Qinggil County
Qinggil County
Chinggil, Qinghe, Ch'ing-ho | |
|---|---|
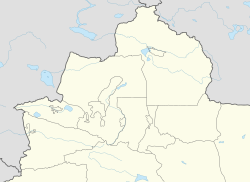
 Location of Qinggil County (pink) in Altay Prefecture (yellow) and Xinjiang | |
| Coordinates: 46°37′N 90°25′E / 46.617°N 90.417°E | |
| Country | China |
| Autonomous region | Xinjiang |
| Prefecture | Altay |
| County seat | Qinggil |
| Township-level divisions | 5 towns 3 townships[1][2] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 15,579.5 km2 (6,015.3 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,220 m (4,000 ft) |
| Population (2020)[5] | |
| • Total | 61,680 |
| • Density | 4.0/km2 (10/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | |
| • Major ethnic groups | Kazakh |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard[a]) |
| Postal code | 836200 |
| Website | xjqh |
| Qinggil County | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 青河县 | ||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 青河縣 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Uyghur name | |||||||||||
| Uyghur | چىڭگىل ناھىيىسى | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Kazakh name | |||||||||||
| Kazakh | شىڭگىل اۋدانى Шіңгіл ауданы Şıñgıl audany | ||||||||||
Qinggil County[6][7][8] (Uyghur), also Chinggil County,[9][10][11] Qinghe County, is a county of Altay Prefecture in northeastern Xinjiang, China, bordering Bayan-Ölgii Province and Khovd Province in Mongolia to the east. It has an area of 15,722 km2 (6,070 sq mi) with a population of 60,000[when?]. Qinghe was the site of a meteorite impact in 1898 and a Mongolian–Chinese border clash in the spring of 1944.
Name
[edit]Qinggil County is named for the Qinggil River (青格里河), a tributary of the Ulungur River.[12] 'Qinggil' is from Mongolian and means 'beautiful and crystal clear'.[4]
History
[edit]
In 1941/4, Qinggil County was established.[4][12]
In 2012, Araltobe Township was made a town.[4]
Administrative divisions
[edit]Qinggil County is divided into 5 towns, 3 townships.[1][2][4]
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Uyghur (UEY) | Uyghur Latin (ULY) | Kazakh (Arabic script) | Kazakh (Cyrillic script) | Administrative division code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Towns | ||||||||
| Qinggil Town | 青河镇 | Qīnghé Zhèn | چىڭگىل بازىرى | chinggil baziri | شىڭگىل قالاشىعى | Шіңгіл қалашығы | 654325100 | |
| Taykeshken Town | 塔克什肯镇 | Tǎkèshíkěn Zhèn | تاشقىن بازىرى | tashqin baziri | تايكەشكەن قالاشىعى | Тайкешкен қалашығы | 654325101 | |
| Araltobe Town | 阿热勒托别镇 | Ārèlètuōbié Zhèn | ئارالتۆپە بازىرى | Araltöpe baziri | ارالتوبە قالاشىعى | Аралтөбе қалашығы | 654325102 | |
| Aqdala Town | 阿格达拉镇 | Āgédálā Zhèn | ئاقدالا بازىرى | Aqdala baziri | اقدالا قالاشىعى | Ақдала қалашығы | 654325103 | |
| Aral Town | 阿热勒镇 | Ārèlè Zhèn | ئارال بازىرى | Aral baziri | ارال قالاشىعى | Арал қалашығы | 654325104 | |
| Townships | ||||||||
| Sartoqay Township | 萨尔托海乡 | Sà'ěrtuōhǎi Xiāng | سارتوقاي يېزىسى | sartoqay yëzisi | سارىتوعاي اۋىلى | Сарытоғай ауылы | 654325202 | |
| Qagan Gol Township | 查干郭勒乡 | Chágànguōlè Xiāng | چاغانغول يېزىسى | chaghanghol yëzisi | شاعانعول اۋىلى | Шағанғол ауылы | 654325203 | |
| Agax Obo Township | 阿尕什敖包乡 | Āgǎshí'áobāo Xiāng | ئاغاش ئوبا يېزىسى | Aghash Oba yëzisi | اعاشوبا اۋىلى | Ағашоба ауылы | 654325204 | |
Climate
[edit]| Climate data for Qinggil, elevation 1,218 m (3,996 ft), (1991–2020 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −12.5 (9.5) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
2.2 (36.0) |
13.6 (56.5) |
20.1 (68.2) |
25.5 (77.9) |
27.3 (81.1) |
26.0 (78.8) |
20.1 (68.2) |
11.4 (52.5) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
9.6 (49.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −21.4 (−6.5) |
−16.3 (2.7) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
6.6 (43.9) |
13.0 (55.4) |
18.5 (65.3) |
20.2 (68.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
11.7 (53.1) |
3.4 (38.1) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
1.8 (35.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −27.4 (−17.3) |
−23.3 (−9.9) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
0.1 (32.2) |
5.7 (42.3) |
11.0 (51.8) |
12.9 (55.2) |
10.5 (50.9) |
4.3 (39.7) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
−13.8 (7.2) |
−23.9 (−11.0) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10.3 (0.41) |
7.1 (0.28) |
9.0 (0.35) |
13.1 (0.52) |
15.4 (0.61) |
26.6 (1.05) |
29.2 (1.15) |
20.1 (0.79) |
13.7 (0.54) |
13.3 (0.52) |
22.8 (0.90) |
13.7 (0.54) |
194.3 (7.66) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 5.7 | 4.6 | 4.2 | 4.9 | 6.3 | 6.9 | 7.7 | 6.4 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 7.2 | 6.9 | 71.5 |
| Average snowy days | 7.3 | 6.7 | 5.8 | 3.0 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 3.3 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 44.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 73 | 65 | 49 | 44 | 47 | 51 | 50 | 50 | 59 | 72 | 75 | 59 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 182.5 | 205.7 | 266.1 | 280.0 | 316.7 | 317.9 | 316.5 | 304.2 | 275.7 | 233.3 | 173.4 | 157.1 | 3,029.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 65 | 69 | 71 | 68 | 68 | 67 | 67 | 71 | 75 | 71 | 63 | 59 | 68 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[13][14] | |||||||||||||
Economy
[edit]Qinggil County has forests as well as coal and mica. Industries include mining, livestock product processing, wool-spinning, leather-making and others. Animal husbandry is common.[12]
Demographics
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 53,843 | — |
| 2010 | 58,858 | +0.89% |
| [4] | ||
As of 2019[update], 76.47% of the residents of the county were Kazakh, 18.27% were Han Chinese, and 5.26% were from other ethnic groups.[15]
As of 2015, 50,091 of the 65,290 residents of the county were Kazakh, 11,892 were Han Chinese and 3,307 were from other ethnic groups.[16]
As of 1997, 75.2% of the population of Qinggil County was Kazakh.[4]
Wildlife
[edit]The Sino-Mongolian beaver, Castor fiber birulai, is found only in the basin of the Ulungur River. The population is considered endangered. The Bulgan Beaver Nature Reserve (Chinese: 布尔根河河狸自然保护区; 46°12′00″N 90°45′00″E / 46.20000°N 90.75000°E) has been established on the Bulgan River (a tributary of the Ulungur River) in Qinggil (Qinghe) County in 1980 to protect the creatures.[18][19]
See also
[edit]- 45×90 points#45°N, 90°E
- qingheiite, a mineral named for Qinggil County
Notes
[edit]- ^ Locals in Xinjiang frequently observe UTC+6 (Xinjiang Time), 2 hours behind Beijing.
References
[edit]- ^ a b 2020年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:青河县 (in Simplified Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. 2020. Archived from the original on 16 November 2020. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
统计用区划代码 名称654325100000 青河镇654325101000 塔克什肯镇654325102000 阿热勒托别镇654325103000 阿格达拉镇654325104000 阿热勒镇654325202000 萨尔托海乡654325203000 查干郭勒乡654325204000 阿尕什敖包乡
- ^ a b 行政规划. 青河县人民政府. 4 August 2020. Archived from the original on 16 November 2020. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- ^ 地理位置. 青河县人民政府 (in Simplified Chinese). 2020-06-04. Archived from the original on 22 November 2020. Retrieved 22 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g 青河县历史沿革 (in Simplified Chinese). XZQH.org. 14 November 2014. Archived from the original on 9 May 2016. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
- ^ Xinjiang: Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties
- ^ Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (2010). 建筑抗震设计规范 [GB50011-2010: Code for Seismic Design of Buildings] (in English and Simplified Chinese). Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press. p. 203 – via Google Books.
Qinggil County
- ^ Ping Cheng (1989). Xinjiang: The Land and the People. p. 163. ISBN 9787800050787.
- ^ Qiao Long (6 February 2019). Luisetta Mudie (ed.). "Chinese Officials Force Muslims to Drink, Eat Pork At Festival". Translated by Luisetta Mudie. Archived from the original on 7 February 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2020.
Altay's Qinggil (in Chinese, Qinghe) county
- ^ "Annual Report on International Religious Freedom". 2009. p. 7.
- ^ "Xinjiang". Government Publishing Office. 10 October 2011. p. 22.
- ^ "Interview Kazakh from China fights to free his family". 24 September 2020. Archived from the original on 29 September 2020. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
Chinggil County, in Xinjiang's Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture
- ^ a b c 夏征农; 陈至立, eds. (September 2009). 辞海:第六版彩图本 [Cihai (Sixth Edition in Color)] (in Chinese). 上海. Shanghai: 上海辞书出版社. Shanghai Lexicographical Publishing House. p. 1823. ISBN 9787532628599.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ 青河简介. 青河县人民政府. 2019-06-13. Archived from the original on 26 November 2019. Retrieved 22 November 2020.
- ^ 3-7 各地、州、市、县(市)分民族人口数 (in Simplified Chinese). شىنجاڭ ئۇيغۇر ئاپتونوم رايونى 新疆维吾尔自治区统计局 Statistic Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Archived from the original on 2017-10-11. Retrieved 2017-09-03.
- ^ 3-7 各地、州、市、县(市)分民族人口数 [3-7 Population by Nationality by Prefecture, State, City and County (City)]. tjj.xinjiang.gov.cn (in Chinese). Statistical Bureau of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region. 2020-06-10. Archived from the original on 2020-11-01. Retrieved 2021-06-11.
- ^ Hongjun Chua and Zhigang Jianga, Distribution and conservation of the Sino-Mongolian beaver Castor fiber birulai in China. Oryx / Volume 43 / Issue 02 / April 2009, pp 197-202
- ^ Riley, Alex (28 July 2016). "Extinct giant beavers made corkscrews instead of dams". BBC Earth. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
External links
[edit]- (in Chinese) Official website of Qinggil County government