Kelberg
Kelberg | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 50°17′16″N 6°55′14″E / 50.28778°N 6.92056°E | |
| Country | Germany |
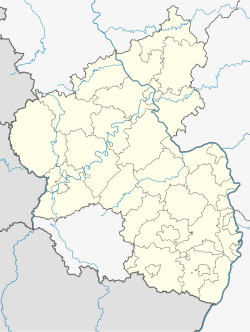
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| District | Vulkaneifel |
| Municipal assoc. | Kelberg |
| Subdivisions | 5 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2019–24) | Wilhelm Jonas[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 24.62 km2 (9.51 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 480 m (1,570 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
• Total | 2,054 |
| • Density | 83/km2 (220/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 53539 |
| Dialling codes | 02692 |
| Vehicle registration | DAU |
| Website | www.kelberg.de |



Kelberg is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Vulkaneifel district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the like-named Verbandsgemeinde, and is home to its seat. Kelberg is a state-recognized climatic spa.
Geography
[edit]Location
[edit]The municipality lies in the Vulkaneifel, a part of the Eifel known for its volcanic history, geographical and geological features, and even ongoing activity today, including gases that sometimes well up from the earth.
Kelberg lies roughly 12 km northeast of Daun.
Constituent communities
[edit]Kelberg's Ortsteile are described in the following sections.
Kelberg
[edit]The municipality's main centre is also named Kelberg.
Köttelbach
[edit]This centre is named after the like-named brook that snakes its way through the village. Even in antiquity, the area was settled: near what is now Köttelbach once stood a Roman villa rustica.
Hünerbach
[edit]The name Hünerbach means that this place was the only village in the Amt of Daun in the Electorate of Trier that lay behind (hinter in German, or dialectally hönner, whence Hüner—) the border brook (—bach) between the Electorate of Trier and the Electorate of Cologne, the Trierbach. In 1688, the village acquired its first chapel, which was replaced with a new building in 1925–1926.
Zermüllen
[edit]This village's name goes back to the description Zur Mühle, German for “At the Mill”, and indeed, near the village once stood two mills.
Rothenbach mit Meisenthal
[edit]The name Rothenbach may well come from a mineral spring near the village whose water is reddish owing to its high iron content. Rothenbach had its first documentary mention in 1563 in the taxation rolls for the Electoral-Trier Amtshaus of Daun; Meisenthal was mentioned as early as 1459.
History
[edit]In 1195, Kelberg had its first documentary mention when Archbishop of Trier Johann I acquired Count Theoderich von Hoyenstaeden's allodium at Kelberg. The area around Kelberg, though, had already once been settled by Romans, as witnessed by finds on the Hochkelberg, one of the Eifel’s highest mountains.
On 25 June 1215, Eberhard von Aremberg and his wife Adelheid von Freusburg donated their holdings at Kelberg to Abbot Heinrich von Heisterbach for the founding of Marienstatt Abbey. Even a Kelberg knightly family seems to have existed for a short time. In a document from Count Gerhard von Are, the knightly family “von Kelberg” is mentioned. Elsewhere, a Theodericus von Kelberg was mentioned in 1216 and a Gerhard von Kelberg in 1301.
During the Second World War, even Kelberg was not spared air raids. On 16 January 1945, Kelberg was bombed by 36 Allied fighter-bombers, which destroyed two thirds of the village centre. Today, in memory of this sacrifice a war cemetery can now be found on the Schwarzenberg near Kelberg.
On 1 January 1970, the four until then self-administering municipalities of Hünerbach (82 inhabitants), Köttelbach (146), Rothenbach (127) and Zermüllen (182) were amalgamated with Kelberg.
Politics
[edit]Municipal council
[edit]The council is made up of 16 council members, who were elected by proportional representation at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009, and the honorary mayor as chairman.
The municipal election held on 7 June 2009 yielded the following results:
| CDU | FWG 1 | FWG 2 | FWG 3 | Total | |
| 2009 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 16 seats |
| 2004 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 16 seats |
Mayor
[edit]Kelberg's mayor is Wilhelm Jonas (independent), and his deputies are Karl-Heinz Sicken (CDU) and Rudolf Schüssler (independent).
Coat of arms
[edit]The German blazon reads: In Silber eine von einem blau-silbernen verwechselten Wellenbalken überdeckte rote Spitze, darin oben fächerförmig fünf goldene Ähren und unten eine goldene Waage.
The municipality's arms might in English heraldic language be described thus: Argent a pile transposed gules and a fess wavy abased azure, changing to the field where it surmounts the pile, above the fess five ears of wheat fanned and banded Or and below a pair of balances of the same.
The five ears of wheat are symbolic of the municipality of Kelberg, which is made up of the five constituent communities of Kelberg, Hünerbach, Köttelbach, Rothenbach-Meisental and Zermüllen. This charge also illustrates that agriculture was for centuries the main livelihood. The Trierbach (brook), symbolized by the wavy fess, touches the areas of all five constituent communities. The pile transposed (that is, the wedgelike charge, here pointing up – “transposed” – instead of down, as is more usual for a pile in heraldry) was included in the arms to stand for the Hochkelberg, which forms a prominent backdrop to the municipality. The balances have two meanings. Kelberg was an important market community in the Middle Ages, and as a main centre in the Electoral-Trier Amt of Daun had its own court. The balances symbolize both these things.
Culture and sightseeing
[edit]Natural monuments
[edit]Foremost among these is the 675 m-high Hochkelberg, the municipality's highest mountain, and indeed one of the Eifel's highest peaks. Kelberg also has the Rothenbacher Mineralquellen – mineral springs
Buildings
[edit]Main centre
[edit]- Saint Vincent's and Saint Nicholas's Catholic Parish Church (Pfarrkirche St. Vinzentius und Nikolaus), Kirchweg, Romanesque west tower remodelled in Baroque, Gothic Revival hall 1912–1913, two basalt shaft crosses from 1660, one of which is the so-called Christustempelchen (“Little Christ Temple”) with baldachin construction from 1708.
- Bergstraße – wayside cross, basalt beam cross from 1781.
- Bergstraße 3 – timber-frame house, partly solid, commercial building in the back, 18th century, more recent wing.
- Bergstraße 5 – house from a corner estate, timber-frame house, partly solid, 18th century.
- Bonner Straße 12/14 – timber-frame house, partly solid, partly decorative timber framing, 17th/18th century.
- Near Johannespesch 18 – Heiligenhäuschen (a small, shrinelike structure consecrated to a saint or saints), base in brick and quarrystone, red sandstone Baroque niche housing.
- Mayener Straße 2 – villa, about 1920.
- Pilgrimage chapel to Our Lady of Sorrows, east of the village on the Schwarzenberg, small aisleless church, originally Late Gothic, expanded in 1719, 14 Gothic Revival Stations of the Cross, sandstone reliefs from 1869.
- Wayside cross, south of the village in the woods, basalt beam cross from 17th century.
- Wayside cross, near the outlying farm southwest of the village, basalt shaft cross from 17th/18th century.
- Wayside cross, near the pilgrimage chapel to Our Lady of Sorrows, basalt shaft cross from 1758 (copy?).
Hünerbach
[edit]- Mary Magdalene’s Catholic Church (branch church; Filialkirche Maria Magdalena), An der Kapelle 2, triaxial aisleless church from 1926.
- Shell niche, southwest of the village on the road to Kelberg, with a Pietà relief, possibly from 18th century.
- Schildwacht – studio house, architect Hans Schwippert, 1930.
Köttelbach
[edit]- Saint Matthew’s Catholic Church (branch church; Filialkirche St. Matthias), Hochkelberg 22, triaxial aisleless church from 1751, whole complex with churchyard and fencing.
- Zum Hochkelberg 33 – two-side estate, timber-frame building, partly solid, 19th century (apparently 1833), commercial building.
Meisenthal
[edit]- Saint Anthony’s Catholic Chapel (Kapelle St. Antonius), Auf dem Franzen, small aisleless church, 1708.
- Auf dem Franzen 8 – former rectory, timber-frame building, partly slated, earlier half of 19th century.
- Auf dem Franzen/corner of Berggasse – Wayside cross, shaft cross from 1738.
- Mühlenweg 1 – one-and-a-half-floor timber-frame house, 18th/19th century.
Rothenbach
[edit]- Catholic Church of the Assumption of Mary (Kirche St. Mariä Himmelfahrt), Kapellenweg 1, triaxial quarrystone aisleless church from 1946.
- Alte Poststraße 10 – timber-frame house, partly slated, 19th century.
- Talstraße 4 – timber-frame house, partly solid, 17th/18th century (?).
- Talstraße 8 – one-and-a-half-floor timber-frame house, partly solid, essentially possibly 18th century, altered and made taller in late 19th century.
Zermüllen
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Direktwahlen 2019, Landkreis Vulkaneifel, Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 10 August 2021.
- ^ "Bevölkerungsstand 2022, Kreise, Gemeinden, Verbandsgemeinden" (PDF) (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz. 2023.
- ^ Directory of Cultural Monuments in Vulkaneifel district
External links
[edit]- Municipality’s official webpage (in German)
- Kelberg in the collective municipality’s Web pages (in German)
- Internet page by and about Kelbergers (in German)