0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsSTARS
STARS
Uploaded by
Nicolás Muñoz GarcíaStars are born from clouds of dust and gas called nebulas. As a nebula contracts under gravity, heat is generated at its center and a protostar forms. Over millions of years, the protostar gains mass and becomes a full-fledged star fuelled by nuclear fusion. As stars age, they evolve through different stages depending on their mass until their death in a white dwarf, nova, supernova or black hole.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
STARS
STARS
Uploaded by
Nicolás Muñoz García0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views21 pagesStars are born from clouds of dust and gas called nebulas. As a nebula contracts under gravity, heat is generated at its center and a protostar forms. Over millions of years, the protostar gains mass and becomes a full-fledged star fuelled by nuclear fusion. As stars age, they evolve through different stages depending on their mass until their death in a white dwarf, nova, supernova or black hole.
Original Description:
Presentación en inglés a cerca de las estrellas.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Stars are born from clouds of dust and gas called nebulas. As a nebula contracts under gravity, heat is generated at its center and a protostar forms. Over millions of years, the protostar gains mass and becomes a full-fledged star fuelled by nuclear fusion. As stars age, they evolve through different stages depending on their mass until their death in a white dwarf, nova, supernova or black hole.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views21 pagesSTARS
STARS
Uploaded by
Nicolás Muñoz GarcíaStars are born from clouds of dust and gas called nebulas. As a nebula contracts under gravity, heat is generated at its center and a protostar forms. Over millions of years, the protostar gains mass and becomes a full-fledged star fuelled by nuclear fusion. As stars age, they evolve through different stages depending on their mass until their death in a white dwarf, nova, supernova or black hole.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
THE EVOLUTION
OF THE STARS
By Mónica Neila Rico, Eduardo D. Francés Rodríguez,
Daniel de la Cruz Sánchez y Nicolás Muñoz García
1. Introduccion of the topic
2. The evolution of a star
INDEX 3. Personal assesment
4. Curiosities
5. Bibliography
INTRODUCTION
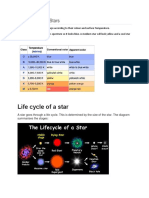
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course
of time.
It's depends on the mass of the star. Its lifetime can range from a few
million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least
massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe.
NEBULA
NEBULA
Like humans, stars birds lives and dies. Their bird places are cold and
enormous clouds of dust and gas called nebulas. A familiar example of a
dust cloud is the Orion Nebula. When the nebula has the enough size, it
starts to contract by his own gravitational attraction. As the cloud
contracts, the material at the center begins to heat up. The center of
the heat nebula, that one day will become into a star, is called protostar.
As the nebula collapses, the center starts to accumulate dust and gas.
Not all this material ends up as part of a star. The remaining dust can
become planets, asteroids, or comets or may remain as dust. A star with
the size of our Sun needs about 50 million years to mature from the
nebula to the adulthood. Stars are fuelled by the nuclear fusion of
hydrogen to form helium in their deep interior. The energy that leaves
the central region the necessary pressure to prevent the star from
collapsing under its own weight and the energy by which it shines.
White
Dwarfs
White Dwarfs.
For average stars like the Sun, the process of ejecting its
outer layers continues until the stellar core is exposed.
This dead, but still ferociously hot stellar cinder is called
a White Dwarf. These types of stars are very common, and
our own Sun will be a white dwarf billions of years from
n o w.
NOVAS
NOVAS
A nova occurs when the white dwarf, which is the dense
core of a once-normal star, gets gas from its nearby
companion star. When enough gas builds up on the surface
of the white dwarf it makes an explosion. For a brief time,
the system can shine up to a million times brighter than
normal. As long as it continues to take gas from its
companion star, the white dwarf can produce nova
explosions.
SUPERNOVA
SUPERNOVA
Supernova is a violent stellar explosion that can shine as
brightly as an entire galaxy of billions of normal stars.
A s t r o n o m e r s d i v i d e s u p e r n o v a e i n t o t w o g r o u p s : Ty p e I a n d
Ty p e I I . Ty p e I s u p e r n o v a e i s t h e m o s t l i k e l y t o f o r m a s
white stars “steals” gas from another star. If it
accumulates a large amount of gas, it can produce a
thermonuclear explosion that blast the star to bits, leaving
n o t h i n g b e h i n d . Ty p e I I s u p e r n o v a e a r e t h e f i n a l s t a g e i n
the evolution of stars that are at least eight times as
massive as the Sun. When a star reaches a point where it
can no longer produce nuclear energy in its core a star
reaches a point where it can no longer produce nuclear
energy in its core. This causes the star ’s core to collapse
to form a neutron star or black hole.
CURIOSITIES
CURIOSITIES
After billions of years the stars can go out which can do
two things:
They can expand to take more matter and use it like fuel.
They can explote causing a supernova.
If a star produce a supernova if would provocate a lot of
waves of dust and gas and we can wath it from the earth
with a telescop.
Normally a small star live more years than a big one
All stars are make with the same components
Stars can be of different colours: Blue, white, red and
even gold.
The sun is a dwarf star
If we coud travel to the nearest star, it would take more
than 70.000 years
PERSONAL
ASSESMENT
PERSONAL
ASSESMENT
In my opinion, this is a very interesting and important
t erm fo r s t u dy, b ecaus e i t ' s v ery b eau t i ful t o see how a
star evolve and is vey important.
With this knowledge we can know when a star is going to
explode or when it will disappear, which would allow us to
predict the explosion and take advantage of it.
Bibliography
https://science.nasa.gov/astrophysics/focus-areas/how-do-stars-form-and-evolve
Some pages of Wikipedia
Some bocks of the space
Questions
• 1. What's the stellar evolution
• 2. Phases of the evolution of a star
• 3. Diferences between a Nova and a Supernova
The
You might also like
- Arihant NCERT Notes India & World Geography - Nihit KishoreDocument369 pagesArihant NCERT Notes India & World Geography - Nihit Kishoreakpatel191182% (11)
- The Life Cycle of StarsDocument6 pagesThe Life Cycle of StarsMary100% (1)
- Ars WorksheetDocument8 pagesArs WorksheetadamgonoloNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A Star NotesDocument10 pagesLife Cycle of A Star NoteslyraNo ratings yet
- English AssignmentDocument4 pagesEnglish AssignmentBrylle Jairus LacamenNo ratings yet
- Research EnglishDocument7 pagesResearch EnglishBrylle Jairus LacamenNo ratings yet
- Stellar EvolutionDocument21 pagesStellar EvolutionJohn Reign Matanguihan100% (1)
- Stellar EvolutionDocument13 pagesStellar EvolutionJayeeta DasNo ratings yet
- Star and Planet FormationDocument18 pagesStar and Planet Formationatul mishraNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report. Stellar EvolutionDocument11 pagesNarrative Report. Stellar Evolutionclarenceegliane204No ratings yet
- Stars and Contellations 1Document13 pagesStars and Contellations 1api-410254072No ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A StarDocument22 pagesLife Cycle of A Starေအာင္ ေက်ာ္ စြာNo ratings yet
- Stellar Evolution - The Birth, Life, and Death of A StarDocument2 pagesStellar Evolution - The Birth, Life, and Death of A StarKaiNo ratings yet
- Astronomy For Kids: StarsDocument2 pagesAstronomy For Kids: StarsOlga Faith BinsonNo ratings yet
- 2021 Worksheet - Life of Stars Amended To Fill inDocument4 pages2021 Worksheet - Life of Stars Amended To Fill inLNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A Star - WorksheetDocument4 pagesLife Cycle of A Star - WorksheetLNo ratings yet
- The StarsDocument19 pagesThe StarsCataSalvàNo ratings yet
- Stars and ConstellationsDocument80 pagesStars and ConstellationsjachinjavaleraNo ratings yet
- SupernovaDocument2 pagesSupernovaveena bhatNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle of A Star - World General Knowledge SeriesDocument3 pagesThe Life Cycle of A Star - World General Knowledge SeriesRida khan khanNo ratings yet
- SupernovaDocument7 pagesSupernovaAndreaNo ratings yet
- Spectral Type Mass (Xsun) Surface Temperature (K) Luminosity (Xsun) Radius (Xsun)Document3 pagesSpectral Type Mass (Xsun) Surface Temperature (K) Luminosity (Xsun) Radius (Xsun)mir696100% (1)
- Life Span of Stars OutlineDocument3 pagesLife Span of Stars OutlinewendelNo ratings yet
- Black Holes: The Story of Collapsing Stars. First Edition. Pankaj S. JoshiDocument20 pagesBlack Holes: The Story of Collapsing Stars. First Edition. Pankaj S. Joshiarshivaji100% (1)
- Star Formation ArticleDocument4 pagesStar Formation Articlemarkjayrecto17No ratings yet
- AST Assignment 6Document6 pagesAST Assignment 6ramiresc76No ratings yet
- TitkeDocument16 pagesTitkeZahid ShahNo ratings yet
- Evolution of StarsDocument3 pagesEvolution of StarsCln CatadNo ratings yet
- Classification of StarsDocument6 pagesClassification of StarsAnonymous N3VvjVSTATNo ratings yet
- Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument29 pagesStars and Galaxies in The UniverseINSYIRAH BINTI M ZAIRURLAIL 105No ratings yet
- Example 2Document16 pagesExample 2oscar.feng2No ratings yet
- Life Cycke of Star InformationDocument14 pagesLife Cycke of Star InformationJasmineNo ratings yet
- D Earth and Space (Structure of The Universe)Document30 pagesD Earth and Space (Structure of The Universe)Mg AikeNo ratings yet
- Stars and GalaxiesDocument4 pagesStars and Galaxiesmuhesidavid70No ratings yet
- Protostar Looks Like A Star But Its Core Is Not Yet Hot Enough For Fusion To Take PlaceDocument4 pagesProtostar Looks Like A Star But Its Core Is Not Yet Hot Enough For Fusion To Take PlaceAira TorrenteNo ratings yet
- Cbl-Threshold #2-Stars-And-ElementsDocument54 pagesCbl-Threshold #2-Stars-And-ElementsBarangay TalisayNo ratings yet
- Outer SpaceDocument3 pagesOuter Spacemeilan.lanie82No ratings yet
- Science 5 - Stars - Worksheet 1 - 4th QuarterDocument3 pagesScience 5 - Stars - Worksheet 1 - 4th QuartercharmaineNo ratings yet
- 10sci Nms Star Trekking Assignment 2015Document6 pages10sci Nms Star Trekking Assignment 2015api-301135290No ratings yet
- Indian Space Research Organisation:: StarDocument4 pagesIndian Space Research Organisation:: StarKishore RaveendiranNo ratings yet
- Stellar Evolution: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesStellar Evolution: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchMikko RamiraNo ratings yet
- Planets and Solar System The Complete Manual 2016Document132 pagesPlanets and Solar System The Complete Manual 2016Sonechka Sonya100% (3)
- 6 2 2-StarsDocument4 pages6 2 2-StarsCK LimNo ratings yet
- Articulo de DivulgacionDocument5 pagesArticulo de DivulgacionLucero BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Astronomy by IcspeDocument3 pagesAstronomy by IcspeicspeplaysNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Text QuestionsDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Text QuestionsTori HubbardNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycles of Stars Part IIDocument4 pagesThe Life Cycles of Stars Part IIYassmine El HusseinyNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A StarDocument8 pagesLife Cycle of A StarHriditi HowladerNo ratings yet
- Life and Death of A StarDocument5 pagesLife and Death of A StarPooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- Star Child 5Document27 pagesStar Child 51sdaasfdasNo ratings yet
- Techzo InfoDocument3 pagesTechzo Infoshivikaraksha2109No ratings yet
- Stars and GalaxiesDocument23 pagesStars and GalaxiesSyahidah SalehNo ratings yet
- L 6 UniverseDocument11 pagesL 6 UniverseAbhay NayakNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - ConstellationsDocument4 pagesScience 9 - ConstellationsJOSHUA CABIGAYANNo ratings yet
- How The Universe, Solar System and Earth Began: Robin Oliver B. MagsombolDocument7 pagesHow The Universe, Solar System and Earth Began: Robin Oliver B. MagsombolsiennNo ratings yet
- 14 Fun Facts About Stars: A 15-Minute BookFrom Everand14 Fun Facts About Stars: A 15-Minute BookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Supernova: Nova (Plural Novae) Means "New" inDocument16 pagesSupernova: Nova (Plural Novae) Means "New" inlyn_celzNo ratings yet
- Supernovae Nasa Imagine ArticleDocument1 pageSupernovae Nasa Imagine Articleapi-26963416No ratings yet
- Student's Guide To Year 9 and 10 Science (Stage 5)Document38 pagesStudent's Guide To Year 9 and 10 Science (Stage 5)dan964100% (1)
- SLOOH Completed Report - Quest Lifecycle - of - Stars-Quest - ReportDocument38 pagesSLOOH Completed Report - Quest Lifecycle - of - Stars-Quest - ReportBrandi Burchell-LeedomNo ratings yet
- Folio Sofea (Space An Stars)Document14 pagesFolio Sofea (Space An Stars)ilamegatNo ratings yet
- Stars and GalaxiesDocument23 pagesStars and GalaxiesSyahidah SalehNo ratings yet
- Smarter Every Day Facts, Trivia, General Knowledge (Elsmere Gracey) (Z-Library)Document175 pagesSmarter Every Day Facts, Trivia, General Knowledge (Elsmere Gracey) (Z-Library)flame77ofc3No ratings yet
- The Harmony of The SphereDocument30 pagesThe Harmony of The SphereRizzo Davide AntonioNo ratings yet
- How It Works - Issue 181 2023Document100 pagesHow It Works - Issue 181 2023eray100% (1)
- PresentationDocument52 pagesPresentationWafuwafuNo ratings yet
- Module 2 AnswersDocument15 pagesModule 2 AnswersIsmail Medhat SalahNo ratings yet
- The Creation of The Elements PowerpointDocument23 pagesThe Creation of The Elements PowerpointMimiento SearNo ratings yet
- 2016 Atpss Written Exam Paper Ans v5Document4 pages2016 Atpss Written Exam Paper Ans v5flyordieNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Astrophysics 2nd Edition Baidyanath Basu 2024 Scribd DownloadDocument58 pagesAn Introduction To Astrophysics 2nd Edition Baidyanath Basu 2024 Scribd Downloadrinmanimai100% (2)
- Astronomy EssayDocument1 pageAstronomy Essayapi-272544257No ratings yet
- GalaxiesDocument177 pagesGalaxieslavinianda100% (4)
- A History of The Solar System (Gnv46)Document110 pagesA History of The Solar System (Gnv46)German Alejandro Diaz100% (4)
- Sase Booster 2024 Science Module 1Document4 pagesSase Booster 2024 Science Module 1Teresita HeyasaNo ratings yet
- HUMBOLDT, Alexander Von. Cosmos Vol.4Document343 pagesHUMBOLDT, Alexander Von. Cosmos Vol.4Diego MontenegroNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Astrophysics NotesDocument26 pagesHSC Physics Astrophysics NotesjackmaloufNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 F2 Stars and GalaxiesDocument35 pagesChapter 11 F2 Stars and GalaxiesBernard67% (3)
- Constituents and StructuresDocument18 pagesConstituents and StructuresHassan BareachNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: Bsc. (Hons.) PhysicsDocument12 pagesTerm Paper: Bsc. (Hons.) PhysicsRigved SharmaNo ratings yet
- Under The Soil (ZEN)Document6 pagesUnder The Soil (ZEN)MM NabeelNo ratings yet
- ABC Geology Book: By: Allison CramerDocument27 pagesABC Geology Book: By: Allison CramerAllison CramerNo ratings yet
- Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument8 pagesOrigin and Structure of The EarthRobin Suarez ViladoNo ratings yet
- 404 Passage 1 The Life Cycle of A StarDocument4 pages404 Passage 1 The Life Cycle of A StarAj AvtarNo ratings yet
- Reviews Synta (120 MM F8.3 and 150 MM F5) .Document1 pageReviews Synta (120 MM F8.3 and 150 MM F5) .Giannis TheodorouNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 Chapter 9 - Stars and Galaxies PDFDocument3 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 9 - Stars and Galaxies PDFFarah Sofea Razali100% (1)
- Spectroscopic Atlas 4.0Document177 pagesSpectroscopic Atlas 4.0Marco Aurelio MinozzoNo ratings yet