Projects
At SenticNet, we are working on several projects spanning from fundamental affective computing research to the application of sentiment analysis techniques to domains like finance, healthcare, and the arts. Each project leverages the specific expertise of one or more members of the Sentic Team but, in fact, all projects are highly interdependent and interconnected with each other. We currently have seven main projects:
• AI FOR BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
• AI FOR SOCIAL MEDIA MONITORING
• AI FOR EDUCATION
• AI FOR SOCIAL GOOD
• AI FOR HEALTHCARE
• AI FOR ONLINE SAFETY
• AI FOR THE ARTS
AI FOR BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
One of the prime applications of sentiment analysis is business intelligence. We apply AI for enhancing decision-making in contexts such as brand positioning and social media marketing. The evolution of the Web from a read-only to a read-write entity made users more enthusiastic about interacting and collaborating through social networks, blogs, wikis and other on-line collaborative media. We use sentic computing to extract sentiment information from such data. Not only textual data but also visual data, by means of image sentiment analysis, and social network data, by means of community embeddings.
We also explore how the ensemble application of sentiment analysis and user modeling can be exploited to create better recommendation systems. In particular, we use deep neural networks to better learn both user and item representations and make these close to binary codes such that the quantization loss is minimized. In addition, we extend the proposed framework for out-of-sample cases, i.e., dealing with new users, new items, and new ratings.
AI FOR SOCIAL MEDIA MONITORING
We employ AI for monitoring public opinions about different topics in social media, e.g., for political forecasting, climate change, but also national and international issues. For example, the project One Belt, One Road, One Sentiment? collects and analyzes the reactions of the different countries involved in the New Silk Road initiative in real time. Many economies, in fact, are affected by the initiative, which has been welcomed by some countries but contrasted by some others, e.g., the supporters of trading arrangements such as the Trans-Pacific Partnership and the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership.
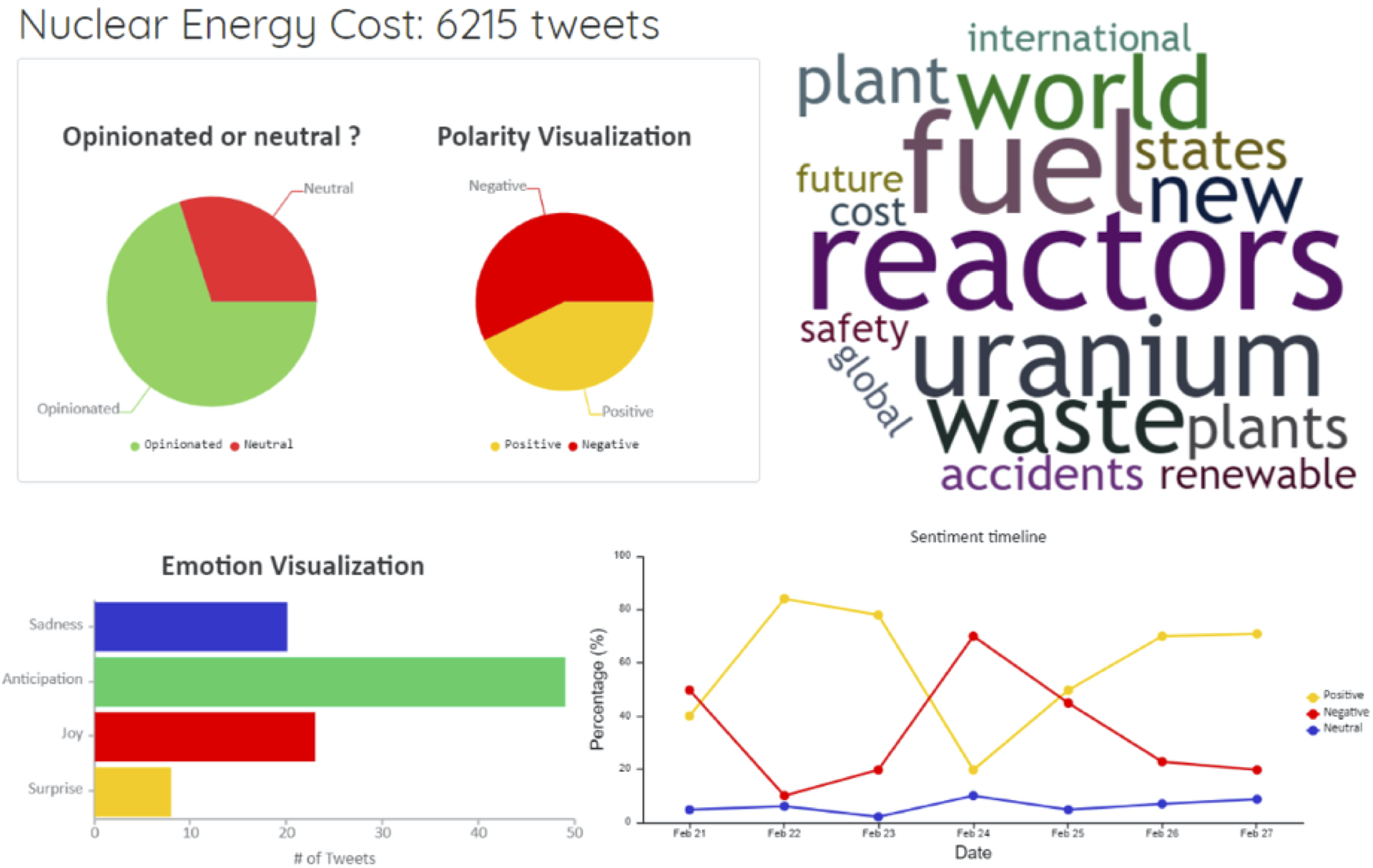
Another similar initiative in this context is PONdER (Public Opinion of Nuclear Energy), a project in collaboration with NTU WKWSCI that aims to collect, aggregate, and analyze opinions towards nuclear energy across South-East Asia. Understanding how the public perceives nuclear energy in the region enables policymakers to make informed national policies and decisions pertaining to nuclear energy, as well as shape communication strategies to inform the public about nuclear energy.
AI FOR EDUCATION
AI algorithms can analyze student data and behaviors to create personalized learning pathways tailored to each student's needs, preferences, and learning styles. This individualized approach helps detect learning engagement and, hence, optimize learning outcomes. AI-powered adaptive learning platforms adjust the difficulty level and content of educational materials in real-time based on students' performance and progress. This enables students to learn at their own pace and receive targeted support when needed.
AI-driven tutoring systems provide students with interactive, personalized tutoring and feedback, simulating one-on-one instruction. These systems can adapt to students' strengths and weaknesses, providing additional support in challenging areas.
AI FOR SOCIAL GOOD
Artificial intelligence is a powerful tool that is neither good or bad: it depends on how we use it. We strive to employ AI for social good. One early project was about using sentiment analysis to automatically detect and block malicious content from online conversations. Recently, we are also using sentic computing to fight online discrimination, sexual harassment and comment toxicity. Due to the social stigma attached to gender-based violence, victims rarely come forward. Implementing policy measures to prevent sexual violence get constrained due to lack of crime statistics. However, the recent outcry on Twitter allows us to study and address this concern. Preliminary findings show that sexual assaults by a family member at home are more frequent than harassments by strangers in a public place.
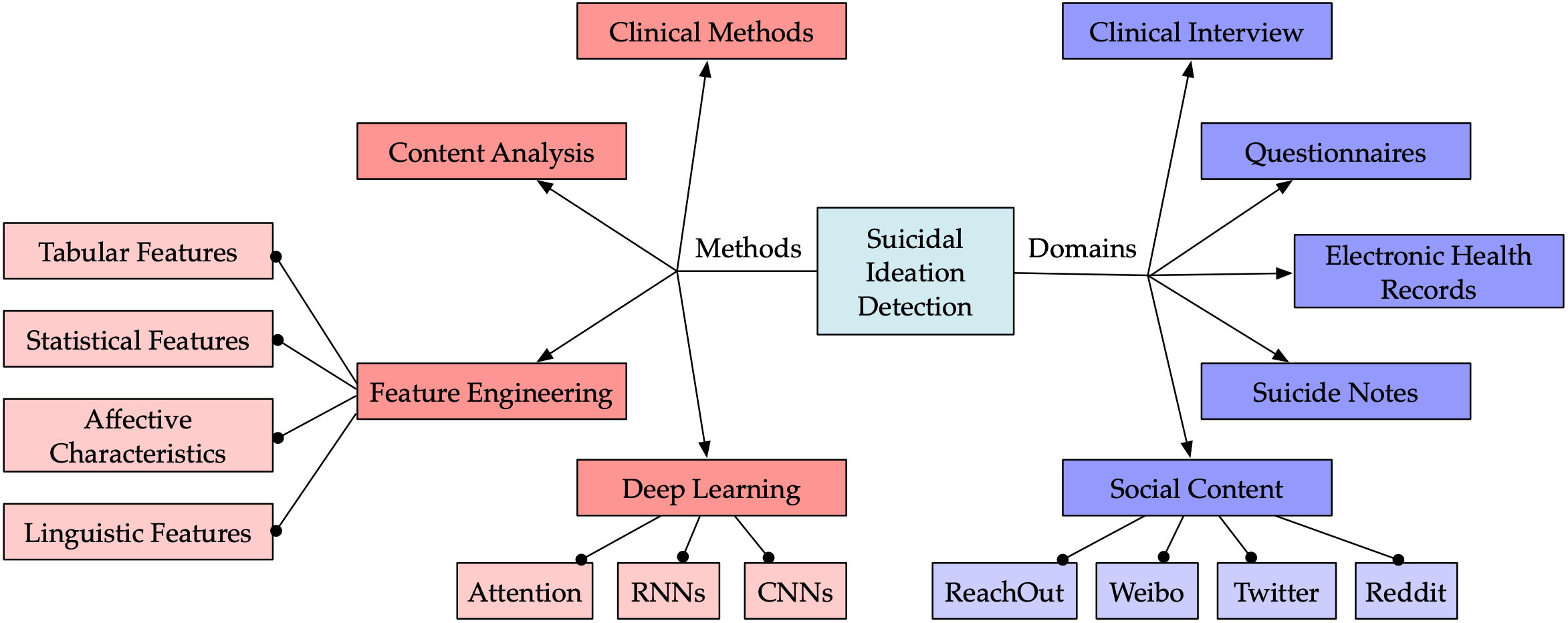
We also utilize advanced AI methodologies to tackle emerging challenges in our rapidly evolving society, which are intricately interwoven with the multifaceted nature of modern life. These challenges encompass a diverse array of issues, including the detection of stress, the influence of religion, and the pervasive effects of societal stigma.
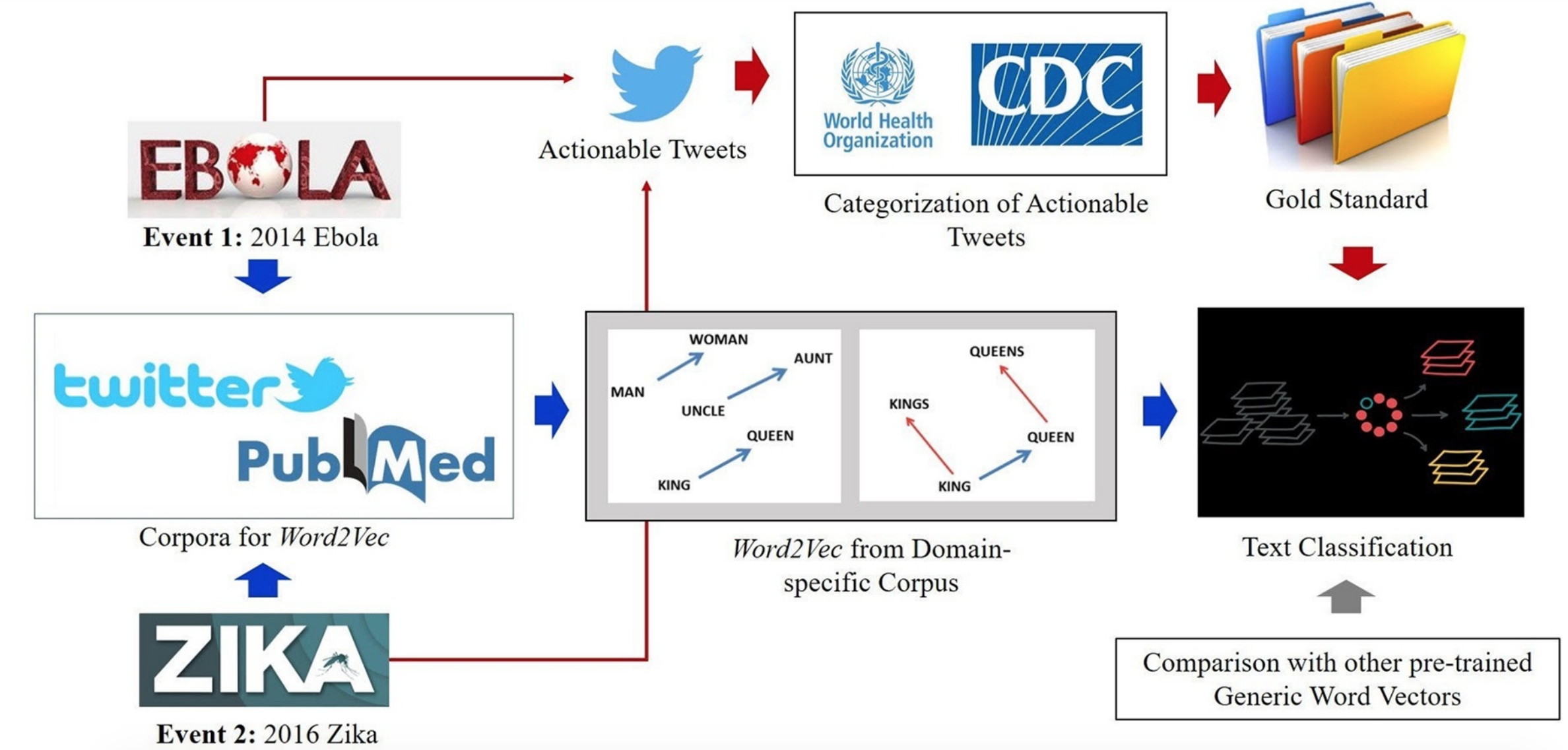
AI FOR HEALTHCARE
We are developing intelligent monitoring tools, e.g., Sentic PROMs, to be used alongside automated systems for medical code prediction. We also explore how sentiment analysis can extract actionable real-time information from social media for outbreak management. Additionally, we also investigate how the application of sentiment analysis in the bio-medical domain can enhance healthcare by mining unstructured medical data from text and converting it into structured machine-processable data.
We also use AI for mental healthcare, e.g., for early detection of emotion-related mental disorders, with particular focus on depression and suicidal ideation detection. Finally, we make our tools as transparent as possible by leveraging explainable AI models that enable clinicians and medical doctors to better understand and intepret the results of such tools.
AI FOR ONLINE SAFETY
AI plays a critical role in enhancing online safety across various aspects of digital interactions. One significant application lies in content moderation, where AI algorithms automatically identify and filter out harmful content like hate speech, violence, and explicit material from online platforms. Moreover, AI systems can detect instances of cyberbullying and discrimination by analyzing digital content, facilitating timely intervention and support for victims.
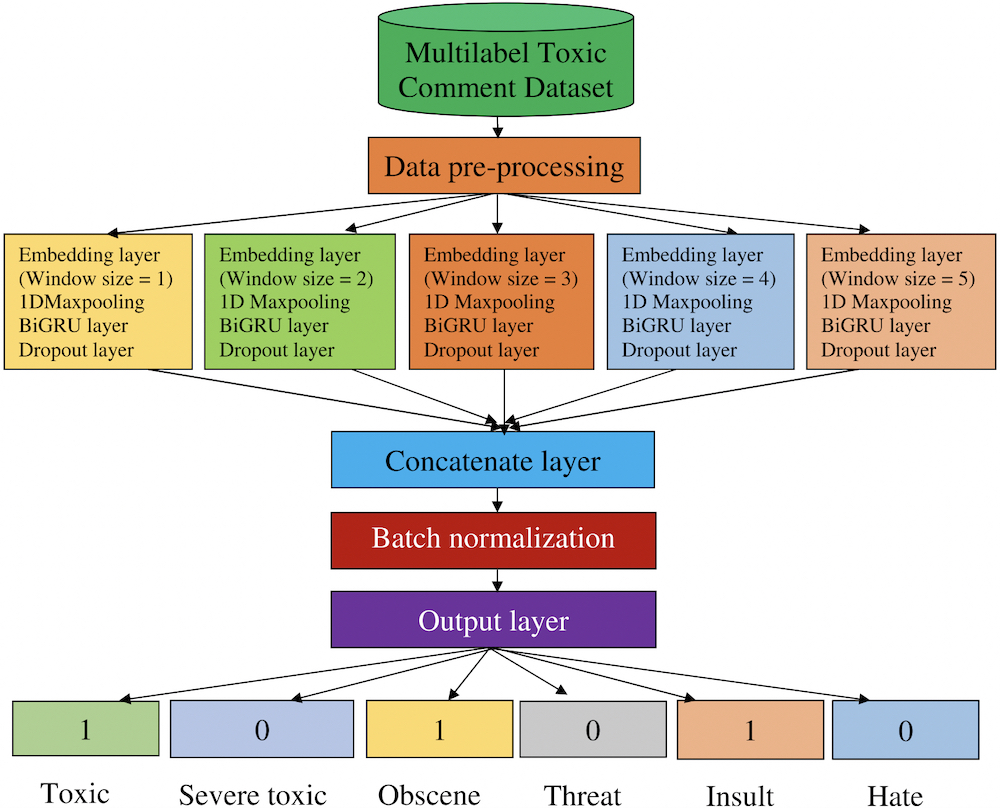
AI algorithms also contribute to the detection of fake reviews and misinformation by analyzing news articles and online content, assisting users in distinguishing credible sources from unreliable ones. Furthermore, AI-powered systems monitor online gaming platforms for inappropriate behavior, harassment, and trolling, ensuring a safer and more enjoyable gaming experience for players.
AI FOR THE ARTS
We have several on-going collaborations with NTU ADM to promote the use of computer science for the arts but also the use of artistic devices for improving data visualization and understanding in the context of information extraction. One of such projects is about performing sentiment analysis of cultural monuments. Another project is Mood of the Planet, an installation that visualizes the emotions expressed on Twitter in real time. Social media data are collected and processed by SenticNet technologies and visualized according to the emotion-color mapping of the Hourglass of Emotions.

The results of such mapping are displayed through an interactive sculpture, a dynamic architectural installation that has as its center-piece a large ‘arch’ or ‘doorway’ that emits colored light and animates in reflection of the live emotions expressed by people around the world via Twitter. This ‘doorway’ is reflected within a wall-mirrored room where it is repeated into a tunnel-like shape, an infinity of doorways that exist as an endless cycle, or echo, of past and future in space and time, and collapsing into the eternal present. A wooden pathway traverses the room through the doorway, and connects the two mirrored walls and thus creates the ‘infinite’ pathway for the audience to walk upon.





