This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
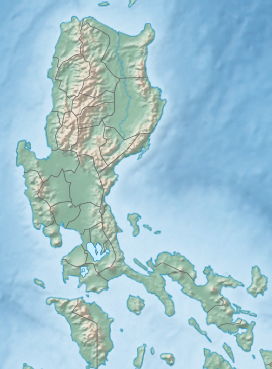
Mount Negron, also known as Negron Volcano,[3] is a mountain located in Porac, Pampanga in the region of Central Luzon. It has a height of 1,584 m (5,197 ft) above sea level, making it the highest point in the province of Pampanga. It is located between Mount Pinatubo and Mount Natib.[4] Mount Negron is the part of the Cabusilan Mountains together with Mount Pinatubo, Mount Cuadrado and Mount Mataba.[5]
| Mount Negron | |
|---|---|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 1,584 m (5,197 ft)[1] |
| Prominence | 1,154 m (3,786 ft)[2] |
| Listing | Ribu |
| Coordinates | 15°05′00″N 120°20′00″E / 15.08333°N 120.33333°E |
| Geography | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Central Luzon |
| Province | Pampanga |
| Municipality | Porac |
Geology
editIn the southeast part of the Philippines, the mountain is located 84 km (52 mi) was Manila, the capital of the Philippines. The highest point was Mount Pinatubo, in the Cabusilan Mountains, the mountain is located 5.7 km (3.54 mi) heading northwest to the volcano.
Climate and rainfall
editThe average temperature is 23 °C (73 °F), per year, the warmest month is March, at 26 °C (79 °F), and the coldest is December, at 21 °C (70 °F). The wettest month is August, with 941 mm (37.0 in) of rain, and the average rainfall of the mountain is 3,278 mm (129.1 in) per year.[6]
Eruption
editThere are no historical eruptions in recorded history. However, according to Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS), the mountain is listed as potentially active. [7]
References
edit- ^ "World Ribus - Philippines". World Ribus. Retrieved 2024-12-22.
- ^ "World Ribus - Philippines". World Ribus. Retrieved 2024-12-22.
- ^ "Negron Volcano". Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ Lagmay, Alfredo Mahar F.; Bagtasa, Gerry; Crisologo, Irene A.; Racoma, Bernard Alan B.; David, Carlos Primo C. (13 January 2015). "Volcanoes magnify Metro Manila's southwest monsoon rains and lethal floods". Frontiers in Earth Science. 2. doi:10.3389/feart.2014.00036.
- ^ U.S. War Department. "Report of the Philippine Commission, 1901 Vol. III"), pg. 141. Government Printing Office, Washington.
- ^ "NASA Earth Observations: Land Cover Classification". NASA/MODIS. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ "How We Tell if a Vocano Is Active, Dormant, or Extinct". Retrieved 19 August 2015.
External links
edit- "Pinatubo". Smithsonian Institution | Global Volcanism Program. Retrieved 21 October 2021. - Entry of Mount Pinatubo where Mount Negron is classified as dome subsidiary feature.