0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsSafety Precautions
Safety Precautions
Uploaded by
kalpitsariyalaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Safety Precautions
Safety Precautions
Uploaded by
kalpitsariyala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views27 pagesOriginal Title
Safety Precautions (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views27 pagesSafety Precautions
Safety Precautions
Uploaded by
kalpitsariyalaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 27
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Workshop Safety
State of being safe is called safety or you can say safety
is the freedom from danger.
Safety is everyone’s business.
From maintenance point of view safety can be divided
into two types:
Safety at the workplace
Safety taken by the personnel
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Cleanliness is essential key to safety and safe
maintenance.
Orderly work arrangements and cleanliness should be
observed during any maintenance work.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Each and every hazards or danger should be properly
marked or painted with distinctive color and signs as
attention getter.
This is a safety measure to prevent accidents
Location of first aid as well as fire point should also be
properly marked.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Safety is a general term and has a broad meaning and
can be explained in detail.
1- Safety related to use of tools.
Hammers
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Safety Around Electricity:
WHY IS IT SO IMPORTANT TO WORK SAFELY
WITH OR NEAR ELECTRICITY?
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
The voltage and the available electrical current in
regular businesses and homes has enough power to
cause death by electrocution.
Even changing a light bulb without unplugging the
lamp can be hazardous because coming in contact
with the "hot", "energized" or "live" part of the socket
could kill a person.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WHAT DO I NEED TO KNOW ABOUT ELECTRICITY?
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
All electrical systems have the potential to cause
harm.
Electricity can be either "static" or "dynamic."
Dynamic electricity is the uniform motion of electrons
through a conductor (this is known as electric
current).
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Conductors are materials that allow the movement of
electricity through it.
Most metals are conductors. The human body is also a
conductor.
Static electricity is accumulation of charge on surfaces
as a result of contact and friction with another surface.
Electric current cannot exist without an unbroken path
to and from the conductor.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
What kinds of injuries result from electrical currents?
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
People are injured when they become part of the
electrical circuit.
Humans are more conductive than the earth (the
ground we stand on) which means if there is no other
easy path, electricity will try to flow through our
bodies.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
There are four main types of injuries:
1- Electrocution (fatal),
2- Electric shock,
3- Burns,
4- falls.
These injuries can happen in various ways:
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Direct contact with exposed energized conductors or
circuit parts. When electrical current travels through our
bodies, it can interfere with the normal electrical signals
between the brain and our muscles (e.g., heart may stop
beating properly, breathing may stop, or muscles may
spasm).
When the electricity arcs (jumps, or "arcs") from an
exposed energized conductor or circuit part (e.g.,
overhead power lines) through a gas (such as air) to a
person who is grounded (that would provide an
alternative route to the ground for the electrical current).
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Thermal burns including burns from heat generated
by an electric arc, and flame burns from materials that
catch on fire from heating or ignition by electrical
currents or an electric arc flash.
Contact burns from being shocked can burn internal
tissues while leaving only very small injuries on the
outside of the skin.
Thermal burns from the heat radiated from an electric
arc flash. Ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) light
emitted from the arc flash can also cause damage to
the eyes.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
An arc blast can include a potential pressure wave
released from an arc flash. This wave can cause
physical injuries, collapse your lungs, or create noise
that can damage hearing.
Muscle contractions, or a startle reaction, can cause a
person to fall from a ladder, scaffold or aerial bucket.
The fall can cause serious injuries.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
What are some general safety tips for working
with or near electricity?
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Inspect portable cord-and-plug connected equipment,
extension cords, power bars, and electrical fittings for
damage or wear before each use. Repair or replace
damaged equipment immediately.
Always tape extension cords to walls or floors when
necessary. Do not use nails and staples because they
can damage extension cords and cause fire and shocks.
Use extension cords or equipment that is rated for the
level of amperage or wattage that you are using.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Always use the correct size fuse. Replacing a fuse with
one of a larger size can cause excessive currents in the
wiring and possibly start a fire.
Be aware that unusually warm or hot outlets or cords may
be a sign that unsafe wiring conditions exists. Unplug any
cords or extension cords from these outlets and do not
use until a qualified electrician has checked the wiring.
Always use ladders made with non-conductive side rails
(e.g., fibreglass) when working with or near electricity or
power lines.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Place halogen lights away from combustible materials
such as cloths or curtains. Halogen lamps can become
very hot and may be a fire hazard.
Risk of electric shock is greater in areas that are wet or
damp. Install Ground Fault Circuit
Interrupters (GFCIs) /ELCB as they will interrupt the
electrical circuit before a current sufficient to cause
death or serious injury occurs.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Make sure that exposed receptacle boxes are made of
non-conductive materials.
Know where the panel and circuit breakers are located
in case of an emergency.
Label all circuit breakers and fuse boxes clearly. Each
switch should be positively identified as to which
outlet or appliance it is for.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Do not use outlets or cords that have exposed wiring.
Do not block access to panels and circuit breakers or
fuse boxes.
Do not touch a person or electrical apparatus in the
event of an electrical incident. Always disconnect the
power source first.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WHAT IS A SAMPLE CHECKLIST FOR BASIC ELECTRICAL SAFETY?
Inspect Cords and Plugs:
Check extension cords and plugs daily. Do not use, and discard cords
and plugs if they are worn or damaged.
Have any extension cord that feels more than comfortably warm
checked by an electrician.
Eliminate Octopus Connections:
Do not plug several items into one outlet.
Pull the plug, not the cord.
Do not disconnect power supply by pulling or jerking the cord from the
outlet. Pulling the cord causes wear and may cause a shock.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Never Break OFF the Third Prong on a Plug:
Replace broken 3-prong plugs and make sure the third
prong is properly grounded.
Never Use Extension Cords as Permanent Wiring:
Use extension cords only to temporarily supply power to an
area that does not have a power outlet.
Keep extension cords away from heat, water and oil. They
can damage the insulation and cause a shock.
Do not allow vehicles to pass over unprotected extension
cords. Extension cords should be put in protective wireway,
conduit, pipe or protected by placing planks alongside
them.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Over all:
To safely deal with electricity, the technician must
have a working knowledge of the principles of
electricity, and a healthy respect for its capability to do
both work and damage.
Two factors that affect safety when dealing with
electricity are fear and overconfidence.
These two factors are major causes of accidents
involving electricity
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Certain amount of respect for electrical equipment is
healthy and a certain level of confidence is necessary,
extremes of either can be deadly.
Lack of respect is often due to lack of knowledge.
Overconfidence leads to risk taking.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Wear or use proper safety equipment to provide
psychological assurance and physically protect one
self.
The use of rubber gloves, safety glasses, rubber or
grounded safety mats, and other safety equipment
contributes to the physiological safety .
You might also like
- Unit 3 IotDocument17 pagesUnit 3 IotKrishna DolasNo ratings yet
- Exercises Problems Answers Chapter 7: Problem 7.8Document11 pagesExercises Problems Answers Chapter 7: Problem 7.8A SibiescuNo ratings yet
- What Is Electrical Safety?Document32 pagesWhat Is Electrical Safety?Zaheed Manoo100% (1)
- Electrical-CCOHS-FactSheet-Electrical SafetyDocument7 pagesElectrical-CCOHS-FactSheet-Electrical SafetyEhsan MazharNo ratings yet
- Hazard and SafetyDocument41 pagesHazard and SafetyMark Francis Hernandez100% (1)
- Electrical Hazards & Safety TrainingDocument45 pagesElectrical Hazards & Safety TrainingMuhammad Munirul AlamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Basic InformationDocument5 pagesElectrical Safety Basic InformationAnge JuanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Guidelines1Document4 pagesElectrical Safety Guidelines1dichosoaries94No ratings yet
- Topic 3 ELECTRICAL SAFETY STANDARDSDocument7 pagesTopic 3 ELECTRICAL SAFETY STANDARDSsmosh.tequila07No ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Awareness TrainingDocument45 pagesElectrical Safety Awareness TrainingManish Deswal50% (2)
- Electrical Safety: Prepared By: Emmanuel Areglo Jericho Andrew Javier Edmhel Jon Reselva (BSEE-3B)Document29 pagesElectrical Safety: Prepared By: Emmanuel Areglo Jericho Andrew Javier Edmhel Jon Reselva (BSEE-3B)EJReselva100% (1)
- What Do I Need To Know About Electricity?Document7 pagesWhat Do I Need To Know About Electricity?unniNo ratings yet
- Types of Hazards, Distribution Systems From Safety Point of ViewDocument37 pagesTypes of Hazards, Distribution Systems From Safety Point of ViewShahbazNo ratings yet
- My Module Basic ElectronicsDocument62 pagesMy Module Basic Electronicspsalmsdavid174No ratings yet
- Workplace Electrical Safety Tips: Cords, Equipment, and Tool GroundingDocument6 pagesWorkplace Electrical Safety Tips: Cords, Equipment, and Tool GroundingjishnusajiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety DataDocument17 pagesElectrical Safety DataSyam SundarNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument21 pagesElectrical SafetyAvina NigNo ratings yet
- Electrical Training Awareness PPT-2020Document45 pagesElectrical Training Awareness PPT-2020Ishmael Tetteh100% (1)
- Electrical SafetyDocument31 pagesElectrical SafetyDennis Ballantyne100% (2)
- Electrical SafetyDocument45 pagesElectrical SafetyAnsarMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument91 pagesElectrical Safetyvimalyadav9424No ratings yet
- Electrical Safety (Pase)Document63 pagesElectrical Safety (Pase)Allan ManumbasNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety and You: Handout ADocument5 pagesElectrical Safety and You: Handout AArum Lupita100% (1)
- Safety, Hazards, Risks in ECE WorkplaceDocument4 pagesSafety, Hazards, Risks in ECE WorkplaceJohn Nate RiveraNo ratings yet
- Electr Part 2Document1 pageElectr Part 2hussein aliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety ReadingDocument12 pagesElectrical Safety Readingcompos24No ratings yet
- Safety Requirement in Marine EngineeringDocument24 pagesSafety Requirement in Marine EngineeringR.W. SaputraNo ratings yet
- 19 OPF Safety Program Manual - Electrical SafetyDocument22 pages19 OPF Safety Program Manual - Electrical SafetyShashi ShekharNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety With Temporary Electrical InstallationDocument39 pagesElectrical Safety With Temporary Electrical InstallationBharath Cj100% (1)
- Electrical Hazard and ControlDocument45 pagesElectrical Hazard and ControlElvira Lopez AndadiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Sefety Module 4 & 5Document108 pagesIndustrial Sefety Module 4 & 5Akhila RNo ratings yet
- 09 Electrical Safety SOS (14!08!2013)Document40 pages09 Electrical Safety SOS (14!08!2013)abaidurrehman100% (1)
- How Does Electricity WorkDocument15 pagesHow Does Electricity WorkJuju FernsNo ratings yet
- Electrical Hazards: How Do You Respond To Electrical Incidents (Electrocution) ?Document4 pagesElectrical Hazards: How Do You Respond To Electrical Incidents (Electrocution) ?roythomascNo ratings yet
- Electrical HazardsDocument56 pagesElectrical HazardsBryan PiguaveNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety: Assignment No. 10Document21 pagesElectrical Safety: Assignment No. 10waqashabib100% (1)
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1eshetutilahun485No ratings yet
- Testing TET113 NOTE 111Document16 pagesTesting TET113 NOTE 111bello musaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical SafetyDocument19 pagesBasic Electrical SafetySAYEDNo ratings yet
- CHIRANJEEVIDocument38 pagesCHIRANJEEVIshanmukhpavantejNo ratings yet
- 18ME753 Module 4Document46 pages18ME753 Module 4MOHAMMED ZAINNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Internship CertificateDocument6 pagesElectrical Engineering Internship Certificatexosim12242No ratings yet
- 3 Electrical SafetyDocument18 pages3 Electrical Safetyosama1928No ratings yet
- Reporting electricity in practiceDocument3 pagesReporting electricity in practicephamviethai7518No ratings yet
- TVL - Ia: Quarter 2Document14 pagesTVL - Ia: Quarter 2Chiarnie LopezNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument24 pagesElectrical SafetyRENIEL PABUNANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Electrical HazardsDocument31 pagesChapter 4-Electrical HazardsShashitharan PonnambalanNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument4 pagesElectrical Safetykevin vadhiya kevin vadhiyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Electrical-HazardsDocument4 pagesLesson 9 Electrical-HazardsDerrick SiameNo ratings yet
- Machinery Selection-Books22Document277 pagesMachinery Selection-Books22miningnova2100% (1)
- M2.A-Basic Electrical SafetyDocument63 pagesM2.A-Basic Electrical SafetyEdwin EspinasNo ratings yet
- Electrical Hazards: Current ReactionDocument18 pagesElectrical Hazards: Current ReactionDharminder SinghNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument59 pagesElectricalVikas SinghNo ratings yet
- Safety PrecautionsDocument8 pagesSafety Precautionschristelmaevirtucio19No ratings yet
- B.electrical SafetyDocument18 pagesB.electrical Safetyismail.elborae95No ratings yet
- EnglishDocument39 pagesEnglishNaufal HammamNo ratings yet
- Safety and Electrical AccidentsDocument26 pagesSafety and Electrical AccidentsJesslyn LimNo ratings yet
- Tool Box Topic: Electrical Safety: What Are The Hazards?Document1 pageTool Box Topic: Electrical Safety: What Are The Hazards?Nick LatumboNo ratings yet
- Electrical SafetyDocument18 pagesElectrical Safetyvij2009No ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Training - EHSDocument20 pagesElectrical Safety Training - EHSJoseph RayaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Safety - M4Document21 pagesIndustrial Safety - M4sonalimani2022No ratings yet
- Electricity Unplugged: A Beginner's Guide to Electrical SafetyFrom EverandElectricity Unplugged: A Beginner's Guide to Electrical SafetyNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide Stellar Plus TM Models - E - fh018 Thru E - fh060 Split-System Heat Pumps Rev C (07 - 00)Document8 pagesTechnical Guide Stellar Plus TM Models - E - fh018 Thru E - fh060 Split-System Heat Pumps Rev C (07 - 00)Shouzab AbbasNo ratings yet
- Đề Cương FP 7 File Tổng Hợp Đề Từ U5-U8Document17 pagesĐề Cương FP 7 File Tổng Hợp Đề Từ U5-U8AnhThư CaoNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 01: Department of Mechanical Engineering National University of Technology Machine Design II (ME-3442)Document1 pageAssignment - 01: Department of Mechanical Engineering National University of Technology Machine Design II (ME-3442)Muscle TVNo ratings yet
- Programme For The 16th Chlorine Symposium - Thyssenkrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers, 15th - 17th June 2016, Dortmund, GermanyDocument2 pagesProgramme For The 16th Chlorine Symposium - Thyssenkrupp Uhde Chlorine Engineers, 15th - 17th June 2016, Dortmund, GermanyChristian Josue Herrera CordobaNo ratings yet
- UNIV-1000Power Pack CatalogDocument3 pagesUNIV-1000Power Pack CatalogFher GallardoNo ratings yet
- 09 Task Performance 1 STS Finals BANGALANDOxDULLAGUExPANGANIBANDocument2 pages09 Task Performance 1 STS Finals BANGALANDOxDULLAGUExPANGANIBANRoje BangalandoNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts 210420 - v1.2. - Eur-MdlDocument1 pageSpare Parts 210420 - v1.2. - Eur-MdlTudor RacuNo ratings yet
- 9 TH WeekDocument66 pages9 TH WeeknaverfallNo ratings yet
- Partipantslist Dec1Document38 pagesPartipantslist Dec1Jigisha VasaNo ratings yet
- MGC 250bpy 2Document1 pageMGC 250bpy 2bereketNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - MTF1 - Properties of Pure Substances - 2021Document29 pagesLesson 5 - MTF1 - Properties of Pure Substances - 2021Thabo MokgosiNo ratings yet
- HW3 ProblemDocument4 pagesHW3 Problem劉德信No ratings yet
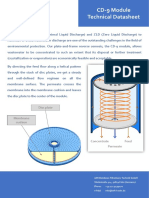
- CD-9 Module DatasheetDocument5 pagesCD-9 Module DatasheetLixiviados Navarro 2021No ratings yet
- Slup 414Document20 pagesSlup 414sciencemoduleNo ratings yet
- Inferential Statistic IIDocument61 pagesInferential Statistic IIThiviyashiniNo ratings yet
- Environmental Cost ManagementDocument37 pagesEnvironmental Cost ManagementKahfi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous MotorsDocument5 pagesAsynchronous MotorsVia Mae CastillanoNo ratings yet
- Solis Certificate IEC&en 62109 1 (2) S6 EH1P (3 8) K L PRO Safety V01Document3 pagesSolis Certificate IEC&en 62109 1 (2) S6 EH1P (3 8) K L PRO Safety V01carrei JohnNo ratings yet
- MFL68881508 Web ENDocument67 pagesMFL68881508 Web EN28m95dzjthNo ratings yet
- Thermal, Stress, and Thermo-Optic Effects in High Average Power Double-Clad Silica Fiber LasersDocument11 pagesThermal, Stress, and Thermo-Optic Effects in High Average Power Double-Clad Silica Fiber Lasersmuyucel3No ratings yet
- Initial Location Selection of Electric Vehicles ChargingDocument15 pagesInitial Location Selection of Electric Vehicles ChargingDuta FickyNo ratings yet
- DongFeng RICH-ZD30D13-4N2-PINOUTDocument3 pagesDongFeng RICH-ZD30D13-4N2-PINOUTEduardo Antonio Barria OjedaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Electrical BrandDocument1 pageInventory Electrical Brand5221asri_maabNo ratings yet
- Ata 47Document74 pagesAta 47Alejandro Siliezar100% (1)
- Development Policy PPT 1Document11 pagesDevelopment Policy PPT 1Suraj MauryaNo ratings yet
- Final Brief of Ipt CaseDocument38 pagesFinal Brief of Ipt CaseIshmael OneyaNo ratings yet
- Principles-of-Sustainability BDocument39 pagesPrinciples-of-Sustainability Bm31844790No ratings yet
- Presented By: Bharat Kumawat ECE DepartmentDocument20 pagesPresented By: Bharat Kumawat ECE DepartmentshankergodwalNo ratings yet