0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
Cissp Domain 2 Asset Security
Uploaded by
srivatsan_eceThis document discusses asset security and information classification. It covers topics such as data classification levels for both public and government data, data ownership and responsibilities, and data security controls related to marking, handling, storing, and destroying data. Data security controls include properly labeling storage media, restricting access to sensitive media, encrypting and securely storing backup media, and destroying media using techniques that prevent data recovery or reuse.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
Cissp Domain 2 Asset Security
Uploaded by
srivatsan_ece0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
This document discusses asset security and information classification. It covers topics such as data classification levels for both public and government data, data ownership and responsibilities, and data security controls related to marking, handling, storing, and destroying data. Data security controls include properly labeling storage media, restricting access to sensitive media, encrypting and securely storing backup media, and destroying media using techniques that prevent data recovery or reuse.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document discusses asset security and information classification. It covers topics such as data classification levels for both public and government data, data ownership and responsibilities, and data security controls related to marking, handling, storing, and destroying data. Data security controls include properly labeling storage media, restricting access to sensitive media, encrypting and securely storing backup media, and destroying media using techniques that prevent data recovery or reuse.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
Cissp Domain 2 Asset Security
Uploaded by
srivatsan_eceThis document discusses asset security and information classification. It covers topics such as data classification levels for both public and government data, data ownership and responsibilities, and data security controls related to marking, handling, storing, and destroying data. Data security controls include properly labeling storage media, restricting access to sensitive media, encrypting and securely storing backup media, and destroying media using techniques that prevent data recovery or reuse.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1/ 8
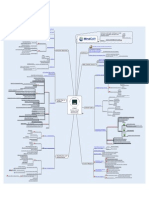
Domain 2 – Asset Security
Information and asset classification – know all layers of public and
government data classification (confidential, private, etc.)
Ownership (data owners, system owners)
Protect privacy
Appropriate retention – a few questions on data destruction
Data security controls – You will see questions regarding shipping
and Chain of Custody
Handling requirements (markings, labels, storage)
Information Classification - Public
Private – data that is defined as private (SSN, bank accounts, credit cards)
Company restricted – Data that is restricted to a subset of employees.
Company confidential – Data that can be viewed by all employees but is not for
general use.
Public – Data that can be viewed or used by employees or the general public.
Information Classification -
Government
Top Secret – Disclosure of top secret data would cause severe damage to national
security
Secret – Disclosure of secret data would cause serious damage to national
security. This data is considered less sensitive than data classified as top secret.
Confidential – Confidential data is usually data that is exempt from disclosure
under laws such as the Freedom of information act but is not classified as national
security data.
Sensitive but unclassified – SBU data is data that is not considered vital to
national security, but its disclosure would do some harm. Many agencies classify
data they collect from citizens as SBU.
Unclassified – Data that has no classification or is not sensitive.
Data Ownership
Data Owner – Usually a member of Senior Management. After all, senior
management is responsible for the asset and, if it is compromised, can be held
responsible. The data owner can delegate some data-to-day duties but cannot
delegate total responsibility; Senior Management is ultimately responsible.
Data Custodian – This is usually someone in IT. The data custodian does not
decide what controls are needed, but he or she does implement controls on behalf
of the data owner. Other responsibilities include the day-to-day management of
the asset. Controlling access, adding and removing privileges for individual users,
and ensuring that the proper controls have been implemented are all part of the
data custodian’s duties.
Data Security Controls - Marking
Storage media should have a physical label identifying the sensitivity of the
information contained.
Labels should indicate whether the data is encrypted.
Media found unlabeled should immediately be labeled with the highest level of
sensitivity until appropriate analysis is done.
Data Security Controls - Handling
Only designated personnel should have access to sensitive media.
Individuals responsible for managing sensitive media should be promulgated.
Important that logs and other records are used to track the activities of individuals
handling backup data.
Manual processes, such as access logs, are necessary to compensate for the lack of
automated controls regarding access to sensitive media.
Data Security Controls - Storing
Sensitive media should not be left lying about where a passerby could access it.
Backup media should be encrypted whenever possible and stored in a security
container, such as a safe or strong box.
Storing encrypted backup media at an off-site location should be considered for
disaster recovery purposes.
Data Security Controls -
Destruction
Media that is no longer needed or is defective should be destroyed rather than
simply disposed of.
A record of destruction should be used that corresponds to any logs used for
handling media.
Security practitioners should implement object reuse controls for any media in
question is unknown rather than simply recycling it.
Record Retention – Data and information should only be kept only as long as it is
required.
Data Remanence – residual physical representation of data
Purge – ensure total removal – data cannot be recovered
Clearing – Removes data but not 100%, lab techniques required for recovery
You might also like
- AZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-1: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500From EverandAZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-1: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500No ratings yet
- 2023+CISSP+Domain+2+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v4 0No ratings yet2023+CISSP+Domain+2+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v4 09 pages
- Complete Guide to Building an Information Security ProgramFrom EverandComplete Guide to Building an Information Security ProgramNo ratings yet
- Domain 01 - Information Security Governance & Risk ManagementNo ratings yetDomain 01 - Information Security Governance & Risk Management75 pages
- 2023+CISSP+Domain+2+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v3 1No ratings yet2023+CISSP+Domain+2+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v3 18 pages
- 008 Thor-Teaches-study-guide-CISSP-domain-1 - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)100% (1)008 Thor-Teaches-study-guide-CISSP-domain-1 - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)24 pages
- CISSP Domain One: Security and Risk Management-What You Need To Know For The Exam100% (1)CISSP Domain One: Security and Risk Management-What You Need To Know For The Exam14 pages
- Isc2cccoursecertifiedincybersecurity Part2 240106173606 fdc45f01No ratings yetIsc2cccoursecertifiedincybersecurity Part2 240106173606 fdc45f0151 pages
- Thor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 5No ratings yetThor Teaches Study Guide CISSP Domain 518 pages
- CISSP 8 Domain Refresh Summary Guide 15042015100% (1)CISSP 8 Domain Refresh Summary Guide 1504201525 pages
- MindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapNo ratings yetMindCert CISSP Application Development MindMap1 page
- Comprehensive Notes for CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Based on Professor Messer's Video CourseNo ratings yetComprehensive Notes for CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Based on Professor Messer's Video Course9 pages
- TYCS SEM - 6 P - 5 ETHICAL HACKING UNIT - 1 Introduction To Information Security100% (1)TYCS SEM - 6 P - 5 ETHICAL HACKING UNIT - 1 Introduction To Information Security11 pages
- Abhishek: 20BCS3591@cuchd - in Chandel-B682061b8No ratings yetAbhishek: 20BCS3591@cuchd - in Chandel-B682061b81 page
- Qualys Pci Compliance Getting Started GuideNo ratings yetQualys Pci Compliance Getting Started Guide12 pages
- Comptia It Industry Outlook 2023 - VfinalNo ratings yetComptia It Industry Outlook 2023 - Vfinal50 pages
- CISA Practice Questions To Prep For The Exam - TechTargetNo ratings yetCISA Practice Questions To Prep For The Exam - TechTarget9 pages
- Fortinet Recommended Security Best Practices v1.2No ratings yetFortinet Recommended Security Best Practices v1.223 pages
- 2016 Cyber Security Checklist For Organisations PDFNo ratings yet2016 Cyber Security Checklist For Organisations PDF5 pages
- Guidance PCI DSS Scoping and Segmentation v1No ratings yetGuidance PCI DSS Scoping and Segmentation v126 pages
- 2023+CISSP+Domain+1+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v3 1No ratings yet2023+CISSP+Domain+1+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v3 131 pages
- Comptia Security+ Study Guide (Sy0-501) : Sample Lab 1: Security Basics DiscussionNo ratings yetComptia Security+ Study Guide (Sy0-501) : Sample Lab 1: Security Basics Discussion10 pages
- 2021 04 27 Csiac Dod Cybersecurity Policy Chart0% (1)2021 04 27 Csiac Dod Cybersecurity Policy Chart1 page
- Domain 4 Communication and Network SecurityNo ratings yetDomain 4 Communication and Network Security9 pages
- Cissp Domain 6 Security Assessment and TestingNo ratings yetCissp Domain 6 Security Assessment and Testing8 pages
- Principles-of-Mangement-MG2351 Notes PDFNo ratings yetPrinciples-of-Mangement-MG2351 Notes PDF156 pages
- Windows Group Policy Pocket Administrator PDF100% (1)Windows Group Policy Pocket Administrator PDF445 pages
- Email Gateway Security Reference Architecture v1 0No ratings yetEmail Gateway Security Reference Architecture v1 041 pages
- Data Privacy Act of 2012 Summary ReviewerNo ratings yetData Privacy Act of 2012 Summary Reviewer2 pages
- Change of Address and Contact Details Form - v012018No ratings yetChange of Address and Contact Details Form - v0120182 pages
- Cyber Crime and Security: Student:Jalba Ion Group:1804No ratings yetCyber Crime and Security: Student:Jalba Ion Group:180420 pages
- Data Privacy: What Every Manager Needs To KnowNo ratings yetData Privacy: What Every Manager Needs To Know10 pages
- Data Privacy and Law: Cs 590: Privacy Edwin DauberNo ratings yetData Privacy and Law: Cs 590: Privacy Edwin Dauber48 pages
- Consent Form: Samar National School of Arts and TradesNo ratings yetConsent Form: Samar National School of Arts and Trades2 pages
- Lecture-6 Introduction To CybersecurityNo ratings yetLecture-6 Introduction To Cybersecurity19 pages
- Free Islamic & Education Books - Free Islamic & Education BooksNo ratings yetFree Islamic & Education Books - Free Islamic & Education Books21 pages
- The Do's and Don'ts of Using Computer and InternetNo ratings yetThe Do's and Don'ts of Using Computer and Internet1 page
- AZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-1: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500From EverandAZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-1: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500
- 2023+CISSP+Domain+2+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v4 02023+CISSP+Domain+2+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v4 0
- Complete Guide to Building an Information Security ProgramFrom EverandComplete Guide to Building an Information Security Program
- Domain 01 - Information Security Governance & Risk ManagementDomain 01 - Information Security Governance & Risk Management
- 2023+CISSP+Domain+2+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v3 12023+CISSP+Domain+2+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v3 1
- 008 Thor-Teaches-study-guide-CISSP-domain-1 - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)008 Thor-Teaches-study-guide-CISSP-domain-1 - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)
- CISSP Domain One: Security and Risk Management-What You Need To Know For The ExamCISSP Domain One: Security and Risk Management-What You Need To Know For The Exam
- Isc2cccoursecertifiedincybersecurity Part2 240106173606 fdc45f01Isc2cccoursecertifiedincybersecurity Part2 240106173606 fdc45f01
- Comprehensive Notes for CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Based on Professor Messer's Video CourseComprehensive Notes for CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701) Based on Professor Messer's Video Course
- TYCS SEM - 6 P - 5 ETHICAL HACKING UNIT - 1 Introduction To Information SecurityTYCS SEM - 6 P - 5 ETHICAL HACKING UNIT - 1 Introduction To Information Security
- CISA Practice Questions To Prep For The Exam - TechTargetCISA Practice Questions To Prep For The Exam - TechTarget
- 2016 Cyber Security Checklist For Organisations PDF2016 Cyber Security Checklist For Organisations PDF
- 2023+CISSP+Domain+1+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v3 12023+CISSP+Domain+1+Study+Guide+by+ThorTeaches Com+v3 1
- Comptia Security+ Study Guide (Sy0-501) : Sample Lab 1: Security Basics DiscussionComptia Security+ Study Guide (Sy0-501) : Sample Lab 1: Security Basics Discussion
- Email Gateway Security Reference Architecture v1 0Email Gateway Security Reference Architecture v1 0
- Change of Address and Contact Details Form - v012018Change of Address and Contact Details Form - v012018
- Cyber Crime and Security: Student:Jalba Ion Group:1804Cyber Crime and Security: Student:Jalba Ion Group:1804
- Data Privacy and Law: Cs 590: Privacy Edwin DauberData Privacy and Law: Cs 590: Privacy Edwin Dauber
- Consent Form: Samar National School of Arts and TradesConsent Form: Samar National School of Arts and Trades
- Free Islamic & Education Books - Free Islamic & Education BooksFree Islamic & Education Books - Free Islamic & Education Books
- The Do's and Don'ts of Using Computer and InternetThe Do's and Don'ts of Using Computer and Internet