0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsVirtulization
Virtulization
Uploaded by
swapnita.srivastavavirtulization cloud computing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Virtulization
Virtulization
Uploaded by
swapnita.srivastava0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views29 pagesvirtulization cloud computing
Original Title
virtulization
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
virtulization cloud computing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views29 pagesVirtulization
Virtulization
Uploaded by
swapnita.srivastavavirtulization cloud computing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 29
Virtualization
Modern computing is more
efficient due to virtualization
Lets think like this
• Have you ever wished you could clone
yourself?
• If you could, would you be more efficient?
Would you do more?
• Virtualization enables computers to be more
efficient in a similar fashion
• Computers that use virtualization optimize
the available compute resources
Lets ponder on this...
• Do you use a smartphone, laptop or home
computer?
• Smartphones, laptops or home computers
are hardware
• Similar to how your brain controls your
actions, software controls hardware
• There are different types of software that
control computer actions
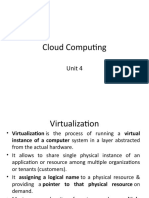
What is a VM
• Virtualization creates virtual hardware by
cloning physical hardware
• The hypervisor uses virtual hardware to
create a virtual machine (VM)
• A VM is a set of files
• With a hypervisor and VMs, one computer
can run multiple OS simultaneously
Terminologies
• Host Operating System: The operating system via which the
Virtual Machines are run. For Type 1 Hypervisors, as in Hyper-V, the
hypervisor itself is the Host OS which schedules the virtual
machines and allocates memory. For Type 2 hypervisors, the OS on
which the hypervisor applications run is the Host OS.
• Guest Operating System: The operating system that uses
virtualized hardware. It can be either Fully Virtualized or Para
Virtualized. An enlightened guest OS knows that its a virtualized
system which can improve performance.
• Virtual Machine Monitor: VMM is the application that virtualizes
hardware for a specific virtual machine and executes the guest OS
with the virtualized hardware.
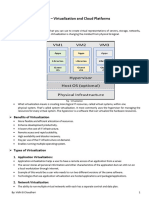
Concepts
• Virtualization is technology that allows you to
create multiple simulated environments or
dedicated resources from a single, physical
hardware system.
• Software called a hypervisor connects directly
to that hardware and allows you to split 1
system into separate, distinct, and secure
environments known as virtual machines (VMs).
Hypervisors
• A hypervisor is a process or a function to isolate operating
system and applications from the underlying hardware.
• Though virtual machines operate on the same physical
hardware, they are separated from each other. This also
depicts that if one virtual machine undergoes a crash, error,
or a malware attack, it doesn't affect the other virtual
machines.
• Another benefit is that virtual machines are very mobile as
they don't depend on the underlying hardware. Since they
are not linked to physical hardware, switching between local
or remote virtualized servers gets a lot easier as compared
to traditional applications.
Types of Hypervisor
• A type-I hypervisor operates directly on the
host's hardware to monitor hardware and
guest virtual machines, and it's referred to
as the bare metal.
• A type-II, also called a hosted hypervisor
because it is usually installed onto an
existing operating system. They are not
much capable to run more complex virtual
tasks. Used for basic development, testing,
and emulation.
Differences
What's the difference between virtualization and cloud
computing?
• It's easy to confuse the two, particularly because they
both revolve around separating resources from hardware
to create a useful environment. Virtualization helps create
clouds, but that doesn't make it cloud computing. Think
about it like this:
• Virtualization is a technology that separates functions
from hardware
• Cloud computing is more of a solution that relies on that
split
X86 Virtualization
• x86 virtualization refers to hardware and
software-based mechanisms to support
virtualization for processors based on the
x86 architecture . Using a hypervisor , it
allows several operating systems to be run in
parallel on an x86 processor and resources to
be distributed in an isolated and efficient
manner between the operating systems
running in parallel.
• In order to be able to allocate resources exclusively to the guest
systems running in parallel, only the host operating system or
the hypervisor may be granted direct access to the processor
hardware, while the guest systems, like all other applications,
may only have limited access rights to the hardware. In
particular, it can be prevented that the guest systems can see or
change memory areas that the hypervisor needs for
management.
• The protected mode was introduced in the x86 world . With it,
four different protection levels or privilege levels, known as
rings, were introduced, which grant the code segments running
on them different rights. Only with the introduction of this
concept was it possible to implement virtualization based on the
x86 architecture: In protected mode, the operating system kernel
runs in a more privileged mode, called Ring 0 , and applications
in a less privileged mode, in usually either ring 1 or ring 3.
• The hypervisor or the host
operating system are
executed with ring 0
authorization due to their
privileged position in
resource management. In
order to guarantee the
protection of the
hypervisor resources, guest
systems must therefore be
run either at authorization
level Ring 1 (in the so-
called Ring 3.
Types of Hardware Virtualization
• Full Virtualization
• Para-virtualization
• Hardware Assisted Virtualization
What to change
• Based on how much change is required and at
what level
• Categories
– Modified Guest OS
• Operating system level
• Para-virtualization.
– Unmodified Guest OS
• Binary Translations
• Hardware assisted
Full virtualization
• In this scenario, data is completely abstracted from the underlying
hardware by the virtualization layer. In this technique guest, OS is
unaware that it is a guest and hypervisor translate all OS calls on-the-fly.
It provides flexibility and no hardware assistance or modification is
required.
• The advantages of full virtualization are that the emulation layer isolates
VMs from the host OS and from each other. It also controls individual VM
access to system resources, preventing an unstable VM from impacting
system performance.
• It also provides the total VM portability by emulating a consistent set of
system hardware, VMs have the ability to transparently move between
hosts with dissimilar hardware without any problems. The products
support this virtualization are VMware, Microsoft, and KVM.
Para Virtualization
• It is an enhancement of virtualization technology in which a
guest OS is recompiled prior to installation inside a virtual
machine. In para-virtualization, the guest OS is modified to
enable communication with the hypervisor to improve
performance and efficiency.
• Its advantages are that the guest system comes closer to
native performance than a fully virtualized guest and also it
does nor require the latest virtualization CPU support. It also
allows for an interface to the virtual machine that can differ
somewhat from that of the underlying hardware.
• VMware and Xen are supported by this type of virtualization.
Hardware-assisted Virtualization
• In enables full virtualization with help of utilizing of a
computer’s physical components to support the software that creates
and manages virtual machines. In this technique of virtualization
unmodified guest is OS and no API are made. The sensitive calls are
trapped by the hypervisor and in 2006 it was added to x86 processors
(Intel VT-x or AMD-V).
• The products supporting hardware-assisted virtualization are VMware,
Xen, Microsoft, and Parallels.
• There is additionally a mix of para-virtualization and full virtualization
called Hybrid Virtualization where parts of the visitor working on
paravirtualization for certain hardware drivers, and the host utilizes full
virtualization for different highlights. This frequently delivers prevalent
execution on the visitor without the requirement for the visitor to be
totally par- virtualized.
Comparisons
PARA HARDWARE
FULL
PARAMETER VIRTUALIZATIO ASSISTED
VIRTUALIZATION
N VIRTUALIZATION
Generation 1st 2nd 3rd
Better in certain
Performance Good Fair
cases
VMware, Xen,
VMware,
Used By VMware, Xen Microsoft,
Microsoft, KVM
Parallels
Guest OS Codified to issue
Unmodified Unmodified
modification hypercalls
Guest OS XenLinux runs
hypervisor Yes only on Yes
independent? Hypervisor
Exit to root mode
Technique Direct execution Hypercalls on privileged
Types of Virtualization
• Apart from hardware
virtualization, other types of
virtualization include:
» Application Virtualization
» Data Virtualization
» Desktop Virtualization
» Network Virtualization
» Server Virtualization
» Storage Virtualization
Application virtualization
• The process of installing an
application on a central
server (single computer
system) that can virtually be
operated on multiple systems
is known as application
virtualization. For end users,
the virtualized application
works exactly like a native
application installed on a
physical machine. With
application virtualization, it’s
easier for organizations to
update, maintain, and fix
• Virtualizing an app allows for seamless use for the end-user,
making it possible for the employee to work remotely with
the same key programs installed in the office. When
virtualized, apps work in what is called a sandbox, an
environment that runs separately from the operating system.
While operating in this sandbox, any changes will appear to
run in the operating system, though the app is pulling
operating power from the sandbox.
• There are two distinct kinds of application virtualization:
– Remote applications run on a server that mimics the
user desktop and can be accessed by authorized users
regardless of their location.
– Streaming apps run just one instance on the server and
provide local access to the app.
• Remote app streaming is the more popular approach, thanks
to the extended reach it grants.
• With just one instance of the app to manage and fix, an
Data Virtualization
• Data virtualization is a data
management approach. It
retrieves, segregates,
manipulates, and delivers
data without any data
specifications.
• Any technical details of the
data like its exact location
and formatting information
are not needed to access it.
It allows the application to
get a singular view of the
overall data with real-time
access.
• Data virtualization software
helps with data warehouse
Desktop virtualization
• Creating a virtual desktop infrastructure, or
VDI, makes it possible to work and store
files in locations that everyone in your team
can easily access no matter where they
work.
• Desktop virtualization allows people to
access multiple applications and operating
systems (OS) on a single computer because
the applications and OSs are installed on
virtual machines that run on a server in the
data centre.
• When it comes to desktop
virtualization, there are two main
methods: local and remote. Local and
remote desktop virtualization are both
possible depending on the business needs.
Network virtualization
• Network virtualization helps manage and monitor the
entire computer network as a single administrative
entity. Admins can keep a track of various elements of
network infrastructure such as routers and switches
from a single software-based administrator’s console.
Network virtualization helps network optimization for
data transfer rates, flexibility, reliability, security, and
scalability. It improves the overall network’s
productivity and efficiency. It becomes easier for
administrators to allocate and distribute resources
conveniently and ensure high and stable network
performance.
Server virtualization
Server virtualization is a process of
partitioning the resources of a single
server into multiple virtual servers.
These virtual servers can run as
separate machines. Server
virtualization allows businesses to run
multiple independent OSs (guests or
virtual) all with different configurations
using a single (host) server. The process
also saves the hardware cost involved in
keeping a host of physical servers, so
businesses can make their server
infrastructure more streamlined.
Storage virtualization
• Storage virtualization performs resource
abstraction in a way that the multiple
physical storage arrays are virtualized as a
single storage pool with direct and
independent access.
• The storage virtualization software
aggregates and manages storage in various
storage arrays and serves it to applications
whenever needed.
• The centralized virtual storage increases
flexibility and availability of resources
needed. This data virtualization and
centralization is easily manageable from a
central console. It allows users to manage
and access multiple arrays as a single
storage unit.
You might also like
- Virtualization Technologies ResarDocument38 pagesVirtualization Technologies Resarkhadidja khadidja100% (1)
- Data Virtuality Best PracticesDocument18 pagesData Virtuality Best PracticesДмитрий МитрофановNo ratings yet
- Infoscale Licensing GuideDocument13 pagesInfoscale Licensing Guideakkati123100% (2)
- Unit 1 Continued 1Document29 pagesUnit 1 Continued 1adamaloudi2017No ratings yet
- Unit1 VirtualizationDocument35 pagesUnit1 VirtualizationBhumika BiyaniNo ratings yet
- Unit1 VirtualizationDocument38 pagesUnit1 VirtualizationdsklfhkshfNo ratings yet
- Unit1 VirtualizationDocument35 pagesUnit1 VirtualizationRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document26 pagesModule 2TECH TEAMNo ratings yet
- x86 Support for VirtualizationDocument8 pagesx86 Support for VirtualizationTheodore YimoNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Part-1Document84 pagesUnit-2 Part-1prateekpuranik3No ratings yet
- VirtualizationDocument28 pagesVirtualization2000520310061No ratings yet
- VirtulizationDocument21 pagesVirtulizationraja usama201No ratings yet
- Virtual IzationDocument6 pagesVirtual IzationG.LAKSHIMIPRIYA Dept Of Computer ScienceNo ratings yet
- CC Unit 2-1Document7 pagesCC Unit 2-1zdnvhxsjrbhtymyafkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Virtualization TechniquesDocument28 pagesLecture 2 Virtualization TechniquesShahad ShahulNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-3Document201 pagesUnit 1-3ranvee01No ratings yet
- CC New VirtulizationDocument48 pagesCC New VirtulizationUnnatii PimpleeNo ratings yet
- 5 Virtualization Structure Tools and MechanismsDocument71 pages5 Virtualization Structure Tools and MechanismsSaravanaKumar MNo ratings yet
- VirtualizationDocument25 pagesVirtualizationMalajebamaniraj MalaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Unit 4 Part 1Document24 pagesCloud Unit 4 Part 1Kanu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Virtualization TechniquesDocument22 pagesVirtualization TechniquesrashmiNo ratings yet
- u 2 bDocument30 pagesu 2 bshivamkashid70No ratings yet
- A1386673771 17671 22 2020 Lecture1-21 PDFDocument201 pagesA1386673771 17671 22 2020 Lecture1-21 PDFMinnakanti Sai Venkata PavanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VirtualizationDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Virtualizationmyou99483No ratings yet
- u 2 aDocument15 pagesu 2 ashivamkashid70No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document9 pagesUnit 1Saurabh TewariNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Unit3Document58 pagesCloud Computing Unit3sudipNo ratings yet
- Vir TypesDocument13 pagesVir Types23mz02No ratings yet
- 4-Implementation Levels-04-09-2023Document46 pages4-Implementation Levels-04-09-2023184609No ratings yet
- Class 2Document34 pagesClass 2Hanar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Virtualization: Ambrish GangalDocument32 pagesVirtualization: Ambrish Gangalnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document38 pagesUnit 4Mohd NadimNo ratings yet
- Hardware & Software VirtualizationDocument15 pagesHardware & Software Virtualizationshifa fatimaNo ratings yet
- Virtualization TechnologiesDocument30 pagesVirtualization Technologiesrpschauhan2003No ratings yet
- unit1 and unit 2Document201 pagesunit1 and unit 2Kunal KumarNo ratings yet
- Virtualization ServerDocument45 pagesVirtualization ServerVasshiniNo ratings yet
- CC (Hypervisor) 2Document18 pagesCC (Hypervisor) 2Ravindra KumarNo ratings yet
- CS3 - Virtualization ContinuedDocument54 pagesCS3 - Virtualization ContinuedAsmita KandarNo ratings yet
- L-wk13Document48 pagesL-wk13pomkarbe22No ratings yet
- Virtualization (Autosaved)Document59 pagesVirtualization (Autosaved)Sakshi KakadeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To VirtualizationDocument29 pagesIntroduction To VirtualizationUzair MayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Lec 4 Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesUnit 2 Lec 4 Cloud ComputingManvendraNo ratings yet
- Lect4 VirtualizationDocument78 pagesLect4 VirtualizationManish DasNo ratings yet
- Virtualization StructuresDocument73 pagesVirtualization Structuresmohanapraba.82102092No ratings yet
- Full VirtualizationDocument4 pagesFull VirtualizationMuhammad Taha AamirNo ratings yet
- Virtualisation SecurityDocument5 pagesVirtualisation SecurityGRD JournalsNo ratings yet
- VirtualizationDocument12 pagesVirtualization21UCS146 Ankita DasNo ratings yet
- VirualisatonDocument14 pagesVirualisatonyorukage29No ratings yet
- Unit Ii Virtualization BasicsDocument24 pagesUnit Ii Virtualization Basicssobowo7302No ratings yet
- 18mcs35e U3Document26 pages18mcs35e U3Vikas AgrohiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Virtual IzationDocument35 pages1 Virtual IzationAyan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Virtualization and Cloud ComputingDocument51 pagesVirtualization and Cloud ComputingDr. Manish T INo ratings yet
- Group 4 Day (Hypervisors)Document9 pagesGroup 4 Day (Hypervisors)Micheal OwenNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Introduction IT Resource ManagementDocument29 pagesChap 1 Introduction IT Resource ManagementMuhammad Sharif HaiderNo ratings yet
- Lec 7Document19 pagesLec 7hw70835No ratings yet
- Types of VirtualizationnDocument32 pagesTypes of VirtualizationnZeyRoX GamingNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Virtualization CCDocument73 pagesUNIT 2 Virtualization CCjetowi8867No ratings yet
- Unit - 3Document32 pagesUnit - 3blackdeathshNo ratings yet
- INTRODocument8 pagesINTROdarshita singhNo ratings yet
- How To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationFrom EverandHow To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationNo ratings yet
- Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V: Deploying Hyper-V Enterprise Server Virtualization PlatformFrom EverandWindows Server 2012 Hyper-V: Deploying Hyper-V Enterprise Server Virtualization PlatformNo ratings yet
- NutanixDocument43 pagesNutanixkailash.mcseNo ratings yet
- EVE Comm BOOK 5.0 2022Document150 pagesEVE Comm BOOK 5.0 2022teamleaderNo ratings yet
- Vsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 602 Host Management GuideDocument200 pagesVsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 602 Host Management GuideMunib AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Recover Point Implementation Lab Guide Supplementv3.2Document43 pagesRecover Point Implementation Lab Guide Supplementv3.2mlinarecNo ratings yet
- IM IT Tools 2023 PDFDocument97 pagesIM IT Tools 2023 PDFArvie LorenzoNo ratings yet
- AzureDocument23 pagesAzureNagaraj RNo ratings yet
- 27.1.5 Lab - Convert Data Into A Universal FormatDocument9 pages27.1.5 Lab - Convert Data Into A Universal Formatbui lamNo ratings yet
- Alphavm Um 1 3 9 Windows PDFDocument22 pagesAlphavm Um 1 3 9 Windows PDFMan CangkulNo ratings yet
- Grid Architecture and Relationship To Other Distributed TechnologiesDocument24 pagesGrid Architecture and Relationship To Other Distributed TechnologiesWaqarAhmadAlvi67% (3)
- AzureDocument8 pagesAzureAhmed AljaberiNo ratings yet
- Vsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 60 Installation Setup GuideDocument272 pagesVsphere Esxi Vcenter Server 60 Installation Setup Guidesorachut1989No ratings yet
- Testng TutorialDocument68 pagesTestng TutorialRamya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- ACC Lead TemplateDocument12 pagesACC Lead Templatepankhuri.singhNo ratings yet
- Citrix Xenserver® 6.5 and Emc™ Xtremio™ All-Flash-ArrayDocument17 pagesCitrix Xenserver® 6.5 and Emc™ Xtremio™ All-Flash-ArrayYang WangNo ratings yet
- Vrealize Operations Manager 75 Config GuideDocument672 pagesVrealize Operations Manager 75 Config GuideAldi YulioNo ratings yet
- Wincc Virtualizadores StandardsDocument41 pagesWincc Virtualizadores StandardsRafael DavidNo ratings yet
- Question 5.20Document11 pagesQuestion 5.20Emiliano DittlerNo ratings yet
- Morris AttackDocument48 pagesMorris Attackpunzango73No ratings yet
- Edu en Vsanft7 Lab SeDocument121 pagesEdu en Vsanft7 Lab SeBenzakour MouadNo ratings yet
- Oracle RAC InstructionsDocument18 pagesOracle RAC Instructionsmlazar20009720100% (1)
- AZ-500 SyllabusDocument4 pagesAZ-500 Syllabusmanishraja4uNo ratings yet
- Horizon Architecture PlanningDocument113 pagesHorizon Architecture PlanninghgergesNo ratings yet
- Ds Nutanix FlowDocument2 pagesDs Nutanix FlowKim Fuk LieNo ratings yet
- Cortex XDR Setup Guide: September 2019Document28 pagesCortex XDR Setup Guide: September 2019Jimmy Alfaro HernandezNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report On Virtualization Techniques in Cloud - ComputingDocument33 pagesA Seminar Report On Virtualization Techniques in Cloud - ComputingParth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Emulation of Iec 60870 5 104 Communication in DigitalDocument12 pagesDokumen - Tips - Emulation of Iec 60870 5 104 Communication in DigitalalextivanNo ratings yet
- Guide Lab CloudDocument115 pagesGuide Lab CloudagussNo ratings yet
- Informatica Enterprise Grid On Vmware: Deployment GuideDocument20 pagesInformatica Enterprise Grid On Vmware: Deployment GuideAlaka KondaNo ratings yet