Transducers & transmitters
- 1. Transducers & Transmitters By Mahnoor Butt M12-CE16
- 2. Transducers Transducers are electric or electronic devices that transform energy from one form to another. For Example: microphones, loudspeakers, thermometers, position and pressure sensors, and antenna.
- 4. Transducer Elements Sensing element Transduction element Transducer contains two parts that are closely related to each other i.e. the sensing element and transduction element.
- 5. Sensing element The sensing element is called as the sensor. It is device producing measurable response to change in physical conditions. A microphone converts sound waves that strike its diaphragm into an electrical signal that can be transmitted over wires.
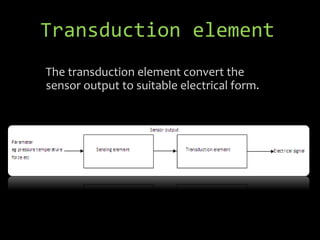
- 6. The transduction element convert the sensor output to suitable electrical form. Transduction element
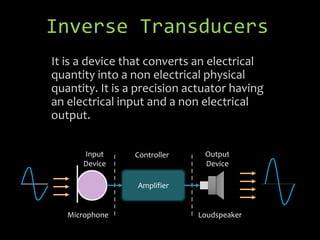
- 7. It is a device that converts an electrical quantity into a non electrical physical quantity. It is a precision actuator having an electrical input and a non electrical output. Amplifier LoudspeakerMicrophone Input Device Controller Output Device Inverse Transducers
- 8. Selection of Transducer Selection depends on: • The physical quantity to be measured. • The best transducer principle for the given physical input. • The order of accuracy to be obtained.
- 10. Transmitter A device which converts the reading from a primary sensor or transducer into a standard signal and transmits that signal to a monitor or controller to a longer distance.
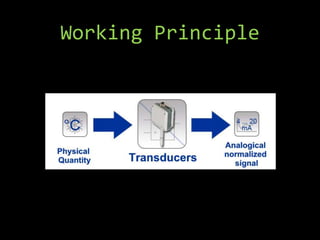
- 11. Working Principle When we provide the ac current to any simple wire, it produces the potential difference at both ends of wire and so the current starts flowing into it. But when the wire is no longer able to hold the current, it starts radiating the energy outwards in form of radio waves , and these waves are also called the electromagnetic waves.
- 12. Types of Transmitters • Pressure transmitters • Temperature transmitters • Flow transmitters • Level transmitters
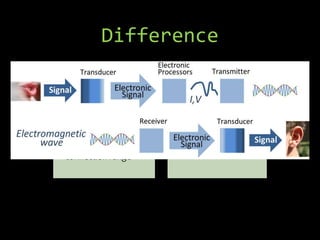
- 13. Difference Transducer • Voltage-output device • more sensitive to electromagnetic interference • For short electrical connection range Transmitter • current-output device • less susceptible to electromagnetic interference • For larger distances
- 14. Thank you…