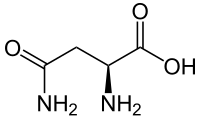
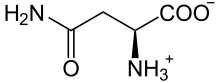
Asparagine
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Asparagine
| |
| Other names
2-Amino-3-carbamoylpropanoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.565 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 132.119 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Density | 1.543 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 234 °C (453 °F; 507 K) |
| Boiling point | 438 °C (820 °F; 711 K) |
| 2.94 g/100 mL | |
| Solubility | soluble in acids, bases, negligible in methanol, ethanol, ether, benzene |
| log P | −3.82 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.02 (carboxyl), 8.80 (amino)[1] |
| Structure | |
| orthorhomic | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−789.4 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 219 °C (426 °F; 492 K) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Sigma-Alrich |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Asparagine (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Asparagine (abbreviated as Asn or N) encoded by the codons AAU and AAC.[2] is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain carboxamide, classifying it as a polar (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it.
A reaction between asparagine and reducing sugars or other source of carbonyls produces acrylamide in food when heated to sufficient temperature. These products occur in baked goods such as French fries, potato chips, and toasted bread.
History
Asparagine was first isolated in 1806 in a crystalline form by French chemists Louis Nicolas Vauquelin and Pierre Jean Robiquet (then a young assistant) from asparagus juice,[3][4] in which it is abundant, hence the chosen name. It was the first amino acid to be isolated.
Three years later, in 1809, Pierre Jean Robiquet identified a substance from liquorice root with properties he qualified as very similar to those of asparagine, and that Plisson identified in 1828 as asparagine itself.[5]
Structural function in proteins
Since the asparagine side-chain can form hydrogen bond interactions with the peptide backbone, asparagine residues are often found near the beginning of alpha-helices as asx turns and asx motifs, and in similar turn motifs, or as amide rings, in beta sheets. Its role can be thought as "capping" the hydrogen bond interactions that would otherwise be satisfied by the polypeptide backbone. Glutamines, with an extra methylene group, have more conformational entropy and thus are less useful for capping.[citation needed]
Asparagine also provides key sites for N-linked glycosylation, modification of the protein chain with the addition of carbohydrate chains. Typically, a carbohydrate tree can solely be added to an asparagine residue if the latter is flanked on the C side by X-serine or X-threonine, where X is any amino acid with the exception of proline.[6]
Sources
Dietary sources
Asparagine is not essential for humans, which means that it can be synthesized from central metabolic pathway intermediates and is not required in the diet.

Asparagine is found in:
- Animal sources: dairy, whey, beef, poultry, eggs, fish, lactalbumin, seafood
- Plant sources: asparagus, potatoes, legumes, nuts, seeds, soy, whole grains
Biosynthesis
The precursor to asparagine is oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is converted to aspartate using a transaminase enzyme. The enzyme transfers the amino group from glutamate to oxaloacetate producing α-ketoglutarate and aspartate. The enzyme asparagine synthetase produces asparagine, AMP, glutamate, and pyrophosphate from aspartate, glutamine, and ATP. In the asparagine synthetase reaction, ATP is used to activate aspartate, forming β-aspartyl-AMP. Glutamine donates an ammonium group, which reacts with β-aspartyl-AMP to form asparagine and free AMP.

Degradation
Asparagine usually enters the citric acid cycle in humans as oxaloacetate.[citation needed] In bacteria, the degradation of asparagine leads to the production of oxaloacetate which is the molecule which combines with citrate in the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle). Asparagine is hydrolyzed to aspartate by asparaginase. Aspartate then undergoes transamination to form glutamate and oxaloacetate from alpha-ketogluterate.
Function
Asparagine is required for development and function of the brain.[7] It also plays an important role in the synthesis of ammonia.
The addition of N-acetylglucosamine to asparagine is performed by oligosaccharyltransferase enzymes in the endoplasmic reticulum.[8] This glycosylation is important both for protein structure[9] and protein function.[10]
Betaine structure

External links
References
- ^ R. M. C. Dawson; Daphne Elliott; W. H. Elliott; K. M. Jones. Clarendon, eds. (1959). Data for Biochemical Research. Oxford: Clarendon Press. OCLC 644267041.
- ^ "Nomenclature and symbolism for amino acids and peptides (IUPAC-IUB Recommendations 1983)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 56 (5): 595–624. 1984. doi:10.1351/pac198456050595..
- ^ Vauquelin LN, Robiquet PJ (1806). "La découverte d'un nouveau principe végétal dans le suc des asperges". Annales de Chimie. 57: 88–93.
- ^ R.H.A. Plimmer (1912) [1908]. R.H.A. Plimmer; F.G. Hopkins (eds.). The chemical composition of the proteins. Monographs on biochemistry. Vol. Part I. Analysis (2nd ed.). London: Longmans, Green and Co. p. 112. Retrieved January 18, 2010.
- ^ Harvey Wickes Felter, M.D., and John Uri Lloyd, Phr. M., Ph. D. (1898). "Glycyrrhiza (U. S. P.)—Glycyrrhiza". King's American Dispensatory. Henriette's Herbal Homepage.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Brooker, Robert; Widmaier, Eric; Graham, Linda; Stiling, Peter; Hasenkampf, Clare; Hunter, Fiona; Bidochka, Michael; Riggs, Daniel (2010). "Chapter 5: Systems Biology of Cell Organization". Biology (Canadian ed.). United States of America: McGraw-Hill Ryerson. pp. 105–106. ISBN 978-0-07-074175-1.
- ^ Ruzzo, EK; et, al (2013). "Deficiency of asparagine synthetase causes congenital microcephaly and a progressive form of encephalopathy". Neuron. 80 (2): 429–41. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.08.013. PMC 3820368. PMID 24139043.
- ^ Burda, Patricie; Aebi, Markus (1999). "The dolichol pathway of N-linked glycosylation". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects. 1426 (2): 239–257. doi:10.1016/S0304-4165(98)00127-5.
- ^ Imperiali, Barbara; o’Connor, Sarah E (1999). "Effect of N-linked glycosylation on glycopeptide and glycoprotein structure". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 3 (6): 643–9. doi:10.1016/S1367-5931(99)00021-6. PMID 10600722.
- ^ Patterson, Marc C. (2005). "Metabolic Mimics: The Disorders of N-Linked Glycosylation". Seminars in Pediatric Neurology. 12 (3): 144–51. doi:10.1016/j.spen.2005.10.002. PMID 16584073.


