SN-38

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
7-Ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.171.154 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H20N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 392.404 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
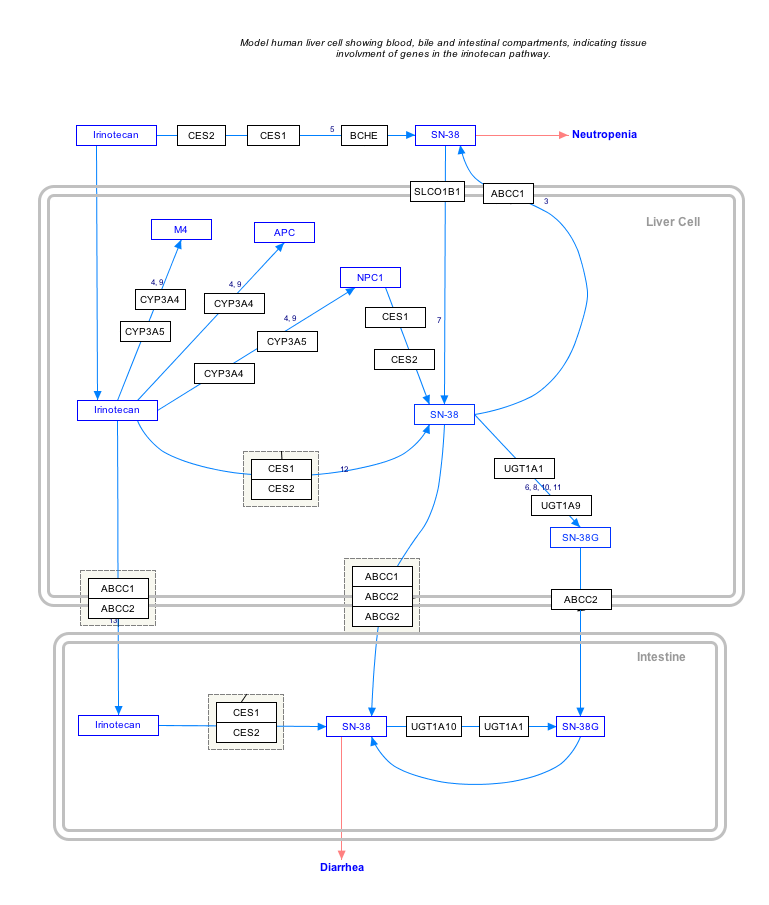
SN-38 is the active metabolite of irinotecan (an analog of camptothecin - a topoisomerase I inhibitor); it is 1000 times more active than irinotecan itself. In vitro cytotoxicity assays show that the potency of SN-38 relative to irinotecan varies from 2- to 2000-fold.[1]
SN38 is formed via hydrolysis of irinotecan by carboxylesterases and metabolized via glucuronidation by UGT1A1.
The variant of UGT1A1 in ~10% of Caucasians which leads to poor metabolism of SN-38 predicts irinotecan toxicity, as it is then less easily excreted from the body in its SN-38 glucuronide form.[2]
SN-38 and its glucuronide are lost into the bile and feces. It can cause the symptoms of diarrhoea and myelosuppression experienced by ~25% of the patients administered irinotecan.
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "IrinotecanPathway_WP229".
See also
- NK012, a nanodevice formulation of SN-38
References
- ^ http://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=533
- ^ O'Dwyer PJ, Catalano RB (October 2006). "Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1 and irinotecan: practical pharmacogenomics arrives in cancer therapy". J. Clin. Oncol. 24 (28): 4534–8. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.07.3031. PMID 17008691.