1. The role of human oversight in ensuring reliability
Human oversight plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability of AI content detectors. While these AI systems have advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities, human intervention is still necessary to mitigate biases, address complex issues, and make accurate assessments. Here, we delve into the significance of human oversight and share examples that highlight its importance.
1. Detecting Contextual Nuances:
AI content detectors may struggle to grasp the subtleties and nuanced meanings within different contexts. For instance, humor and sarcasm are challenging for AI systems to comprehend accurately, as they heavily rely on contextual clues and shared cultural knowledge. Human oversight can bridge this gap by applying contextual understanding and decoding complex linguistic elements, thereby minimizing the risk of misleading or inappropriate content being flagged or overlooked.
2. Bias Mitigation:
AI algorithms are not entirely immune to biases. They often learn from biased datasets or absorb implicit biases present within the existing content. Human oversight is necessary to identify and rectify these biases, ensuring that the AI detectors do not perpetuate harmful stereotypes or discriminate against specific demographic groups. By actively analyzing and counterbalancing these biases, human intervention is crucial to maintaining fairness and neutrality in the AI detection process.
3. Handling Edge Cases:
In some instances, AI detectors may face challenges in accurately classifying content that falls into a gray area or exists at the boundaries of defined categories. These ambiguous cases demand human judgment, which can draw upon their broader understanding, experiences, and values to identify the appropriate classification or action to be taken. By incorporating human oversight, AI systems can improve their adaptability and offer more refined and precise content detection.
4. Assessing Unforeseen Variables:
The ever-evolving nature of online content poses a constant challenge for AI content detectors. As new types of content emerge, AI algorithms may struggle in categorizing or accurately interpreting them. Human oversight is essential for staying ahead of emerging trends and content patterns, as human reviewers can continuously update guidelines, train algorithms, and adapt the detection systems to include these novel variables. This flexibility ensures that AI detectors can keep pace with evolving content landscapes.
5. Quality Assurance:
Human oversight acts as a quality assurance check for AI content detection systems. By monitoring and verifying the accuracy of the flagged content, human reviewers can provide necessary feedback and refine the system's performance. This iterative process allows AI algorithms to continually learn and improve, relying on the expertise and judgment of human reviewers to enhance the reliability of the content detection.
6. Accountability and Ethical Considerations:
When dealing with sensitive content or potential false positives and negatives, human oversight provides a human touch and accountability that AI alone cannot offer. Reviewers can make judgment calls and assess the potential consequences of mistakenly flagging or missing content. This aspect of human oversight ensures ethical considerations are taken into account and safeguards against the potential harm that could arise from solely relying on AI content detectors.
In conclusion, human oversight in AI content detection systems plays a pivotal role in ensuring reliability, neutrality, and adaptability. By factoring in contextual nuances, mitigating biases, assessing ambiguous cases, addressing unforeseen variables, conducting quality assurance, and considering ethical considerations, human reviewers enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of AI detectors. The collaboration between humans and AI is crucial for unlocking the full potential of content detection systems while maintaining trust, fairness, and reliability in an ever-evolving digital landscape.

The role of human oversight in ensuring reliability - Accuracy unveiled assessing reliability of ai content detectors
2. The Role of Human Resources in Addressing Workplace Misconduct
1. Conducting Thorough Investigations: One of the primary responsibilities of the Human Resources (HR) department is to ensure that workplace misconduct is addressed promptly and effectively. When allegations of misconduct arise, HR plays a crucial role in conducting thorough investigations to gather all relevant facts and evidence. This includes interviewing witnesses, reviewing documents, and assessing the credibility of the parties involved. By conducting a comprehensive investigation, HR can make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to address workplace misconduct.
2. Implementing Policies and Procedures: HR professionals are responsible for developing and implementing policies and procedures that clearly define acceptable behavior in the workplace. These policies should outline the consequences of misconduct and provide guidance on how to report and address such issues. For example, a company may have a policy prohibiting harassment and providing steps for reporting incidents. By having these policies in place, HR creates a framework for addressing workplace misconduct and ensures that employees are aware of the expected standards of behavior.
3. Providing Training and Education: HR plays a vital role in providing training and education to employees regarding workplace misconduct. This includes educating employees about their rights, the company's policies, and the consequences of engaging in misconduct. By conducting regular training sessions, HR can help create a culture of respect and inclusivity, where employees understand the importance of treating each other with dignity and professionalism. For instance, HR can provide training on preventing sexual harassment or discrimination, which equips employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and address such misconduct.
4. Mediating Conflict Resolution: HR often serves as a mediator when conflicts arise between employees. In cases of workplace misconduct, HR professionals can facilitate discussions between the parties involved, aiming to resolve the issue amicably. By acting as neutral third parties, HR helps foster open communication and understanding, ultimately leading to a resolution that benefits all parties involved. For example, if two employees have a dispute over a project, HR can mediate the conversation and find a compromise that satisfies both parties.
5. Taking Appropriate Disciplinary Action: When workplace misconduct is substantiated, HR must take appropriate disciplinary action to address the issue. This can range from issuing warnings, implementing corrective actions, to terminating the employment of the offending party. HR ensures that the disciplinary actions are fair, consistent, and align with the company's policies and legal requirements. For instance, if an employee is found guilty of bullying, HR may implement a progressive discipline approach, starting with a verbal warning and escalating to more severe consequences if the behavior persists.
6. Case Study: In a recent case, an employee made a complaint of racial discrimination against their supervisor. The HR department conducted a thorough investigation, interviewing both the complainant and the supervisor, as well as gathering any relevant evidence. The investigation revealed that the supervisor had indeed engaged in discriminatory behavior. HR promptly took disciplinary action against the supervisor, which included sensitivity training and a final written warning. By addressing the misconduct and providing appropriate consequences, HR ensured a fair and inclusive work environment for all employees.
Tips for HR Professionals in Addressing Workplace Misconduct:
- Act promptly and take every complaint seriously, regardless of its nature or severity.
- Ensure confidentiality throughout the investigation process to protect the privacy of the parties involved.
- Document all steps taken during the investigation, including interviews conducted and evidence reviewed.
- Provide support and resources for both the complainant and the accused, such as access to counseling or employee assistance programs.
- Regularly review and update policies and procedures to adapt to changing workplace dynamics and legal requirements.
By actively fulfilling their role in addressing workplace misconduct, HR professionals contribute to creating a safe, respectful, and inclusive work environment for all employees.

The Role of Human Resources in Addressing Workplace Misconduct - Addressing Workplace Misconduct: The Role of the After Acquired Clause
3. The Role of Human Capital in Gaining the Upper Hand
Recruiting top talent is a critical aspect of gaining the upper hand in today's competitive business landscape. Human capital, the collective skills, knowledge, and abilities of an organization's workforce, plays a pivotal role in driving innovation, productivity, and ultimately, success. In this section, we will explore the significance of human capital in gaining a competitive edge and discuss strategies for recruiting and retaining top talent.
1. Importance of Human Capital:
Human capital is often considered the most valuable asset of an organization. It encompasses the intellectual and creative capabilities of employees, which can be leveraged to develop new products, improve processes, and outperform competitors. By recruiting top talent, businesses gain access to individuals with specialized expertise, diverse perspectives, and a drive for excellence. These employees can contribute to a culture of innovation, foster collaboration, and propel the organization forward.
2. enhancing Employer branding:
To attract top talent, organizations must actively cultivate a strong employer brand. This entails creating a compelling narrative that showcases the company's values, mission, and unique offerings. A positive employer brand not only attracts high-caliber candidates but also enhances employee retention. For example, technology giant Google has successfully built a reputation as an innovative and employee-friendly organization, attracting top talent from around the world.
3. Leveraging Technology:
In today's digital age, technology plays a crucial role in recruiting top talent. Companies can utilize applicant tracking systems and online job portals to streamline the hiring process, reach a wider pool of candidates, and identify the most qualified individuals. Additionally, leveraging social media platforms and professional networking sites can help organizations proactively identify potential candidates and engage with them on a more personal level.
4. Offering Competitive Compensation and Benefits:
Competitive compensation and benefits packages are essential for attracting and retaining top talent. Organizations must benchmark their offerings against industry standards to ensure they remain competitive. However, it's important to note that compensation is not solely limited to salary. Companies can differentiate themselves by providing unique perks, such as flexible work arrangements, professional development opportunities, and comprehensive health and wellness programs.
5. Emphasizing Cultural Fit:
While technical skills and qualifications are crucial, cultural fit should not be underestimated. Hiring employees who align with the organization's values, mission, and work culture can contribute to a harmonious and productive work environment. For instance, Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, places a strong emphasis on cultural fit during their hiring process. This focus has allowed them to build a workforce that thrives on their core values of customer service and innovation.
6. Developing a Robust Employee Referral Program:
Employee referrals can be a highly effective way to recruit top talent. Current employees are often well-positioned to recommend individuals who possess the necessary skills and fit the organization's culture. To encourage referrals, organizations can implement a structured employee referral program that offers incentives for successful hires. This not only attracts high-quality candidates but also strengthens employee engagement and loyalty.
7. Partnering with Educational Institutions:
Building relationships with educational institutions can provide access to a pool of talented individuals. Companies can collaborate with universities, colleges, and vocational schools to offer internships, co-op programs, and apprenticeships. By doing so, organizations can identify and nurture promising talent early on, potentially leading to long-term employment relationships.
Recruiting top talent is a continuous effort that requires a strategic and multifaceted approach. By recognizing the importance of human capital and implementing effective recruitment strategies, organizations can gain the upper hand in attracting, retaining, and developing the best talent in the industry.

The Role of Human Capital in Gaining the Upper Hand - Advantage: Gaining the Upper Hand: The Upside of Competitive Edge
4. The Role of Human Resources in Safeguarding Mothers Rights
Human Resources (HR) departments play a crucial role in safeguarding mothers' rights in the workplace. They are responsible for ensuring that pregnant employees are not discriminated against and that their rights are protected. HR professionals must be knowledgeable about the laws and regulations that protect pregnant employees and be able to advise managers and supervisors on how to comply with these laws. HR must also work closely with employees to ensure that they are aware of their rights and have access to the resources they need to protect those rights.
1. Educate Managers and Supervisors on Pregnancy Discrimination
One of the most important roles HR plays in safeguarding mothers' rights is to educate managers and supervisors about pregnancy discrimination. HR must ensure that managers and supervisors understand the laws and regulations that protect pregnant employees and are aware of the consequences of violating these laws. HR should also provide training to managers and supervisors on how to handle pregnancy-related issues and how to avoid discriminatory practices.
2. Accommodate Pregnant Employees
HR must work with pregnant employees to ensure that they are accommodated appropriately. This may include providing reasonable accommodations such as modified work schedules, additional breaks, or a temporary transfer to a less physically demanding job. HR must also ensure that pregnant employees are not subjected to harassment or discriminatory treatment.
3. Provide Resources and Support
HR must provide pregnant employees with the resources they need to protect their rights. This may include information on their rights under the law, access to legal resources, and support in filing complaints if they believe their rights have been violated. HR should also provide support to employees who are experiencing difficult pregnancies or complications that may impact their ability to work.
4. Ensure Compliance with Laws and Regulations
HR must ensure that the company is in compliance with all laws and regulations that protect pregnant employees. This includes the Pregnancy Discrimination Act, the Americans with Disabilities Act, and the Family and Medical Leave Act. HR should also ensure that the company has policies in place that protect pregnant employees and that these policies are enforced.
5. Foster a Culture of Inclusion and Support
HR must work to foster a culture of inclusion and support for pregnant employees. This means creating an environment where pregnant employees feel comfortable discussing their needs and concerns and where they are not subjected to discriminatory treatment. HR should also work to ensure that all employees understand the importance of supporting pregnant colleagues and that they are aware of the resources available to them.
HR plays a critical role in safeguarding the rights of pregnant employees. By educating managers and supervisors, accommodating pregnant employees, providing resources and support, ensuring compliance with laws and regulations, and fostering a culture of inclusion and support, HR can help to ensure that pregnant employees are treated fairly and with respect in the workplace.

The Role of Human Resources in Safeguarding Mothers Rights - Adverse Action and Pregnancy Discrimination: Safeguarding Mothers: Rights
5. The Role of Human Resources in Addressing Workplace Harassment
The issue of workplace harassment is a major concern for employers and employees alike. It can lead to a toxic work environment, low morale, and decreased productivity. Human Resources (HR) plays a significant role in addressing workplace harassment, ensuring that all employees are treated with respect, and taking appropriate action when harassment occurs. In this section, we will explore the role of HR in addressing workplace harassment.
1. Creating a Harassment-Free Workplace
The first step in addressing workplace harassment is to create a harassment-free workplace. HR can lead the charge in creating a culture of respect and inclusivity. This can be achieved by implementing policies and procedures that prohibit harassment, providing training to employees on what constitutes harassment, and establishing a reporting mechanism for employees to report incidents of harassment. HR can also work with management to ensure that harassment is not tolerated and that employees who engage in harassment are held accountable.
2. Investigating Incidents of Harassment
When an incident of harassment is reported, HR has a responsibility to investigate the matter thoroughly. This involves interviewing the victim, the accused, and any witnesses to the incident. HR should also review any evidence that is available, such as emails, text messages, or social media posts. The investigation should be conducted in a timely and confidential manner, and the victim should be kept informed of the progress of the investigation.
3. Taking Appropriate Action
If the investigation finds that harassment has occurred, HR must take appropriate action. This may involve disciplinary action, up to and including termination of employment. HR must also take steps to ensure that the victim is protected from further harassment and that the harasser is not allowed to retaliate against the victim. HR should also provide support to the victim, such as counseling or time off work, if needed.
4. Providing Training and Education
HR should provide ongoing training and education to employees on what constitutes harassment, how to report incidents of harassment, and the consequences of engaging in harassment. This training should be provided to all employees, including management, and should be conducted on a regular basis. HR should also provide training on how to create a respectful and inclusive workplace.
5. Ensuring Compliance with Legal Requirements
HR must ensure that the company is in compliance with all legal requirements related to workplace harassment. This includes federal and state laws, as well as any industry-specific regulations. HR should stay up-to-date on any changes to these laws and regulations and ensure that the company is following them.
HR plays a critical role in addressing workplace harassment. By creating a harassment-free workplace, investigating incidents of harassment, taking appropriate action, providing training and education, and ensuring compliance with legal requirements, HR can help to create a respectful and inclusive workplace where all employees feel safe and valued.

The Role of Human Resources in Addressing Workplace Harassment - Adverse Action and Workplace Harassment: A Comprehensive Guide
6. The Role of Human Creativity alongside AI in Writing
While AI can automate certain aspects of the writing process, human creativity remains essential in crafting compelling and engaging content. Human writers bring their unique perspectives, experiences, and emotions to the table, allowing them to create content that resonates with readers on a deeper level.
1. Craftsmanship: Writing is a craft that requires a deep understanding of language, storytelling techniques, and audience engagement. Human writers possess the ability to craft content that is not only informative but also entertaining, thought-provoking, and emotionally resonant.
2. Context and nuance: AI algorithms excel at analyzing data and generating text based on patterns and structures. However, they may struggle with understanding context, nuance, and the subtleties of language. Human writers excel at capturing the intricacies of human emotions, experiences, and cultural nuances.
3. Creativity and originality: Human creativity is a product of personal experiences, emotions, and unique perspectives. Human writers have the ability to think outside the box, challenge conventional norms, and create content that is truly original and groundbreaking.
4. Collaboration: The collaboration between AI algorithms and human writers can lead to the best of both worlds. By leveraging AI as a tool, human writers can enhance their creative process, improve efficiency, and explore new possibilities.

The Role of Human Creativity alongside AI in Writing - Ai generated content and its impact on creative writing
7. The Role of Human Writers in the Age of AI-Generated Copywriting
1. Collaboration and creativity: AI-generated copywriting tools are not designed to replace human writers but rather to assist them. Human writers bring creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence to the table, which cannot be replicated by AI. Collaboration between AI and human writers can lead to more innovative and engaging content.
2. Editing and quality control: Human writers play a crucial role in editing and refining the content generated by AI. They ensure that the copy aligns with the brand's voice and meets the desired quality standards. Human writers also have the ability to inject creativity and adjust the content based on real-time feedback and market insights.
3. Strategy and storytelling: Human writers excel in strategic thinking and storytelling, which are essential elements of effective copywriting. They can craft narratives, develop brand personas, and create compelling stories that resonate with the target audience. AI-generated copywriting tools can assist in generating content ideas and providing inspiration, but it is the human touch that brings these stories to life.
4. emotional connection and empathy: Human writers have the ability to create an emotional connection with the audience through their writing. They can empathize with the readers, understand their pain points, and address them effectively. AI-generated copywriting tools may lack this emotional intelligence and empathy, making the role of human writers vital in establishing meaningful connections with the audience.
5. Adaptability and agility: Human writers are adaptable and can quickly respond to market trends and changes in consumer behavior. They can adjust the copy based on real-time insights, customer feedback, and emerging opportunities. Human writers bring a level of agility and flexibility that complements the automation and efficiency of AI-generated copywriting.

The Role of Human Writers in the Age of AI Generated Copywriting - Ai generated copywriting new era of writing
8. The Role of Human Input in AI-Generated Music
While the emergence of AI-generated music has sparked both excitement and skepticism in the music industry, one crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is the role of human input in the creative process. Although AI algorithms have the ability to compose original melodies and harmonies, it is the human touch that adds depth, emotion, and context to these compositions.
1. Emotional Interpretation:
One area where human input plays a vital role in AI-generated music is emotional interpretation. AI algorithms are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data to generate music that fits within a specific genre or style. However, it is the human musician who can infuse these compositions with genuine emotion, drawing from personal experiences and understanding the nuances of musical expression. By adding their unique interpretation to AI-generated music, musicians can elevate the emotional impact of the composition.
For example, an AI algorithm may generate a melancholic piano melody, but it is the human pianist who can add subtle dynamics, expressive phrasing, and delicate nuances to evoke a deep sense of longing or nostalgia.
2. Creative Direction:
While AI algorithms can create impressive musical pieces, they often lack the ability to understand the larger creative vision or narrative behind a composition. This is where human input becomes indispensable. Musicians and producers can provide creative direction to AI-generated music, guiding the algorithms towards achieving a specific artistic goal.
For instance, a musician may use an AI algorithm to generate a basic chord progression for a song, but it is their expertise and creativity that allows them to build upon it, adding unique melodies, lyrics, and arrangements that align with their intended message or concept.
3. Collaborative Possibilities:
AI-generated music also opens up exciting collaborative possibilities between humans and machines. Musicians can use AI algorithms as creative tools, experimenting with different AI-generated melodies, rhythms, or textures, and then incorporating them into their own compositions. This collaboration allows musicians to explore new musical territories and push the boundaries of traditional music-making.
Case studies have shown how artists like Taryn Southern, a singer-songwriter, have successfully integrated AI-generated music into their work. Southern used AI algorithms to generate melodies and harmonies for her album "I AM AI," but she still provided the human touch by writing lyrics, adding vocals, and overseeing the entire production process.
Tips for Harnessing Human Input in AI-Generated Music:
- Experiment with different AI algorithms and explore their capabilities to find one that aligns with your creative vision.
- Use AI-generated music as a starting point or inspiration and build upon it with your own musical ideas and expertise.
- Don't be afraid to mix AI-generated music with traditional instrumentation and human performance to create a unique hybrid sound.
- Embrace the collaborative possibilities that AI-generated music offers, working alongside algorithms to enhance your creative process.
In the realm of AI-generated music, the human input serves as the driving force behind its artistic value and emotional impact. By harnessing the power of AI algorithms while infusing them with their own creativity, musicians can unlock new artistic possibilities and shape the future of this exciting form of art.

The Role of Human Input in AI Generated Music - Ai generated music new form of art
9. The role of human oversight in AI-generated news production
While AI-generated news articles offer increased efficiency and productivity, it is vital to incorporate human oversight to ensure the integrity and quality of the content produced. Human involvement can provide critical thinking, context, and ethical considerations that machines may lack.
6.1 Editorial control
Incorporating editorial control in AI-generated news production is essential for maintaining journalistic standards. Human editors can review and revise AI-generated content to ensure accuracy, coherence, and adherence to ethical guidelines. This human oversight can help minimize potential biases and inaccuracies that may arise from automated systems.
6.2 Ethical considerations
AI-generated news articles raise ethical considerations regarding the responsibility and accountability of news organizations. Human oversight can address these concerns by ensuring that AI systems are used ethically, adhering to privacy laws, avoiding misinformation, and respecting individuals' rights. Human editors can scrutinize the content generated by machines to identify and rectify any ethical breaches.
6.3 Collaborative approach
The most effective approach to incorporating human oversight in AI-generated news production is a collaborative one. By fostering collaboration between AI systems and human journalists, news organizations can harness the strengths of both to deliver accurate, reliable, and ethical news content. This collaboration ensures that AI-generated news articles undergo rigorous scrutiny while leveraging the speed and efficiency offered by automated systems.

The role of human oversight in AI generated news production - Ai generated news articles accuracy and reliability
10. The role of human input in AI-generated product descriptions
1. Review and refinement: Human editors play a crucial role in reviewing and refining the AI-generated product descriptions. They can provide feedback, make necessary adjustments, and ensure that the descriptions meet the desired standards.
2. Brand voice and guidelines: Human input is essential in maintaining the brand voice and following the brand guidelines. Human writers can contribute their creativity and expertise to ensure that the descriptions align with the overall brand strategy and communication style.
3. Quality control: Human input is necessary to ensure the accuracy, relevance, and quality of the product descriptions. Human editors can perform grammar and spelling checks, verify the information presented in the descriptions, and make adjustments as needed.
4. Legal and ethical considerations: Human oversight is crucial in addressing legal and ethical considerations associated with AI-generated product descriptions. Human writers can ensure that the descriptions do not infringe on any copyright or intellectual property laws and adhere to ethical standards.
5. Customer feedback and engagement: Human input can help businesses gather and analyze customer feedback on the AI-generated product descriptions. This feedback can be used to further refine the AI algorithms and improve the overall quality of the descriptions.

The role of human input in AI generated product descriptions - Ai generated product descriptions new approach
11. The Role of Human Touch in the Creation of AI Generated Video Content
1. Creative Input: The role of humans remains crucial in providing creative input, developing innovative ideas, and ensuring the emotional connection and authenticity in AI-generated video content.
2. Quality Control: Humans play a vital role in reviewing and approving AI-generated video content, ensuring its alignment with brand guidelines, maintaining quality, and avoiding potential errors.
3. Domain Expertise: Human expertise is valuable in setting objectives, defining video content strategy, and maintaining a deep understanding of target audiences, ensuring AI-generated videos meet specific business goals.
4. Adaptive Learning: The collaboration between humans and AI allows for iterative improvements in AI algorithms, with humans providing feedback, insights, and fine-tuning the AI models.
5. Enhancing Emotional Appeal: Human creativity and intuition are instrumental in infusing AI-generated videos with emotional appeal, capturing the essence of human experiences and establishing deeper connections with viewers.

The Role of Human Touch in the Creation of AI Generated Video Content - Ai generated video content possibilities and limitations
12. The Role of Human Input in Contextual Adaptability
The role of human input in contextual adaptability is an essential aspect of AI systems. As AI becomes more prevalent in our daily lives, it is crucial to understand how context plays a vital role in the development of AI systems. Contextual adaptability is the ability of AI systems to understand and respond to changing contexts, such as changes in the environment or user preferences. In this section, we will explore the role of human input in contextual adaptability.
1. Importance of Human Input:
Human input is crucial in the development of contextual adaptability in AI systems. Human input provides the necessary context for the AI system to adapt to new situations. Humans can provide context by providing feedback, correcting errors, and suggesting improvements. For example, in the case of a chatbot, human input can help improve the chatbot's responses to different queries. Human input can help the chatbot understand the context of the query and provide a more accurate response.
2. Types of Human Input:
There are different types of human input that can be used to improve contextual adaptability in AI systems. These include explicit feedback, implicit feedback, and user data. Explicit feedback is when users provide direct feedback to the AI system, such as rating a response. Implicit feedback is when users provide feedback indirectly, such as navigating away from a page or clicking on a link. User data is the data collected from user interactions with the AI system. This data can be used to train the AI system to adapt to different contexts.
3. Challenges in Using Human Input:
While human input is essential for contextual adaptability in AI systems, there are challenges in using human input. One challenge is the quality of the input. Human input can be biased, inaccurate, or incomplete. Another challenge is the volume of input. AI systems can generate a large amount of data, which can be challenging to manage and analyze. Finally, there is the challenge of privacy. User data needs to be collected and used responsibly, with the user's consent.
4. Best Practices for Using Human Input:
To overcome the challenges of using human input, there are best practices that can be followed. These include collecting diverse feedback from different users, using algorithms to filter out biased or inaccurate input, and ensuring user privacy. Additionally, it is essential to have a human in the loop to monitor and correct errors in the AI system's responses.
The role of human input in contextual adaptability is crucial in the development of AI systems. Human input provides the necessary context for AI systems to adapt to changing situations. While there are challenges in using human input, following best practices can help overcome these challenges and improve the contextual adaptability of AI systems.

The Role of Human Input in Contextual Adaptability - And GPT: Exploring Contextual Adaptability in AI Systems
13. The Role of Human Expertise in Pilotfishing Defense
The role of human expertise in pilotfishing defense is crucial in ensuring the effectiveness of the defense system. Although artificial intelligence (AI) has made significant strides in detecting and preventing pilotfishing attacks, the human element is still necessary to provide the necessary context, intuition, and decision-making capabilities that machines cannot replicate. In this section, we will explore the different ways in which human expertise can contribute to pilotfishing defense.
1. Contextual knowledge: One of the essential roles that humans play in pilotfishing defense is providing contextual knowledge. Human experts have a deep understanding of the organization's operations, processes, and procedures, which can help identify potential vulnerabilities in the system. This knowledge can also help in identifying suspicious activities that may not be detected by AI systems. For example, a human expert may detect that an email is unusual because it does not adhere to the organization's communication protocols, even if the email's content does not contain any malicious intent.
2. Decision-making capabilities: While AI systems can detect pilotfishing attacks, they may not always be able to make informed decisions on how to respond to them. In contrast, human experts can use their judgment and experience to make decisions on how to mitigate the risk of an attack. For example, a human expert may decide to quarantine a potentially malicious email and investigate it further instead of simply deleting it, which could provide valuable insights into the attacker's methods.
3. Intuition: Humans also have the ability to use intuition to detect pilotfishing attacks. Intuition is the ability to recognize patterns and anomalies that are not immediately obvious. While AI systems can detect patterns, they may not always be able to recognize anomalies that are outside of their programming. For example, a human expert may detect that an email is suspicious because it contains an unusual phrase or tone that is not typical of the sender's communication style.
4. Communication: Effective communication is essential in pilotfishing defense. Human experts can communicate with other members of the organization to raise awareness about potential attacks and provide guidance on how to respond to them. They can also communicate with AI systems to provide feedback and improve their accuracy in detecting pilotfishing attacks.
While AI systems have made significant progress in detecting and preventing pilotfishing attacks, the role of human expertise is still essential in ensuring the effectiveness of the defense system. Human experts can provide contextual knowledge, decision-making capabilities, intuition, and effective communication, which are all crucial components of a comprehensive pilotfishing defense strategy.

The Role of Human Expertise in Pilotfishing Defense - Artificial Intelligence: A Double Edged Sword in Pilotfishing Defense
14. The Role of Human Rights in ASEAN
The ASEAN region has been rapidly developing over the past few decades, which has brought many benefits to the people and economies of the region. However, this development has also come at a cost to the environment and the natural resources that are essential to human survival. Balancing economic development with environmental protection is a complex issue that requires careful consideration of the social, economic, and environmental impacts of development. The role of human rights in this equation is also critical, as the rights of individuals and communities must be protected as development takes place.
1. Economic development and environmental protection are often seen as conflicting goals, but they can be balanced through sustainable development practices. For example, investments in renewable energy and green infrastructure can create economic opportunities while also reducing carbon emissions and protecting natural resources.
2. Human rights must be at the center of any development agenda, as they provide a framework for protecting the rights of individuals and communities. This includes the right to a clean and healthy environment, which is essential for human well-being. The ASEAN Human Rights Declaration, adopted in 2012, recognizes the right to a clean and healthy environment and the duty of states to protect this right.
3. The ASEAN Intergovernmental Commission on Human Rights (AICHR) plays an important role in promoting human rights in the region, including the right to a clean and healthy environment. The AICHR has developed guidelines on human rights and the environment, which provide a framework for addressing environmental issues from a human rights perspective.
4. Despite these efforts, there are still challenges in balancing economic development with environmental protection and human rights. For example, the development of large-scale infrastructure projects, such as dams and highways, can have significant environmental and social impacts on local communities. It is important to ensure that these projects are developed in a way that respects the rights of affected communities and minimizes negative impacts on the environment.
5. Civil society organizations and grassroots movements play an important role in advocating for human rights and environmental protection in the ASEAN region. For example, the Save the Mekong coalition has been working to raise awareness about the impacts of large-scale dams on the Mekong River and the communities that depend on it. These organizations can help to ensure that the voices of affected communities are heard and that their rights are protected.
Balancing economic development with environmental protection and human rights is a complex issue that requires careful consideration of multiple factors. By adopting sustainable development practices, protecting human rights, and engaging with civil society organizations, the ASEAN region can work towards a more equitable and sustainable future.

The Role of Human Rights in ASEAN - ASEAN s Human Rights Agenda: Striving for Equality
15. The Role of Human Trafficking in the Movement of Economic Refugees
1. Economic Refugees: The Victims of Human Trafficking
Human trafficking is a grave issue affecting millions of people worldwide, and economic refugees are particularly vulnerable to this heinous crime. As individuals flee their home countries in search of better economic opportunities, they often fall prey to traffickers who exploit their desperation and lack of legal protection. This section will delve into the role of human trafficking in the movement of economic refugees, shedding light on the complexities and challenges faced by those seeking economic refuge.
2. Understanding the Dynamics of Human Trafficking
Human trafficking involves the recruitment, transportation, and exploitation of individuals through force, fraud, or coercion. Economic refugees, driven by poverty, unemployment, or lack of opportunities in their home countries, become easy targets for traffickers who promise them better lives in other nations. These individuals often embark on perilous journeys, placing their trust in smugglers who may ultimately exploit them for forced labor, sexual exploitation, or other forms of modern-day slavery.
3. The Vulnerability of Economic Refugees
Economic refugees face numerous challenges and vulnerabilities that make them susceptible to human trafficking. Their lack of legal status, limited access to social services, and language barriers leave them isolated and marginalized in their host countries. Traffickers exploit these vulnerabilities, preying on their desperation and offering false promises of employment, education, or a pathway to citizenship. In their pursuit of economic refuge, these individuals often find themselves trapped in exploitative situations, with limited means to escape.
4. The Role of Smuggling Networks
Smuggling networks play a significant role in facilitating the movement of economic refugees, often overlapping with human trafficking operations. While human trafficking involves exploitation, smuggling focuses on facilitating illegal entry or transit across borders. However, the line between smuggling and trafficking can blur, and economic refugees may find themselves coerced or deceived into situations of trafficking during their journey. Smuggling networks exploit the demand for migration and profit from the vulnerabilities of economic refugees, further exacerbating their plight.
5. The Impact of Policy and Legal Frameworks
Policy and legal frameworks play a crucial role in addressing the issue of human trafficking among economic refugees. Governments and international organizations must prioritize the protection of economic refugees, ensuring they have access to legal pathways for migration and avenues to regularize their status. Strengthening labor laws and regulations can also help prevent exploitation in the workforce, while providing comprehensive support services to economic refugees can help alleviate their vulnerabilities.
6. Collaboration and International Cooperation
Addressing human trafficking among economic refugees necessitates international cooperation and collaboration. Governments, civil society organizations, and international bodies must work together to dismantle smuggling networks, prosecute traffickers, and provide protection and support to victims. Sharing intelligence, resources, and best practices can help develop comprehensive strategies to combat human trafficking and provide a safer environment for economic refugees.
7. The Role of Awareness and Empowerment
Raising awareness about the risks and realities of human trafficking is essential to empower economic refugees and prevent them from falling victim to exploitation. Providing information about their rights, available resources, and potential dangers can equip these individuals with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions during their journey. empowering economic refugees through education, vocational training, and access to legal assistance can also enhance their resilience and reduce their vulnerability to trafficking.
8. Conclusion
The role of human trafficking in the movement of economic refugees is a distressing reality that demands urgent attention and action. By understanding the dynamics of trafficking, addressing vulnerabilities, strengthening legal frameworks, fostering collaboration, and empowering economic refugees, we can strive to protect these individuals and ensure their journey towards economic refuge is free from exploitation.

The Role of Human Trafficking in the Movement of Economic Refugees - Asylum Seeker: Seeking Economic Refuge: The Plight of Economic Refugees
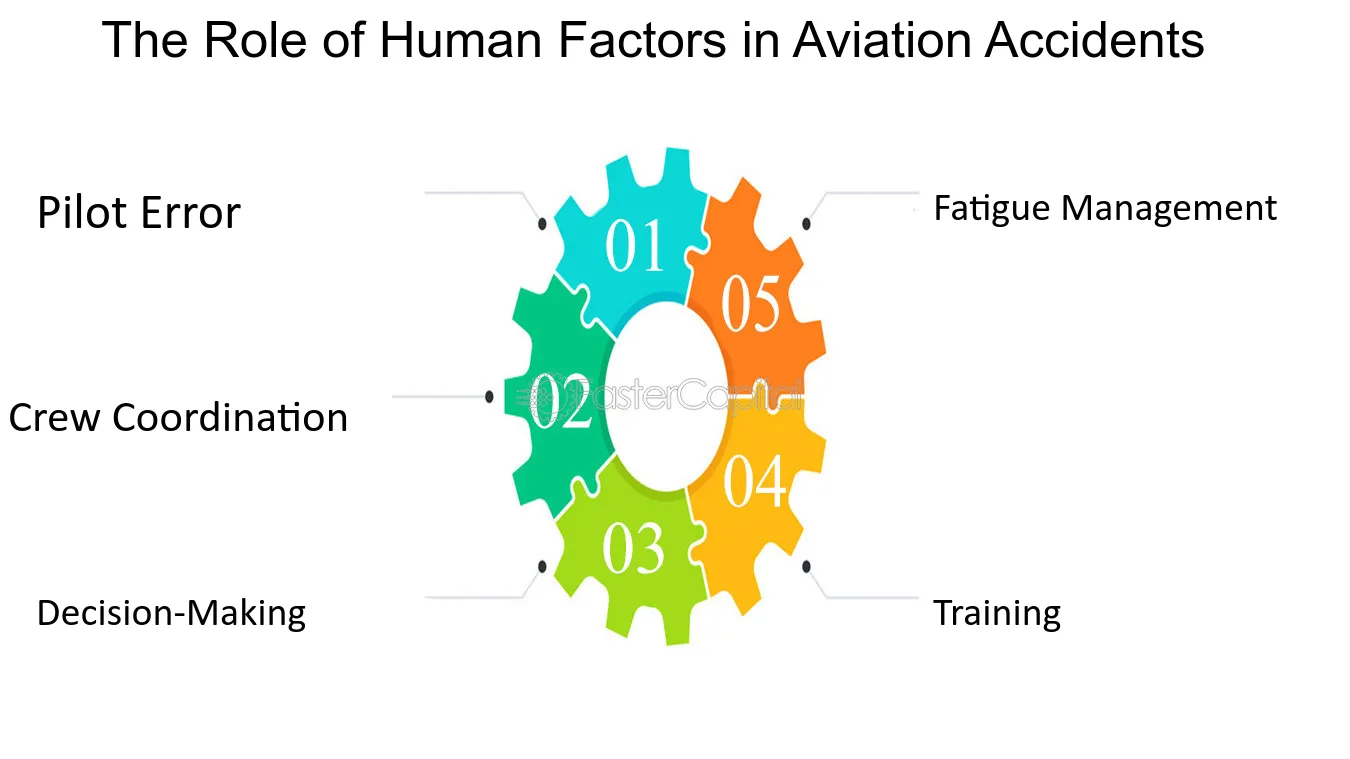
16. The Role of Human Factors in Aviation Accidents
When it comes to investigating aviation accidents, one cannot overlook the crucial role that human factors play in these incidents. Human factors refer to the interaction between humans and their environment, equipment, and procedures. In the context of aviation accidents, human factors encompass a wide range of elements, including pilot error, crew coordination, decision-making, training, and fatigue management. Understanding and addressing these human factors is essential in unraveling the puzzle of aviation accident investigations.
1. Pilot Error: One of the most common human factors contributing to aviation accidents is pilot error. This can occur due to a lack of situational awareness, poor decision-making, or inadequate training. For example, in the case of the Air France Flight 447 crash in 2009, pilot error played a significant role. The crew failed to react appropriately to a loss of airspeed indications, leading to a series of errors that ultimately resulted in the tragedy. Investigating pilot error involves analyzing the actions, decisions, and thought processes of the crew during critical moments.
2. Crew Coordination: Effective communication and coordination among the flight crew are essential for safe flight operations. However, breakdowns in crew coordination can lead to misunderstandings, errors, and ultimately, accidents. For instance, the crash of Eastern Air Lines Flight 401 in 1972 was partly attributed to a lack of crew coordination. The crew was preoccupied with troubleshooting a landing gear indicator light, causing them to lose situational awareness and subsequently crash into the Florida Everglades. Investigating crew coordination involves examining communication protocols, teamwork dynamics, and crew resource management.
3. Decision-Making: The ability to make sound decisions under challenging circumstances is critical for aviation safety. However, decision-making can be influenced by various factors, such as time pressure, cognitive biases, and incomplete or inaccurate information. For example, in the case of the Tenerife airport disaster in 1977, decision-making played a significant role. Miscommunication and poor decision-making by both air traffic control and the pilots resulted in a collision between two aircraft on the runway, leading to the deadliest aviation accident in history. Investigating decision-making involves analyzing the factors that influenced the choices made by individuals involved in the accident.
4. Training: Adequate training is paramount in ensuring that aviation professionals possess the necessary knowledge and skills to perform their duties safely. However, deficiencies in training programs can contribute to human errors and accidents. For instance, the crash of Asiana Airlines Flight 214 in 2013 was partly attributed to inadequate training on the use of the aircraft's automated systems. The pilots' lack of understanding and proficiency in managing these systems resulted in the aircraft stalling and crashing during landing. Investigating training involves evaluating the effectiveness of training programs, simulator exercises, and recurrent training requirements.
5. Fatigue Management: Fatigue can impair human performance, leading to reduced alertness, slower reaction times, and impaired decision-making abilities. Fatigue-related accidents can occur due to long duty hours, inadequate rest periods, and circadian rhythm disruptions. For example, the crash of Colgan Air Flight 3407 in 2009 was partly attributed to fatigue. The crew had been commuting overnight before their duty and did not have adequate rest, which likely contributed to their performance deficiencies. Investigating fatigue management involves assessing crew scheduling practices, duty time limitations, and rest requirements.
Understanding the role of human factors in aviation accidents is crucial for improving aviation safety. By examining elements such as pilot error, crew coordination, decision-making, training, and fatigue management, investigators can unravel the complex puzzle of aviation accident investigations. By identifying and addressing these human factors, the aviation industry can work towards preventing similar accidents in the future and ensuring the safety of both passengers and crew.
The Role of Human Factors in Aviation Accidents - Aviation Accident Investigation: Unraveling the AAR Puzzle
17. The Role of Human Capital in Capital Accumulation
The role of human capital in capital accumulation cannot be overstated. Human capital refers to the knowledge, skills, and abilities that people possess, which enable them to perform work and create value. In other words, human capital is the education, experience, and expertise of individuals that contribute to the production of goods and services. The accumulation of human capital is a critical driver of economic growth, and it is closely linked to the accumulation of physical capital.
1. human capital is a key input in the production process: Human capital is a critical factor in the production process, as it enables workers to perform tasks more efficiently and effectively. For example, a highly skilled software developer can write code much faster and with fewer errors than an inexperienced developer. This increased efficiency translates into higher productivity and output.
2. Human capital enables innovation and technological progress: Human capital plays a critical role in the development of new technologies and the advancement of existing ones. The accumulation of human capital is essential in fields such as science, engineering, and medicine, where new discoveries and innovations are made regularly. For example, the development of the internet and the smartphone was made possible by highly skilled engineers, programmers, and designers.
3. Education is the primary means of accumulating human capital: Education is the primary means of accumulating human capital, as it provides individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to perform work and create value. This can include formal education, such as attending university or vocational training, or informal education, such as on-the-job training or self-learning. Investment in education is critical for individuals and society as a whole, as it leads to higher wages, increased productivity, and improved standard of living.
The accumulation of human capital is essential for capital accumulation and economic growth. Investment in education and training is critical to building a highly skilled workforce that can perform tasks more efficiently, innovate, and drive technological progress. By investing in human capital, countries can create a virtuous cycle of economic growth, where increased productivity leads to higher wages, which in turn drives consumption and further economic expansion.

The Role of Human Capital in Capital Accumulation - Capital Accumulation: The Key Driver of Neoclassical Growth
18. Understanding the Y Chromosomes Role in Human Diversity
Understanding the Y Chromosome's Role in Human Diversity
The Y chromosome has long been a topic of fascination and intrigue in the field of genetics. As one of the two sex chromosomes, it plays a crucial role in determining the sex of an individual, with males having one X and one Y chromosome, while females possess two X chromosomes. However, the Y chromosome is not solely responsible for determining biological sex; it also holds significant insights into human diversity. In this section, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of the Y chromosome and explore its role in shaping the diverse tapestry of humanity.
1. The Origin and Evolution of the Y Chromosome:
The Y chromosome has a unique evolutionary history, stemming from its ancient ancestor, the Y-MRCA (Y-chromosomal Most Recent Common Ancestor). Through the passage of time, the Y chromosome has undergone a series of genetic changes, including deletions, inversions, and mutations, which have shaped its current structure. These changes have not only contributed to the diversity of the Y chromosome itself but have also played a role in shaping the genetic diversity among human populations. For instance, the relatively recent expansion of certain Y-chromosomal haplogroups, such as R1b and E1b1b, can be traced back to specific migration events, providing insights into the ancestry and migration patterns of different populations.
2. Patrilineal Inheritance and Lineage Tracing:
One of the most fascinating aspects of the Y chromosome is its unique mode of inheritance. Unlike other chromosomes, which undergo recombination during meiosis, the Y chromosome is passed down

Understanding the Y Chromosomes Role in Human Diversity - Celebrating Diversity: Unveiling the Wonders of the Y Chromosome
19. The role of human oversight in maintaining the quality of AI-generated content
While AI-generated content offers significant advantages, human oversight is essential to ensure the quality, accuracy, and relevance of the content. Human involvement can help address the limitations and challenges of AI-generated content, including:
1. Review and refinement: Human content creators can review and refine the AI-generated text, ensuring it aligns with the organization's vision, values, and desired messaging. They can add context, clarify ambiguous statements, and inject creativity into the content.
2. Editing and proofreading: Human editors can play a vital role in checking the accuracy of AI-generated content, correcting any grammatical errors, and improving overall readability. Their expertise ensures that the content maintains a high standard of quality.
3. Contextual understanding: Human content creators possess a deep understanding of the organization's culture and can provide the necessary context to AI algorithms. They can guide the algorithms to generate content that accurately captures the nuances and intricacies of company culture.
4. Continuous improvement: Human oversight allows organizations to continually refine and improve the AI models used for generating content. By analyzing the feedback and input from human content creators, organizations can iteratively train the AI algorithms, enhancing their performance and relevance over time.
For example, a human content creator can review the AI-generated content for a company culture article and make edits to ensure that it reflects the organization's cultural nuances, captures employee experiences accurately, and aligns with the desired messaging.

The role of human oversight in maintaining the quality of AI generated content - Chatgpt and future of ai generated content for company culture articles
20. The role of human supervision in AI-generated content creation for native ads
While AI-generated content has the potential to streamline content creation and enhance user engagement, human supervision and review are essential to ensure the quality, accuracy, and ethical standards of the content. Here are some key roles human supervision plays in AI-generated content creation for native ads:
1. Training and fine-tuning: Human experts play a crucial role in training and fine-tuning AI models like ChatGPT. They provide the initial data and guidelines to train the AI model and continuously monitor and update the model as it generates content. Human experts can identify and correct any inaccuracies or biases in the AI-generated content, ensuring its quality and accuracy.
2. Content review and editing: Human review is necessary to ensure the coherence, relevance, and accuracy of the AI-generated content. Human editors can review and edit the content generated by the AI model, adding their creative touch and ensuring that the content aligns with the brand's voice and values. They can also identify and correct any grammatical or syntactical errors in the AI-generated content.
3. Ethical and legal compliance: Human experts are responsible for ensuring that the AI-generated content complies with ethical and legal standards. They can review the content to identify and address any potential ethical or legal concerns, such as misleading information, copyright infringement, or defamation. Human experts play a crucial role in upholding the brand's ethical standards and ensuring that the AI-generated content meets the audience's expectations.
4. Quality control and user feedback: Human supervision is necessary to maintain quality control and address user feedback. Human experts can monitor the performance of the AI model, analyze user engagement metrics, and make adjustments as needed. They can also gather user feedback to identify any issues or areas for improvement in the AI-generated content and take appropriate action.
In summary, human supervision is indispensable in AI-generated content creation for native ads. Human experts play a critical role in training and fine-tuning AI models, reviewing and editing the generated content, ensuring ethical and legal compliance, and maintaining quality control.

The role of human supervision in AI generated content creation for native ads - Chatgpt and future of ai generated content for native advertising
21. The Role of Human Oversight in AI Generated Content
1. Human oversight is crucial in ensuring the quality, accuracy, and ethical implications of AI-generated content. While AI models like ChatGPT have made significant advancements, they still require human intervention to maintain their reliability.
2. Human writers play a vital role in reviewing and editing AI-generated content. They can ensure that the content aligns with the brand's voice and style, fact-check information, and add a layer of creativity and originality that AI models may lack.
3. Human oversight is particularly important in industries that require specialized knowledge or expertise. Highly technical or industry-specific content often requires a deep understanding that AI models may not possess.
4. Human oversight is also necessary to address biases that may be present in AI-generated content. By critically reviewing the outputs of AI models, human writers can identify and mitigate biased or discriminatory content.
5. Human writers can also provide the necessary context and nuance that AI models may struggle to understand. This helps ensure that AI-generated content accurately reflects the intended meaning and purpose.
6. Collaboration between AI models and human writers is key to harnessing the full potential of AI-generated content. By working together, businesses can leverage the efficiency and scalability of AI models while maintaining the expertise and creativity of human writers.
7. In addition to human oversight during content creation, ongoing monitoring and quality assurance processes are essential. Regular evaluations of AI models and feedback loops between human writers and AI systems help improve the performance and reliability of AI-generated content.

The Role of Human Oversight in AI Generated Content - Chatgpt and future of ai generated content
22. The Evolving Role of Human Writers in the Age of AI
The rise of AI-generated copywriting has sparked discussions about the future role of human writers. While AI technologies are undoubtedly powerful, human creativity and critical thinking remain paramount. Here's how the role of human writers is evolving in the age of AI:
1. Strategic Thinking: Human writers bring strategic thinking and creative insights that AI models may lack. They possess the ability to conceptualize marketing campaigns, understand target audience nuances, and tailor content to elicit specific emotional responses.
2. Brand Voice and Storytelling: Human writers are integral to maintaining a brand's unique voice and telling compelling stories. They possess the intuition to craft narratives that resonate with audiences and build meaningful connections.
3. Contextual Understanding: Human writers excel at understanding nuanced contexts, cultural references, and current trends. They possess the ability to incorporate timely and relevant elements into their writing, thereby engaging readers on a deeper level.
4. Adaptability: Human writers can adapt to changing circumstances and requirements, adjusting their writing style and approach as needed. This flexibility ensures that content remains relevant and effective in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
5. Collaboration with AI: Human writers can collaborate with AI technologies to enhance their own capabilities. By leveraging AI-generated prompts, suggestions, and improvements, human writers can elevate their writing and produce more impactful content.
In the age of AI, the role of human writers is shifting towards a more collaborative and augmented approach. By embracing AI technologies as allies rather than adversaries, human writers can harness the strengths of AI-generated copy and continue to deliver exceptional and creative content.

The Evolving Role of Human Writers in the Age of AI - Chatgpt and future of ai generated copywriting
23. The Role of Human Activity in Climate Change and Depletion
Human activity has been a major contributor to climate change and depletion of natural resources. The increase in population, industrialization, and technological advancements have led to an increase in carbon emissions, deforestation, and pollution. The impact of these activities has been felt across the globe, and it is important that we take action to reverse the damage.
1. Carbon Emissions: The burning of fossil fuels for energy is one of the leading causes of carbon emissions. The transportation sector, which includes cars, trucks, and airplanes, is responsible for a significant portion of these emissions. To reduce carbon emissions, we need to shift towards renewable sources of energy such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. We can also reduce our carbon footprint by using public transportation, carpooling, or biking to work.
2. Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture, logging, and urbanization has contributed to the loss of biodiversity and increased greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation also reduces the ability of forests to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. To combat deforestation, we need to promote sustainable agriculture and forestry practices, protect forests through conservation efforts, and reduce the demand for products that contribute to deforestation such as palm oil.
3. Pollution: Industrialization has led to an increase in pollution, which has negative impacts on both human health and the environment. Air pollution, for example, can cause respiratory problems and contribute to climate change. To reduce pollution, we need to implement stricter regulations on industries, promote clean technologies, and reduce our reliance on single-use plastics.
4. Sustainable Consumption: Our consumption patterns also play a major role in climate change and depletion. We need to reduce our consumption of meat and dairy products, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. We can also reduce waste by recycling, composting, and reducing our use of single-use products.
5. Policy Changes: To effectively address climate change and depletion, we need policy changes at both the national and international level. Governments can implement regulations and incentives to promote sustainable practices, invest in renewable energy, and reduce carbon emissions. International cooperation is also crucial in addressing global issues such as climate change.
Human activity has played a significant role in climate change and depletion of natural resources. To reverse this damage, we need to shift towards sustainable practices, reduce our carbon footprint, and promote policy changes at both the national and international level. By taking action now, we can ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.

The Role of Human Activity in Climate Change and Depletion - Climate change: Climate Change and Depletion: A Looming Crisis
24. Evaluating the Role of Human Resources
When it comes to understanding the cost of goods sold (COGS), one crucial component that often gets overlooked is direct labor. This section delves into the role of human resources in the COGS calculation and sheds light on the significance of evaluating direct labor costs.
1. Understanding Direct Labor:
Direct labor refers to the wages and benefits paid to employees who directly contribute to the production of goods or services. These employees are involved in tasks such as assembling products, operating machinery, or providing specialized skills in the manufacturing process. Evaluating direct labor costs is essential as it helps businesses determine the true cost of producing their goods or services.
2. Importance of Accurate Direct Labor Costing:
Accurately calculating direct labor costs is crucial for businesses as it affects their profitability and competitiveness. Overestimating or underestimating these costs can lead to incorrect pricing decisions, which may result in lost sales or reduced profit margins. Therefore, human resources play a vital role in ensuring that direct labor costs are accurately captured and accounted for.
3. Factors Affecting Direct Labor Costs:
Several factors can influence direct labor costs, including wage rates, productivity levels, and employee turnover. Wage rates vary across industries, regions, and skill levels, and it is essential to consider these variations when calculating direct labor costs. Additionally, employee productivity levels can impact labor costs, as higher productivity translates to more output per labor hour. Finally, high employee turnover can increase direct labor costs due to recruitment, training, and onboarding expenses.
4. Strategies for Optimizing Direct Labor Costs:
To optimize direct labor costs, businesses can adopt various strategies. One approach is to invest in employee training and development programs to enhance productivity and reduce errors. By providing employees with the necessary skills and knowledge, businesses can minimize rework and improve overall efficiency. Another strategy is to implement performance-based incentives or reward systems to motivate employees and increase productivity. Additionally, businesses can analyze their workforce utilization and identify areas where automation or process improvements can reduce the reliance on direct labor.
5. Case Study: Automotive Manufacturing:
Let's consider an example from the automotive industry to illustrate the importance of evaluating direct labor costs. Company X produces automobiles and employs a significant number of workers on the assembly line. By accurately tracking direct labor costs, Company X realizes that a particular model's production is consistently slower than others due to a complex assembly process. By investing in employee training and process improvements, the company reduces the time required for assembly, ultimately lowering direct labor costs and increasing overall profitability.
6. The Role of Human Resources:
Human resources departments play a crucial role in evaluating and managing direct labor costs. They are responsible for accurately tracking employee hours, wages, benefits, and other labor-related expenses. HR professionals collaborate with operations and finance teams to ensure that direct labor costs are properly captured and allocated to the COGS calculation. Moreover, HR teams can provide valuable insights into workforce planning, talent management, and strategies for optimizing direct labor costs.
Evaluating the role of human resources in understanding and managing direct labor costs is vital for businesses aiming to decode the cost of goods sold. Accurate costing of direct labor helps businesses make informed pricing decisions, maintain profitability, and drive operational efficiencies. By recognizing the significance of human resources in this process, businesses can leverage their expertise to optimize direct labor costs and enhance overall competitiveness.

Evaluating the Role of Human Resources - Cost of goods sold: Prime Cost Unveiled: Decoding Cost of Goods Sold
25. The Role of Human Intelligence in AGI Cybersecurity
As the world moves towards the age of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), the role of human intelligence in cybersecurity becomes increasingly important. While AGI is expected to be capable of self-learning and self-improvement, it is not clear whether it will be able to detect and prevent cyber-attacks on its own. This implies that human intervention in cybersecurity will continue to play a vital role, even in the age of AGI.
Here are some insights on the topic:
1. AGI will require human input to learn about cybersecurity threats: AGI will need to be trained on a vast amount of data to be able to detect and prevent cyber-attacks. This training data will need to be curated by humans to ensure that the AGI is exposed to diverse and relevant cybersecurity threats. Even after the training, AGI will need to be supervised by humans to ensure that it is not making false positives or false negatives.
2. human intelligence can help agi learn from mistakes: AGI, like any other technology, is not immune to bugs and vulnerabilities. In the event of a cyber-attack, human experts will be needed to investigate the cause and provide remediation strategies. The insights gained from such investigations can then be used to improve the AGI's cybersecurity capabilities.
3. The human factor remains a key vulnerability in cybersecurity: No matter how advanced the technology, humans remain one of the weakest links in cybersecurity. Human errors such as clicking on malicious links or weak passwords can provide an easy entry point for cyber-attackers. Therefore, it is essential to educate humans on cybersecurity best practices and ensure that they are aware of the risks.
4. Cybersecurity strategy must be a human-AI collaboration: To ensure effective cybersecurity in the age of AGI, a collaborative approach that leverages the strengths of both humans and AGI will be required. Human experts can provide insights on emerging threats and design security policies, while AGI can help detect and prevent attacks in real-time.
While AGI is expected to play a crucial role in cybersecurity, human intelligence will remain a key element in maintaining security. A collaborative approach that leverages the strengths of both humans and AGI will be crucial in ensuring effective cybersecurity in the age of AGI.

The Role of Human Intelligence in AGI Cybersecurity - Cybersecurity: Maintaining Security in the Age of AGI
26. The Role of Human Error in Dispatching Disasters
The role of human error in dispatching disasters is a critical aspect that cannot be overlooked when examining the occurrence of missent items. While technological advancements have undoubtedly improved the efficiency and accuracy of dispatching systems, the potential for human error still exists. Whether it is due to fatigue, lack of training, or simply a momentary lapse in judgment, human error can lead to disastrous consequences in the dispatching process.
1. Fatigue and Stress: Dispatchers often work long hours and are required to make split-second decisions that can have significant implications. Fatigue and stress can impair their cognitive abilities, leading to errors in judgment or oversight. For example, a tired dispatcher may inadvertently misread an address or fail to notice a crucial detail, resulting in a missent item.
2. Lack of Training: Dispatching requires specialized knowledge and skills to effectively coordinate logistics and ensure accurate deliveries. Insufficient training can leave dispatchers ill-equipped to handle complex situations or navigate unforeseen challenges. Without proper training, they may struggle to prioritize tasks correctly or misinterpret instructions, leading to mistakes in dispatching.
3. Communication Breakdowns: Effective communication is vital in the dispatching process, involving coordination between dispatchers, drivers, and other stakeholders. Miscommunication or misunderstandings can occur at any point along this chain, leading to missent items. For instance, if a dispatcher fails to convey accurate information about an item's destination or delivery requirements, it could result in the wrong item being dispatched.
4. Distractions and Multitasking: Dispatchers often face high-pressure situations that require them to multitask and handle multiple requests simultaneously. This can increase the likelihood of distractions and decrease their ability to focus on each task adequately. A distracted dispatcher may overlook critical details or make hasty decisions without considering all relevant factors.
5. Inadequate quality Control measures: Dispatching systems should ideally incorporate robust quality control measures to minimize the risk of errors. However, if these measures are inadequate or not followed diligently, missent items can still occur. For example, if a dispatcher fails to double-check the accuracy of an address before dispatching an item, it may end up being sent to the wrong location.
6. Lack of Standardization: In some cases, missent items can be attributed to a lack of standardized procedures or protocols within the dispatching process. Without clear guidelines and standardized practices, there is room for interpretation and inconsistency, increasing the likelihood of errors. Implementing standardized procedures can help reduce human error

The Role of Human Error in Dispatching Disasters - Dispatching Disaster: How Missent Items Happen
27. The Role of Human Activity in Beartrap Creation and Mitigation
Human beings play an integral role in the creation and mitigation of beartraps. While beartraps may seem like a natural phenomenon, the truth is that they are often created by human activities. For example, logging and deforestation can alter the landscape and create conditions that are favorable for the creation of beartraps. Additionally, construction and development projects can also contribute to the creation of beartraps. On the other hand, humans can also play a role in mitigating the effects of beartraps through various measures, such as restoring the ecosystem and implementing policies that promote responsible land use. Here are some ways in which human activity impacts beartraps:
1. Logging and deforestation: These activities can lead to soil erosion, which can create unstable slopes that are more prone to beartraps. Deforestation can also lead to changes in the water cycle, which can exacerbate the problem.
2. Construction and development: These activities can lead to changes in the landscape that alter the natural flow of water, which can create conditions that are favorable for the creation of beartraps.
3. Restoration: Restoring the ecosystem can help to mitigate the effects of beartraps by stabilizing slopes and promoting the growth of vegetation. This can be achieved through various measures, such as planting trees and shrubs, restoring wetlands, and implementing erosion control measures.
4. Policies: Policies that promote responsible land use can also help to mitigate the effects of beartraps. For example, zoning laws can restrict development in areas that are prone to beartraps, and building codes can require that structures be built to withstand the forces of nature.
Overall, human activity plays a significant role in the creation and mitigation of beartraps. While some human activities can contribute to the problem, others can help to mitigate its effects. By understanding the ways in which human activity impacts beartraps, we can work towards creating a more balanced and sustainable ecosystem.

The Role of Human Activity in Beartrap Creation and Mitigation - Ecosystem Disruption: Beartraps and Their Impact on Ecosystem Balance
28. The Role of Human Error in Transposition Errors
1. The role of Human error in Transposition Errors
Transposition errors are a common type of error that can occur when entering or transcribing data. These errors involve the swapping of two adjacent characters or digits, resulting in a distorted or incorrect representation of the intended information. While technological advancements have significantly reduced the occurrence of such errors, human involvement in data entry continues to play a crucial role in their persistence.
1.1. The Fallibility of Human Perception and Attention
One of the primary reasons for transposition errors is the fallibility of human perception and attention. Our brains are wired to recognize patterns and make assumptions based on prior experiences, which can lead to overlooking minor discrepancies in data entry. For example, when manually inputting a series of numbers, such as a phone number or a financial transaction amount, our brains may inadvertently switch the positions of two adjacent digits, resulting in a transposition error.
1.2. Fatigue and Cognitive Load
Fatigue and cognitive load also contribute significantly to the occurrence of transposition errors. When individuals are tired or mentally overloaded, their attention and concentration levels decrease, making them more prone to making mistakes. This is especially true when performing repetitive tasks, such as data entry, where the mind can easily wander. In such cases, the likelihood of transposing characters or digits increases, leading to errors in the entered data.
1.3. Lack of Training and Familiarity
Another factor that can contribute to transposition errors is the lack of proper training and familiarity with the data entry process. In some cases, individuals may be tasked with entering data without receiving adequate training or understanding the importance of accuracy. Without a clear understanding of the consequences of transposition errors, they may not prioritize double-checking their work or employing effective error-checking techniques.
1.4. Comparison of Options: Automated Validation vs. Manual Double-Checking
To mitigate the impact of human error in transposition errors, organizations have implemented various strategies. Two commonly adopted approaches are automated validation and manual double-checking.
Automated validation involves using software or algorithms to detect potential transposition errors in real-time. These systems can compare entered data against predefined patterns or algorithms to identify inconsistencies and prompt the user to review and correct any potential errors. While automated validation is efficient and can significantly reduce the occurrence of transposition errors, it may not catch all instances, especially if the error follows a valid pattern (e.g., swapping "12" with "21").
On the other hand, manual double-checking involves having a second individual review the entered data for errors. This approach relies on human scrutiny and attention to detail to catch any transposition errors that may have occurred during data entry. However, it is time-consuming and may introduce additional human error if the reviewer is fatigued or lacks familiarity with the data being reviewed.
Considering the strengths and weaknesses of both options, a combination of automated validation and manual double-checking seems to be the most effective approach. By utilizing automated validation to catch most transposition errors and then having a second individual perform a manual review to catch any remaining errors, organizations can reduce the risk of transposition errors while ensuring a higher level of accuracy in their data.
In summary, human error plays a significant role in the occurrence of transposition errors. Factors such as fallibility of perception, fatigue, and lack of training contribute to these errors. To mitigate their impact, organizations can leverage automated validation and manual double-checking. By combining these approaches, organizations can minimize the occurrence of transposition errors and maintain the integrity of their data.
Looking for a CTO? Search no more!
FasterCapital provides you with full CTO services, takes the responsibility of a CTO and covers 50% of the total costs
29. The Role of Human Factors in Error Propagation
Human factors play a crucial role in error propagation within complex systems. These factors refer to the ways in which human beings interact with technology, equipment, and other people in their environment. They include cognitive, social, and physical factors that can influence the likelihood of error, as well as the extent to which errors are propagated throughout a system. Understanding these factors is essential for identifying and mitigating potential sources of error in complex systems.
1. Cognitive Factors: One of the most significant human factors that contribute to error propagation is cognitive load. When individuals are required to process large amounts of information or make complex decisions quickly, they may be more susceptible to making errors. This can be exacerbated by factors such as stress, fatigue, and distractions. To reduce the risk of cognitive overload, systems should be designed with simplicity and clarity in mind. Additionally, training and support should be provided to help individuals manage their cognitive load effectively.
2. Social Factors: Social factors can also influence error propagation. For example, communication breakdowns between team members can lead to misunderstandings, resulting in errors. Similarly, conflicts between team members or a lack of trust can create a hostile environment that can impede effective collaboration and increase the likelihood of errors. To address these issues, it is essential to establish clear communication channels, build trust among team members, and foster a culture of collaboration and mutual support.
3. Physical Factors: Physical factors such as equipment design and ergonomics can also contribute to error propagation. Poorly designed equipment or workstations can lead to physical discomfort or injury, which can impair an individual's ability to perform their job effectively. Additionally, equipment that is difficult to use or maintain can increase the likelihood of errors. To mitigate these risks, systems should be designed with user-centered principles in mind. This involves considering the needs and capabilities of the individuals who will be using the equipment and ensuring that it is easy to use and maintain.
4. Training and Support: Effective training and support are critical in reducing the risk of error propagation. Individuals should be provided with the knowledge and skills they need to perform their jobs effectively, as well as ongoing support to help them manage the challenges they may encounter. This includes access to resources such as job aids, checklists, and feedback mechanisms that can help individuals identify and correct errors before they propagate throughout the system.
5. Monitoring and Feedback: Finally, monitoring and feedback mechanisms are essential for identifying and addressing errors as they occur. These mechanisms should be designed to provide real-time feedback to individuals and teams, allowing them to identify and correct errors as quickly as possible. Additionally, they should be used to track trends and patterns in error propagation, enabling organizations to identify systemic issues that may require more comprehensive solutions.
Human factors play a crucial role in error propagation within complex systems. By understanding these factors and implementing strategies to address them, organizations can reduce the risk of errors and minimize their impact when they do occur. Effective training and support, clear communication channels, user-centered design, and real-time monitoring and feedback are all critical components of a comprehensive approach to error prevention and mitigation.
The Role of Human Factors in Error Propagation - Error propagation: Tracing the Ripple Effects of Errors in Complex Systems
30. The Role of Human Input in AI Writing Assistance
While AI writing assistants have undoubtedly revolutionized the way we approach content creation, there is an ongoing ethical dilemma surrounding the balance between authenticity and automation. One crucial aspect that plays a significant role in addressing this dilemma is the involvement of human input in AI writing assistance.
1. Enhancing creativity and personalization:
AI writing assistants, although capable of generating coherent and grammatically correct content, often lack the creative flair and personal touch that humans bring to the table. By incorporating human input into the process, AI can be guided to produce content that aligns with the brand's voice, resonates with the target audience, and reflects a genuine human touch. For instance, a human writer can provide specific instructions, share personal experiences, or inject humor, ensuring the content remains authentic and engaging.
2. Ensuring factual accuracy and ethical considerations:
While AI writing assistants excel at generating content quickly, they may not always possess the ability to fact-check or make ethical judgments. Human input becomes crucial in verifying information, ensuring that the content is accurate and reliable. Additionally, ethical considerations, such as avoiding biased or discriminatory language, require human intervention to ensure that AI-generated content aligns with societal values and norms.
3. Addressing context and cultural nuances:
AI writing assistants often struggle with understanding context and cultural nuances, which can lead to misinterpretations or inappropriate content. Human input becomes vital in providing the necessary context, cultural sensitivity, and knowledge of current events to ensure that the AI-generated content remains relevant and appropriate. For example, a human writer can recognize potential pitfalls or sensitive topics and guide the AI in producing content that respects cultural diversity and avoids unintended offense.
4. Continuous improvement and feedback loop:
Human input plays a crucial role in the development and improvement of AI writing assistants. By providing feedback on the output generated by the AI, human writers can identify areas for improvement, refine algorithms, and train the AI to better understand and mimic human writing styles. This feedback loop between human input and AI technology fosters continual growth and innovation, ultimately leading to more advanced and effective writing assistance tools.
In conclusion, the role of human input in AI writing assistance is indispensable for striking the delicate balance between authenticity and automation. By leveraging human creativity, fact-checking abilities, cultural understanding, and continuous improvement, AI writing assistants can enhance their capabilities and provide valuable assistance while maintaining the authenticity and ethical standards required in content creation.

The Role of Human Input in AI Writing Assistance - Ethical dilemma of ai writing assistants balancing authenticity and automation
31. The Impact on Creative Industries and the Role of Human Creativity
AI content tools have the potential to disrupt creative industries such as writing, music, and art, raising questions about the role of human creativity in content creation.
7.1. Augmentation, Not Replacement: AI content tools should be seen as tools that augment human creativity rather than replacing it entirely. The distinctive qualities of human creativity, such as emotional intelligence, imagination, and critical thinking, cannot be replicated by AI.
7.2. Collaboration and Integration: Encouraging collaboration between AI tools and human creators can result in more innovative and engaging content. By leveraging the strengths of both AI and human creativity, new possibilities for content creation can emerge.
7.3. Fostering Uniqueness and Originality: Content creators should focus on developing unique and original content that showcases their creativity and expertise. By offering content that goes beyond what AI tools can produce, creators can establish their value and differentiate themselves in the market.

The Impact on Creative Industries and the Role of Human Creativity - Ethical implications of using ai content tools
32. The Role of Human Oversight in AI-Driven Content
AI-driven content creation should not eliminate human oversight entirely. Marketers must retain human involvement in the content creation process to ensure ethical standards are upheld. Here's why human oversight is crucial:
1. Ethical Decision-Making: Humans provide the moral compass necessary to make ethical decisions in content creation. They can identify and address ethical concerns that AI algorithms may overlook.
2. Quality Assurance: Human oversight ensures the quality of AI-generated content. Humans can review and refine AI-generated output to ensure accuracy, coherence, and alignment with brand values.
3. Adapting to Context: Humans understand nuances and can adapt content to specific contexts. They can ensure that AI-generated content aligns with cultural sensitivities and avoids potential pitfalls.
4. Accountability and Responsibility: Humans are accountable for the actions and decisions made by AI systems. Marketers must take responsibility for any negative consequences resulting from AI-generated content.
Human oversight acts as a safeguard, ensuring that AI-driven content creation remains ethical, aligned with brand values, and resonates with audiences.

The Role of Human Oversight in AI Driven Content - Ethics of ai in content creation what marketers need to know 1
33. The Role of Human Creativity in Writing
Human creativity plays a vital role in the process of writing, bringing a unique perspective, originality, and depth to the content produced. While AI content tools have undoubtedly revolutionized the writing industry, it is important to recognize that they are merely tools and cannot replicate the innate creativity of human writers. Here, we delve into the significance of human creativity in writing and how it sets us apart from AI-generated content.
1. Originality and Uniqueness:
One of the most notable aspects of human creativity in writing is the ability to generate original and unique ideas. Human writers can draw inspiration from personal experiences, emotions, and observations, allowing them to create content that is distinct and thought-provoking. For instance, a human writer might craft an engaging story by incorporating personal anecdotes, whereas an AI tool can only rely on pre-existing data to generate content.
2. Emotional Connection:
Human creativity enables writers to establish an emotional connection with the readers through their words. By tapping into their own emotions and experiences, writers can convey authenticity and evoke empathy in their audience. For example, an article describing a personal struggle or triumph can resonate deeply with readers, as they can relate to the writer's emotions and experiences. AI-generated content, on the other hand, lacks the emotional depth and personal touch that human creativity brings.
3. Adaptability and Flexibility:
Human writers possess the ability to adapt their writing style, tone, and voice according to the intended audience or purpose. They can effortlessly switch between formal and conversational language, depending on the context. This adaptability allows writers to cater to specific requirements and effectively communicate their message. AI content tools, while capable of generating content for various purposes, often lack the versatility and adaptability that human writers possess.
4. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving:
Writing often involves critical thinking and problem-solving, especially when it comes to crafting persuasive arguments or developing complex narratives. Human writers excel at analyzing information, synthesizing ideas, and presenting logical arguments. They can identify gaps in knowledge and propose innovative solutions. On the other hand, AI tools rely on pre-programmed algorithms and lack the ability to engage in complex reasoning or offer creative solutions to problems.
5. Artistic Expression:
Writing is an art form, and human writers have the unique ability to express themselves artistically through their craft. They can employ literary techniques, such as metaphors, similes, and symbolism, to add depth and richness to their work. Poets, novelists, and creative writers, in particular, rely heavily on their creative prowess to produce works that resonate with readers on a profound level. AI-generated content, while proficient in generating functional text, often falls short in capturing the essence of artistic expression.
In conclusion, human creativity is an indispensable aspect of writing that sets it apart from AI-generated content. The ability to produce original and unique ideas, establish emotional connections, adapt to different writing styles, engage in critical thinking, and express oneself artistically are just a few ways in which human writers contribute to the richness and depth of written content. While AI content tools can aid in the writing process, they cannot fully replicate the ingenuity and creative capacity of human writers.

The Role of Human Creativity in Writing - Ethics of using ai content tools in writing
34. Understanding the Role of Human Error in False Alarms
In any field that involves monitoring and alerting systems, false alarms are a common occurrence. False alarms can be caused by a number of factors, including equipment malfunction, environmental factors, and, most commonly, human error. understanding the role of human error in false alarms is crucial to minimizing their frequency and ensuring that legitimate alarms are not overlooked.
1. The Psychology of Human Error
Human error is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that can be difficult to understand and predict. However, by examining the psychology of human error, we can gain valuable insights into why false alarms occur and how to prevent them. One common cause of human error is cognitive overload, which occurs when an individual is presented with too much information or too many tasks to perform at once. This can lead to errors such as misinterpretation of data or failure to notice important details. Another common cause of human error is confirmation bias, which occurs when an individual interprets information in a way that confirms their pre-existing beliefs or expectations. This can lead to false alarms if an individual
35. Understanding Financial Crimes and Their Role in Human Trafficking
Human trafficking is an unfortunate reality that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a form of modern-day slavery that involves the exploitation of individuals for various purposes such as forced labor, sexual exploitation, and organ trafficking. While human trafficking is a complex issue that involves various factors, money laundering is a significant contributor to its perpetuation. understanding the role of financial crimes in human trafficking is crucial in the fight against this heinous crime. This section will provide insights into this issue from different perspectives and highlight the FinCEN's contribution to the cause.
Here are some key points to consider:
1. Money laundering and human trafficking are closely linked. Human traffickers often use various methods to disguise the proceeds of their criminal activities to avoid detection. This includes using cash smuggling, shell companies, and other methods to launder their ill-gotten gains. By breaking the financial infrastructure that supports human trafficking, law enforcement agencies can disrupt the operations of traffickers and bring them to justice.
2. The use of financial intelligence is critical in combating human trafficking. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) is a vital agency in the fight against human trafficking. It collects and analyzes financial intelligence to detect and prevent money laundering activities that are linked to human trafficking. The FinCEN works with other law enforcement agencies to share information and provide support in criminal investigations.
3. Financial institutions play a crucial role in detecting and reporting financial crimes related to human trafficking. They are required by law to report suspicious transactions that may be linked to money laundering activities. Their compliance with anti-money laundering regulations can help identify and prevent financial crimes that support human trafficking.
4. Technology can help in the fight against human trafficking. For example, blockchain technology can be used to track financial transactions and identify suspicious activities that may be linked to human trafficking. It can also provide transparency in supply chains, making it easier to detect and prevent human trafficking in industries such as agriculture and manufacturing.
Financial crimes are a significant contributor to the perpetuation of human trafficking. By breaking the financial infrastructure that supports this crime, law enforcement agencies can disrupt the operations of traffickers and bring them to justice. The FinCEN plays a vital role in this effort by collecting and analyzing financial intelligence and working with other law enforcement agencies to combat human trafficking. Financial institutions also have a crucial role to play in detecting and reporting suspicious transactions that may be linked to money laundering activities. Technology can also be used to help in the fight against human trafficking by providing transparency in supply chains and tracking financial transactions.

Understanding Financial Crimes and Their Role in Human Trafficking - Fighting Human Trafficking: FinCEN s Contribution to the Cause
36. The Role of Human Editors in AI Content Generation
While AI content generation offers significant benefits, human editors play a vital role in maintaining quality, ensuring accuracy, and injecting creativity into the content creation process.
Key points:
1. Human oversight: Human editors can provide the critical thinking and judgment necessary to identify and rectify errors or biases in AI-generated content.
2. Creative input: Human editors can add a unique perspective, storytelling, and emotional intelligence to content that AI algorithms may struggle to replicate.
3. Quality control: Human editors ensure that content meets the desired standards, maintaining brand identity and reputation.
4. Strategic guidance: Human editors can guide AI algorithms and adjust their parameters to align with the organization's content strategy.
The collaboration between AI algorithms and human editors allows for the creation of high-quality, engaging, and reliable content.
Example:
The New York Times uses AI to automate the generation of personalized newsletters. However, human editors curate and select the content that goes into these newsletters, ensuring that it is relevant, accurate, and aligns with the publication's standards.

The Role of Human Editors in AI Content Generation - Future is here ai content generation and its implications
37. The Role of Human Creativity in the Future of Writing
While AI technologies are transforming the writing industry, the role of human creativity remains crucial for the future of writing. In a world where AI-generated content is readily available, human writers can leverage their unique ability to think creatively, communicate effectively, and evoke emotional responses in readers.
1. Creative storytelling: Storytelling is an essential aspect of writing that relies on human creativity and imagination. Human writers have the ability to create compelling narratives, develop relatable characters, and evoke emotions through their storytelling. These qualities make human-written content more engaging and impactful.
2. Unique perspectives and insights: Human writers bring their own perspectives, experiences, and insights to their writing, which adds depth and authenticity to their work. These unique perspectives enable writers to analyze complex issues, offer thought-provoking insights, and generate fresh ideas that AI algorithms struggle to replicate.
3. Adaptability and innovation: Human writers possess the adaptability and innovation required to keep up with changing trends, evolving audience preferences, and emerging technologies. They can adapt their writing style, tone, and approach to suit different clients and target audiences, ensuring that their content remains relevant and impactful.
4. Emotional connection and empathy: Writing is a powerful tool for connecting with readers on an emotional level and evoking empathy. Human writers can tap into their own emotions, experiences, and understanding of human nature to create content that resonates with readers, elicits emotional responses, and drives action.

The Role of Human Creativity in the Future of Writing - Future of freelance writing and impact of artificial intelligence
38. The Role of Human Journalists in an AI-Driven World
In an era dominated by AI-generated content, the role of human journalists may appear uncertain. However, human journalists continue to play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy, credibility, and ethical aspects of news reporting. While AI systems are capable of automating certain tasks, they lack the contextual understanding, critical thinking, and empathetic approach that humans bring to journalism. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which human journalists can thrive and collaborate within an AI-driven world.
1. Contextualizing AI-Generated Content:
AI algorithms excel in gathering, organizing, and analyzing vast amounts of data. However, they often fall short when it comes to providing the necessary context. Human journalists possess the ability to understand complex issues, observe subtle nuances, and connect dots that an AI system might miss. By contextualizing the information generated by AI, journalists can present a more comprehensive and nuanced view of the story.
For example, AI systems may accurately report data related to a political scandal but fail to capture the underlying emotions and implications involved. It is the role of human journalists to investigate, interview relevant sources, and present the story with a deeper understanding of the political dynamics, public sentiment, and the consequences of the scandal on the wider society.
2. Uncovering Deep-Rooted Issues:
While AI algorithms can analyze patterns and provide data-driven insights, they often struggle to uncover deep-rooted societal issues and hold the powerful accountable. Human journalists, on the other hand, have the capability to dig deep, investigate, and uncover stories that an AI system might overlook. Journalists' experience, intuition, and investigative skills enable them to challenge the status quo and bring hidden issues to light.
For instance, a human journalist might notice a sudden increase in public complaints against a particular corporation and decide to investigate further. By interviewing affected individuals, gathering evidence, and uncovering corporate malpractices, the journalist can expose a story that goes beyond the mere analysis of data.
3. maintaining Ethical standards:
Ethics are the bedrock of journalism and play a critical role in maintaining the public's trust. While AI systems can provide news updates at lightning speed, they sometimes struggle with ethical decision-making. Human journalists, on the other hand, are bound by a code of ethics, enabling them to address conflicts of interest, protect sources, and make responsible decisions about what gets reported.
For example, human journalists may be faced with the choice of reporting on an individual's private life, which could have far-reaching consequences. By evaluating the news value against privacy rights and public interest, journalists can make ethical choices that AI systems are incapable of.
In conclusion, the integration of AI in journalism does not overshadow the importance of human journalists. Instead, it enhances their capabilities by providing valuable tools for data analysis and research. The in-depth understanding, critical thinking, and ethical considerations that human journalists bring to their work continue to be indispensable in an AI-driven world. Rather than replacing human journalists, AI serves as a powerful ally, enabling them to focus on higher-level tasks, such as investigative journalism, storytelling, and delivering news with context and empathy.

The Role of Human Journalists in an AI Driven World - Future of journalism with ai generated content
39. The Role of Human Writers in a Future Dominated by AI Writing Programs
While AI writing programs offer significant advantages, human writers will continue to play a vital role in the future of writing. Here are some key areas where human writers excel:
1. Creativity and originality: Human writers have an innate ability to think creatively, producing original and unique content that can captivate and engage readers.
2. Emotional intelligence and storytelling: Human writers are skilled at crafting narratives and evoking emotions through their writing. They can connect with readers on a deeper level, creating impactful and memorable content.
3. Critical thinking and analysis: Human writers excel in critical thinking and analyzing complex topics. They can delve into subjects with depth, assessing multiple perspectives, and providing nuanced insights that AI writing programs may struggle to replicate.
4. Adaptability and flexibility: Human writers can adapt to changing requirements and adjust their writing style to suit different audiences and purposes. They can pivot quickly, responding to emerging trends or shifts in the market.
5. Quality control and editing: Human writers possess the ability to review, edit, and refine content generated by AI writing programs. They can ensure that the content meets the necessary standards of clarity, accuracy, and relevance.

The Role of Human Writers in a Future Dominated by AI Writing Programs - Future of writing exploring ai writing programs
40. The Role of Human Activity in Shaping the Evolution of Archipelago Species
Humans have been a significant factor in shaping the evolution of archipelago species. Their activities have affected the natural environment, leading to changes in the genetic makeup of species. Human activity has been both positive and negative, depending on the context. In this section, we will explore the different ways human activity has impacted archipelago species.
1. Habitat Destruction
Habitat destruction is one of the primary ways human activity has impacted archipelago species. As humans clear land for agriculture, urbanization, or other development purposes, they destroy habitats that support a variety of species. This leads to a loss of biodiversity and can cause certain species to go extinct. For example, the deforestation of Madagascar has led to the loss of habitat for many species, including lemurs, which are now critically endangered.
2. Introduction of Non-Native Species
Human activity has also led to the introduction of non-native species to archipelagos. These species can outcompete native species for resources, leading to a decline in their population. For example, the introduction of rats to the Galapagos Islands has had a devastating effect on the native bird population. Rats prey on the eggs and young of birds, leading to a decline in their numbers.
3. Conservation Efforts
Despite the negative impact of human activity on archipelago species, humans have also played a positive role in their evolution. Conservation efforts, such as the establishment of protected areas and the reintroduction of species to their natural habitats, have helped to preserve and even increase the population of certain species. For example, the conservation efforts in the Galapagos Islands have led to the recovery of the giant tortoise population, which was once on the brink of extinction.
4. Human-Induced Evolution
Human activity has also led to the evolution of certain archipelago species. For example, the introduction of goats to the Galapagos Islands led to the evolution of the Galapagos finches. The goats destroyed the vegetation, which led to a decline in the population of the finches' primary food source. As a result, the finches evolved larger beaks to enable them to eat seeds and nuts.
5. The Best Option
The best option for human activity in shaping the evolution of archipelago species is to minimize negative impacts and maximize positive impacts. This can be achieved through sustainable development practices, such as reforestation and the use of eco-friendly technologies. Conservation efforts should also be prioritized, and the introduction of non-native species should be avoided. By taking a responsible approach to human activity, we can ensure the continued evolution of archipelago species for generations to come.
Human activity has had a significant impact on the evolution of archipelago species. It is up to us to ensure that our actions are responsible and sustainable, so that we can preserve the biodiversity of these unique ecosystems.

The Role of Human Activity in Shaping the Evolution of Archipelago Species - Geographical Isolation: Evolutionary Marvels of Archipelago Species
41. The Role of Human Resources in Globalized Companies
In the era of global expansion, companies are increasingly operating in a globalized environment, where they face unique challenges and opportunities. One crucial aspect that plays a pivotal role in the success of these diversified companies is the function of Human Resources (HR). HR departments in globalized companies have a multifaceted role, as they not only manage the traditional HR functions but also navigate through cultural differences, language barriers, and diverse legal frameworks across different countries. This section will delve into the significance of HR in globalized companies from various perspectives, highlighting key responsibilities and strategies employed by HR professionals to ensure effective management of human capital in this complex landscape.
1. Talent Acquisition and Management:
In globalized companies, HR plays a vital role in attracting and retaining top talent from diverse backgrounds. They develop recruitment strategies that align with the company's global objectives while considering local market conditions. For instance, a multinational technology company like Google has successfully implemented this approach by tailoring their recruitment processes to suit different regions. They focus on hiring local talent who possess cultural knowledge and language skills necessary for effective operations in specific markets.
2. Cross-Cultural Competence:
Globalization brings together individuals from various cultures, requiring HR professionals to possess cross-cultural competence. They must understand cultural nuances, values, and norms to foster an inclusive work environment that respects diversity. For example, when managing teams across different countries, HR may organize cross-cultural training programs to enhance employees' understanding of each other's cultures and promote collaboration.
3. Compliance with Local Laws and Regulations:
Operating globally means adhering to diverse legal frameworks and regulations. HR departments play a critical role in ensuring compliance with employment laws specific to each country of operation. They must stay updated on labor laws, taxation requirements, work permits, and immigration policies to avoid legal complications. For instance, when expanding into new markets, HR professionals collaborate with legal experts to navigate complex employment regulations.
4. Global Performance Management:
HR departments in globalized companies face the challenge of implementing consistent performance management practices across different regions. They develop performance evaluation systems that consider cultural differences, local market conditions, and individual employee goals. For instance, a multinational retail company like Walmart has implemented a balanced scorecard approach to evaluate employee performance globally. This system aligns individual goals with the company's overall objectives while considering regional variations.
5. Employee Engagement and Communication:
Maintaining effective communication channels and fostering employee engagement is crucial in globalized companies. HR professionals play a key role in ensuring transparent communication across different locations and cultures.

The Role of Human Resources in Globalized Companies - Globalization: Diversified Companies in the Era of Global Expansion
42. The Role of Human Expertise in Data-Driven Investing
While data analysis and technology play a critical role in investment decision making, human expertise remains indispensable. data-driven investing should be seen as a collaboration between data analysis tools and human judgment, with each complementing and enhancing the other.
Human expertise adds value to data-driven investing in the following ways:
1. Contextual Interpretation: Human experts can provide the necessary context to interpret data-driven insights accurately. They can identify nuances, assess market conditions, and incorporate qualitative factors that are not captured by data analysis alone. By combining quantitative and qualitative analysis, human experts can generate a more comprehensive and informed investment decision.
2. Judgment and Decision Making: Human judgment is crucial in making investment decisions that go beyond statistical models or algorithms. While machines can process vast amounts of data and identify patterns, they lack the ability to assess complex, evolving economic and market dynamics. Human experts can integrate their experience, intuition, and industry knowledge to make informed judgments and decisions.
3. Ethical Considerations: With the increased use of data analytics and AI in investment decision making, ethical considerations become paramount. Human experts play a crucial role in ensuring that investment strategies align with ethical guidelines, comply with regulatory frameworks, and engage in responsible data usage.
4. Relationship Management: Investment decisions often involve client relationships and stakeholder interactions. Human experts bring essential interpersonal skills, communication abilities, and client-centric approaches that machines cannot replicate. Building trust and understanding clients' unique preferences and goals are paramount in delivering successful investment strategies.
In conclusion, while data plays a pivotal role in investment decision making, the human touch remains essential. Human expertise adds value by providing context, judgment, ethical considerations, and relationship management skills that complement data analysis and AI technologies.

The Role of Human Expertise in Data Driven Investing - Harnessing Data for Informed Investment Decisions
43. Analyzing the Role of Human Error in Head-On Collisions
1. Understanding the Prevalence of Human Error in Head-On Collisions
When it comes to head-on collisions, the role of human error cannot be overstated. In fact, it is often cited as one of the primary causes of these catastrophic crashes. Human error encompasses a wide range of factors, including distracted driving, impaired driving, reckless behavior, and failure to adhere to traffic laws. Analyzing the role of human error in head-on collisions is crucial in order to identify potential solutions and prevent such accidents from occurring in the future. Let's dive into some key aspects and case studies that shed light on this issue.
2. Distracted Driving: A Leading Cause of Head-On Collisions
One of the most prevalent forms of human error leading to head-on collisions is distracted driving. This can include activities such as texting, talking on the phone, eating, or using in-car technology while behind the wheel. Studies have shown that drivers who engage in distracted driving are significantly more likely to drift into oncoming traffic, resulting in devastating head-on collisions.
For example, a case study conducted by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that a driver who was texting while driving crossed over the centerline, causing a head-on collision with another vehicle. This tragic incident highlights the importance of eliminating distractions and remaining focused on the road at all times.
3. Impaired Driving: A Dangerous Choice with Severe Consequences
Impaired driving, whether due to alcohol, drugs, or prescription medication, is another significant contributor to head-on collisions. Drivers under the influence often exhibit impaired judgment, reduced reaction times, and impaired coordination, making them more prone to veering into oncoming traffic.
Consider the case of a driver who consumed excessive amounts of alcohol and chose to get behind the wheel. As a result, they lost control of their vehicle and crashed head-on into another car, resulting in severe injuries for both parties involved. This unfortunate incident underscores the critical need for awareness campaigns, stricter penalties, and effective enforcement to deter impaired driving and prevent future head-on collisions.
4. Reckless Behavior: Speeding and Aggressive Driving
Speeding and aggressive driving are two common forms of reckless behavior that contribute to head-on collisions. Drivers who exceed the speed limit or engage in aggressive maneuvers, such as tailgating or unsafe passing, significantly increase the likelihood of losing control and colliding with oncoming vehicles.
A notable example is a case where a driver was rushing to reach their destination and chose to overtake multiple vehicles in a no-passing zone. In doing so, they collided head-on with an oncoming vehicle, resulting in severe injuries for both drivers. This incident serves as a reminder of the importance of obeying traffic laws, maintaining a safe speed, and refraining from aggressive driving behaviors.
5. Failure to Adhere to Traffic Laws: Ignoring the Basics
Lastly, a significant factor in head-on collisions is the failure to adhere to basic traffic laws. This can include running red lights, making illegal U-turns, or failing to yield the right of way. Such violations put both the offending driver and others at risk, increasing the chances of a head-on collision.
For instance, a driver who failed to yield at an intersection caused a head-on collision with another vehicle that had the right of way. The consequences were severe, resulting in fatalities and life-altering injuries. This case emphasizes the importance of educating drivers about traffic laws and the potential consequences of failing to follow them.
Human error plays a pivotal role in head-on collisions. Through analyzing various aspects such as distracted driving, impaired driving, reckless behavior, and failure to adhere to traffic laws, we gain valuable insights to develop strategies aimed at reducing these catastrophic crashes. By raising awareness, implementing stricter regulations, and promoting responsible driving habits, we can strive towards a safer future on our roads.

Analyzing the Role of Human Error in Head On Collisions - Head On Collisions: The Anatomy of Catastrophic Crashes
44. The Role of Human Expertise in AI Development
1. The crucial role of human expertise in AI development
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), one might be tempted to believe that machines alone are responsible for the remarkable progress we are witnessing. However, the reality is that human expertise plays a pivotal role in the development and advancement of AI technologies. While AI systems possess immense computational power and can process vast amounts of data, it is the human touch that imbues these systems with the ability to understand, learn, and make informed decisions.
2. Human guidance for training AI models
One of the key aspects of AI development is the training of AI models. machine learning algorithms require large datasets to learn patterns and make predictions or decisions. However, the quality and relevance of the data used for training greatly depend on human expertise. Domain experts, data scientists, and engineers work together to curate and annotate datasets, ensuring that the AI models are exposed to the right information and can learn effectively.
For example, in the medical field, AI systems are being trained to assist in diagnosing diseases. Doctors and medical professionals provide their expertise to label and annotate medical images, enabling AI algorithms to recognize patterns indicative of various conditions. This collaboration between human experts and AI technology improves diagnostic accuracy and enhances patient care.
3. Human input for refining AI algorithms
While AI models can learn from existing data, they are often limited by the biases and limitations of the data they are exposed to. Human expertise is crucial in identifying and rectifying these biases, ensuring that AI systems provide fair and unbiased outcomes. By examining the output of AI algorithms and analyzing their decision-making process, human experts can identify areas for improvement and fine-tune the algorithms accordingly.
A notable case study in this regard is the development of AI-powered language translation systems. Initially, these systems produced translations that were grammatically correct but lacked nuance and context. Human linguists and translators provided their expertise by reviewing and refining the output of the AI algorithms. This iterative process of feedback and improvement has led to the development of more accurate and contextually appropriate translation systems.
4. Human oversight and ethical considerations
As AI technology progresses, it becomes increasingly important to address ethical concerns and ensure that AI systems align with human values and societal norms. Human expertise is vital in defining the boundaries and constraints within which AI systems operate. By establishing ethical guidelines and overseeing the development process, human experts can prevent AI systems from making harmful or biased decisions.
For instance, autonomous vehicles rely on AI algorithms to make split-second decisions on the road. However, human experts are responsible for programming these algorithms to prioritize human safety, adhere to traffic rules, and make ethical choices when faced with potentially dangerous situations. This collaboration between human expertise and AI technology ensures that autonomous vehicles are not only efficient but also safe and responsible.
5. The future of human-AI collaboration
The role of human expertise in AI development is not diminishing; rather, it is evolving. As AI systems become more sophisticated, human experts will continue to play a crucial role in refining and improving these technologies. The collaboration between humans and AI is a symbiotic relationship, where each complements the other's strengths and compensates for their respective limitations.
In this ever-changing landscape, it is essential for individuals to acquire the necessary skills to work alongside AI systems effectively. By understanding AI technology, harnessing their domain expertise, and embracing collaboration, human experts can shape the future of AI development and ensure that these technologies serve humanity's best interests.

The Role of Human Expertise in AI Development - Human AI Collaboration: The Future of AAI Partnership
45. The Role of Human Capital in the Porter Diamond Framework
Human capital, defined as the knowledge, skills, and abilities that individuals possess, plays a crucial role in the Porter Diamond Framework. Developed by Michael Porter, this framework aims to explain why certain nations are more competitive than others in specific industries. It emphasizes the interplay between various factors, including human capital, in determining a nation's competitive advantage.
1. Human capital as a driver of innovation:
In today's knowledge-based economy, innovation is a key driver of competitiveness. Human capital, with its diverse skill sets and knowledge, fuels innovation by enabling individuals to generate new ideas, develop cutting-edge technologies, and improve processes. For example, Silicon Valley's success can be attributed to its abundance of highly skilled engineers and entrepreneurs, who continuously push the boundaries of technological innovation.
2. Human capital as a source of productivity:
A skilled and educated workforce enhances productivity, which is a critical component of competitiveness. Nations with a well-developed human capital base tend to have higher productivity levels, as their workforce is equipped with the necessary knowledge and expertise to perform tasks efficiently. Germany's manufacturing sector, renowned for its precision and quality, benefits from a highly skilled workforce that undergoes rigorous vocational training programs.
3. Human capital as a facilitator of knowledge spillovers:
Knowledge spillovers, the diffusion of knowledge from one entity to another, are vital for innovation and competitiveness. Human capital acts as a conduit for these spillovers, as individuals with high levels of knowledge and expertise can transfer their insights to others. This knowledge sharing can occur within firms, industries, or even across nations. For instance, the concentration of skilled workers in Silicon Valley facilitates knowledge spillovers through networking, collaboration, and the exchange of ideas.
4. Human capital as a determinant of industry clusters:
Industry clusters, geographic concentrations of interconnected firms, suppliers, and supporting institutions, often emerge in regions with a strong human capital base. Skilled workers attract firms in related industries, creating a virtuous cycle of knowledge exchange and specialization. The fashion industry in Milan, Italy, thrives due to the presence of highly skilled designers, craftsmen, and fashion schools, which foster a supportive ecosystem for the industry.
5. Human capital as a factor influencing factor conditions:
In the Porter Diamond Framework, factor conditions refer to a nation's endowment of resources, including human capital. The quality and quantity of a nation's human capital significantly impact factor conditions, shaping the competitiveness of industries. For example, the availability of a large pool of software development.
6. Human capital as a catalyst for continuous improvement:
Human capital serves as a catalyst for continuous improvement within industries. Skilled workers, equipped with up-to-date knowledge and expertise, drive the adoption of best practices, innovation, and efficiency gains. Japan's automotive industry is renowned for its relentless pursuit of perfection, driven by a highly skilled workforce committed to continuous improvement and lean manufacturing principles.
Human capital plays a multifaceted role within the Porter Diamond Framework, influencing competitiveness through innovation, productivity, knowledge spillovers, industry clusters, factor conditions, and continuous improvement. Nations that prioritize the development of their human capital stand to gain a competitive advantage in today's globalized and knowledge-intensive economy. By investing in education, training, and skills development, countries can unleash the full potential of their human capital and foster sustainable economic growth.

The Role of Human Capital in the Porter Diamond Framework - Human Capital: Unleashing Potential in the Porter Diamond Framework
46. The Role of Human Capital in Maximizing MRP
Human capital, often referred to as the knowledge, skills, and experience that individuals bring to the workplace, plays a pivotal role in maximizing material Requirements planning (MRP). In the context of human capital development and MRP maximization, it is crucial to understand how employees' competencies and capabilities can significantly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of production and supply chain processes. In this section, we will delve into the multifaceted role of human capital in the world of MRP. We will explore different perspectives, examples, and insights that shed light on the importance of nurturing and harnessing human capital for optimizing MRP.
1. Enhanced Decision-Making:
One of the fundamental aspects of MRP is making accurate and timely decisions regarding inventory levels, production schedules, and procurement. Human capital, in the form of knowledgeable and experienced personnel, can significantly impact the quality of these decisions. For instance, a seasoned supply chain manager can use their expertise to better forecast demand and ensure optimal stock levels, reducing excess inventory costs and stockouts.
2. Continuous Improvement Culture:
A culture of continuous improvement is essential in MRP to adapt to changing market conditions and technological advancements. Skilled employees can drive this culture by identifying process inefficiencies and suggesting innovative solutions. For example, a production line worker with expertise in lean manufacturing principles might suggest workflow changes that lead to significant cost savings.
3. Data Analysis and Interpretation:
MRP heavily relies on data, and the ability to analyze and interpret this data is a human capital asset. Data scientists and analysts can use their skills to mine valuable insights from historical data, helping to refine demand forecasting and optimize inventory levels.
4. Effective Communication:
MRP success is often contingent on seamless communication within an organization. Individuals with strong communication skills can bridge the gap between various departments, ensuring that production, procurement, and logistics teams are aligned. For example, a proficient communicator can prevent bottlenecks in the supply chain by coordinating production schedules with suppliers and distributors.
5. Training and Skill Development:
Human capital development is an ongoing process. Companies can maximize MRP by investing in the training and development of their workforce. This investment can empower employees to stay updated with the latest industry trends and technologies. For instance, offering training in advanced inventory management software can enable staff to make the most of available tools for more efficient MRP.
6. Adaptability and Innovation:
The world of MRP is ever-evolving, with changing market dynamics, customer preferences, and global events. Human capital's ability to adapt and innovate is paramount. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies with innovative employees quickly adapted their MRP systems to accommodate new demand patterns, ensuring business continuity.
7. Cross-Functional Collaboration:
Collaborative human capital, capable of working across various functions, is invaluable. A product development engineer who can effectively collaborate with both the engineering and supply chain teams can streamline the introduction of new products into the MRP system, ensuring smooth transitions and avoiding production disruptions.
8. Leadership and Vision:
Effective leadership and visionary individuals within an organization can steer MRP strategies towards long-term success. They can set the direction for MRP implementation and align it with overall business goals. A visionary leader might recognize the importance of sustainable sourcing and implement eco-friendly practices within the MRP system.
9. Employee Engagement and Motivation:
Engaged and motivated employees are more likely to contribute positively to MRP. Recognizing and rewarding their efforts can boost morale and productivity. As an example, an employee of the month program can motivate staff to actively participate in MRP optimization efforts.
10. Quality Control and Risk Management:
Skilled quality control and risk management teams can ensure that the products produced meet the highest standards. This minimizes the risk of costly recalls or product defects and safeguards the reputation of the company.
In summary, the significance of human capital in maximizing MRP cannot be overstated. From informed decision-making and innovative thinking to adaptability and employee engagement, human capital development is a cornerstone of MRP success. By recognizing and nurturing the potential of their workforce, organizations can unlock the full potential of Material Requirements Planning, ensuring efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability in the ever-changing business landscape.

The Role of Human Capital in Maximizing MRP - Human capital development and MRP maximization
47. Understanding the Role of Human Capital in Investments
1. Human capital, often referred to as the knowledge, skills, and abilities possessed by individuals, plays a crucial role in successful investments. As investors, it is imperative to understand how human capital impacts the decision-making process and ultimately influences the outcomes of our investment endeavors. By recognizing the importance of human capital, we can better assess the risks and rewards associated with different investment opportunities.
2. One aspect to consider is the expertise and experience of the individuals involved in the investment process. A team with diverse backgrounds and a wide range of skills can bring valuable perspectives to the table. For example, an investment team consisting of professionals from various fields such as finance, technology, and marketing can provide a comprehensive analysis of potential investments. This multidisciplinary approach enhances the decision-making process and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
3. Another important consideration is the ability of individuals to adapt to changing market conditions. In today's fast-paced and dynamic business environment, the ability to quickly identify and respond to market trends is crucial. Investors with a high level of human capital can effectively navigate through market uncertainties and seize opportunities. For instance, a well-versed investor who understands emerging technologies may recognize the potential of a disruptive innovation and make timely investment decisions, reaping substantial returns.
4. Additionally, the continuous development of human capital through ongoing learning and skill enhancement is vital for successful investments. Individuals who actively seek knowledge and stay updated with industry trends are better equipped to make informed investment decisions. This might include attending workshops, seminars, or pursuing advanced degrees in relevant fields. By constantly upgrading their skills, investors can mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
5. The role of human capital in investments can also be seen in the context of managing risk. Investors with a deep understanding of risk management techniques can better assess the potential risks associated with an investment opportunity. For example, a skilled investor may conduct thorough due diligence, analyzing financial statements, market trends, and regulatory factors to assess the risk-reward tradeoff. This comprehensive evaluation minimizes the chances of making ill-informed investment decisions that could lead to significant losses.
6. Finally, the ability to build and maintain strong professional networks is another aspect of human capital that influences successful investments. Networking provides access to valuable resources, information, and potential investment opportunities. Investors who actively engage with industry professionals, attend conferences, and participate in relevant communities can gain insights that might not be readily available otherwise. These connections can lead to fruitful collaborations, partnerships, and access to exclusive investment deals.
Understanding the role of human capital in investments is essential for investors seeking successful outcomes. By considering the expertise and experience of individuals, their adaptability to changing market conditions, continuous skill development, risk management abilities, and networking capabilities, investors can make informed decisions that maximize their returns while minimizing potential risks. Human capital is a valuable asset that should not be overlooked when evaluating investment opportunities.

Understanding the Role of Human Capital in Investments - Human Capital s Impact on Successful Investments
48. The Role of Human Capital in Risk Management and Decision Making
1. Human capital plays a crucial role in risk management and decision making within the realm of investments. The skills, knowledge, and experience of individuals involved in these processes can greatly impact the outcomes and success of investment strategies. Whether it is analyzing market trends, assessing potential risks, or making informed investment decisions, human capital is a key factor that cannot be overlooked.
2. One aspect of human capital in risk management is the ability to identify and evaluate potential risks associated with investments. Professionals with expertise in risk management can effectively assess the likelihood and impact of various risks, such as market volatility, economic downturns, or regulatory changes. They can also develop strategies to mitigate these risks and protect investments. For example, a risk management expert might recommend diversifying a portfolio to spread risk across different asset classes and industries.
3. Another important role of human capital is the ability to make informed decisions based on comprehensive analysis. Investment professionals with strong analytical skills can evaluate financial data, market trends, and other relevant factors to identify attractive investment opportunities. They can also assess the potential risks and rewards associated with each option. For instance, an investment analyst might compare the historical performance, growth potential, and competitive advantages of different companies before recommending an investment in a particular stock.
4. Human capital also plays a crucial role in adapting to changing market conditions and making informed decisions in real-time. In today's fast-paced investment landscape, professionals need to stay updated with the latest market trends, news, and developments. This requires continuous learning, staying abreast of industry knowledge, and leveraging technology to gather and analyze data efficiently. For example, investment managers who utilize advanced data analytics tools can quickly identify emerging trends and adjust investment strategies accordingly.
5. Collaboration and effective communication within investment teams are also essential components of human capital. By working together, individuals can combine their expertise and perspectives to make more informed decisions. This collaborative approach allows for a comprehensive evaluation of potential risks and rewards, as well as a wider range of investment options. For instance, a team consisting of analysts, portfolio managers, and risk management experts can collectively assess the viability of different investment strategies and provide a well-rounded perspective.
6. While human capital is undoubtedly crucial in risk management and decision making, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of relying solely on human judgment. Human biases, emotions, and cognitive limitations can sometimes cloud decision-making processes and lead to suboptimal outcomes. To mitigate these risks, investment professionals can leverage technology and data-driven tools to augment their decision-making processes. By combining human judgment with advanced analytics and algorithms, investors can make more objective and data-backed decisions, reducing the impact of individual biases.
7. In conclusion, human capital plays a vital role in risk management and decision making within the realm of investments. The skills, knowledge, and experience of individuals involved in these processes are instrumental in identifying risks, analyzing opportunities, adapting to market conditions, and making informed decisions. However, it is important to leverage technology and data-driven tools to supplement human judgment and mitigate the impact of biases. Ultimately, a combination of human capital and technological advancements can lead to more successful and profitable investment strategies.

The Role of Human Capital in Risk Management and Decision Making - Human Capital s Impact on Successful Investments
49. The Role of Human Rights in Upholding Human Dignity
Human rights and human dignity are inextricably linked. While human dignity can be seen as a fundamental value that all individuals possess simply by virtue of being human, human rights serve as the legal and moral framework that upholds and protects this inherent worth. The role of human rights in upholding human dignity is crucial, as it ensures that individuals are treated with respect, equality, and fairness, regardless of their background or circumstances.
1. Recognition and Protection: Human rights serve as a means of recognizing and protecting the inherent dignity of every individual. They provide a set of standards and principles that governments and societies must adhere to in order to ensure that the rights and dignity of all people are respected and upheld. For example, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted by the United Nations in 1948, explicitly recognizes the inherent dignity and equal rights of all human beings.
2. Equality and Non-Discrimination: Human rights play a vital role in promoting equality and non-discrimination, which are essential components of human dignity. They ensure that no one is discriminated against based on factors such as race, gender, religion, or socioeconomic status. By guaranteeing equal rights and opportunities for all, human rights help create a society where everyone can live with dignity. For instance, laws prohibiting discrimination in employment or housing are aimed at promoting equal treatment and safeguarding the dignity of individuals.
3. Freedom and Autonomy: Human rights also play a crucial role in protecting individual freedoms and autonomy, which are integral to human dignity. They grant people the right to express their opinions, practice their religion, and live their lives according to their own choices and beliefs. Without these rights, individuals would be deprived of their autonomy and their ability to live with dignity. For example, the freedom of speech allows individuals to voice their opinions and participate in public discourse, which is essential for a thriving democracy and the protection of human dignity.
4. Access to Basic Needs and Services: Human rights encompass not only civil and political rights but also economic, social, and cultural rights. These rights ensure that individuals have access to basic needs such as food, shelter, healthcare, and education, which are essential for living a life of dignity. By providing the necessary resources and services, human rights help to address inequalities and uphold the dignity of individuals. For instance, the right to education ensures that every child has the opportunity to develop their full potential and lead a dignified life.
5. Accountability and Justice: Human rights serve as a means of holding governments and individuals accountable for their actions. They provide a framework for seeking justice and redress in cases where rights have been violated. This accountability is crucial for upholding human dignity, as it ensures that individuals are protected from abuse and mistreatment. For example, human rights mechanisms such as courts or tribunals allow victims of human rights violations to seek justice and hold perpetrators accountable.
Human rights are indispensable in upholding human dignity. They provide a legal and moral framework that recognizes and protects the inherent worth of every individual. By promoting equality, freedom, access to basic needs, and accountability, human rights ensure that individuals can live with dignity and respect. Upholding human rights is not only a moral imperative but also a necessary condition for creating a just and equitable society.

The Role of Human Rights in Upholding Human Dignity - Human dignity: Renounceable Rights and Human Dignity: A Moral Imperative
50. The Role of Human Factors in Design and Ergonomics
Human factors are an essential element in the design of products and systems for human use. Human factors refer to the psychological, social, and physical characteristics of humans that influence their interactions with products, systems, and environments. The role of human factors in design and ergonomics is crucial in developing products that are user-friendly, efficient, and safe. Human factors engineering involves designing products, systems, and environments that are safe, efficient, and effective for human use. It is an interdisciplinary field that draws on various disciplines such as psychology, engineering, and ergonomics to ensure that products are designed with the user in mind.
Here are some points that highlight the role of human factors in design and ergonomics:
1. human-Centered design: Human factors play a critical role in human-centered design, a design approach that focuses on the needs, wants, and limitations of end-users. By understanding the needs and limitations of users, designers can create products that are more effective, efficient, and satisfying to use. For example, a smartphone's user interface is designed with human factors in mind, such as the size of the buttons and the placement of the functions, to make it easier and more intuitive to use.
2. Usability: Human factors are essential in ensuring product usability. Usability refers to the ease of use and learnability of a product. Designers use human factors principles to create products that are easy to learn and use. For example, a car's dashboard is designed with human factors in mind, such as the placement of the speedometer and the visibility of the warning lights, to make it easy for the driver to monitor the car's performance.
3. Safety: Human factors play a crucial role in ensuring product safety. Designers use human factors principles to identify potential hazards and to develop products that are safe for use. For example, the design of a medical device is crucial to ensure that it is safe and effective in its use. The design should take into account the user's physical abilities, visual acuity, and cognitive abilities to minimize the risk of injury or harm.
4. Ergonomics: Human factors engineering is also known as ergonomics, which is the science of designing products, systems, and environments to fit the needs and capabilities of the user. Ergonomics principles are used to design products that minimize physical effort, reduce fatigue, and prevent injury. For example, ergonomic keyboards are designed to reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries by reducing the strain on the user's wrists and hands.
The role of human factors in design and ergonomics is crucial in developing products that are user-friendly, efficient, and safe. By understanding the needs, wants, and limitations of end-users, designers can create products that are more effective, efficient, and satisfying to use. Human factors engineering is an interdisciplinary field that draws on various disciplines such as psychology, engineering, and ergonomics to ensure that products are designed with the user in mind.
The Role of Human Factors in Design and Ergonomics - Human Factors: Examining the Hawthorne Effect in Design and Ergonomics
51. Understanding the Role of Human Resources in Your Business Plan
As a business owner, you may be wondering what role human resources (HR) plays in your business plan. Some may argue that HR is simply a support function, while others view it as a strategic partner that can help drive business success. Regardless of where you stand, it's important to understand the value of HR and the impact it can have on your business.
Here are some key insights to help you understand the role of human resources in your business plan:
1. Recruitment and Retention: HR plays a critical role in attracting and retaining top talent. This involves developing job descriptions, sourcing candidates, conducting interviews, and negotiating salaries and benefits. Effective HR practices can help ensure that you have the right people in the right roles, which can lead to increased productivity and profitability.
2. Training and Development: HR is responsible for building a strong learning culture within the organization. This involves developing training programs, providing coaching and mentoring, and creating opportunities for career growth. By investing in employee development, you can increase employee engagement and job satisfaction, which can lead to a more motivated and productive workforce.
3. compliance and Risk management: HR is responsible for ensuring that the organization is in compliance with employment laws and regulations. This includes managing employee records, ensuring workplace safety, and handling legal disputes. Effective HR practices can help minimize legal risks and protect the organization from potential lawsuits.
4. Culture and Employee Engagement: HR plays a key role in creating a positive workplace culture and fostering employee engagement. This involves developing policies and practices that support diversity and inclusion, recognizing and rewarding employee achievements, and creating a supportive work environment. By prioritizing employee well-being, you can improve morale and build a strong sense of community within the organization.
In summary, HR is a critical function that can have a significant impact on your business. By understanding the role of HR and investing in effective HR practices, you can attract and retain top talent, develop a strong learning culture, minimize legal risks, and create a positive workplace culture.

Understanding the Role of Human Resources in Your Business Plan - Human Resources: Nurturing Talent: Human Resources in Your Business Plan