Customer Satisfaction
Chapter Three
�Introduction
Customers- the most important asset Organizations success depends upon: --how many customers it has --how much they buy --how often they buy
Satisfied customers will increase in number, buy more and buy more frequently
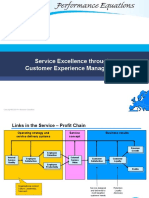
Customer satisfaction organizational diagram.
�Introduction
Customer satisfaction is one the greatest purpose of any QMS. Quality products/ services at a reasonable price customers To achieve this state, QMS should be continually examined to see if its responsive to ever-changing needs of customers. Customer satisfaction should be the primary goal instead of profit seeking.
�Introduction
Dr. Deming added that quality also means anticipating the future needs of the customer. Teboul model (Customer satisfaction model) Customer satisfaction is subjective( more like a feeling or attitude), so its hard to measure. Teboul model flaws When surveying customers, views about competitors product can be beneficial to see the customer loyalty.
�Who is the customer?
Two distinct types internal and external
An external customer can be defined in many ways:
--the one who uses the product/ service --the one who purchases the product/ service --the one who influences the sale of product/ service e.g. McDonald's happy meal. Three categories- current, prospect and lost customers Internal customers
�Customer- Supplier chains
Inputs from external suppliers
Internal customers
Outputs to external customers
What do you need from me? What do you do with my output? Are there any gaps between what you need and what you get?
�Customer Satisfaction
Customers perception of quality
�Customers perception of quality
ASQ survey on end user perceptions of important factors that influenced purchase decision:
Performance
Features
Service warranty Price reputation
�Performance
Fitness for use- the product and service is ready for customers use at the time of sale. Other considerations are:
Availabilitythe product will operate when needed
Reliabilitythe quality of being dependable Maintainabilityease of keeping the product operable
�Features
Features are secondary attributes of the product
E.g. car-stereo system
Remote control
�Service
Customer service is an intangible Intangible characteristics are not quantifiable yet contribute greatly to customer satisfaction. Providing excellent customer service is different from and difficult to achieve than excellent product quality. E.g. hospital, telecommunication sector, hotel
�Warranty
Difference between guarantee and warranty
The warranty encourages customer to buy a service by reducing the risk of the purchase decision. E.g. Mobile warranties, t.v
�Benefits of warranty
It forces the organization to focus on the customers definition of product and service quality. Warranty generates feedback by providing information on product and service quality. It forces an organization to develop a corrective action system. The warranty encourages customers to buy a product or service by reducing the risk of purchase decision It generates more sales from existing customers by enhancing loyalty.
�Price
Todays customer is willing to pay a higher price to obtain value. An amount, as of goods, services, or money, considered to be a fair and suitable equivalent for something else; a fair price or return. Customers seek who provides the greatest value.
Concept of value varies from person to person.
�Reputation
We rate organizations by our over all experience with them Total customer satisfaction is based on the entire experience not just product. Good experiences are repeated to six 6 people and bad experiences are repeated to 15 people.
�Feedback
The voice of the customer
�Benefits of Feedback
It enables the organization to: Discover customer dissatisfaction Discover relative priorities of quality Compare performance with competitors Identify customers Determine opportunities for improvement
�Information collecting Tools and techniques
Comment cards Customer questionnaire Focus groups Toll-free numbers Customer visits Report card Internet and computers Employee feedback Mass customization
��Comment cards
Low- cost method Can be attached to warranty card and included with the product
The intent is to have simple information
Generally people report back to the company if something very bad or extra-ordinary happened. Hotels, restaurants, petrol pumps etc
�Customer questionnaire
Costly and time consuming Administered by mail or telephone
Typical 1-5 or 1-10 scale approach
1-5 scale approach flaws
�Mail administered surveys
Its best to remember eight points: Clients and customers arent the same. Surveys raise customer expectations How you ask question will determine how the question is answered.
The more specific the question, the better the answer.
�Mail administered surveys
You have only one chance and only 15 minutes The more time you spend in survey development, the less time you will spend in data analysis and interpretation. Who you ask is as important as what you ask.
Before the data is collected, you should know how you want to analyze and use the data.
�Telephone administered surveys
Rapidly changing telecommunications Gallup 800 surveyautomated and voice gathering polling service. Organizations can now effectively reach large populations, analyze the results quickly and determine what their customer are thinking on a nearly real-time basis
�Focus Groups
�Focus groups
Very expensive Very effective for gathering information on customer expectations and requirements
Customers are asked structured questions by a skill moderator.
Meetings are designed to focus on current, proposed and future products and services Imprint analysisto analyze the intrinsic feelings of a customere.g. ice cream company
�Toll-free numbers (800/888)
Organization can respond faster and cheaply to the complaints. Implementation of toll- free numbers have grown tremendously E.g Cadillac division of general motors have 24 toll-free numbers for 24 hours road service
�Customer visits
Usually in a B-2-B environment Senior managers should visit the customers and shouldnt delegate the visits to any one else. Taking operational personal with senior managers however is an effective way. E-g U.S steel and Ford motors
�Report cards
Usually sent to each customer on a quarterly basis The data is analyzed to determine areas for improvement. e.g. university of California using report cards for its campus business services like bookstore
�Internet and computers
Timely, cost minimal and source of creative ideas Monitoring the discussions of customers on internet Management shouldnt intervene Some third-party web sites ([Link]) Organizational websites (e-mails)
�Employee feedback
Timely and cost-effective than customer surveys
Brainstorming sessions to find out solutions to the complaints
E.g. Chrysler motors
�Mass customization
Giving customers exactly what they want. Way to provide variety at an affordable cost.
Direct result of advances in manufacturing such as flexible manufacturing technologies, JIT and cycle-time reduction. E.g Levi Strauss jeans, dell computers
�Using customer complaints
How to handle customer complaints?
�How to handle customer complaints?
Investigate customer experiences by actively soliciting feedback, both +ve and ve and then acting on it promptly.
Develop procedures for complaint resolution that include empowering front-line people.
Analyze complaints but understand that complaints dont always fit into neat categories.
Work to identify process and material variations and then eliminate the root cause. More inspection is not corrective action. When a survey response is received, a senior manager should contact the customer to resolve the issue
�How to handle customer complaints?
Establish customer satisfaction measures and constantly monitor them Communicate complaint information as well as results to all personnel Provide a monthly complaint report to the quality council Identify customers expectations before the complaints rather than after complaint analysis.
�Service Quality
�Customer service
Customer service is the set of activities uses to win or retain customer satisfaction. It can be provides before, during and after the sale of the product. Elements of customer service are: organization, customer care, communication, front-line people and leadership.
�Organization
Identify each market segment Write down the requirements
Communicate the requirements
Organize processes
Organize physical spaces
�Customer care
Meet the customers expectations
Get the customers point of view
Deliver what is promised
Make the customer feel valued
Respond to all complaints Over-respond to the customer Provide a clean and comfortable customer reception area
�Communication
Optimize the trade-off between time and personal attention Minimize the number of contact points Provide pleasant, knowledgeable and enthusiastic employees
Write documents in a customer-friendly language
�Front-line people
Hire the people who like people Challenge them to develop better methods
Give them the authority to solve problems
Serve them as internal customers Be sure they are adequately trained Recognize and reward performance
�Leadership
Lead by example Listen to the front-line people
Strive for continuous process improvement
�Customer Retention
�Customer retention
Customer retention is more powerful and effective than customer satisfaction. Customer satisfaction surveys, questionnaire, interviews, focus groups etc show what customers think of the product or service. What people say and think is often different from what they actually do.
�Customer retention
Customer satisfaction should also be measured by cash register receipts, market share, level of customer retention and number of referrals from customer. Customer satisfaction is the connection between customer satisfaction and the bottom line---net income is informally called bottom line Employee retention