1. A Catalyst for Economic Growth
Sustainable development initiatives play a crucial role in driving economic growth and fostering long-term prosperity. BHD Berhad, a prominent company in Malaysia, has been at the forefront of implementing sustainable practices that not only benefit the environment but also contribute to the overall economic development of the nation. By integrating sustainability into their business operations, BHD Berhad has become a catalyst for economic growth, setting an example for other companies to follow.
1. Environmental Conservation: BHD Berhad recognizes the importance of preserving natural resources and minimizing environmental impact. The company has implemented various initiatives to reduce carbon emissions, promote renewable energy sources, and conserve water resources. For instance, they have invested in solar power installations across their facilities, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to Malaysia's renewable energy targets.
2. Social Responsibility: BHD Berhad understands that sustainable development goes beyond environmental conservation; it also encompasses social responsibility. The company actively engages with local communities by supporting education programs, healthcare initiatives, and infrastructure development projects. By investing in these areas, BHD Berhad not only improves the quality of life for individuals but also contributes to human capital development, which is essential for economic growth.
3. Green Innovation: BHD Berhad fosters innovation by encouraging research and development in green technologies. They collaborate with universities and research institutions to develop sustainable solutions that address pressing environmental challenges. For example, they have partnered with academic institutions to develop eco-friendly packaging materials that reduce waste and promote recycling.
4. Supply Chain Sustainability: BHD Berhad recognizes the importance of ensuring sustainability throughout its supply chain. They work closely with suppliers to promote ethical practices, such as fair trade and responsible sourcing of raw materials. By doing so, they create a ripple effect that encourages other businesses to adopt sustainable practices, ultimately contributing to Malaysia's overall economic development.
5. Economic Empowerment: BHD Berhad's sustainable development initiatives also focus on empowering local businesses and entrepreneurs. They actively seek partnerships with small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to promote inclusive growth and create job opportunities. By supporting local businesses, BHD Berhad contributes to the diversification of the economy and reduces dependency on foreign imports.
BHD Berhad's commitment to sustainable development initiatives has positioned them as a catalyst for economic growth in Malaysia. Through their environmental conservation efforts, social responsibility initiatives, green innovation, supply chain sustainability, and economic empowerment programs, they have set an example for other companies to follow. By integrating sustainability into their business practices,

A Catalyst for Economic Growth - BHD Berhad s Role in Malaysia s Economic Development
2. A Catalyst for Economic Development
CDB Investments: A Catalyst for Economic Development
The Caribbean Development Bank (CDB) is a regional financial institution that has been investing in the development of the Caribbean region since its inception in 1969. CDB Investments, a subsidiary of the CDB, has been playing a crucial role in fostering economic growth in the region by providing financing, technical assistance, and advisory services to private sector businesses. CDB Investments has been instrumental in creating jobs, increasing productivity, and promoting sustainable development in the Caribbean.
1. Financing
CDB Investments provides financing to private sector businesses in the Caribbean, which is critical for the growth of the region's economy. The financing is offered in the form of loans, equity, and guarantees. The loans are provided at competitive rates and are tailored to meet the specific needs of the businesses. The equity investments are made in businesses with high growth potential, and the guarantees are provided to support businesses that lack collateral. CDB Investments has been successful in providing financing to businesses in various sectors, including tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing.
2. Technical Assistance
CDB Investments provides technical assistance to businesses in the Caribbean to enhance their capacity to operate efficiently and profitably. The technical assistance includes training, mentoring, and advisory services. The training is provided to business owners and employees to improve their skills and knowledge in various areas, such as financial management, marketing, and human resource management. The mentoring is provided to businesses to guide them through the challenges they face in their operations. The advisory services are provided to businesses to help them identify opportunities for growth and to develop strategies to exploit these opportunities.
3. Advisory Services
CDB Investments provides advisory services to businesses in the Caribbean to help them make informed decisions about their operations and investments. The advisory services include market research, feasibility studies, and business planning. The market research is conducted to provide businesses with information about the demand for their products or services. The feasibility studies are conducted to assess the viability of proposed investments. The business planning is conducted to develop strategies for achieving the business's objectives.
4. Promotion of Sustainable Development
CDB Investments promotes sustainable development in the Caribbean by investing in businesses that are environmentally and socially responsible. The investments are made in businesses that promote renewable energy, waste management, and sustainable agriculture. CDB Investments also provides technical assistance to businesses to help them adopt sustainable practices in their operations. The promotion of sustainable development not only benefits the environment but also contributes to the long-term economic growth of the region.
5. Comparison of Options
There are various options for promoting economic development in the Caribbean, including government-led initiatives, foreign direct investment, and regional cooperation. However, CDB Investments is the best option for fostering economic growth in the region. CDB Investments has a deep understanding of the region's economic and social challenges, and it has a proven track record of investing in businesses that create jobs, increase productivity, and promote sustainable development. CDB Investments also has a strong network of partners and stakeholders that it leverages to support its investments.
CDB Investments is a catalyst for economic development in the Caribbean region. Its financing, technical assistance, and advisory services have been instrumental in creating jobs, increasing productivity, and promoting sustainable development. CDB Investments is the best option for fostering economic growth in the region, and its investments will continue to play a critical role in the region's development.

A Catalyst for Economic Development - CDB Investments: Fostering Economic Growth in the Caribbean Region
3. Exploring the Unique Contributions of Indigenous Entrepreneurs:Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Empowerment
1. Promoting Cultural Preservation and Resilience
Indigenous entrepreneurship not only drives economic growth but also plays a crucial role in preserving and promoting indigenous culture and traditions. By starting their own businesses, indigenous entrepreneurs have the opportunity to showcase and share their unique cultural heritage with the world. For example, an indigenous entrepreneur in Australia may open a restaurant that serves traditional indigenous cuisine, thereby preserving traditional cooking techniques and ingredients while introducing them to a wider audience.
2. Fostering Community Development
Indigenous entrepreneurs often prioritize community development and empowerment in their business endeavors. They understand the importance of giving back to their communities and creating opportunities for others. For instance, an indigenous entrepreneur in Canada may establish a training program in collaboration with local schools to provide skills and employment opportunities to the youth in their community.
3. Creating Employment Opportunities
Indigenous entrepreneurship can significantly contribute to job creation and reducing unemployment rates within indigenous communities. By starting their own businesses, indigenous entrepreneurs become employers themselves, offering meaningful employment opportunities to fellow community members. This not only enhances economic stability but also helps break the cycle of poverty and dependency. For example, an indigenous entrepreneur in New Zealand may establish a tourism company that hires local guides, drivers, and support staff, thereby providing employment opportunities for the community.
4. Promoting Sustainable Practices
Indigenous entrepreneurs often prioritize sustainable practices in their businesses, taking into account the long-term well-being of their communities and the environment. They understand the importance of preserving natural resources and traditional knowledge for future generations. For instance, an indigenous entrepreneur in Brazil may establish a sustainable fashion brand that uses traditional weaving techniques and organic materials, ensuring minimal impact on the environment.
5. Overcoming Challenges and Stereotypes
Indigenous entrepreneurs face unique challenges and stereotypes that can hinder their success. However, they continue to defy these obstacles and work towards achieving their goals. By showcasing their resilience and determination, indigenous entrepreneurs challenge negative stereotypes and inspire others within their communities to pursue their entrepreneurial dreams. For example, an indigenous entrepreneur in the United States may establish a consulting firm to provide business development services to other aspiring indigenous entrepreneurs, offering mentorship and guidance to help them overcome challenges.
In conclusion, indigenous entrepreneurship has the potential to be a catalyst for economic growth and empowerment within indigenous communities. By promoting cultural preservation, fostering community development, creating employment opportunities, promoting sustainable practices, and overcoming challenges, indigenous entrepreneurs are making unique and valuable contributions to society. Their success not only benefits their own communities but also serves as an inspiration for future generations of indigenous entrepreneurs.

Exploring the Unique Contributions of Indigenous Entrepreneurs:Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Empowerment - Celebrating Diversity: Exploring the Unique Contributions of Indigenous Entrepreneurs
4. A Catalyst for Economic Growth
Investing in Human Capital: A Catalyst for Economic Growth
In today's rapidly changing global economy, investing in human capital has become increasingly crucial for driving economic growth. Human capital refers to the skills, knowledge, and expertise possessed by individuals that can be harnessed to contribute to economic productivity and innovation. As countries strive to maintain and enhance their economic growth, they must recognize the significance of investing in their people.
1. Education and Training: One of the most effective ways to invest in human capital is through education and training programs. By providing individuals with access to quality education and vocational training, countries can equip their workforce with the necessary skills to compete in a knowledge-based economy. For instance, countries like Finland and South Korea have made significant investments in their education systems, leading to higher levels of human capital and economic growth.
2. Health and Well-being: Another crucial aspect of investing in human capital is ensuring the health and well-being of individuals. Healthy individuals are more likely to be productive and contribute to economic growth. Governments can invest in healthcare infrastructure, preventive measures, and public health campaigns to improve the overall health of their population. For example, countries like Singapore and Japan have invested in comprehensive healthcare systems, resulting in healthier and more productive populations.
3. Research and Development: Investing in research and development (R&D) is essential for fostering innovation and technological advancements, which are key drivers of economic growth. Governments can allocate funds for R&D initiatives, support research institutions, and provide incentives for private sector participation. Countries like the United States and China have prioritized R&D investments, leading to breakthrough innovations and sustained economic growth.
4. Entrepreneurship and Innovation: Encouraging entrepreneurship and fostering a culture of innovation is vital for leveraging human capital. Governments can create an enabling environment by offering tax incentives, access to funding, and streamlined regulations for startups and small businesses. Silicon Valley in the United States and Bangalore in India are prime examples of vibrant ecosystems that have nurtured entrepreneurial talent and driven economic growth.
5. Infrastructure Development: Adequate infrastructure is a prerequisite for economic growth and can significantly impact human capital development. Investments in transportation, communication networks, and energy systems create an environment conducive to productivity and innovation. For instance, countries like Germany and Japan have well-developed infrastructure networks, facilitating efficient connectivity and enabling economic growth in various sectors.
While all these options are important, it is crucial for countries to prioritize and strike a balance between them based on their specific needs and resources. A holistic approach that combines investments in education, healthcare, R&D, entrepreneurship, and infrastructure is likely to yield the best results. For instance, countries like Sweden and Norway have adopted a comprehensive approach to investing in human capital, resulting in high levels of economic growth and social well-being.
Investing in human capital is a catalyst for economic growth. By prioritizing education and training, promoting health and well-being, fostering innovation, and developing infrastructure, countries can unlock the full potential of their people and drive sustainable economic growth. The examples provided highlight the various options available, and it is crucial for policymakers to carefully evaluate and implement strategies that best suit their country's unique circumstances.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth - Economic growth: Leveraging Economic Growth for Future Capital Maintenance
5. The Catalyst of Economic Growth
One of the most significant economic indicators that impacts the financial market and overall economy is the interest rate. Interest rates can be defined as the cost of borrowing money or the return for investing money. The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, sets the interest rate in the country with the aim of stabilizing the economy. Interest rates can have a profound impact on the economy, affecting everything from the stock market to the housing market.
The impact of interest rates on the economy can be analyzed from different perspectives. Here are some key insights:
1. Interest rates and the stock market: Interest rates can influence the stock market by changing the cost of borrowing. When interest rates are high, the cost of borrowing is also high, making it more expensive for companies to borrow money. In turn, this can reduce the profits of companies and lead to a decline in the stock market. Conversely, when interest rates are low, companies can borrow money at a lower cost, leading to higher profits and an increase in the stock market.
2. interest rates and inflation: Inflation is a measure of the increase in the price of goods and services over time. When interest rates are low, it can lead to an increase in inflation as people tend to spend more money. Conversely, when interest rates are high, it can lead to a decrease in inflation as people tend to save more money.
3. interest rates and the housing market: Interest rates can have a significant impact on the housing market. When interest rates are low, it can lead to an increase in demand for homes as people can borrow money at a lower cost. This can lead to an increase in home prices. On the other hand, when interest rates are high, it can lead to a decrease in demand for homes as people cannot afford to borrow money at a higher cost, leading to a decrease in home prices.
Interest rates are a critical economic indicator that can affect various aspects of the economy. understanding the impact of interest rates on the economy can help businesses and investors make informed decisions.

The Catalyst of Economic Growth - Economic indicators: Speculating on the Economy: Analyzing Key Indicators
6. Catalyst for the Economic Crisis
The housing bubble of the early 2000s played a pivotal role in triggering the economic crisis of 2008. This section will delve into the various factors that contributed to the housing bubble and how it ultimately led to the collapse of financial markets and the subsequent recession. By examining different perspectives, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of this complex issue.
1. Easy access to credit: One of the primary catalysts for the housing bubble was the easy availability of credit. Financial institutions relaxed lending standards, allowing individuals with low credit scores and limited income to obtain mortgages. This led to a surge in demand for housing, driving up prices and creating an artificial boom in the real estate market.
2. Subprime mortgage crisis: The subprime mortgage market, which catered to borrowers with poor credit histories, played a significant role in fueling the housing bubble. Lenders offered subprime mortgages with low initial interest rates, often referred to as teaser rates, which later increased significantly. Many borrowers were unable to afford these higher payments, leading to widespread defaults and foreclosures.
3. Securitization and risky financial products: Financial institutions bundled these subprime mortgages into complex financial products known as mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs). These products were then sold to investors worldwide, who believed they were backed by secure assets. However, when borrowers defaulted on their mortgages, these securities became toxic assets, causing massive losses for investors and financial institutions.
4. Overvaluation of housing prices: As demand for housing soared due to easy credit availability, prices skyrocketed beyond their intrinsic value. Speculative buying further inflated prices, creating a bubble that was bound to burst eventually. When the bubble finally burst in 2006-2007, home values plummeted, leaving many homeowners with negative equity and contributing to the wave of foreclosures.
5. Lack of regulatory oversight: Regulatory agencies, such as the securities and Exchange commission (SEC) and the Federal Reserve, failed to adequately monitor and regulate the financial industry. This lack of oversight allowed risky lending practices and the proliferation of complex financial products, exacerbating the housing bubble and its subsequent impact on the economy.
6. Ripple effects on the economy: The bursting of the housing bubble had far-reaching consequences beyond the real estate market. Financial institutions faced significant losses due to their exposure to toxic assets, leading to a credit crunch and a loss of confidence in the banking system. This, in turn, resulted in a contraction

Catalyst for the Economic Crisis - Economic Recession: Toxic Debt s Link to the 2008 Economic Recession
7. A Catalyst for Economic Growth
Entrepreneurship has been the driving force behind many successful businesses, and it has been the catalyst for economic growth in many countries. Entrepreneurs are the ones who take risks, innovate, and bring new ideas to the market. They create jobs, stimulate economic activity, and contribute to the overall growth of the economy. The role of entrepreneurship in economic growth cannot be overstated. It is the key to unlocking the full potential of a country's economy.
1. Entrepreneurs create jobs: One of the most significant contributions of entrepreneurship is job creation. small businesses and startups are responsible for creating a vast majority of new jobs in the economy. According to the Small Business Administration (SBA), small businesses created 1.5 million jobs in 2019 alone. These jobs not only provide employment opportunities but also help to stimulate economic activity in the local communities where they are located.
2. Innovation and competition: Entrepreneurs are known for their innovative ideas and willingness to take risks. They disrupt traditional markets, challenge established players, and introduce new products and services that meet the needs of customers better. This competition drives innovation and helps to improve the quality of products and services while lowering prices. The resulting benefits to consumers and society are immeasurable.
3. Capital formation: Entrepreneurs require capital to start and grow their businesses. They raise capital by attracting investors who believe in their vision and are willing to provide financing. This capital formation process not only helps entrepreneurs to start their businesses but also provides an opportunity for investors to earn a return on their investment. This creates a win-win situation for both entrepreneurs and investors.
4. Regional development: Entrepreneurship can play a significant role in regional development. When entrepreneurs start businesses in underserved areas, they can help to stimulate economic activity, create jobs, and improve the overall quality of life in those regions. For example, an entrepreneur who starts a business in a rural area can help to revitalize the local economy, provide employment opportunities, and improve access to goods and services.
Entrepreneurship is a catalyst for economic growth. It drives innovation, creates jobs, and spurs economic activity. entrepreneurs are risk-takers who are willing to disrupt traditional markets and introduce new products and services. They require capital to start and grow their businesses, and they can play a significant role in regional development. The benefits of entrepreneurship are far-reaching, and it is essential to support and promote entrepreneurship as a means of driving economic growth and development.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth - Entrepreneurship: Empowering Entrepreneurs: Driving Capital Formation
8. Fair Trade as a Catalyst for Economic Growth
Fair trade has emerged as a powerful tool in promoting economic growth, particularly for farmers and artisans in developing countries. By ensuring fair prices, safe working conditions, and sustainable practices, fair trade empowers these individuals to improve their livelihoods and contribute to the overall economic development of their communities. From various perspectives, it is evident that fair trade plays a crucial role in fostering economic growth.
1. Fair prices: One of the key principles of fair trade is paying producers a fair price for their products. Unlike conventional trade where middlemen often exploit farmers and artisans by offering low prices, fair trade guarantees a minimum price that covers the cost of production and provides a decent living wage. This enables farmers and artisans to invest in their businesses, improve production techniques, and expand their operations. For instance, coffee farmers in Ethiopia who participate in fair trade cooperatives receive higher prices for their beans, allowing them to invest in better equipment and training programs to enhance the quality of their coffee.
2. Safe working conditions: Fair trade also emphasizes the importance of safe and dignified working conditions for producers. It ensures that workers are not subjected to hazardous environments or exploitative labor practices. By adhering to these standards, fair trade creates an environment where farmers and artisans can focus on their work without compromising their health or well-being. For example, fair trade certification requires cocoa farmers in West Africa to eliminate child labor from their operations and provide education opportunities for children instead.
3. Sustainable practices: Another aspect of fair trade is promoting environmentally sustainable practices. Producers are encouraged to adopt organic farming methods, reduce chemical usage, conserve water resources, and protect biodiversity. These sustainable practices not only benefit the environment but also enhance the long-term viability of agricultural systems. In Peru, fair trade-certified quinoa farmers have implemented soil conservation techniques such as crop rotation and terracing to prevent erosion and maintain soil fertility, ensuring the sustainability of their quinoa production.
4. Market access: Fair trade organizations also assist farmers and artisans in accessing global markets, which can be challenging for small-scale producers. By connecting them directly with buyers, fair trade eliminates the need for intermediaries and enables producers to negotiate better prices and establish long-term relationships. This market access empowers farmers and artisans to expand their customer base, increase sales, and ultimately contribute to economic growth in their communities. For instance, fair trade cooperatives in India have been able to export their handcrafted textiles to

Fair Trade as a Catalyst for Economic Growth - Fair trade: Promoting Fair Trade through Green Economics
9. A Catalyst for Economic Disaster
The housing bubble of the early 2000s was a significant catalyst for the global financial crisis that unfolded in 2008. This section will delve into the causes and consequences of the housing bubble, shedding light on how it led to an economic disaster of unprecedented proportions. By examining various perspectives and providing detailed insights, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of this pivotal event.
1. Excessive lending practices: One of the primary factors contributing to the housing bubble was the lax lending standards prevalent during this period. Financial institutions, driven by the desire for higher profits, began offering subprime mortgages to borrowers with low creditworthiness. These loans often had adjustable interest rates or required minimal down payments, making them attractive to individuals who would not have qualified for traditional mortgages. As a result, there was a surge in demand for housing, leading to inflated prices and an unsustainable market.
2. Speculative investing: The housing bubble was further fueled by speculative investing in real estate. Many individuals saw housing as a lucrative investment opportunity and purchased multiple properties with the intention of selling them at a higher price in the future. This speculative behavior created an artificial demand for housing, driving up prices even further. However, when the bubble burst, these investors were left with properties they couldn't sell at a profit, exacerbating the crisis.
3. securitization and toxic debt: To maximize profits from mortgage lending, financial institutions bundled thousands of mortgages together and sold them as mortgage-backed securities (MBS) to investors worldwide. These MBS were often given high credit ratings despite being backed by risky subprime mortgages. As more and more subprime borrowers defaulted on their loans, these MBS became toxic assets that triggered massive losses for investors and financial institutions alike.
4. impact on financial institutions: The collapse of the housing bubble had severe repercussions on financial institutions that held significant amounts of toxic debt. Many banks faced insolvency as their balance sheets were laden with nonperforming loans and plummeting asset values. The subsequent credit freeze caused interbank lending to seize up, leading to a liquidity crisis that spread throughout the global financial system.
5. Ripple effects on the economy: The bursting of the housing bubble had far-reaching consequences for the broader economy. As home prices plummeted, homeowners found themselves underwater, owing more on their mortgages than their homes were worth. This led to a wave of foreclosures and a sharp decline in consumer spending as households faced financial distress. The resulting decrease in demand further weakened the economy, leading

A Catalyst for Economic Disaster - Global financial crisis: Tracing the Origins of Toxic Debt
10. Regenerative Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Innovation
1. creating Sustainable business Models
Regenerative entrepreneurship is transforming industries by championing sustainable business models that prioritize environmental and social impact alongside profit. These entrepreneurs are challenging the traditional notion of business as solely profit-driven and are instead focusing on creating businesses that regenerate and restore the planet. One example of regenerative entrepreneurship in action is the rise of circular economy businesses.
2. Embracing the Circular Economy
Circular economy businesses aim to eliminate waste and maximize the use of resources by designing products and services with a focus on longevity, repairability, and recyclability. These businesses are disrupting traditional linear models of production and consumption, where resources are extracted, consumed, and discarded. Instead, they are adopting circular models that promote the reuse, repair, and recycling of products, creating a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and reduces the strain on natural resources.
3. Case Study: Patagonia
Patagonia, the outdoor clothing and gear company, is a prime example of regenerative entrepreneurship in action. The company has long been committed to environmental sustainability, and its business practices reflect this dedication. Patagonia not only produces durable and high-quality products but also encourages customers to repair and reuse their items through its Worn Wear program. The company even goes a step further by offering free repairs for its products, reducing waste and extending the lifespan of its products. By embracing regenerative practices, Patagonia has not only created a loyal customer base but has also become a leader in sustainability within the industry.
4. Fostering Innovation through Collaboration
Regenerative entrepreneurship also fosters innovation by encouraging collaboration and knowledge-sharing among entrepreneurs, businesses, and stakeholders. This collaborative approach allows for the exchange of ideas, resources, and expertise, leading to the development of innovative solutions to complex environmental and social challenges. For example, organizations like B Lab and the Global Impact Investing Network (GIIN) bring together entrepreneurs, investors, and policymakers to drive positive change through regenerative entrepreneurship.
5. Case Study: The Ocean Cleanup
The Ocean Cleanup, founded by Boyan Slat, is a prime example of how collaboration and innovation can drive regenerative entrepreneurship. The organization aims to rid the world's oceans of plastic waste by developing advanced technologies and systems. By partnering with governments, businesses, and researchers, The Ocean Cleanup has been able to deploy its innovative cleanup systems and make significant progress in tackling the global issue of plastic pollution.
6. Conclusion
Regenerative entrepreneurship is a catalyst for economic growth and innovation, driving positive change in industries worldwide. By prioritizing sustainability, embracing circular economy principles, and fostering collaboration, regenerative entrepreneurs are reshaping the business landscape and creating a more sustainable future. Examples like Patagonia and The Ocean Cleanup illustrate the power of regenerative entrepreneurship in driving positive environmental and social impact while also achieving economic success. As more entrepreneurs embrace regenerative practices, the potential for transformative change across industries is immense.

Regenerative Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Innovation - How Regenerative Entrepreneurship is Driving Positive Change in Industries Worldwide
11. Human Rights as a Catalyst for Economic Development
Human rights and economic development are often seen as separate issues, with human rights being viewed as a moral imperative and economic development as a means to improve living standards. However, the two are intricately linked, and human rights can actually serve as a catalyst for economic development. When individuals' rights are respected and protected, it creates an environment that fosters economic growth and stability. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which human rights can drive economic development.
1. Empowering individuals: Human rights empower individuals by providing them with the necessary tools and opportunities to participate in economic activities. When individuals have access to education, healthcare, and equal opportunities, they are more likely to contribute to the workforce and drive economic growth.
For example, in countries where education is not a fundamental right, many children are denied access to quality education. This hinders their ability to acquire the skills and knowledge necessary for employment, ultimately stifling economic development. On the other hand, countries that prioritize education as a human right see higher literacy rates and a more skilled workforce, which in turn attracts investment and drives economic growth.
2. fostering social cohesion: Human rights promote social cohesion by ensuring that all members of society are treated with dignity and respect. This inclusivity creates a sense of trust and stability, which are essential for economic development. When individuals feel safe and secure in their rights, they are more likely to invest in their communities and contribute to economic activities.
For instance, in societies where discrimination based on race, gender, or religion is prevalent, certain groups may be marginalized and excluded from economic opportunities. This not only perpetuates inequality but also hinders overall economic progress. Conversely, societies that prioritize human rights and equality see greater social cohesion, leading to increased cooperation and economic development.
3. Attracting foreign investment: Respecting human rights can also attract foreign investment. Companies and investors are increasingly concerned about the ethical and social impact of their operations. They are more likely to invest in countries that have a strong human rights record, as it reduces the risk of negative publicity and potential legal issues.
For example, companies that operate in countries with lax labor laws and poor human rights records may face boycotts and reputational damage. On the other hand, companies that operate in countries where workers' rights are protected and respected are more likely to attract socially responsible investors and consumers, leading to increased investment and economic growth.
4. enhancing productivity and innovation: Human rights can enhance productivity and drive innovation by ensuring that individuals have the freedom to express their ideas and participate in decision-making processes. When individuals are empowered to exercise their rights, they are more likely to contribute to the development of new technologies, products, and services.
For instance, countries that prioritize freedom of expression and protect intellectual property rights create an environment that encourages innovation. This fosters entrepreneurship and attracts investments in research and development, leading to economic growth.
Human rights serve as a catalyst for economic development by empowering individuals, fostering social cohesion, attracting foreign investment, and enhancing productivity and innovation. It is crucial for governments, businesses, and individuals to recognize the interconnectedness of human rights and economic development and work towards creating an inclusive and rights-respecting society. By ensuring that human rights are protected, we can create an environment that not only upholds the dignity and well-being of individuals but also drives sustainable economic growth.

Human Rights as a Catalyst for Economic Development - Human rights: Protecting Human Rights: A Pillar of Social License
12. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Introduction: The Power of Indigenous Entrepreneurship
1. Historical Context: The Resilience of Indigenous Entrepreneurship
Indigenous entrepreneurship has a rich and resilient history that dates back centuries. Despite the challenges and barriers they have faced, indigenous communities have long showcased their entrepreneurial spirit and resourcefulness. From trading networks that spanned vast territories to the creation of innovative products and services, indigenous entrepreneurs have made significant contributions to their communities and the broader economy.
2. Cultural Heritage: Preserving and Revitalizing Indigenous Traditions
Indigenous entrepreneurship is deeply rooted in cultural heritage and traditions. Many indigenous entrepreneurs draw inspiration from their ancestors and the wisdom passed down through generations. By incorporating traditional knowledge, practices, and craftsmanship into their businesses, they not only preserve their heritage but also create unique products and services that cater to a growing market demand for authentic and sustainable offerings.
For example, in Canada, the Haida Gwaii Indigenous community has established successful enterprises that showcase their art, including totem poles and intricate carvings. These businesses not only provide economic opportunities for the community but also serve as a way to share their cultural heritage with the world.
3. Economic Empowerment: Building Prosperity within Indigenous Communities
Indigenous entrepreneurship has the power to drive economic growth and prosperity within indigenous communities. By creating businesses and generating employment opportunities locally, indigenous entrepreneurs contribute to reducing poverty, improving living standards, and fostering self-sufficiency.
In New Zealand, the Māori people have embraced entrepreneurship as a means of economic empowerment. Their businesses span various sectors, from tourism and hospitality to arts and crafts. These enterprises not only generate income but also create a sense of pride and identity within the community, leading to improved social well-being.
4. Social Impact: Addressing Community Needs and Challenges
Indigenous entrepreneurs often have a deep understanding of the unique challenges and needs within their communities. They leverage their entrepreneurial skills to develop innovative solutions that address social issues, such as access to healthcare, education, and clean energy.
For instance, in the United States, the Navajo Nation has embraced renewable energy entrepreneurship as a way to address energy poverty and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Through the development of solar and wind farms, Navajo entrepreneurs are not only creating sustainable energy sources but also generating employment opportunities for the community.
5. Collaboration and Partnerships: Strengthening Indigenous Entrepreneurship
Collaboration and partnerships with non-indigenous businesses, governments, and organizations play a crucial role in supporting and strengthening indigenous entrepreneurship. By working together, these stakeholders can provide access to capital, mentorship, and market opportunities, while also fostering cross-cultural understanding and appreciation.
One successful example of collaboration is the Manitoba Indigenous Cultural Education Centre (MICEC) in Canada. MICEC works with both indigenous and non-indigenous partners to support the growth of indigenous businesses through training, networking, and access to funding. This collaborative approach has led to the development of sustainable enterprises that preserve indigenous traditions and contribute to economic growth.
In conclusion, indigenous entrepreneurship is a powerful catalyst for economic growth and social change. Through their resilience, cultural heritage, economic empowerment, social impact, and collaborative efforts, indigenous entrepreneurs are driving positive transformations within their communities and beyond. By recognizing and supporting their unique contributions, we can create a more inclusive and prosperous future for all.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Introduction: The Power of Indigenous Entrepreneurship - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
13. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Historical Context: Challenges and Opportunities for Indigenous People
1. Loss of Land and Resources: One of the most significant historical challenges faced by Indigenous people is the loss of their traditional lands and resources. Throughout history, colonization and forced assimilation policies have resulted in the displacement of Indigenous communities, leading to the loss of their connection to the land and the resources it provides. This loss has had a profound impact on Indigenous cultures, spirituality, and economies.
For example, the forced removal of Indigenous people from their ancestral lands in North America resulted in the disruption of traditional hunting, fishing, and gathering practices. This not only affected their ability to sustain themselves but also led to the erosion of cultural practices and knowledge that had been passed down through generations.
2. Cultural Suppression and Discrimination: Indigenous people have also faced significant challenges in preserving their cultural identity and facing discrimination. Historical policies aimed at assimilating Indigenous people into mainstream society often suppressed their cultural practices, languages, and beliefs. This has had a detrimental effect on Indigenous communities, leading to a loss of cultural heritage and a sense of identity.
For instance, the Canadian residential school system, which operated from the late 19th century to the late 20th century, forcibly removed Indigenous children from their families and communities, aiming to assimilate them into Euro-Canadian culture. This traumatic experience resulted in the loss of language, cultural practices, and intergenerational trauma that continues to impact Indigenous communities today.
3. Economic Marginalization: Indigenous people have historically faced economic marginalization, with limited access to education, employment opportunities, and resources. This has hindered their ability to participate fully in the economy and has perpetuated cycles of poverty and inequality.
In many cases, Indigenous people have been excluded from mainstream economic activities and have faced systemic barriers to entrepreneurship and economic development. Lack of financial resources, limited access to capital, and cultural biases have made it difficult for Indigenous entrepreneurs to start and grow businesses.
However, despite these historical challenges, there are also opportunities for Indigenous people to reclaim their economic power and create positive change:
4. Cultural Revitalization: Indigenous entrepreneurs have been at the forefront of cultural revitalization efforts, using their businesses as a means to preserve and promote their cultural heritage. By incorporating traditional knowledge, art, and practices into their products and services, Indigenous entrepreneurs are not only creating economic opportunities but also fostering a sense of pride and connection to their cultural roots.
For example, Indigenous artists and artisans are leveraging their skills and creativity to produce traditional crafts, artwork, and fashion that celebrate their cultural identity. These products not only generate income but also help to educate and raise awareness about Indigenous cultures.
5. Collaborative Partnerships: Indigenous entrepreneurs are increasingly forging partnerships with non-Indigenous businesses, governments, and organizations to create economic opportunities and address historical injustices. These partnerships can provide access to resources, markets, and mentorship, enabling Indigenous entrepreneurs to overcome some of the systemic barriers they face.
For instance, Indigenous communities in Canada have partnered with mining companies to negotiate agreements that ensure Indigenous participation and benefit from resource development projects. These agreements often include provisions for job creation, training programs, and revenue sharing, providing economic opportunities for Indigenous communities.
In conclusion, the historical challenges faced by Indigenous people, such as the loss of land and resources, cultural suppression, and economic marginalization, have had a profound impact on their communities. However, there are also opportunities for Indigenous people to reclaim their economic power and create positive change through cultural revitalization and collaborative partnerships. By supporting Indigenous entrepreneurship, we can contribute to economic growth and social change that respects and celebrates Indigenous cultures and identities.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Historical Context: Challenges and Opportunities for Indigenous People - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
14. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:The Economic Impact of Indigenous Entrepreneurship
1. Increased Job Creation: Indigenous entrepreneurship has a significant economic impact on communities by creating job opportunities. When indigenous entrepreneurs establish and grow their businesses, they often hire locally, providing employment to members of their community. This not only reduces unemployment rates but also fosters economic self-sufficiency within indigenous communities.
For instance, the Maasai Treads shoe company in Kenya, founded by a Maasai entrepreneur, employs members of the Maasai community to produce and sell their handmade shoes. This not only generates income for the employees but also preserves traditional craftsmanship and cultural heritage.
2. Community Development: Indigenous entrepreneurs contribute to community development through their businesses. They often reinvest their profits back into the community by supporting local infrastructure projects, education initiatives, healthcare facilities, and social programs. This, in turn, drives economic growth and improves the overall standard of living within indigenous communities.
One such example is the Red Cloud Renewable Energy Center on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in South Dakota, USA. The center, founded by Henry Red Cloud, a member of the Oglala Lakota tribe, provides training in renewable energy technologies and helps install solar panels in tribal homes. This initiative not only promotes sustainable energy but also creates employment opportunities and reduces energy costs for the community.
3. Cultural Preservation: Indigenous entrepreneurship plays a vital role in preserving and promoting indigenous cultures and traditions. By starting businesses that incorporate traditional practices and knowledge, indigenous entrepreneurs are able to showcase their cultural heritage to a wider audience while also preserving it for future generations. This not only fosters cultural pride but also creates unique selling points for their products and services.
For example, the Yolngu Aboriginal Art Gallery in Australia showcases and sells artwork created by Yolngu artists. The gallery not only provides a platform for indigenous artists to exhibit their work but also educates visitors about the cultural significance of traditional Aboriginal art forms.
4. Economic Diversification: Indigenous entrepreneurship contributes to economic diversification by introducing new industries and business models to indigenous communities. By creating businesses in sectors such as tourism, agriculture, arts and crafts, and technology, indigenous entrepreneurs reduce their communities' reliance on a single industry or source of income. This diversification strengthens the local economy and improves its resilience against economic shocks.
In New Zealand, the Māori-owned seafood company, Moana New Zealand, has successfully diversified its operations to include not only fishing but also aquaculture, processing, and marketing. This has not only created employment opportunities but also contributed to the sustainable management of marine resources and the economic well-being of Māori communities.
In conclusion, indigenous entrepreneurship has a profound economic impact, leading to job creation, community development, cultural preservation, and economic diversification. By supporting and empowering indigenous entrepreneurs, societies can reap the benefits of their innovation, creativity, and unique perspectives, while also promoting social change and inclusive economic growth.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:The Economic Impact of Indigenous Entrepreneurship - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
15. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Case Studies: Successful Indigenous Entrepreneurs
1. Wahkohtowin: Building a Sustainable Future
One remarkable example of a successful Indigenous entrepreneur is Shawn A-in-chut Atleo, a member of the Ahousaht First Nation in British Columbia, Canada. Atleo founded Wahkohtowin Development LP, a company focused on sustainable economic development and social change within indigenous communities.
Wahkohtowin has implemented various initiatives to empower Indigenous communities and foster economic growth. For instance, they have established partnerships with local businesses, government agencies, and educational institutions to create employment opportunities and promote skills development. Through their efforts, Wahkohtowin has not only revitalized the economy of Ahousaht First Nation but has also enhanced the community's overall well-being.
2. Tanka Bar: Embracing Traditional Foods
Another inspiring Indigenous entrepreneur is Karlene Hunter, a member of the Oglala Lakota Sioux Tribe. Hunter co-founded Tanka Bar, a company that produces nutrient-dense, buffalo-based food products while honoring traditional Native American values.
Tanka Bar's success lies in their commitment to sustainability and cultural preservation. By incorporating buffalo meat, a staple of Native American diets for centuries, into their products, Tanka Bar not only promotes healthier eating habits but also supports the preservation of Indigenous heritage. Additionally, the company actively engages with Native American communities, providing economic opportunities for local producers and ranchers.
3. Raven Indigenous Capital Partners: Investing in Indigenous Innovation
Raven Indigenous Capital Partners is a groundbreaking venture capital firm that focuses on investing in Indigenous-led businesses. Led by entrepreneur and investor Paul Lacerte, this firm aims to address the funding gap experienced by Indigenous entrepreneurs and support their growth and success.
By providing capital, mentorship, and business development support, Raven Indigenous Capital Partners has played a crucial role in empowering Indigenous entrepreneurs across various sectors. Their investments have led to the creation of jobs, the development of innovative products and services, and the overall economic empowerment of Indigenous communities.
4. Eighth Generation: Celebrating Indigenous Artistry
Louie Gong, a Nooksack tribal member, founded Eighth Generation, a Native-owned and operated company that showcases and promotes Indigenous artistry. Eighth Generation produces a wide range of products, including blankets, apparel, and accessories, all featuring authentic Indigenous designs.
Through their commitment to fair trade practices and collaboration with Indigenous artists, Eighth Generation has created a platform for Indigenous artists to showcase their work and generate income. By blending cultural heritage with contemporary design, they have successfully captured a broad market and increased awareness and appreciation for Indigenous art and culture.
These case studies highlight the incredible achievements of Indigenous entrepreneurs who have not only achieved personal success but have also positively impacted their communities. Their stories serve as inspiration for aspiring Indigenous entrepreneurs and demonstrate the immense potential for economic growth and social change through Indigenous entrepreneurship.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Case Studies: Successful Indigenous Entrepreneurs - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
16. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Cultural Preservation through Indigenous Entrepreneurship
1. Building Sustainable Economies: Indigenous Entrepreneurship as a Tool for Cultural Preservation
Indigenous entrepreneurship is not just about economic growth and social change; it also plays a crucial role in preserving and promoting indigenous cultures worldwide. By harnessing their unique cultural heritage and traditional knowledge, indigenous entrepreneurs are able to create business ventures that not only generate income but also serve as powerful vehicles for cultural preservation.
2. Revitalizing Traditional Crafts and Art Forms
One way indigenous entrepreneurs contribute to cultural preservation is by revitalizing traditional crafts and art forms. Many indigenous communities possess unique artistic traditions that have been passed down through generations. However, with the pressures of modernization and globalization, these traditional art forms are at risk of being lost. Indigenous entrepreneurs step in by creating businesses that focus on preserving and promoting these art forms.
For example, in the Maori community of New Zealand, there has been a resurgence in traditional carving and weaving practices. Indigenous entrepreneurs have established businesses that not only produce and sell traditional Maori crafts but also provide training and employment opportunities for community members. These initiatives not only help to preserve Maori culture but also ensure that traditional knowledge and skills are passed on to future generations.
3. Indigenous Tourism: Sharing Cultural Experiences
Indigenous entrepreneurship in the tourism industry is another powerful tool for cultural preservation. Many indigenous communities boast rich cultural traditions, unique languages, and vibrant customs that attract tourists from around the world. By creating their own tourism businesses, indigenous entrepreneurs can showcase their culture and offer authentic experiences that are respectful and beneficial to their communities.
For instance, in Canada, Indigenous-owned tour operators offer visitors the opportunity to learn about and engage with First Nations, Inuit, and Métis cultures. These tours provide insights into indigenous history, traditions, and ways of life, while also providing economic opportunities for local communities. By participating in these tourism ventures, indigenous entrepreneurs ensure that their cultural heritage remains vibrant and appreciated.
4. Traditional Knowledge as a Source of Innovation
Indigenous entrepreneurship also taps into traditional knowledge as a source of innovation. Indigenous communities possess deep knowledge of their local ecosystems, sustainable agricultural practices, and traditional medicines. By incorporating this traditional knowledge into their businesses, indigenous entrepreneurs not only create unique products and services but also contribute to the preservation of their cultural heritage.
For example, in the Amazon rainforest, indigenous entrepreneurs are harnessing their traditional knowledge of medicinal plants to create natural skincare and wellness products. These businesses not only provide income for indigenous communities but also raise awareness about the importance of preserving the rainforest and indigenous cultures.
In conclusion, indigenous entrepreneurship serves as a catalyst for economic growth and social change, but its impact goes beyond mere financial success. Through their businesses, indigenous entrepreneurs actively contribute to the preservation of their cultural heritage, revitalizing traditional crafts, sharing cultural experiences through tourism, and incorporating traditional knowledge into innovative ventures. By supporting and promoting indigenous entrepreneurship, we can help safeguard indigenous cultures for future generations.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Cultural Preservation through Indigenous Entrepreneurship - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
17. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Empowering Indigenous Communities through Business Ownership
1. Preserving Cultural Heritage
One of the significant benefits of empowering indigenous communities through business ownership is the preservation of their cultural heritage. When indigenous individuals establish their businesses, they have the opportunity to integrate their traditional practices, arts, crafts, and values into their products or services. For example, a Native American entrepreneur may open a shop that sells handmade jewelry, showcasing their cultural designs and techniques. This not only allows them to pass down their traditions to future generations but also helps to educate and raise awareness about their culture among the wider population.
2. Economic Self-Sufficiency
Business ownership provides indigenous communities with a pathway to economic self-sufficiency. By creating their enterprises, they can generate income and reduce their reliance on external sources of support. This financial independence enables them to invest in education, housing, healthcare, and other crucial needs within their communities. For instance, a group of indigenous farmers may establish a cooperative to collectively cultivate and sell their organic produce. This not only allows them to achieve economic stability but also contributes to the overall development of their community.
3. job Creation and employment Opportunities
Indigenous business ownership plays a vital role in creating job opportunities within their communities. By starting their enterprises, indigenous entrepreneurs are not only able to provide employment to themselves but also to others within their community. This helps to combat the issue of high unemployment rates often experienced by indigenous populations. For example, a Maori entrepreneur may establish a cultural tourism company, employing local community members as guides, artisans, or administrative staff. By creating jobs, indigenous business owners contribute to reducing poverty and improving the overall well-being of their community members.
4. Fostering Community Development
Business ownership within indigenous communities fosters community development by encouraging collaboration and collective decision-making. When indigenous individuals come together to start businesses, they often form partnerships, cooperatives, or community-based organizations. Through these collaborative efforts, they can pool resources, share knowledge, and support each other's growth. For instance, a group of indigenous artists may establish a cooperative gallery, where they can collectively market and sell their artwork. This not only strengthens their economic prospects but also promotes a sense of unity and empowerment within the community.
5. Advocating for Indigenous Rights
Indigenous business ownership can serve as a platform for advocating for indigenous rights and addressing social issues. By owning and operating their businesses, indigenous entrepreneurs can create awareness about the challenges faced by their communities and work towards finding solutions. They can use their businesses as a means to educate the public, policymakers, and other stakeholders about the importance of indigenous rights and the need for inclusive and equitable policies. For example, an indigenous-owned media company may produce documentaries or news articles that shed light on the struggles of indigenous communities and highlight their contributions to society. This advocacy work can lead to positive social change and contribute to the broader movement for indigenous rights and recognition.
In conclusion, empowering indigenous communities through business ownership brings numerous benefits, including the preservation of cultural heritage, economic self-sufficiency, job creation, community development, and advocacy for indigenous rights. By supporting and promoting indigenous entrepreneurship, we can help foster economic growth while respecting and valuing the unique contributions and perspectives of indigenous peoples.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Empowering Indigenous Communities through Business Ownership - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
18. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Government Support and Policies for Indigenous Entrepreneurs
1. Financial Support Programs:
One of the key ways in which governments support Indigenous entrepreneurs is through various financial support programs. These programs aim to provide funding and resources to help Indigenous entrepreneurs start and grow their businesses. For example, in Canada, the government has established programs like the Aboriginal business Development program (ABDP) and the Indigenous Entrepreneur Loan Fund (IELF). These programs offer financial assistance in the form of loans, grants, and equity investments to support Indigenous entrepreneurs in accessing capital.
2. business development Support:
In addition to financial support, governments also provide Indigenous entrepreneurs with business development support services. These services are designed to help entrepreneurs develop their business ideas, create business plans, and access training and mentorship opportunities. For instance, the Australian government has established the Indigenous Business Australia (IBA) program, which offers business development support services such as business planning, financial management, and marketing assistance.
3. Procurement Policies:
Governments can also play a crucial role in supporting Indigenous entrepreneurs through procurement policies. These policies aim to increase the participation of Indigenous businesses in government procurement processes. For example, the United States government has implemented the Buy Indian Act, which gives preference to Indian-owned businesses in the procurement of goods and services for federal agencies. This policy not only provides Indigenous entrepreneurs with opportunities to secure government contracts but also helps to promote economic development in Indigenous communities.
4. Capacity Building Initiatives:
To further support Indigenous entrepreneurs, governments often invest in capacity building initiatives. These initiatives focus on equipping Indigenous entrepreneurs with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the business world. For instance, the New Zealand government has established the Te Puni Kōkiri Māori Women's Development Fund, which provides funding for training and development programs specifically targeted at Māori women entrepreneurs. Such initiatives help to empower Indigenous entrepreneurs and enable them to overcome barriers to success.
5. Collaborative Partnerships:
Another important aspect of government support for Indigenous entrepreneurs is the establishment of collaborative partnerships. Governments often work with Indigenous organizations, industry associations, and non-profit organizations to provide comprehensive support to Indigenous entrepreneurs. For example, the Canadian government partners with organizations like the National Aboriginal Capital Corporations Association (NACCA) and the Canadian Council for Aboriginal Business (CCAB) to deliver financial and business development support programs to Indigenous entrepreneurs. These partnerships help to leverage resources and expertise, ensuring that Indigenous entrepreneurs have access to a wide range of support services.
In conclusion, government support and policies play a critical role in fostering the growth and success of Indigenous entrepreneurs. Through financial support programs, business development services, procurement policies, capacity building initiatives, and collaborative partnerships, governments around the world are working towards creating an enabling environment for Indigenous entrepreneurship. These efforts not only contribute to economic growth but also promote social change by empowering Indigenous communities and improving their socio-economic well-being.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Government Support and Policies for Indigenous Entrepreneurs - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
19. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Overcoming Barriers: Access to Capital and Resources
1. Identifying Barriers: Access to Capital and Resources
Indigenous entrepreneurs face unique challenges when it comes to accessing capital and resources. These barriers can hinder their ability to start and grow successful businesses. However, there are strategies and initiatives in place that aim to overcome these obstacles and create opportunities for Indigenous entrepreneurs to thrive.
2. Limited Financial Resources
One of the main barriers Indigenous entrepreneurs face is a lack of financial resources. Many Indigenous communities have historically faced economic disadvantages, which can make it difficult for individuals to access traditional funding sources such as banks or venture capitalists. This limited access to capital can hinder the growth and development of Indigenous-owned businesses.
To overcome this barrier, various organizations have been established to provide financial support specifically tailored to the needs of Indigenous entrepreneurs. For example, the National Aboriginal Capital Corporations Association (NACCA) in Canada offers loans and business support services to Indigenous entrepreneurs. These organizations understand the unique challenges faced by Indigenous entrepreneurs and provide resources to help them succeed.
3. Limited Access to Networks and Markets
Another barrier for Indigenous entrepreneurs is limited access to networks and markets. Building connections and finding customers can be challenging, especially for those operating in remote or marginalized communities. Without access to wider markets, Indigenous entrepreneurs may struggle to scale their businesses and reach their full potential.
To address this barrier, initiatives like Indigenous business networks have emerged to connect Indigenous entrepreneurs with opportunities and resources. These networks provide a platform for Indigenous entrepreneurs to collaborate, share knowledge, and access new markets. For instance, the Canadian Council for Aboriginal Business (CCAB) organizes networking events and connects Indigenous entrepreneurs with corporations looking to support Indigenous businesses.
4. Cultural and Language Barriers
Cultural and language barriers can also pose challenges for Indigenous entrepreneurs. traditional business models may not align with Indigenous values and practices, making it difficult to navigate the business world. Additionally, language barriers can limit access to resources and information necessary for business success.
To overcome these barriers, culturally sensitive entrepreneurship programs and training have been developed. These programs provide guidance and support tailored to the cultural context of Indigenous entrepreneurs. For example, the First Nations University of Canada offers an Indigenous Business and Entrepreneurship program that integrates Indigenous culture and business practices.
5. Government Support and Partnerships
Governments have recognized the importance of supporting Indigenous entrepreneurship and have implemented various programs and policies to address these barriers. For example, in Canada, the federal government has established the Indigenous Entrepreneurship Initiative, which provides funding and support for Indigenous entrepreneurs. Additionally, partnerships between government agencies, Indigenous organizations, and private sector companies have been formed to create opportunities and support the growth of Indigenous businesses.
In conclusion, while Indigenous entrepreneurs face significant barriers when it comes to accessing capital and resources, there are strategies and initiatives in place to overcome these challenges. By providing tailored financial support, fostering networks and partnerships, and addressing cultural and language barriers, Indigenous entrepreneurs can be empowered to succeed and contribute to economic growth and social change in their communities.
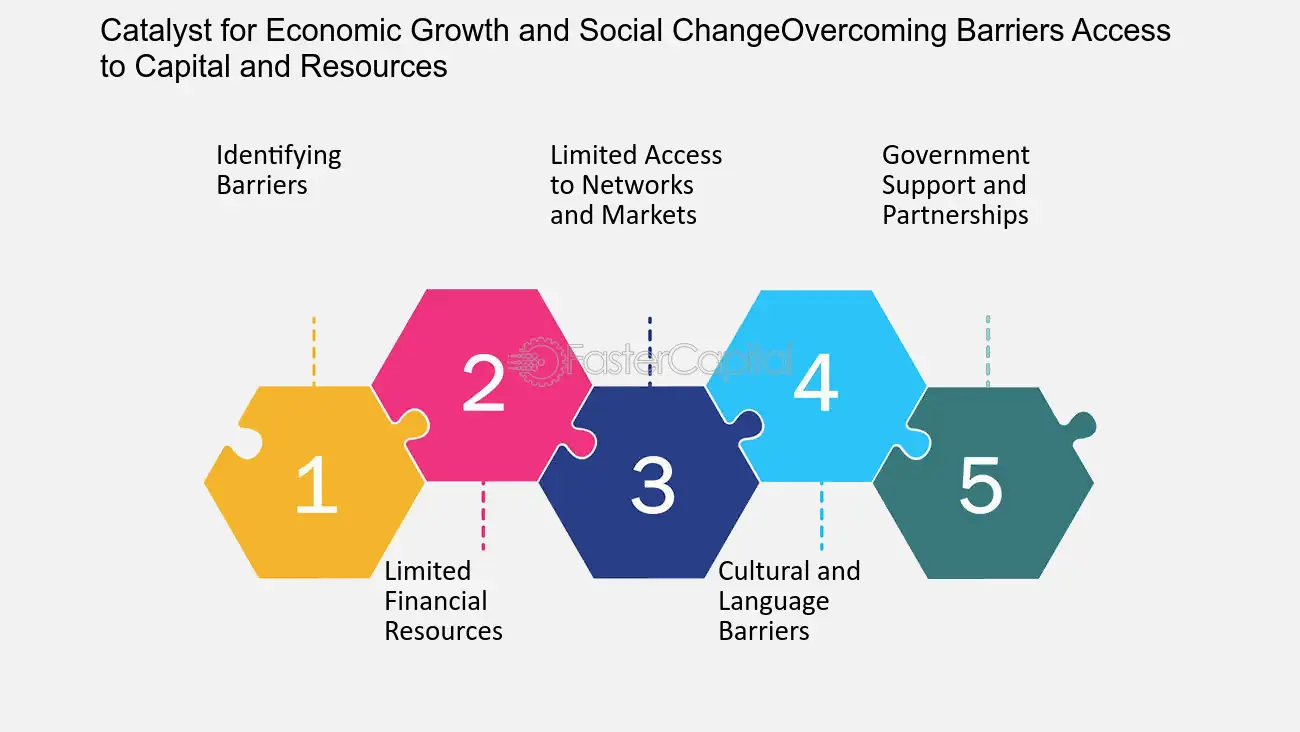
A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Overcoming Barriers: Access to Capital and Resources - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
20. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:The Role of Education and Skills Development in Indigenous Entrepreneurship
1. Access to Education: A Key Driver of Indigenous Entrepreneurship
Access to quality education plays a crucial role in empowering indigenous communities and fostering their entrepreneurial spirit. Education equips individuals with the necessary knowledge, skills, and mindset to identify and seize opportunities, effectively manage resources, and navigate the complexities of the business world.
2. Breaking the Cycle of Poverty
Education serves as a powerful tool to break the cycle of poverty that plagues many indigenous communities. By providing access to education, individuals can acquire the skills needed to create sustainable businesses and generate income, thus improving their economic well-being and that of their communities.
For example, in the Maasai community of Kenya, the Maasai Women's Education and Empowerment Program (MWEEP) focuses on providing education and entrepreneurial training to Maasai women. Through this program, women gain the necessary skills to start and manage their own businesses, such as beadwork and farming cooperatives. As a result, these women have been able to enhance their economic independence, improve their families' livelihoods, and contribute to the overall development of their community.
3. Preserving Indigenous Culture and Traditions
Education can also play a vital role in preserving and promoting indigenous culture and traditions. By incorporating indigenous knowledge and practices into educational curricula, indigenous entrepreneurship can thrive while maintaining cultural integrity.
For instance, the Nunavut Sivuniksavut program in Canada provides Inuit students with a culturally relevant education that combines traditional teachings with modern business skills. This unique approach not only empowers Inuit students to become successful entrepreneurs but also ensures the preservation and celebration of their cultural heritage.
4. Fostering Innovation and Adaptability
Education and skills development are essential in fostering innovation and adaptability within indigenous communities. By equipping individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills, they are better prepared to identify and respond to market trends, technological advancements, and changing consumer demands.
In New Zealand, the Māori Innovation Network (Te Aho Tāmaka) focuses on fostering innovation and entrepreneurship among the Māori community. Through various programs, workshops, and mentorship initiatives, Māori entrepreneurs are encouraged to develop innovative business solutions that align with their cultural values and address the needs of their communities. This approach not only empowers Māori entrepreneurs but also contributes to the overall economic growth and social well-being of the Māori people.
5. Building Networks and Collaborations
Education and skills development provide opportunities for indigenous entrepreneurs to build networks and collaborations, both within their communities and beyond. These connections can lead to knowledge sharing, partnerships, and access to new markets, thus amplifying the impact of indigenous entrepreneurship.
In Australia, the Indigenous Business Australia (IBA) organization offers a range of programs and support services to Indigenous entrepreneurs. These initiatives not only provide access to education and skills development but also facilitate networking opportunities, mentorship, and access to capital. By connecting indigenous entrepreneurs with industry leaders and like-minded individuals, IBA creates a supportive ecosystem that fosters collaboration and accelerates the growth of indigenous businesses.
In conclusion, education and skills development are fundamental pillars in promoting and nurturing indigenous entrepreneurship. By providing access to education, breaking the cycle of poverty, preserving culture, fostering innovation, and facilitating networks and collaborations, indigenous communities can harness their entrepreneurial potential to drive economic growth and social change.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:The Role of Education and Skills Development in Indigenous Entrepreneurship - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
21. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Building Networks and Collaborations within the Indigenous Business Community
1. Attend Indigenous Business Conferences and Events: One of the most effective ways to build networks and collaborations within the Indigenous business community is by attending conferences and events specifically tailored for Indigenous entrepreneurs. These gatherings provide an opportunity to connect with like-minded individuals, learn from industry experts, and forge new partnerships. For instance, the annual National Indigenous Economic Development Board conference brings together Indigenous business leaders from across the country, providing a platform to share experiences, showcase success stories, and establish valuable connections.
2. Join Indigenous Business Associations and Networks: Another avenue to build networks within the Indigenous business community is by joining Indigenous business associations and networks. These organizations are dedicated to supporting and promoting Indigenous entrepreneurship, and they often offer networking events, mentorship programs, and business development resources. For example, the Canadian Council for Aboriginal Business (CCAB) is a national association that connects Indigenous businesses with corporate partners, government agencies, and other stakeholders, fostering collaboration and economic growth.
3. Collaborate on Indigenous-led Economic Development Projects: Collaborating on Indigenous-led economic development projects is not only a great way to build networks within the Indigenous business community but also to contribute to the growth of Indigenous economies. By partnering with other Indigenous entrepreneurs, businesses can leverage their collective strengths, share resources, and pursue larger-scale opportunities. A prime example of such collaboration is the partnership between the Fort McKay First Nation and Enoch Cree Nation, who joined forces to establish the Alberta First Nations Energy Centre. This innovative project aims to provide training and employment opportunities in the energy sector while promoting sustainability and Indigenous self-determination.
4. Engage in Mentorship and Knowledge-Sharing Initiatives: Mentorship and knowledge-sharing initiatives play a crucial role in building networks and collaborations within the Indigenous business community. By connecting experienced entrepreneurs with aspiring ones, these programs facilitate the transfer of valuable skills, insights, and connections. For instance, the Jane Glassco Northern Fellowship program, offered by the Gordon Foundation, pairs emerging northern leaders with experienced mentors to support the development of sustainable businesses and community initiatives.
5. utilize Social media and Online Platforms: In today's digital age, social media and online platforms offer powerful tools to connect and collaborate with Indigenous entrepreneurs across geographical boundaries. Joining online communities, participating in webinars, and engaging with relevant hashtags can help expand networks and foster collaboration. The #IndigenousBusiness and #SupportIndigenousBusiness hashtags on platforms like Twitter and Instagram provide a glimpse into the vibrant Indigenous business community and offer opportunities for networking and collaboration.
Building networks and collaborations within the Indigenous business community is vital for driving economic growth and social change. By actively participating in conferences, joining associations, collaborating on projects, engaging in mentorship initiatives, and utilizing online platforms, Indigenous entrepreneurs can establish valuable connections, share knowledge, and collectively work towards a more prosperous future.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Building Networks and Collaborations within the Indigenous Business Community - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
22. A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Indigenous Entrepreneurship as a Vehicle for Social Change
1. Empowering Indigenous Communities through Entrepreneurship
Indigenous entrepreneurship has emerged as a powerful tool for driving social change within indigenous communities around the world. By harnessing their skills, knowledge, and cultural values, Indigenous entrepreneurs are not only creating economic opportunities but also challenging societal norms and addressing social issues that affect their communities. Here are some examples of how Indigenous entrepreneurship is serving as a vehicle for social change:
2. Preserving Cultural Heritage
Indigenous entrepreneurs often incorporate their cultural heritage into their business models, thus preserving and promoting their traditions and values. For instance, in Canada, Indigenous-owned tourism companies offer authentic cultural experiences that educate visitors about Indigenous history, traditions, and practices. By sharing their stories and showcasing their cultural heritage, these entrepreneurs contribute to the preservation and celebration of Indigenous culture while creating economic opportunities for their communities.
3. Fostering Environmental Stewardship
Many Indigenous entrepreneurs are deeply connected to their lands and have a profound respect for the environment. This connection is often reflected in their business ventures, which prioritize sustainability and environmental stewardship. For example, Indigenous communities in Australia have started their own eco-tourism businesses, offering guided tours that emphasize the importance of protecting and conserving their natural resources. By promoting sustainable practices, these entrepreneurs not only generate income but also raise awareness about environmental issues and inspire others to adopt more sustainable lifestyles.
4. Empowering Indigenous Women
Indigenous women entrepreneurs are breaking barriers and challenging gender norms within their communities. They are not only creating economic opportunities for themselves but also empowering other women by providing mentorship and employment opportunities. For instance, in the United States, the National Center for American Indian Enterprise Development supports Indigenous women entrepreneurs through mentorship programs, business training, and networking opportunities. By promoting women's economic empowerment, these initiatives contribute to greater gender equality within Indigenous communities and beyond.
5. Addressing Social Issues
Indigenous entrepreneurs are taking proactive steps to address social issues that disproportionately affect their communities. They are developing innovative solutions to combat poverty, improve access to education and healthcare, and support community development. For example, in New Zealand, the Māori Women's Development Inc. Provides financial support and business development services to Māori women entrepreneurs, enabling them to start or expand their businesses. By addressing economic disparities and promoting self-sufficiency, these initiatives contribute to the overall well-being and social progress of Indigenous communities.
In conclusion, Indigenous entrepreneurship is more than just a means of economic growth; it is a catalyst for social change. By embracing their cultural heritage, fostering environmental stewardship, empowering women, and addressing social issues, Indigenous entrepreneurs are reshaping the narrative and driving positive change within their communities. Their innovative business models and commitment to social responsibility serve as an inspiration for others, creating a ripple effect that extends far beyond economic prosperity.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change:Indigenous Entrepreneurship as a Vehicle for Social Change - Indigenous Entrepreneurship: A Catalyst for Economic Growth and Social Change
23. Interchange as a Catalyst for Economic Development and Urban Growth
1. Efficient transportation systems are crucial for economic development and urban growth, and one key component that plays a vital role in connecting different transportation networks is the interchange. Interchanges serve as the intersection points between highways, railways, and other modes of transportation, facilitating the smooth flow of goods, services, and people. They act as catalysts for economic development by improving accessibility, reducing travel times, and enhancing connectivity between various regions and urban centers.
2. Accessibility is a fundamental factor in driving economic growth, and interchanges greatly contribute to improving accessibility within and between cities. By providing convenient access points to major transportation routes, interchanges allow businesses to expand their markets and reach a larger customer base. For example, the construction of the Golden Quadrilateral highway network in India, which includes numerous interchanges, has significantly boosted trade and economic activity in the regions it connects.
3. Interchanges also play a crucial role in reducing travel times and congestion. Efficient interchanges enable the seamless movement of vehicles, reducing delays and improving overall transportation efficiency. This not only saves time for commuters but also enhances the productivity of businesses by reducing transportation costs and improving supply chain management. The Tom Moreland Interchange in Atlanta, Georgia, is a prime example of how a well-designed interchange can alleviate congestion and improve traffic flow, benefiting both commuters and businesses alike.
4. Enhancing connectivity is another key aspect of interchanges that promotes economic development and urban growth. By seamlessly connecting different modes of transportation, interchanges enable people and goods to move more easily between various regions, stimulating trade and economic activity. The Port of Rotterdam in the Netherlands serves as a prime example of how an interchange can facilitate economic growth. With direct access to multiple transportation modes, including waterways, railways, and highways, the port has become a major hub for international trade, attracting businesses and generating employment opportunities.
5. In addition to their economic benefits, interchanges also have a significant impact on urban growth. Well-planned interchanges can act as catalysts for urban development by attracting investment and spurring the growth of commercial and residential areas. The Shinagawa Interchange in Tokyo, Japan, is a prime example of how a strategically located interchange can transform an area. The interchange's proximity to major business districts and transportation hubs has led to the development of high-rise office buildings, hotels, and retail centers, making it a thriving economic and commercial hub.
6. To maximize the economic potential of interchanges, it is crucial to consider various factors during their design and planning stages. These include proper integration with existing transportation networks, efficient traffic flow management, and the provision of adequate amenities and services for travelers. By incorporating these considerations, interchanges can effectively serve as catalysts for economic development and urban growth, creating vibrant and interconnected cities.
Interchanges play a vital role in driving economic development and urban growth by improving accessibility, reducing travel times, and enhancing connectivity. They act as catalysts for economic activity, attracting businesses, stimulating trade, and generating employment opportunities. Through strategic planning and design, interchanges can maximize their economic potential and contribute to the growth and prosperity of cities and regions.

Interchange as a Catalyst for Economic Development and Urban Growth - Link: Interchange: The Vital Link between Transportation Networks
24. A Catalyst for Economic Growth
1. Introduction
The Morris Plan Bank, with its innovative approach to lending and financial services, has proven to be a catalyst for economic growth in local communities across the United States. By focusing on providing credit to individuals and small businesses who were previously excluded from traditional banking institutions, the Morris Plan Bank played a crucial role in revitalizing local economies during the early 20th century. In this section, we will explore how the Morris Plan Bank achieved this feat and examine its impact on economic growth.
2. Expansion of Credit Opportunities
One of the key ways in which the Morris Plan Bank stimulated economic growth was by expanding credit opportunities for individuals and small businesses. Prior to the establishment of the Morris Plan Bank, many working-class individuals and small businesses struggled to access credit due to their limited financial resources or lack of collateral. The Morris Plan Bank introduced the concept of installment lending, allowing borrowers to repay loans in regular installments, making credit more accessible to a wider range of individuals.
3. Support for Small Businesses
Small businesses are the backbone of local economies, and the Morris Plan Bank recognized their importance. The bank actively supported small businesses by providing them with the necessary capital to expand their operations, purchase equipment, and hire additional employees. This injection of capital into small businesses not only helped them thrive but also created job opportunities and stimulated economic activity within the communities they served.
4. Financial Education and Empowerment
The Morris Plan Bank understood the importance of financial education and empowerment in driving economic growth. The bank offered financial literacy programs and workshops to educate borrowers on responsible borrowing, budgeting, and financial planning. By equipping individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills, the Morris Plan Bank empowered them to make informed financial decisions and effectively manage their finances, ultimately contributing to the overall economic well-being of the community.
5. Case Study: Morris Plan Bank in Dayton, Ohio
A notable example of the Morris Plan Bank's impact on economic growth can be seen in Dayton, Ohio. In the early 20th century, Dayton was a thriving industrial city with a growing population. However, many individuals and small businesses struggled to access credit, hindering their ability to participate fully in the local economy. The establishment of the Morris Plan Bank in Dayton provided much-needed financial support to these underserved groups. As a result, small businesses flourished, unemployment rates decreased, and the overall economic vitality of the city improved significantly.
6. Tips for Revitalizing Local Economies
Drawing inspiration from the Morris Plan Bank's success, there are several key strategies that can be employed to revitalize local economies today. These include:
- Establishing community development financial institutions (CDFIs) or credit unions that focus on providing credit to underserved individuals and small businesses.
- Offering financial education programs and resources to empower individuals and equip them with the necessary financial skills.
- Encouraging entrepreneurship and supporting small businesses through access to capital and business development resources.
- Collaborating with local government agencies, nonprofit organizations, and community leaders to foster an environment conducive to economic growth.
The Morris Plan Bank serves as an inspiring example of how a financial institution can play a pivotal role in revitalizing local economies. Through its expansion of credit opportunities, support for small businesses, and focus on financial education, the Morris Plan Bank successfully acted as a catalyst for economic growth. By adopting similar strategies today, we can work towards creating vibrant and thriving local economies that benefit all members of the community.

A Catalyst for Economic Growth - Morris Plan Bank: Revitalizing Local Economies
25. Remittances as a Catalyst for Economic Growth in Home Countries
Remittances as a catalyst for Economic growth in Home Countries
Remittances play a significant role in supporting the economies of many countries around the world. These financial transfers from migrants working abroad to their families back home are often a lifeline for families in developing nations. However, the impact of remittances extends far beyond individual households, as they can act as a catalyst for overall economic growth in home countries. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which remittances contribute to economic development and discuss the best options for maximizing their positive effects.
1. Increased consumption and investment: Remittances provide families with additional income, which in turn leads to increased consumption of goods and services. This boost in domestic demand stimulates economic activity, leading to increased production and job creation. Moreover, remittances can also serve as a source of investment, as families may choose to start businesses or invest in existing enterprises. For example, in the Philippines, remittances have fueled the growth of the retail sector, with many families using the funds to open small shops or stalls.
2. Poverty reduction and social welfare: Remittances have proven to be effective in reducing poverty levels in home countries. When families receive additional income through remittances, they are better able to meet their basic needs and improve their living standards. This, in turn, reduces the strain on social welfare programs and allows governments to allocate resources to other areas, such as education and healthcare. For instance, in Mexico, remittances have played a crucial role in lifting millions of people out of poverty, enabling them to access better education and healthcare services.
3. Financial sector development: The influx of remittances into home countries can also contribute to the development of the financial sector. As more people receive remittances, there is an increased demand for financial services, such as banking, savings, and insurance. This demand drives innovation and competition within the financial sector, leading to the expansion of banking networks and the development of new products tailored to the needs of remittance recipients. For example, in India, the growth of remittances has prompted the establishment of specialized financial institutions that offer remittance-related services, including low-cost money transfers and investment options.
4. Entrepreneurship and innovation: Remittances not only provide immediate financial support to families but also have the potential to foster entrepreneurship and innovation. With access to additional funds, individuals may choose to start their own businesses, creating employment opportunities and driving economic growth. Additionally, remittance recipients often acquire new skills and knowledge while working abroad, which they can bring back to their home countries. This transfer of skills and ideas can lead to the development of new industries and the promotion of innovation. For instance, in Nigeria, remittances have played a crucial role in the growth of the tech startup ecosystem, with returning migrants bringing back expertise and capital to launch innovative ventures.
Remittances have the potential to act as a catalyst for economic growth in home countries. Through increased consumption and investment, poverty reduction, financial sector development, and entrepreneurship, remittances can significantly contribute to overall economic development. To maximize the positive impact of remittances, governments and policymakers should focus on creating an enabling environment that supports entrepreneurship, promotes financial inclusion, and encourages investment in sectors with high growth potential. By harnessing the power of remittances, countries can leverage the contributions of their economic refugees to build stronger and more prosperous economies.

Remittances as a Catalyst for Economic Growth in Home Countries - Remittances: Economic Refugees Supporting Their Home Countries
26. Microcredit as a Catalyst for Economic Growth
Microcredit has emerged as a powerful tool in fostering entrepreneurship and driving economic growth in communities around the world. By providing small loans to individuals who lack access to traditional banking services, microcredit programs have enabled aspiring entrepreneurs to start or expand their businesses, creating employment opportunities and stimulating local economies. This section will delve into the transformative power of microcredit from various perspectives, shedding light on its impact on individuals, communities, and the broader economy.
1. Empowering Individuals:
Microcredit empowers individuals by giving them the means to pursue their entrepreneurial dreams. For instance, consider Maria, a talented artisan in a rural village who lacked the necessary funds to purchase raw materials for her handicraft business. Through a microcredit program, Maria was able to secure a small loan that allowed her to buy supplies and grow her business. This not only improved Maria's financial situation but also boosted her self-confidence and sense of agency.
2. Creating Employment Opportunities:
One of the key benefits of microcredit is its ability to generate employment opportunities within communities. As entrepreneurs receive loans and expand their businesses, they often require additional manpower, leading to job creation. For example, in a bustling urban neighborhood, a microcredit recipient named Ahmed used his loan to open a small grocery store. As his business flourished, Ahmed hired local residents to assist him with daily operations, thereby contributing to reducing unemployment rates and enhancing community well-being.
3. Promoting Financial Inclusion:
Microcredit plays a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion by extending credit facilities to those who are excluded from traditional banking systems. This is particularly significant for marginalized groups such as women and low-income individuals who face barriers when seeking loans from conventional banks due to lack of collateral or credit history. By providing access to credit without stringent requirements, microcredit programs enable these underserved populations to participate in economic activities and improve their livelihoods.
4. Encouraging innovation and Economic growth:
Microcredit has been instrumental in fostering innovation and driving economic growth in communities. By providing aspiring entrepreneurs with the necessary capital, microcredit programs encourage experimentation and the development of new business ideas. This leads to the creation of innovative products and services, which not only meet local demands but also have the potential to expand into larger markets, contributing to overall economic growth.
5. strengthening Social capital:
Microcredit programs often operate within close-knit communities, fostering social cohesion and strengthening social capital. As individuals come together to form

Microcredit as a Catalyst for Economic Growth - Social Impact: The Transformative Power of Microcredit on Communities
27. Traditional Craftsmanship Startups in the Modern Age:Empowering Local Communities: Traditional Craftsmanship as a Catalyst for Economic Development
1. Preserving Cultural Heritage
Traditional craftsmanship not only represents the cultural heritage of a community, but it also plays a vital role in preserving and passing down traditional skills and knowledge from one generation to another. By supporting and empowering local artisans, we can ensure that these valuable traditions are safeguarded for future generations.
One example of this is the revival of handloom weaving in a small village in India. The introduction of power looms had threatened to wipe out the traditional handloom weaving industry, as it provided faster and cheaper production. However, with the support of local organizations and the demand for handmade textiles, the artisans were able to revive their craft and create sustainable livelihoods for themselves and their community.
2. Boosting the Local Economy
When traditional craftsmanship is embraced and supported, it has the potential to become a catalyst for economic development in local communities. By investing in the skills and talents of local artisans, we can create a thriving market for their products, which in turn stimulates the local economy.
Take the case of a small town in Italy known for its exquisite ceramics. By organizing workshops and training programs for aspiring ceramic artists, the town was able to attract tourists and buyers from all over the world. This not only created employment opportunities for the locals but also brought in revenue through tourism and exports, thereby boosting the overall economic growth of the community.
3. Fostering Sustainable Practices
Traditional craftsmanship often involves using natural materials and adopting sustainable production methods. This focus on sustainability aligns with the growing global trend towards eco-friendly and ethical consumerism. By promoting traditional crafts, we are encouraging the use of sustainable materials and techniques, which can have a positive impact on the environment.
For instance, in a remote village in Indonesia, traditional woodcarvers have embraced sustainable practices by using only locally sourced timber from responsibly managed forests. This not only helps in preserving the environment but also ensures a continuous supply of raw materials for future generations of artisans.
4. Encouraging Entrepreneurship
Empowering local artisans through traditional craftsmanship can also foster entrepreneurship within the community. By providing them with the necessary skills and resources, artisans can start their own businesses and become self-reliant.
In a rural village in Mexico, a group of women artisans came together to form a cooperative that specializes in weaving traditional textiles. With support from local organizations, they were able to access training, marketing assistance, and financial resources to start their venture. Today, they run a successful business, selling their products both locally and internationally. This not only empowers the women economically but also brings recognition and pride to their community.
5. Revitalizing Cultural Tourism
Traditional craftsmanship has the potential to attract tourists who are seeking authentic cultural experiences. By promoting and showcasing the unique crafts of a region, we can revitalize cultural tourism and put local communities on the map.
For example, in a small town in Morocco, the art of pottery has become a major tourist attraction. Visitors flock to the town to witness the skillful artisans at work, and many even participate in pottery-making workshops. This not only provides income for the artisans but also brings economic benefits to the entire community through increased tourism revenue.
In conclusion, empowering local communities through traditional craftsmanship can have far-reaching benefits. It not only preserves cultural heritage but also boosts the local economy, fosters sustainable practices, encourages entrepreneurship, and revitalizes cultural tourism. By supporting and investing in traditional artisans, we can create a brighter future for both the craftsmen and their communities.

Traditional Craftsmanship Startups in the Modern Age:Empowering Local Communities: Traditional Craftsmanship as a Catalyst for Economic Development - The Artisans' Renaissance: Traditional Craftsmanship Startups in the Modern Age
28. Microloans as a Catalyst for Economic Growth and Poverty Alleviation
Microloans have a far-reaching impact on economic growth and poverty alleviation. By providing access to capital, microloans enable entrepreneurs to invest in their businesses, create jobs, and stimulate local economies. This, in turn, leads to increased income levels, improved living standards, and reduced poverty rates.
A study conducted by the World Bank found that microloans have a positive effect on household income, with borrowers experiencing an average increase of 5-15% in their annual earnings. This additional income not only benefits individual borrowers and their families but also has a multiplier effect on the wider community. As borrowers reinvest their profits into their businesses, they create job opportunities for others, fostering economic growth and development.
Moreover, microloans have proven to be an effective tool for poverty alleviation, particularly among women. Women make up a significant proportion of microloan borrowers, as they are often more excluded from traditional financial services. By providing women with access to capital, microloans empower them to become financially independent, improve their social standing, and contribute to their communities. Numerous studies have shown that empowering women through microloans has a positive ripple effect on education, healthcare, and overall community development.
29. A Catalyst for Economic Stability
Preserving cultural heritage has long been recognized as a crucial aspect of sustainable development, with the potential to not only enrich the lives of individuals but also serve as a catalyst for economic stability. As countries around the world strive to recover from the devastating impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, leveraging their cultural heritage for tourism development becomes even more imperative. This section delves into the multifaceted benefits of preserving cultural heritage and how it can contribute to economic stabilization from various perspectives.
1. Boosting Tourism Revenue:
Preserving cultural heritage sites and traditions can attract tourists from near and far, generating substantial revenue for local economies. For instance, the ancient city of Petra in Jordan, a unesco World Heritage site, draws thousands of visitors each year who contribute to the local economy through accommodation, dining, transportation, and souvenir purchases. By investing in the preservation and promotion of such sites, countries can tap into the vast potential of tourism revenue.
2. Job Creation and Local Employment:
Cultural heritage preservation initiatives often require skilled labor and expertise, providing employment opportunities for local communities. Restoration projects, archaeological excavations, museum operations, and tour guiding are just a few examples of jobs that can be created through heritage preservation efforts. These employment opportunities not only contribute to reducing unemployment rates but also empower local communities by allowing them to actively participate in preserving their own cultural identity.
3. revitalizing Local economies:
Preserving cultural heritage can breathe new life into struggling or underdeveloped regions by attracting investment and fostering entrepreneurship. When historical buildings are restored or traditional crafts are revived, it creates opportunities for small businesses to flourish. For instance, in the town of Oaxaca in Mexico, the preservation of traditional textile weaving techniques has led to the establishment of numerous artisan cooperatives that produce high-quality textiles sought after by both locals and tourists alike.
4. Cultural Exchange and Education:
Preserving cultural heritage not only benefits the economy but also fosters cultural exchange and understanding. When tourists visit heritage sites, they have the opportunity to learn about different cultures, traditions, and histories. This exchange of knowledge can promote tolerance, respect, and appreciation for diversity. Moreover, educational programs centered around cultural heritage can be developed to engage local communities and schools, ensuring that future generations are aware of their rich cultural legacy.
5. Sustainable Development:
Preserving cultural heritage aligns with the principles of sustainable development by promoting responsible tourism practices and environmental conservation. By implementing sustainable tourism strategies, such as

A Catalyst for Economic Stability - Tourism Development Fund: Leveraging Heritage for Economic Stabilization
30. Transshipment as a Catalyst for Economic Growth and Development
1. Transshipment as a catalyst for Economic growth and Development
Transshipment plays a crucial role in driving economic growth and development in countries that serve as key hubs in the global trade network. By facilitating the movement of goods between different regions, transshipment enables efficient logistics and enhances trading opportunities for businesses. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which transshipment acts as a catalyst for economic growth, supported by real-world examples, tips, and case studies.
2. Enhancing Connectivity and Trade Networks
One of the primary benefits of transshipment is its ability to enhance connectivity between different regions, thereby expanding trade networks. By serving as a central hub, transshipment ports enable the consolidation and redistribution of goods, connecting various shipping routes and facilitating trade between distant markets. For instance, the Port of Singapore, known for its strategic location, acts as a transshipment hub for the Asia-Pacific region, linking major shipping routes and fostering trade between countries.
3. Boosting Employment and Economic Activity
Transshipment operations require a vast workforce, ranging from dockworkers and logistics personnel to customs officers and support staff. As a result, transshipment hubs generate significant employment opportunities, driving economic activity and contributing to local economies. For example, the Port of Rotterdam in the Netherlands, one of the world's largest transshipment ports, provides jobs for thousands of people and contributes substantially to the country's GDP.
4. Attracting Investments and Infrastructure Development
Transshipment hubs often attract substantial investments, both from the private sector and governments, leading to infrastructure development and economic growth. Governments recognize the potential of transshipment to boost trade and attract foreign direct investment, prompting them to invest in port facilities, transportation networks, and logistics infrastructure. The recent expansion of the Panama Canal is a prime example of how a country leveraged transshipment to attract investments and strengthen its position as a key trade hub.
5. Facilitating Specialization and Value

Transshipment as a Catalyst for Economic Growth and Development - Transshipment: A Key Strategy in Entrepot Trade Unveiled
31. Redefining Success in the Entrepreneurial World:UBI as a Catalyst for Economic Growth
1. Encouraging Entrepreneurship
One of the key ways in which Universal Basic Income (UBI) can act as a catalyst for economic growth is by encouraging entrepreneurship. With a guaranteed basic income, individuals have the financial security to take risks and pursue their entrepreneurial dreams. They no longer have to worry about meeting their basic needs or the fear of failure, which often holds people back from starting their own businesses.
For example, consider a talented software engineer who has always dreamed of launching a tech startup. However, without a safety net, they may be hesitant to leave their stable job and take the leap into entrepreneurship. But with UBI in place, they have the financial stability to quit their job and focus on building startup. This not only allows them to pursue their passion but also creates new job opportunities and contributes to economic growth.
2. Stimulating Innovation
UBI can also act as a catalyst for economic growth by stimulating innovation. When individuals are freed from the constant struggle to make ends meet, they have more time and energy to invest in creative and innovative pursuits. This can lead to the development of new products, services, and technologies that drive economic progress.
For instance, imagine a struggling artist who is barely able to make a living from their art. With UBI providing a consistent income, they no longer have to rely solely on selling their artwork to survive. This financial stability allows them to explore new artistic techniques, experiment with different mediums, and take risks in their creative endeavors. As a result, they may produce groundbreaking artwork that attracts attention and contributes to the growth of the art industry as a whole.
3. Boosting Consumer Spending
Another way in which UBI can fuel economic growth is by boosting consumer spending. When individuals have a guaranteed income, they are more likely to spend money on goods and services, which in turn drives demand and stimulates economic activity.
For example, consider a low-income family struggling to make ends meet. With UBI, they now have additional income to cover their basic needs and even have some discretionary spending. This extra money can be used to purchase goods and services, such as household appliances, education, healthcare, or entertainment. Increased consumer spending not only supports local businesses but also creates a multiplier effect, as businesses hire more employees to meet the growing demand, leading to further economic growth.
4. Supporting Job Transitions
UBI can also act as a catalyst for economic growth by supporting job transitions. In a rapidly changing economy, where automation and technology are replacing certain jobs, UBI provides individuals with the financial security to adapt and retrain for new employment opportunities.
For instance, consider a factory worker whose job becomes obsolete due to automation. Without UBI, they may struggle to find new employment and face financial hardship. However, with UBI, they have the means to pursue further education, acquire new skills, and transition into a new job or career. This flexibility and support for job transitions help individuals stay relevant in the job market, fostering economic growth by ensuring a skilled and adaptable workforce.
In conclusion, Universal Basic Income has the potential to be a catalyst for economic growth by encouraging entrepreneurship, stimulating innovation, boosting consumer spending, and supporting job transitions. By providing individuals with financial security, UBI enables them to take risks, pursue their passions, and contribute to economic progress. As societies continue to grapple with income inequality and the changing nature of work, exploring the implementation of UBI may offer a new path towards redefining success in the entrepreneurial world.

Redefining Success in the Entrepreneurial World:UBI as a Catalyst for Economic Growth - Universal Basic Income: Redefining Success in the Entrepreneurial World
32. UBI as a Catalyst for Economic Growth and Job Creation
1. UBI as a catalyst for Economic growth and Job Creation
1.1. Reducing Financial Barriers to Entrepreneurship
One of the key benefits of implementing Universal Basic Income (UBI) is its potential to unlock entrepreneurial potential by reducing financial barriers to starting a business. With a guaranteed income, individuals would have the financial security to take risks and pursue their entrepreneurial dreams. This could lead to an increase in the number of new businesses being created, which in turn would stimulate economic growth and job creation.
1.2. Encouraging Innovation and Risk-Taking
UBI can also foster a culture of innovation and risk-taking. When individuals are not worried about meeting their basic needs, they are more likely to take calculated risks and explore innovative business ideas. This could lead to the development of new industries and technologies, creating new job opportunities in the process.
For example, imagine a young aspiring entrepreneur who has a groundbreaking idea for a tech startup. However, without a stable income, they are unable to secure funding or take the time off from work to fully pursue their idea. With UBI in place, this entrepreneur would have the financial support needed to dedicate their time and resources to developing their business concept. This could potentially lead to the creation of a successful tech company, employing a significant number of people and contributing to economic growth.
1.3. Supporting Job Transition and Reskilling
In today's rapidly changing job market, many individuals may find themselves in need of transitioning to new industries or acquiring new skills. UBI can act as a safety net during these times of transition, ensuring that individuals have the financial means to retrain or acquire new skills that are in demand.
For instance, let's say a manufacturing worker is displaced due to automation. With UBI, they would have the financial resources to enroll in retraining programs or pursue higher education to acquire new skills that align with emerging industries. This would not only enable them to secure new employment but also contribute to overall economic growth by ensuring a skilled workforce.
1.4. Boosting Consumer Demand
Another way UBI can stimulate economic growth is by boosting consumer demand. With a guaranteed basic income, individuals at the lower end of the income spectrum would have more disposable income to spend on goods and services. This increased consumer spending would drive demand, leading to increased production and job creation.
For example, consider a scenario where a small town implements UBI. Residents who were previously struggling to make ends meet now have extra income to spend on local businesses. This increased consumer demand could lead to the growth of local businesses, creating new job opportunities and revitalizing the local economy.
In conclusion, Universal Basic Income has the potential to act as a catalyst for economic growth and job creation. By reducing financial barriers to entrepreneurship, encouraging innovation and risk-taking, supporting job transition and reskilling, and boosting consumer demand, UBI can unlock entrepreneurial potential and stimulate economic growth in various ways.
33. Social Impact as a Catalyst for Economic Development
1. Social impact as a catalyst for economic development: Business initiatives that empower communities can have a significant impact on economic development. By creating jobs, supporting local suppliers, and promoting entrepreneurship, businesses can contribute to poverty reduction, economic growth, and sustainable development.
2. Employee engagement and social impact: Engaging employees in social impact initiatives not only enhances their sense of purpose and job satisfaction but also drives business performance. Businesses can empower employees by providing volunteering opportunities, skill development programs, and support for employee-led initiatives.
3. Supporting marginalized communities: Businesses can support marginalized communities by promoting diversity and inclusion, providing training and employment opportunities for disadvantaged groups, and supporting social enterprises.
4. Case study: Grameen Bank, founded by Nobel Laureate Muhammad Yunus, exemplifies the power of empowering communities. Grameen Bank provides microcredit and other financial services to low-income individuals, particularly women, empowering them to start small businesses and improve their economic circumstances. The bank's innovative model has had a transformative impact on poverty reduction in Bangladesh and has inspired similar initiatives worldwide.
By empowering communities, businesses can not only make a meaningful social impact but also unlock opportunities for economic growth and sustainable development.

Social Impact as a Catalyst for Economic Development - Unlocking Opportunities for Growth and Social Impact
34. A Catalyst for Economic Stabilization
Preserving heritage is not just about maintaining historical buildings and cultural artifacts; it can also serve as a catalyst for economic stabilization in urban areas. When cities invest in the restoration and revitalization of their heritage sites, they create opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and increased tourism. This section will explore the various ways in which preserving heritage can contribute to economic stability from different perspectives.
1. Tourism Boost: Heritage sites have a unique appeal that attracts tourists from all over the world. By preserving and showcasing these sites, cities can tap into the lucrative tourism industry. Visitors are often willing to spend money on accommodations, dining, shopping, and entertainment, thereby injecting revenue into the local economy. For example, the restoration of historic neighborhoods like Charleston's Battery Park in South Carolina has transformed them into popular tourist destinations, generating millions of dollars in revenue annually.
2. Job Creation: The preservation of heritage sites requires skilled laborers such as architects, engineers, craftsmen, and artisans. These projects provide employment opportunities for local residents and stimulate job growth in related industries. Additionally, the increased tourism resulting from heritage preservation creates demand for hospitality workers, tour guides, and other service providers. For instance, the restoration of Barcelona's iconic Sagrada Familia cathedral not only preserved a cultural landmark but also created numerous jobs for architects, construction workers, and tourism professionals.
3. small Business development: Preserving heritage can spur the growth of small businesses within the surrounding communities. As tourists flock to these areas, entrepreneurs seize the opportunity to establish new businesses catering to their needs. This could include boutique hotels, restaurants serving local cuisine, souvenir shops selling handmade crafts or specialty products tied to the heritage site's history. The revitalization of New Orleans' French Quarter after Hurricane Katrina not only preserved its historic charm but also provided a platform for small businesses to thrive.
4. Community Engagement: Heritage preservation projects often involve community participation and engagement. This fosters a sense of pride and ownership among local residents, leading to increased community cohesion. When communities are actively involved in preserving their heritage, they are more likely to invest in the overall development of their neighborhoods. This can lead to improved infrastructure, better public spaces, and enhanced quality of life for residents. The restoration of London's King's Cross Station not only preserved its architectural heritage but also transformed the surrounding area into a vibrant community hub.
5. Cultural Identity: Preserving heritage is crucial for maintaining a city's cultural identity. By safeguarding historical landmarks and traditions, cities can differentiate

A Catalyst for Economic Stabilization - Urban Revitalization Fund: Restoring Heritage for Economic Stabilization