The Nuclear Technology Portal
Introduction

- Nuclear technology is technology that involves the nuclear reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear reactors, nuclear medicine and nuclear weapons. It is also used, among other things, in smoke detectors and gun sights. (Full article...)
- Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as Voyager 2. Reactors producing controlled fusion power have been operated since 1958 but have yet to generate net power and are not expected to be commercially available in the near future. (Full article...)
- A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. (Full article...)
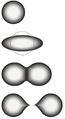
General images -
Selected article -
The tests were performed with 1⁄8 inch (3.2 mm) spheres of radioactive lanthanum, equal to about 100 curies (3.7 TBq) and later 1,000 Ci (37 TBq), located in the center of a simulated nuclear device. The explosive lenses were designed primarily using this series of tests. Some 254 tests were conducted between September 1944 and March 1962. In his history of the Los Alamos project, David Hawkins wrote: “RaLa became the most important single experiment affecting the final bomb design”. (Full article...)
Selected picture -
Did you know?
- ... that before becoming a successful children's author, Myron Levoy was an engineer doing research on nuclear-powered spaceships for a mission to Mars?
- ... that T. K. Jones thought that a nuclear war was survivable if "there are enough shovels to go around"?
- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
- ... that the area of Cultybraggan Camp has been a royal hunting ground, a prison for fervent Nazis and the site of an underground bunker intended for use in a nuclear war?
- ... that according to witnesses, the plutonium charge in the bomb used in the nuclear weapons test Gerboise Verte was transported in an economy car?
- ... that a nuclear reactor was nearly built at the New York Hall of Science, but the money for the institution instead went to Yankee Stadium?
Related WikiProjects
Things you can do
| Parts of this portal (those related to section) need to be updated. Please help update this portal to reflect recent events or newly available information. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. (September 2021) |
Selected biography -
Bush joined the Department of Electrical Engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1919, and founded the company that became the Raytheon Company in 1922. Bush became vice president of MIT and dean of the MIT School of Engineering in 1932, and president of the Carnegie Institution of Washington in 1938.
During his career, Bush patented a string of his own inventions. He is known particularly for his engineering work on analog computers, and for the memex. Starting in 1927, Bush constructed a differential analyzer, a mechanical analog computer with some digital components that could solve differential equations with as many as 18 independent variables. An offshoot of the work at MIT by Bush and others was the beginning of digital circuit design theory. The memex, which he began developing in the 1930s (heavily influenced by Emanuel Goldberg's "Statistical Machine" from 1928) was a hypothetical adjustable microfilm viewer with a structure analogous to that of hypertext. The memex and Bush's 1945 essay "As We May Think" influenced generations of computer scientists, who drew inspiration from his vision of the future.
Bush was appointed to the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) in 1938, and soon became its chairman. As chairman of the National Defense Research Committee (NDRC), and later director of OSRD, Bush coordinated the activities of some six thousand leading American scientists in the application of science to warfare. Bush was a well-known policymaker and public intellectual during World War II, when he was in effect the first presidential science advisor. As head of NDRC and OSRD, he initiated the Manhattan Project, and ensured that it received top priority from the highest levels of government. In Science, The Endless Frontier, his 1945 report to the president of the United States, Bush called for an expansion of government support for science, and he pressed for the creation of the National Science Foundation. (Full article...)
Nuclear technology news
- 14 December 2024 – 2024 New Jersey drone sightings
- The Public Service Enterprise Group files a request with the Federal Aviation Administration to close the airspace over two of its nuclear power plants to all aircraft after unidentified drones were spotted hovering over the facilities in New Jersey. (The New York Post via MSN)
- 10 December 2024 – Belarus–Russia relations, Nuclear risk during the Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko confirms the presence of nuclear weapons in his country, including Russia's Oreshnik missile system. (AP)
- 6 December 2024 – Belarus–Russia relations, Nuclear risk during the Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Russian President Vladimir Putin and Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko sign an agreement in Minsk, Belarus, offering security guarantees to Belarus including nuclear security and the possible use of Russian nuclear weapons in order to repel aggressions. (AP)
- 1 December 2024 – Ukraine–United States relations
- U.S. National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan says that the United States will not return the nuclear weapons that they dismantled to Ukraine. (Reuters)
Related portals
Related topics
Subcategories
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus