inhibiting calcium and potassium currents. It can both stimulate and inhibit spontaneous contractions in the gastrointestinal tract depending on its concentration. Common side effects include dry mouth and gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, while overdosage is treated with gastric lavage.
Original Description:
Trimebutin
Original Title
trimebutine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Trimebutine is a spasmolytic agent used to treat irritable bowel syndrome and other gastrointestinal motility disorders. It exists as both a white to off-white powder and as the maleate salt trimebutine maleate. Trimebutine regulates intestinal and colonic motility by targeting ion conductance involved in gastrointestinal motility through various mechanisms including inhibiting calcium and potassium currents. It can both stimulate and inhibit spontaneous contractions in the gastrointestinal tract depending on its concentration. Common side effects include dry mouth and gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, while overdosage is treated with gastric lavage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views12 pagesTrimebutine: Drug Delivery Systems Ii
Trimebutine: Drug Delivery Systems Ii
Uploaded by
merve yamanTrimebutine is a spasmolytic agent used to treat irritable bowel syndrome and other gastrointestinal motility disorders. It exists as both a white to off-white powder and as the maleate salt trimebutine maleate. Trimebutine regulates intestinal and colonic motility by targeting ion conductance involved in gastrointestinal motility through various mechanisms including inhibiting calcium and potassium currents. It can both stimulate and inhibit spontaneous contractions in the gastrointestinal tract depending on its concentration. Common side effects include dry mouth and gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, while overdosage is treated with gastric lavage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Trimebutine
DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS II
M E RV E YA M A N
524517016
Trimebutine
Proper Name: Trimebutine
Chemical Name: 2-dimethyl amino-2-phenyl-butyl 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate
Molecular Formula: C22H29NO5
Structural Formula:
Molecular Weight: 387.5
Description: Trimebutine is a white to off-white powder practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol, ether, n-
hexane, and methanol and freely soluble in acetone and chloroform.
Melting Point: 78 to 82 °C
Trimebutine Maleate
The maleate salt of trimebutine (C22 H29 NO5 C4 H4 O4; M.W.: 503.6) is a white to off-white powder
(M.P. 128- 134°C ) very slightly soluble in ether and n-hexane, sparingly soluble in water, soluble
in acetone, ethanol and methanol and freely soluble in chloroform.
Description
Trimebutine is a spasmolytic agent that regulates intestinal and colonic motility and relieves
abdominal pain with antimuscarinic and weak opioid agonist effects.
It is marketed for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and lower gastrointestinal(GI)
tract motility disorders, with IBS being one of the most common multifactorial GI disorders.
IBS and GI SYMPTOMS
Description
It is used to restore normal bowel function and is commonly present in pharmaceutical mixtures
as trimebutine maleate salt form.
Trimebutine is not a FDA-approved drug, but it is available in Canada and several other
international countries
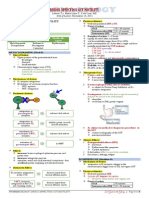
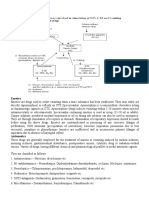
Pharmacodynamics
Trimebutine is a spasmolytic agent that acts directly on smooth muscle to modulate gastric
motility.
It shows a "dual function" that stimulates or inhibits spontaneous contractions depending on
the concentration and prior contractile activity in the preparation.
Pharmacodynamics
•Targeting ion conductance that regulates GI(gastroinstestinal) motility, trimebutine inhibits the
inward calcium currents and calcium-dependent potassium currents in a concentration-
dependent manner.
•At lower concentrations (1-10uM), trimebutine depolarizes the resting membrane potential
without affecting the amplitude of contractions, which is thought to be mediated by inhibition of
outward potassium currents. It is also shown to activate T-type Ca2+ channel and increase gastric
emptying, intestinal and colonic contractility.
•At higher concentrations (100-300uM), reduced amplitude of spontaneous contractions and
action potentials is thought to be mediated by inhibition of L-type Ca2+ channels and inward
calcium current. Trimebutine mediates a local anesthetic action by acting as a weak agonist at mu
opioid receptors.
Mechanism of action
At high concentrations, trimebutine is shown to inhibit the
extracellular Ca2+ influx in the smooth muscle cells through
voltage dependent L-type Ca2+ channels and further Ca2+
release from intracellular Ca2+ stores.
Trimebutine is suggested to bind to the inactivated state of the
calcium channel with high affinity. Reduced calcium influx
attenuates membrane depolarization and decrease colon
peristalsis. It also inhibits outward K+ currents in response to
membrane depolarization of the GI smooth muscle cells at
resting conditions through inhibition of delayed rectifier K+
channels and Ca2+ dependent K+ channels, which results in
induced muscle contractions.
Trimebutine binds to opioid receptors with more selectivity
compared to delta or kappa opioid receptors but with lower
affinity than their natural ligands. Its metabolites (N-
monodesmethyl-trimebutine or nor-trimebutine), are also
shown to bind to opoid receptors on brain membranes and
myenteric synaptosomes.
Toxicity
Common gastrointestinal adverse effects include;
dry mouth,
foul taste,
diarrhea,
dyspepsia,
epigastric pain,
nausea and
constipation.
Some CNS effects include drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, hot/cold sensations and headaches.
Toxicity
In case of overdosage, gastric lavage is recommended.
Trimebutine is not reported to display teratogenic, mutagenic or carcinogenic potential.
Dosage Forms
FORM ROUTE STRENGTH
Tablet Oral 200 mg
Liquid Intramuscular; Intravenous 10 mg
Tablet Oral 100 mg
THANK YOU...
You might also like
- Drugs Acting On Digestive System of AnimalsDocument11 pagesDrugs Acting On Digestive System of AnimalsSunil100% (4)
- Di InspectioninDocument38 pagesDi InspectioninJanith Saumya BandaraNo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 3 PDFDocument13 pages08 - Chapter 3 PDFKuberBajgainNo ratings yet
- IRBESARTANDocument5 pagesIRBESARTANraviNo ratings yet
- Diet Sheet1 Tmau 2010 PDFDocument14 pagesDiet Sheet1 Tmau 2010 PDFsoltero2100% (3)
- Trimebutine PMDocument21 pagesTrimebutine PMGr 3ckoNo ratings yet
- Nda 20-850/S-022/S-023: CH3 CH3Document12 pagesNda 20-850/S-022/S-023: CH3 CH3Nexi anessaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The GITDocument83 pagesPharmacology of The GITJohn Wesley OmbogoNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 LipidModifyingAgentsDocument25 pagesLecture2 LipidModifyingAgentsPeter MaithyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document23 pagesPresentation 2Ali TasleemNo ratings yet
- Systemic Veterinary Pharmacology in A NutshellDocument165 pagesSystemic Veterinary Pharmacology in A NutshellSunil100% (1)
- Omega-3 Fatty Acid Based Nanolipid Formulation ofDocument10 pagesOmega-3 Fatty Acid Based Nanolipid Formulation ofamalia.afifahNo ratings yet
- Zantac 150: (Ranitidine Hydrochloride) Tablets, USPDocument15 pagesZantac 150: (Ranitidine Hydrochloride) Tablets, USPbmartindoyle6396No ratings yet
- Treviamet Tab Leaflet PakistanDocument2 pagesTreviamet Tab Leaflet PakistanAmir IntizarNo ratings yet
- New DS3Document3 pagesNew DS3dakieNo ratings yet
- Lipitor: (Atorvastatin Calcium) TabletsDocument29 pagesLipitor: (Atorvastatin Calcium) TabletsEvelinaĐulbićNo ratings yet
- Orlistat Anti-Obesity Agent, Gastric and Pancreatic Lipase InhibitorDocument3 pagesOrlistat Anti-Obesity Agent, Gastric and Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitorsportcar2000No ratings yet
- Pharma - Drugs Affecting Git MotilityDocument6 pagesPharma - Drugs Affecting Git MotilityBobet ReñaNo ratings yet
- Lip It orDocument16 pagesLip It orluvly_nurulNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument6 pagesMefenamic AcidArisa VijungcoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On GitDocument35 pagesDrugs Acting On GitPridho GaziansyahNo ratings yet
- ANTIMETDocument49 pagesANTIMETWAHYU NOFANDARI HERDIYANTINo ratings yet
- Emetics and Antiemetics DrugsDocument15 pagesEmetics and Antiemetics DrugsrajenderNo ratings yet
- Metabolism HW1 Energy Vitamins SP24Document5 pagesMetabolism HW1 Energy Vitamins SP24raybuaNo ratings yet
- S 019 LBLDocument23 pagesS 019 LBLامیرحسین محمدیNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyUCN606 SUGITHA SNo ratings yet
- 2006-4254b - 16 - 02 - KP Atorvastatin Label FDA 8-7-06Document24 pages2006-4254b - 16 - 02 - KP Atorvastatin Label FDA 8-7-06Dikdik AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Pharmacology Review: Dhiren Patel, Pharmd, CdeDocument74 pagesCardiology Pharmacology Review: Dhiren Patel, Pharmd, Cdeshannon_marrero_1No ratings yet
- Cancer Chemotherapy 2017-1Document58 pagesCancer Chemotherapy 2017-1drkipkemboiNo ratings yet
- DRUGS AFFECTING the KIDNEY and UTERUS FUNCTIONDocument11 pagesDRUGS AFFECTING the KIDNEY and UTERUS FUNCTIONAnya LuxNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudymatthewchadNo ratings yet
- Strattera LBLDocument21 pagesStrattera LBLDermot BrennanNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Sistem Gastrointestinal 1 - FiksDocument77 pagesFarmakologi Sistem Gastrointestinal 1 - FiksINDRINo ratings yet
- TriheptanoinDocument46 pagesTriheptanoinMustafa IdaisNo ratings yet
- Agents Used in HyperlipidemiaDocument37 pagesAgents Used in HyperlipidemiacreativejoburgNo ratings yet
- Cisapride Is Also Used When Nothing Else Works But Has Fatal Cardiac Arrhythmias PossibleDocument5 pagesCisapride Is Also Used When Nothing Else Works But Has Fatal Cardiac Arrhythmias PossibleKristin DouglasNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument33 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsJuwairia tariqNo ratings yet
- At or Vast at inDocument22 pagesAt or Vast at inVelpandian PathyNo ratings yet
- Gastointestinal Diseases and Its DrugDocument38 pagesGastointestinal Diseases and Its DrugNicole EncinaresNo ratings yet
- vitaminsDocument44 pagesvitaminsDaniel ShebiruNo ratings yet
- Exercise - Toxiclogy - ToxicodynamicsDocument1 pageExercise - Toxiclogy - ToxicodynamicsJorge TinayaNo ratings yet
- Lipiget Tab Leaflet PakistanDocument2 pagesLipiget Tab Leaflet PakistanSohaib KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Lowering AngentDocument22 pagesLipid Lowering AngentDave BraveNo ratings yet
- KetamineDocument37 pagesKetamineRajesh Reddy Chintakunta100% (1)
- Ketamine FinalDocument9 pagesKetamine Finalatangaapeter4No ratings yet
- Farmako PDFDocument16 pagesFarmako PDFIsney HanindyaNo ratings yet
- 5 AntihyperlipidemicDocument35 pages5 Antihyperlipidemicabdelrahmanmosleh75No ratings yet
- Note 3Document3 pagesNote 3HossamJamaykaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of TryptophanDocument38 pagesMetabolism of Tryptophanjagan mohan rao vanaNo ratings yet
- Nutrigenomics BookletDocument36 pagesNutrigenomics BookletJohnny Atman100% (2)
- Newer DrugsDocument18 pagesNewer Drugsmahnoorsra1No ratings yet
- C - VVV VV VVVV VVV - VVV VV - VVVV VV VVDocument3 pagesC - VVV VV VVVV VVV - VVV VV - VVVV VV VVBea Angela Bithao AnonoyNo ratings yet
- Enzyme SummaryDocument7 pagesEnzyme SummaryAira Jane GamboaNo ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate Citrate Lyase: Emerging Target in The Treatment of DyslipidemiaDocument6 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate Citrate Lyase: Emerging Target in The Treatment of Dyslipidemiarufus991No ratings yet
- Principles of Diuretic Therapy: Dr. Rania Magadmi, MBBS, PHDDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Diuretic Therapy: Dr. Rania Magadmi, MBBS, PHDمشاعرمبعثرةNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument40 pagesGastrointestinal Agentse_sagadNo ratings yet
- 12.proteins DenaturationDocument26 pages12.proteins Denaturationmnouma1612No ratings yet
- Anti Hyperlipidemic Agent PDFDocument11 pagesAnti Hyperlipidemic Agent PDFStefanus Surya100% (2)
- Anticancer Drugs: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & Hod Dept. of PharmacologyDocument69 pagesAnticancer Drugs: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & Hod Dept. of PharmacologyMarlindah SNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Matrix Tablet of Losartan For Gastro-Retentive Drug DeliveryDocument6 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Floating Matrix Tablet of Losartan For Gastro-Retentive Drug DeliveryRaja AbhilashNo ratings yet
- PumpsDocument35 pagesPumpsMuhammad Ahmed Saleem67% (3)
- Rene Industries Limited General Test ProcedureDocument2 pagesRene Industries Limited General Test ProcedureMubarak PatelNo ratings yet
- Unidad N°8 MATERIALSDocument10 pagesUnidad N°8 MATERIALSFelipeNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument2 pagesPollutionLaramaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument24 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationWENDY MENDIOLANo ratings yet
- Polystone G Sds 2015Document3 pagesPolystone G Sds 2015TitikTriKuntartiNo ratings yet
- Rembrandt Water Colour ENGDocument1 pageRembrandt Water Colour ENGbetonowy88No ratings yet
- My TestDocument6 pagesMy TestMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Soya Milk, Paneer, CurdDocument11 pagesSoya Milk, Paneer, Curdpankaj_kalita100No ratings yet
- AmberDocument14 pagesAmbertemp111tempNo ratings yet
- Medication Study GuideDocument22 pagesMedication Study GuideArcenciel26100% (1)
- Steam TrapsDocument24 pagesSteam Trapsiran1362No ratings yet
- Indonesian Fossil CoralDocument9 pagesIndonesian Fossil CoralAgianto MutiadjajaNo ratings yet
- Parts List FerraraDocument8 pagesParts List Ferraramark_59No ratings yet
- Trickling FilterDocument24 pagesTrickling FilterMarufa YeasminNo ratings yet
- Convert Rectangular and Oval Duct Geometry To A Equivalent Circular Diameter PDFDocument7 pagesConvert Rectangular and Oval Duct Geometry To A Equivalent Circular Diameter PDFDavid MessierNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1, 2, & 3 - MUODocument99 pagesChapters 1, 2, & 3 - MUOamanuelNo ratings yet
- EN3203 SB-Hochdruck KatalogversionDocument6 pagesEN3203 SB-Hochdruck KatalogversionAung MhNo ratings yet
- Razm2019Document39 pagesRazm2019M Iqbal RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory: Chem 103 InorganicDocument11 pagesChemistry Laboratory: Chem 103 InorganicShemiah Caminos GeorsuaNo ratings yet
- List of Importable Items SGDocument1 pageList of Importable Items SGKiko KokiNo ratings yet
- Thesiswritingfinal Tao XuDocument201 pagesThesiswritingfinal Tao XuAnugerah IndrajiNo ratings yet
- The Zeroth Law of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThe Zeroth Law of ThermodynamicsBahrilNo ratings yet
- 4 FlangesDocument27 pages4 Flangesvu ngocNo ratings yet
- Analysis Nitrite HIGHDocument3 pagesAnalysis Nitrite HIGHvandrake10No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Durability of Concrete MaterialDocument32 pagesChapter 6 - Durability of Concrete Materialeyob yohannesNo ratings yet
- 2014 12 05 - Wi PFX GRP 0001Document22 pages2014 12 05 - Wi PFX GRP 0001hariharanoilgasNo ratings yet
- Types of Fire ExtinguishersDocument2 pagesTypes of Fire Extinguishersfaisalhotline9500No ratings yet
- Assignment ON: Jet Flow Dyeing MachinesDocument23 pagesAssignment ON: Jet Flow Dyeing MachinesMonirul Islam MonirNo ratings yet