0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsTralse
Tralse
Uploaded by
GLORY MALIGANGThe document discusses various aspects of auditing including:
1) The audit program lists procedures to gather audit evidence and tests of controls include procedures like inquiry, inspection, and recalculation.
2) Analytical procedures in planning help understand transactions and identify unusual items that could indicate misstatements.
3) Noncompliance includes personal transactions by employees/management. Materiality represents the maximum financial misstatement that wouldn't affect user decisions.
4) The auditor only tests controls they intend to rely on and the audit strategy guides the detailed audit plan.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Tralse
Tralse
Uploaded by
GLORY MALIGANG0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views15 pagesThe document discusses various aspects of auditing including:
1) The audit program lists procedures to gather audit evidence and tests of controls include procedures like inquiry, inspection, and recalculation.
2) Analytical procedures in planning help understand transactions and identify unusual items that could indicate misstatements.
3) Noncompliance includes personal transactions by employees/management. Materiality represents the maximum financial misstatement that wouldn't affect user decisions.
4) The auditor only tests controls they intend to rely on and the audit strategy guides the detailed audit plan.
Original Title
tralse
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document discusses various aspects of auditing including:
1) The audit program lists procedures to gather audit evidence and tests of controls include procedures like inquiry, inspection, and recalculation.
2) Analytical procedures in planning help understand transactions and identify unusual items that could indicate misstatements.
3) Noncompliance includes personal transactions by employees/management. Materiality represents the maximum financial misstatement that wouldn't affect user decisions.
4) The auditor only tests controls they intend to rely on and the audit strategy guides the detailed audit plan.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views15 pagesTralse
Tralse
Uploaded by
GLORY MALIGANGThe document discusses various aspects of auditing including:
1) The audit program lists procedures to gather audit evidence and tests of controls include procedures like inquiry, inspection, and recalculation.
2) Analytical procedures in planning help understand transactions and identify unusual items that could indicate misstatements.
3) Noncompliance includes personal transactions by employees/management. Materiality represents the maximum financial misstatement that wouldn't affect user decisions.
4) The auditor only tests controls they intend to rely on and the audit strategy guides the detailed audit plan.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
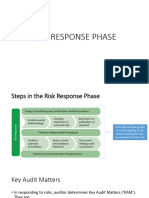
• The audit program is a list of procedures used
to gather sufficient and appropriate audit
evidence.
Tests of controls generally consist of
combination of procedures such as inquiry of
client personnel, inspection and observation,
and recalculation
• The objective of performing analytical procedures in
planning an audit is to obtain an understanding of the
transactions and events that are reflected in the financial
statements, and determining unusual items which could
indicate possible misstatements in the financial
statements.
For financial reporting purposes, an entity’s risk
assessment process is its identification, analysis, and
management of risks relevant to the preparation of
financial statements following GAAP.
• Noncompliance includes transactions entered by
the entity’s employees and management in their
personal capacity.
The preliminary judgment or estimate about
materiality represents the maximum amount by
which a set of financial statements could be
misstated and still not cause the auditor to believe
that the decisions of reasonable users would be
affected.
• The auditor will only test the controls on
which the auditor intends to rely.
• The overall audit strategy sets the scope,
timing, and direction of the audit, and guides
the development of the more detailed audit
plan.
• The auditor shall plan the audit so that in can
be performed effectively.
The auditor shall study and evaluate the
internal control system of the client to express
an opinion about the operating effectiveness
of such internal control system
• Studying the relationship of financial
information with another information,
whether financial or non-financial, is an
example of an analytical procedure.
To reduce audit risk to an acceptable low level,
the auditor should determine overall
responses to assessed risks at the assertion
level.
• A related party transaction is a transfer of
resources, services, or obligations between
related parties when no consideration is
involved.
The auditor assesses control risk as high or at
the maximum level when the internal controls
of the client have not been effectively
designed or have not operated effectively.
• Generally, the more reliable internal controls
are, the lesser the substantive test procedures
the auditor would need to perform in auditing
year-end account balances.
The industry in which the client operates may
give rise to specific risks of material
misstatements arising from the nature of the
business or the degree of regulations.
• Toward the end of an engagement, after all audit evidence
has been gathered by the auditor, the auditor again
considers materiality by comparing the combined
misstatements with the preliminary or revised estimate for
the entire set of the financial statements as a whole.
Changes in the regulatory or operating environment can
result in changes in competitive pressures and significantly
different risks.
• Group of answer choices
• The lower the materiality level, the higher the
amount of required evidence from substantive
procedures to compensate for increased risk.
Further audit procedures include risk
assessment procedures, test of controls and
substantive tests.
• Supervision and review are essential parts of
managing an engagement.
When the auditor obtains audit evidence
about the operating effectiveness of controls
during an interim period, that is enough to
support reliance to reduce substantive
procedures to be performed at year-end.
• It is necessary for the audit team members to
have a collective knowledge needed to carry
out the engagement.
An important responsibility of an auditor is
the establishment and maintenance of
internal control on an ongoing basis.
• In first time audits, the audit program is
completed during the planning phase of the
audit.
The auditor’s primary consideration regarding
client’s internal controls is the provision of
constructive suggestions to management
regarding the company’s internal controls.
• Regarding materiality, both amount and
nature of misstatements should be
considered.
One of the inherent limitations of internal
control is the lack of segregation of duties.
You might also like
- Audit PlanningDocument27 pagesAudit Planningrietzhel22No ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument26 pagesAudit PlanningDev PipilNo ratings yet
- Auditing Principle_ I Ch 4Document8 pagesAuditing Principle_ I Ch 4Akalu DugumaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Audit PlanningDocument39 pagesChapter 5 Audit PlanningRoxane EsabinianoNo ratings yet
- .Financial Statement Audit PlanningDocument39 pages.Financial Statement Audit Planningpamelajanmea2018No ratings yet
- Auditing I Ch IVDocument28 pagesAuditing I Ch IVAkalu DugumaNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning TechniquesDocument12 pagesAudit Planning TechniquesRahul KadamNo ratings yet
- Effective Internal Control - R: Procedures To Be Performed Are Matters For The Professional Judgment of The AuditorDocument5 pagesEffective Internal Control - R: Procedures To Be Performed Are Matters For The Professional Judgment of The Auditorlorie anne valleNo ratings yet
- W6 - Audit PlanningDocument6 pagesW6 - Audit PlanningverronabellagarcipleimitiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Topic 2 in Service MarketingDocument19 pagesModule 1 Topic 2 in Service MarketingSabillon JennivelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Completing The IT AuditDocument21 pagesLecture 8 Completing The IT Auditbarbie robertsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - AUDIT PLANNINGDocument8 pagesChapter 5 - AUDIT PLANNINGAljean Castro DuranNo ratings yet
- Audting Chapter4Document12 pagesAudting Chapter4Getachew JoriyeNo ratings yet
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument4 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlFritzie Ann ZartigaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Chapter 1 - An Introduction To Assurance and Financial Statement AuditingDocument32 pagesLECTURE 1 - Chapter 1 - An Introduction To Assurance and Financial Statement AuditingThảo Nhi Đinh TrầnNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Review of Financial StatementsDocument25 pages1.0 Review of Financial Statementsmujuni brianmjuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1124Document24 pagesLecture 1124jasonnumahnalkelNo ratings yet
- Audit in Nursing Management and AdministrationDocument31 pagesAudit in Nursing Management and Administrationbemina jaNo ratings yet
- Auditing I Ch IIIDocument24 pagesAuditing I Ch IIIAkalu DugumaNo ratings yet
- CT - 1Document3 pagesCT - 1Sameer HossainNo ratings yet
- Practical AuditingDocument61 pagesPractical Auditinglloyd100% (2)
- Introduction, Concepts and Overview of Financial Attest Audit ManualDocument47 pagesIntroduction, Concepts and Overview of Financial Attest Audit ManualMayurdhvajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- PPT. Chapter 2 AuditingDocument21 pagesPPT. Chapter 2 AuditingJerlmilline Serrano Jose100% (2)
- Audit PlanningDocument29 pagesAudit PlanningchamalixNo ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument12 pagesAudit PlanningDeryl GalveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Asuncion HandoutDocument8 pagesChapter 2. Asuncion HandoutCiel ArvenNo ratings yet
- AUDIT1. 4 The Audit Process Accepting An EngagementDocument32 pagesAUDIT1. 4 The Audit Process Accepting An EngagementRyhbskkmyrtNo ratings yet
- Topic3 Engagement PlanningDocument29 pagesTopic3 Engagement PlanningPRINCESS MENDOZANo ratings yet
- 2.A Statutory Audit of Bank Chapter 2 Audit Planning & Provisions Relating To AuditDocument24 pages2.A Statutory Audit of Bank Chapter 2 Audit Planning & Provisions Relating To Audithivamol906No ratings yet
- Kunci Ganjil Chapter 13Document7 pagesKunci Ganjil Chapter 13indahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER5 AudTheoDocument18 pagesCHAPTER5 AudTheoadarose romaresNo ratings yet
- The Risk of Material MisstatementDocument4 pagesThe Risk of Material Misstatementlkt11152No ratings yet
- Audit PlanningDocument5 pagesAudit PlanningDeopito BarrettNo ratings yet
- Audit I Chapter 3Document26 pagesAudit I Chapter 3bezaadane644No ratings yet
- Auditing Practices and Procedures Lecture-03Document18 pagesAuditing Practices and Procedures Lecture-03humaNo ratings yet
- Semi Final Exam at ReviewerDocument18 pagesSemi Final Exam at ReviewerXyra GeveraNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Handout RectifiedDocument11 pagesGroup 1 Handout RectifiedNe BzNo ratings yet
- Audit Approach (Class Synopsis-05 - 06) 04-02-2021Document12 pagesAudit Approach (Class Synopsis-05 - 06) 04-02-2021iftekharNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa AuditDocument6 pagesReviewer Sa Auditprincess manlangitNo ratings yet
- 5 Audit PlanningDocument31 pages5 Audit PlanningEliza BethNo ratings yet
- Tests of Controls: Control Risk Assessment and Audit Strategy Assessing The Control RiskDocument10 pagesTests of Controls: Control Risk Assessment and Audit Strategy Assessing The Control RiskVanadisa SamuelNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Revision SlidesDocument21 pagesCH 11 Revision SlidesRoite BeteroNo ratings yet
- 2operational Audit - Objectives and Phases of Operational AuditsDocument22 pages2operational Audit - Objectives and Phases of Operational AuditsGia Sarah Barillo Bandola100% (1)
- Chapter 6 PlanningDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Planningrishi kareliaNo ratings yet
- Considering Materiality and Audit RiskDocument3 pagesConsidering Materiality and Audit RiskIrish SanchezNo ratings yet
- Chapter01 - Overview of The Audit ProcessDocument3 pagesChapter01 - Overview of The Audit ProcessCristy Estrella0% (1)
- Auditing 1 Final Chapter 10Document7 pagesAuditing 1 Final Chapter 10PaupauNo ratings yet
- Compensating ControlDocument10 pagesCompensating Controlkasim_arkin2707100% (2)
- Knowledge Based QuestionsDocument17 pagesKnowledge Based Questions5mh8cyfgt4No ratings yet
- 2019 CIA P2 SI 2C Assurance EngagementsDocument128 pages2019 CIA P2 SI 2C Assurance EngagementsHenry James NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- 2-Ch 4-Overview Audit Process-7eDocument25 pages2-Ch 4-Overview Audit Process-7eAsho AliNo ratings yet
- Test of Control And/or Substantive Procedure, Developed To Assess The Efficacy of Controls inDocument4 pagesTest of Control And/or Substantive Procedure, Developed To Assess The Efficacy of Controls inIsabell CastroNo ratings yet
- Annual Update and Practice Issues for Preparation, Compilation, and Review EngagementsFrom EverandAnnual Update and Practice Issues for Preparation, Compilation, and Review EngagementsNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsFrom EverandThe Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsNo ratings yet
- Engagement Essentials: Preparation, Compilation, and Review of Financial StatementsFrom EverandEngagement Essentials: Preparation, Compilation, and Review of Financial StatementsNo ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Follow-up ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Follow-up ProcessRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Audit Risk Alert: Government Auditing Standards and Single Audit Developments: Strengthening Audit Integrity 2018/19From EverandAudit Risk Alert: Government Auditing Standards and Single Audit Developments: Strengthening Audit Integrity 2018/19No ratings yet
- Audit Risk Alert: General Accounting and Auditing Developments, 2017/18From EverandAudit Risk Alert: General Accounting and Auditing Developments, 2017/18No ratings yet
- 2022 Mayha ES Training DesignDocument8 pages2022 Mayha ES Training DesignGLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Request For Garden ToolsDocument1 pageRequest For Garden ToolsGLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Training Design 2023Document8 pagesTraining Design 2023GLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q2 - W7Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q2 - W7GLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Recommendation LetterDocument1 pageRecommendation LetterGLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Div Memo239 S 2021Document2 pagesDiv Memo239 S 2021GLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W7Document8 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W7GLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Div Memo237 S 2021Document4 pagesDiv Memo237 S 2021GLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Div Memo226 S 2021Document3 pagesDiv Memo226 S 2021GLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Div Memo238 S 2021Document3 pagesDiv Memo238 S 2021GLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Div Memo219 S 2021Document20 pagesDiv Memo219 S 2021GLORY MALIGANGNo ratings yet
- Suggested Topics For Lac SessionDocument1 pageSuggested Topics For Lac SessionGLORY MALIGANG100% (2)
- Jane Et - Al (1) - Action Research - FinalDocument50 pagesJane Et - Al (1) - Action Research - FinalGLORY MALIGANG100% (1)
- Technical Assistance FormDocument2 pagesTechnical Assistance FormGLORY MALIGANG100% (1)
- Rangkuman Audit InternalDocument28 pagesRangkuman Audit InternalNur SubekhiNo ratings yet
- Merabima Insurance Brokers Private Limited NOP Premium Pending As On DateDocument433 pagesMerabima Insurance Brokers Private Limited NOP Premium Pending As On DatePEACE SHIVALINo ratings yet
- The Impact of The Use of IT in Improving The Quality of External AuditDocument10 pagesThe Impact of The Use of IT in Improving The Quality of External Auditecomptable875No ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Internal Control System - Part 2-StudentDocument9 pagesTopic 3 - Internal Control System - Part 2-Studentnnmnghi1409No ratings yet
- AT - Presentation Slides On Audit ReportsDocument110 pagesAT - Presentation Slides On Audit Reportsby ScribdNo ratings yet
- Final Audit - New Questions For May 2024 ExamsDocument48 pagesFinal Audit - New Questions For May 2024 ExamsPankaj SinghNo ratings yet
- 2023 Resolution No. LT-04 Establishment of External Audit CommitteeDocument3 pages2023 Resolution No. LT-04 Establishment of External Audit CommitteeRAMIL AMILNo ratings yet
- LK Audited 2023Document234 pagesLK Audited 2023muhammad3gibran03No ratings yet
- أهمية التدقيق الداخلي في الرفع من جودة القوائم المالية في المؤسسات الجزائرية.Document17 pagesأهمية التدقيق الداخلي في الرفع من جودة القوائم المالية في المؤسسات الجزائرية.asmaatr44No ratings yet
- Practice Questions - Module 5Document8 pagesPractice Questions - Module 5Rosda DhangNo ratings yet
- New Auditors Report 2022Document4 pagesNew Auditors Report 2022Sattaki RoyNo ratings yet
- Session 6 PlanningDocument64 pagesSession 6 Planningmbangumilu15No ratings yet
- Risk-Based Audit Best PracticesDocument7 pagesRisk-Based Audit Best PracticesGerman ChavezNo ratings yet
- CA Ravi Agarwal's CA Final Audit CompilerDocument820 pagesCA Ravi Agarwal's CA Final Audit Compiler6dzk78g2vyNo ratings yet
- 2 Into To FS Audit and Pre-Engagement ActivitiesDocument40 pages2 Into To FS Audit and Pre-Engagement ActivitiesKane BuendiaNo ratings yet
- HO2-A - Risk-Based Audit of Financial Statements Part 1 (Overview) - RevisedDocument8 pagesHO2-A - Risk-Based Audit of Financial Statements Part 1 (Overview) - RevisedJaynalyn MonasterialNo ratings yet
- Audit Sample Paper and Suggested AnswerDocument60 pagesAudit Sample Paper and Suggested AnswerAyush GargNo ratings yet
- Individual Opinion, 2ND ReadingDocument1 pageIndividual Opinion, 2ND Reading1CV25 Nava Peralta Christian XavierNo ratings yet
- Bot Regulation On Internal AuditDocument18 pagesBot Regulation On Internal AuditkivaraNo ratings yet
- CH 3 6Document15 pagesCH 3 6Gizachew MayebetNo ratings yet
- SUF PR 14 Quality AuditingDocument8 pagesSUF PR 14 Quality AuditingAvnish YadavNo ratings yet
- Empanelment Extension Letter - 24.06.2024Document1 pageEmpanelment Extension Letter - 24.06.2024a.bhattacherjee79No ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka Skripsi UnairDocument5 pagesDaftar Pustaka Skripsi UnairAyu PramestiNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Responding To Risks in A Financial Statement Audi Part IIDocument10 pagesAssessing and Responding To Risks in A Financial Statement Audi Part IIGerman Chavez100% (1)
- Annex - 1 Org ChartDocument1 pageAnnex - 1 Org ChartMohamed HabibNo ratings yet
- CIS Promotions FY19Document42 pagesCIS Promotions FY19manu.whatsup1986No ratings yet
- Impact of Ownership Characteristics On Modified Audit Opinion in JordanDocument13 pagesImpact of Ownership Characteristics On Modified Audit Opinion in JordankesianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter13 BWDocument14 pagesChapter13 BWLiliNo ratings yet
- Auditing Sem VDocument193 pagesAuditing Sem Vadityakamble070103100% (2)
- Review Questions Sec 456Document8 pagesReview Questions Sec 456trthph2001No ratings yet