0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 viewsPython HTTPSERVER
An HTTP server is a software process that listens for incoming HTTP requests on a specific TCP port and handles requests by responding with the appropriate content. It serves this content, such as HTML files, from its file system. To create a simple HTTP server, one imports Python's HTTP server and socket server modules, defines a port number, and instantiates a TCP server object bound to that port with a request handler, which serves files from the current directory. Running the server script launches the server process to listen for and respond to requests on the designated port.
Uploaded by
rahulchaudhary27075Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 viewsPython HTTPSERVER
An HTTP server is a software process that listens for incoming HTTP requests on a specific TCP port and handles requests by responding with the appropriate content. It serves this content, such as HTML files, from its file system. To create a simple HTTP server, one imports Python's HTTP server and socket server modules, defines a port number, and instantiates a TCP server object bound to that port with a request handler, which serves files from the current directory. Running the server script launches the server process to listen for and respond to requests on the designated port.
Uploaded by
rahulchaudhary27075Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 14
HTTP SERVER
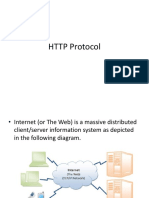
HTTP Server
• An HTTP web server is nothing but a process
that is running on your machine and does
exactly two things:
1- Listens for incoming http requests on a specific
TCP address (IP address and a port number )
2- Handles this request and sends a response back
to the user.
Example
• when you type www.yahoo.com on your browser,
your browser will create a network message called
an HTTP request.
• This Request will travel all the way to a Yahoo
computer that has a web server running on it. This
web server will intercept your request, and handle
it by responding back with the html of the Yahoo
home page.
• Finally your browser renders this html on the screen
and that’s what you see on your screen.
Example
HTTP SERVER
• Every interaction with the Yahoo home page after that (for
example, when you click on a link) initiates a new request and
response exactly like the first one.
• To reiterate, the machine that receives the http request has a
software process called a web server running on it. This web
server is responsible for intercepting these
requests and handling them appropriately.
how does the request reach that yahoo
machine
• Any http message (whether it is a request or response) needs
to know how to reach its destination.
• In order to reach its destination, each http message carries an
address called the destination TCP address.
• And each TCP address is composed of an IP address and
a port number.
• So where is that address when all you did was
type www.yahoo.com on your browser?
• This domain name is converted into an IP address through a
large distributed database called the DNS.
HTTP SERVER
• The IP address alone will allow the HTTP message to arrive at
the right machine, but you still need the port number in order
for the HTTP request to arrive exactly at the web server.
• In other words, the web server is a regular network
application that is listening on a specific port.
• And the http request must be addressed to that port.
• So where is the port number when you
type www.yahoo.com?
• By default, the port number is 80 for http and 443 for https,
so even though you haven’t explicitly specified the port
number, it is still there.
HTTP SERVER
• And if the web server is listening on a non-
default port number (neither 80 nor 443), you
must explicitly specify the port number like
this:
• Yahoo.com:443
Creating simple http server
• We want to create a simple http server that serves a static html
web page.
• Create a simple HTML file and save this file as index.html
• <html>
• <head>
• <title>Python is awesome!</title>
• </head>
• <body>
• <h1>FIRST SERVER </h1>
• <p>Congratulations! The HTTP Server is working!</p>
• </body>
• </html>
Create an HTTP web server
• The next step is to create a web server that will serve this html page.
Save the following script (server.py) in same directory where index.html
is stored because by default the SimpleHTTPRequestHandler will look for
a file named index.html in the current directory.
• import http.server
• import socketserver
• PORT = 8080
• Handler = http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
• with socketserver.TCPServer(("", PORT), Handler) as httpd:
• print("serving at port", PORT)
• httpd.serve_forever()
HTTP SERVER
• http.server.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler is: a simple
HTTP request handler that serves files from the
current directory and any of its subdirectories.
• socketserver.TCPServer class.
• An instance of TCPServer describes a server that uses
the TCP protocol to send and receive messages (http is
an application layer protocol on top of TCP).
• To instantiate a TCP Server, we need two things:
• 1- The TCP address (IP address and a port number)
• 2- The handler
HTTP SERVER
• The TCP address is passed as a tuple of (ip address, port
number)
• Passing an empty string as the ip address means that the
server will be listening on any network interface (all available
IP addresses).
• And since PORT stores the value of 8080, then the server will
be listening on incoming requests on that port.
• serve_forever is a method on the TCPServer instance that
starts the server and begins listening and responding to
incoming requests.
HTTP SERVER
• Start the web server by executing server.py
• By doing that, you now have an HTTP server
that is listening on any interface at port 8080
waiting for incoming http requests.
• Open your browser and type localhost:8080 in
the address bar.
OUTPUT
You might also like
- Introduction to PHP Web Services: PHP, JavaScript, MySQL, SOAP, RESTful, JSON, XML, WSDLFrom EverandIntroduction to PHP Web Services: PHP, JavaScript, MySQL, SOAP, RESTful, JSON, XML, WSDLNo ratings yet
- Inroduction To Servlet Inroduction To Servlet: Made By:-Pankaj Malik Mba (It)No ratings yetInroduction To Servlet Inroduction To Servlet: Made By:-Pankaj Malik Mba (It)92 pages
- Network Computing (Rt605) : Hyper Text Transfer ProtocolNo ratings yetNetwork Computing (Rt605) : Hyper Text Transfer Protocol19 pages
- Lecture07 - Apache Server - Installation and ConfigurationNo ratings yetLecture07 - Apache Server - Installation and Configuration16 pages
- Maharishi Markandeshwar (Deemed To Be University), Mullana (Ambala)No ratings yetMaharishi Markandeshwar (Deemed To Be University), Mullana (Ambala)10 pages
- Intro To Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)No ratings yetIntro To Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)18 pages
- Name Any Three Client Applications To Connect With FTP ServerNo ratings yetName Any Three Client Applications To Connect With FTP Server5 pages
- CS-504 (A) Internet & Web Technology Unit-1No ratings yetCS-504 (A) Internet & Web Technology Unit-121 pages
- Apache HTTP Server (Usually Called Just Apache) Is An Open-Source Web ServerNo ratings yetApache HTTP Server (Usually Called Just Apache) Is An Open-Source Web Server4 pages
- Certificate: Mr. Gaurav Arora (Project Guide)No ratings yetCertificate: Mr. Gaurav Arora (Project Guide)148 pages
- Web Essentials: Client, Server and CommunicationNo ratings yetWeb Essentials: Client, Server and Communication18 pages
- Accenture Networking and Cloud ComputingNo ratings yetAccenture Networking and Cloud Computing81 pages
- Simple Python HTTP (S) Server - Example AnvilEight BlogNo ratings yetSimple Python HTTP (S) Server - Example AnvilEight Blog7 pages
- EContent 11 2023 03 01 18 07 21 02Unit2ApplicationLayerpptx 2023 01 31 08 52 45No ratings yetEContent 11 2023 03 01 18 07 21 02Unit2ApplicationLayerpptx 2023 01 31 08 52 4583 pages
- COEN 445 Communication Networks and Protocols Lab 4: Socket Programming With Python: Web ServerNo ratings yetCOEN 445 Communication Networks and Protocols Lab 4: Socket Programming With Python: Web Server10 pages
- 20.19. SimpleHTTPServer - Simple HTTP Request Handler - Python 2.7.16 DocumentationNo ratings yet20.19. SimpleHTTPServer - Simple HTTP Request Handler - Python 2.7.16 Documentation2 pages
- Introduction of Web Server and Web BrowserNo ratings yetIntroduction of Web Server and Web Browser9 pages
- Unit I: Introduction To Web DevelopmentNo ratings yetUnit I: Introduction To Web Development28 pages
- Group Assignment Course Tittle System & Network Administration Group 1No ratings yetGroup Assignment Course Tittle System & Network Administration Group 117 pages
- Introduction: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol: Set Up An HTTP Proxy100% (1)Introduction: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol: Set Up An HTTP Proxy4 pages
- Discussion: Social Engine Forum Members Help Shoutbox Subscriptions Awards Connect Search Status AboutNo ratings yetDiscussion: Social Engine Forum Members Help Shoutbox Subscriptions Awards Connect Search Status About7 pages
- Mysql Database:: How To Connect To DatabseNo ratings yetMysql Database:: How To Connect To Databse9 pages
- Asas Sains Komputer (ASK) - 1-3 September 2020 (Online) : Masa: 9:00 PG - 11:00 PG Kod GC: 7evdl66No ratings yetAsas Sains Komputer (ASK) - 1-3 September 2020 (Online) : Masa: 9:00 PG - 11:00 PG Kod GC: 7evdl662 pages
- Raw Password Files 2024-12-17 Lummac Spc - Spc Spc at Ottohelp Spc - Spc Ottomancloud Spc -11kpcs-Freegift Spc Freelog- Spc at Ottohelp Spc - Spc Ottomancloud6520 Password File100% (1)Raw Password Files 2024-12-17 Lummac Spc - Spc Spc at Ottohelp Spc - Spc Ottomancloud Spc -11kpcs-Freegift Spc Freelog- Spc at Ottohelp Spc - Spc Ottomancloud6520 Password File134 pages
- Personalizing Mahara Views With Custom SkinsNo ratings yetPersonalizing Mahara Views With Custom Skins9 pages
- Performance Report For:: Executive SummaryNo ratings yetPerformance Report For:: Executive Summary10 pages
- Client-Side Storage in Web Applications PDFNo ratings yetClient-Side Storage in Web Applications PDF14 pages
- Workshop 2B: Web Scraping With Beautifulsoup 4: Comp20008 Elements of Data ProcessingNo ratings yetWorkshop 2B: Web Scraping With Beautifulsoup 4: Comp20008 Elements of Data Processing5 pages