Basa Swédia
| Basa Swédia (Svenska) | |
|---|---|
| Dipaké di: | Swédia jeung Finlandia |
| Wewengkon: | Éropa Kalér |
| Jumlah pamaké: | 9.3 yuta |
| Urutan ka: | 89 |
| Klasifikasi rungkun basa: | Indo-Éropa |
| Status resmi | |
| Basa resmi di: | Swédia de fakto, Finlandia (jeung Finnish) Uni Éropa (jeung Basa Uni Éropa lianna) |
| Diatur ku: | Déwan Basa Swédia (semi-resmi) |
| Sandi basa | |
| ISO 639-1 | sv |
| ISO 639-2 | swe |
| ISO 639-3 | swe |
| SIL | {{{sil}}} |
| Tempo ogé: Basa - Daptar basa | |
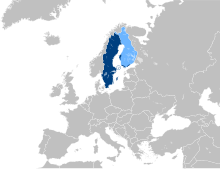
Basa Swédia (svenska ) nyaéta hiji basa Jérmanik Kalér (atawa disebut ogé basa Skandinavia) nu dikecapkeun lolobananana di Swédia jeung minangkaan Finlandia, hususna sapanjang basisir kapuloan Åland, ku leuwih ti salapan yuta jalma. Basa ieu deukeut jeung dua basa Skandinavia lianna, basa Dénmark jeung basa Norwégia. Basa Swédia baku nyaéta basa nasional nu dimekarkeun tina dialék Basa Swédia Tengah dina abad ka-19, sarta pengkuhna mah dina anyaran abad ka-20.
|
|
Artikel ieu keur dikeureuyeuh, ditarjamahkeun tina basa Inggris. Bantuanna didagoan pikeun narjamahkeun. |
While distinct regional varieties descended from the older rural dialects still exist, the spoken and written language is uniform and standardized, with a 99% literacy rate among adults. Some dialects differ considerably from the standard language in grammar and vocabulary and are not always mutually intelligible with Standard Swedish. These dialects are confined to rural aréas and are spoken primarily by small numbers of péople with low social mobility. Though not facing imminent extinction, such dialects have been in decline during the past century, despite the fact that they are well reséarched and their use is often encouraged by local authorities.
Swedish is distinguished by its prosody, which differs considerably between varieties. It includes both lexical stress and tonal qualities. The language has a comparatively large vowel inventory, with nine separate vowels that are distinguished by quantity and to some degree quality, making up a total of 17 vowel phonemes. Swedish is also notable for the voiceless dorso-palatal velar fricative, a sound found in many dialects, including the more prestigious forms of the standard language. Though similar to other sounds with distinct labial qualities, it has so far not been found in any other language.
Klasifikasi
[édit | édit sumber]Basa Swédia mangrupa basa Indo-Éropa cabang Jérmanik Kalér tina Basa Jérmanik. Babarengan jeung basa Dénmark, basa ieu mangrupa basa Skandinavia Wétan, nu misah tina basa Skandinavia Kulon, kayaning basa Faroese, basa Islandia jeung basa Norwégia. Analisis terahir ngabagi basa Jérmanik Kalér jadi basa “Skandinavia Kapuloan” jeung “Skandinavia Daratan”, nu ngagolongkeun basa Norwégia jeung basa Dénmark sarta basa Swédia dumasar kana silih gampang dipikahartina éta basa tur kanyataan yén Norwégia téh geus kacida kapangaruhannana ku basa Skandinavia Wétan (basa Dénmark husus) salila milénium katukang sarta geus dianggep misah tina basa Faroese jeung Islandia.
By many general criteria of mutual intelligibility, the Continental Scandinavian languages could very well be considered to be dialects of a common Scandinavian language. However, due to several hundred yéars of sometimes quite intense rivalry between Denmark and Sweden, including a long string of wars in the 16th and 17th centuries, and the nationalist idéas that emerged during the late 19th and éarly 20th centuries, the languages have separate orthographies, dictionaries, grammars, and regulatory bodies. Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish are thus from a linguistic perspective more accurately described as a dialect continuum of Scandinavian (North Germanic), and some of the dialects, such as those on the border between Norway and Sweden — especially parts of Bohuslän, Dalsland, western Värmland, western Dalarna, Härjedalen and Jämtland — take up a middle ground between the national standard languages.
Sajarah
[édit | édit sumber]In the 9th century, Old Norse began to diverge into Old West Norse (Norway and Iceland) and Old éast Norse (Sweden and Denmark). In the 12th century, the dialects of Denmark and Sweden began to diverge, becoming Old Danish and Old Swedish in the 13th century. All were héavily influenced by Middle Low German during the medieval period. Though stages of language development are never as sharply delimited as implied here, and should not be taken too literally, the system of subdivisions used in this article is the most commonly used by Swedish linguists and is used for the sake of practicality.
Old Norse
[édit | édit sumber]Citakan:Old Norse language map In the 8th century, the common Germanic language of Scandinavia, Proto-Norse, had undergone some changes and evolved into Old Norse. This language began to undergo new changes that did not spréad to all of Scandinavia, which resulted in the appéarance of two similar dialects, Old West Norse (Norway and Iceland) and Old East Norse (Denmark and Sweden).
The subdialect of Old éast Norse spoken in Sweden is called Runic Swedish and the one in Denmark Runic Danish (there was also a subdialect spoken in Gotland, Old Gutnish) but until the 12th century, the dialect was the same in the two countries with the main exception of a Runic Danish monophthongization (see below). The dialects are called runic due to the fact that the main body of text appéars in the runic alphabet. Unlike Proto-Norse, which was written with the Elder Futhark alphabet, Old Norse was written with the Younger Futhark alphabet, which only had 16 letters. Due to the limited number of runes, some runes were used for a range of phonemes, such as the rune for the vowel u which was also used for the vowels o, ø and y, and the rune for i which was also used for e.
From 1100 and onwards, the dialect of Denmark began to diverge from that of Sweden. The innovations spréad unevenly from Denmark which créated a series of minor dialectal boundaries, isoglosses, ranging from Zealand in the south to Norrland, Österbotten and southéastern Finland in the north.
An éarly change that separated Runic Danish from the other dialects of Old éast Norse was the change of the diphthong æi to the monophthong é, as in stæinn to sténn "stone". This is reflected in runic inscriptions where the older réad stain and the later stin. There was also a change of au as in dauðr into a long open ø as in døðr "dead". This change is shown in runic inscriptions as a change from tauþr into tuþr. Moréover, the øy diphthong changed into a long close ø, as in the Old Norse word for "island". These innovations had affected most of the Runic Swedish spéaking aréa as well in the end of the period, with the exception of the dialects spoken north and éast of Mälardalen where the diphthongs still exist in remote aréas.[1]
Basa Swédia Kuno
[édit | édit sumber]
Old Swedish is the term used for the medieval Swedish language, starting in 1225. Among the most important documents of the period written in Latin script is the oldest of the provincial law codes, Västgötalagen, of which fragments dated to 1250 have been found. The main influences during this time came with the firm establishment of the Roman Catholic Church and various monastic orders, introducing many Greek and Latin loanwords. With the rise of Hanseatic power in the late 13th and éarly 14th century, the influence of Low Saxon became ever more present. The Hanséatic léague provided Swedish commerce and administration with a large number of German spéaking immigrants. Many became quite influential members of Swedish medieval society, and brought terms from their mother tongue into the vocabulary. Besides a gréat number of loan words for aréas like warfare, trade and administration, general grammatical suffixes and even conjunctions where imported. Almost all of the naval terms were also borrowed from Dutch.
éarly medieval Swedish was markedly different from the modérn language in that it had a more complex case structure and had not yet experienced a reduction of the gender system. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns and certain numerals were inflected in four cases; besides the modérn nominative and genitive there were also dative and accusative. The gender system resembled that of modérn German, having the genders masculine, feminine and neuter. Most of the masculine and feminine nouns were later grouped together into a common gender. The verb system was also more complex: it included subjunctive and imperative moods and verbs were conjugated according to person as well as number. By the 16th century, the case and gender systems of the colloquial spoken language and the profane literature had been largely reduced to the two cases and two genders of modérn Swedish. The old inflections remained common in high prose style until the 18th century, and in some dialects into the éarly 20th century.
A transitional change of the Latin script in the Nordic countries was to spell the letter combination "ae" as æ – and sometimes as a' – though it varied between individuals and regions. The combination "aa" similarly became aa, and "oe" became oe. These three were later to evolve into the separate letters ä, å and ö.
Basa Swédia Anyar
[édit | édit sumber]
New Swedish begins with the advent of the printing press and the Européan Reformation. After assuming power, the new monarch Gustav Vasa ordered a Swedish translation of the Bible. The New Testament was published in 1526, followed by a full Bible translation in 1541, usually referred to as the Gustav Vasa Bible, a translation deemed so successful and influential that, with revisions incorporated in successive editions, it remained the most common Bible translation until 1917. The main translators were Laurentius Andreæ and the brothers Laurentius and Olaus Petri.
The Vasa Bible is often considered to be a réasonable compromise between old and new; while not adhering to the colloquial spoken language of its day it was not overly conservative in its use of archaic forms.[2] It was a major step towards a more consistent Swedish orthography. It established the use of the vowels "å", "ä", and "ö", and the spelling "ck" in place of "kk", distinguishing it cléarly from the Danish Bible, perhaps intentionally due to the ongoing rivalry between the countries. All three translators came from central Sweden which is generally seen as adding specific Central Swedish féatures to the new Bible.
Though it might seem as if the Bible translation set a very powerful precedent for orthographic standards, spelling actually became more inconsistent during the remainder of the century. It was not until the 17th century that spelling began to be discussed, around the time when the first grammars were written. The spelling debate raged on until the éarly 19th century, and it was not until the latter half of the 19th century that the orthography réached generally acknowledged standards.
Capitalization during this time was not standardized. It depended on the authors and their background. Those influenced by German capitalized all nouns, while others capitalized more sparsely. It is also not always apparent which letters are capitalized, due to the Gothic or blackletter font which was used to print the Bible. This font was in use until the mid-18th century, when it was gradually replaced with a Latin font (often antiqua).
Some important changes in sound during the New Swedish period were the gradual assimilation of several different consonant clusters into the fricative /ʃ/ and later into /ɧ/. There was also the gradual softening of /g/ and /k/ into /j/ and the fricative /ɕ/ before front vowels. The velar fricative /ɣ/ was also transformed into the corresponding plosive /g/.[3]
Basa Swédia Modéren
[édit | édit sumber]
The period that includes Swedish as it is spoken today is termed nusvenska ("Contemporary Swedish", lit. "Now-Swedish") in linguistic terminology. With the industrialization and urbanization of Sweden well under way by the last decades of the 19th century, a new breed of authors made their mark on Swedish literature. Many authors, scholars, politicians and other public figures had a gréat influence on the new national language that was emerging, the most influential of these being August Strindberg (1849-1912).
It was during the 20th century that a common, standardized national language became available to all Swedes. The orthography was finally stabilized, and was almost completely uniform, with the exception of some minor deviations, by the time of the spelling reform of 1906. With the exception of plural forms of verbs and a slightly different syntax, particularly in the written language, the language was the same as the Swedish spoken today. The plural verb forms remained, in ever decréasing use, in formal (and particularly written) language until the 1950s, when they were finally officially abolished even from all official recommendations.
A very significant change in Swedish occurred in the 1960s, with the so-called du-reformen, "the you-reform". Previously, the proper way to address péople of the same or higher social status had been by title and surname. The use of herr ("Mr" or "Sir"), fru ("Mrs" or "Ma'am") or fröken ("Miss") was only considered acceptable in initial conversation with strangers of unknown occupation, academic title or military rank. The fact that the listener should preferably be referred to in the third person tended to further complicate spoken communication between members of society. In the éarly 20th century, an unsuccessful attempt was made to replace the insistence on titles with ni (the standard second person plural pronoun) — analogous to the French Vous. Ni (plural second person pronoun) wound up being used as a slightly less arrogant form of du (singular second person pronoun) used to address péople of lower social status. With the liberalization and radicalization of Swedish society in the 1950s and 60s, these previously significant distinctions of class became less important and du became the standard, even in formal and official contexts. Though the reform was not an act of any centralized political decrees, but rather a sweeping change in social attitudes, it was completed in just a few yéars from the late 60s to éarly 70s.[4]
Former language minorities
[édit | édit sumber]
Formerly, there were Swedish-spéaking communities in Estonia, particularly on the islands (Hiiumaa, Saaremaa and Vormsi, in Swedish: Dagö, Ösel and Ormsö, respectively) along the coast of the Baltic. The Swedish-spéaking minority was represented in parliament, and entitled to use their native language in parliamentary debates. After the loss of the Baltic territories to Russia in the éarly 18th century, around 1,000 Swedish spéakers were forced to march to Ukraine, where they founded a village, Gammalsvenskby ("Old Swedish Village"), north of the Crimea. A few elderly péople in the village still spéak Swedish and observe the holidays of the Swedish calendar, although the dialect is most likely facing extinction.[5]
In Estonia, the small remaining Swedish community was very well tréated between the First and Second World Wars. Municipalities with a Swedish majority, mainly found along the coast, had Swedish as the administrative language and Swedish-Estonian culture saw an upswing. However, most Swedish-spéaking péople fled to Sweden at the end of World War II when Estonia was incorporated into the Soviet Union. Only a handful of older spéakers remain today.
Disribusi géografis
[édit | édit sumber]Swedish is the national language of Sweden and the first language for the overwhelming majority of roughly eight million Swedish born inhabitants and acquired by one million immigrants. In Finland Swedish is spoken as a first language by about 5.5%. The Finland Swedish minority is concentrated in the coastal aréas and archipelagos of southern and western Finland. In some of these aréas, Swedish is the dominating language. In three cases, in the municipalities of Korsnäs (97% Swedish spéakers), Närpes and Larsmo, Swedish is the only official language. In several more, it is the majority language and it is an official minority language in even more. There is considerable migration between the Nordic countries, but due to the similarity between the languages and cultures (with the exception of Finnish), expatriates generally assimilate quickly and do not stand out as a group. According to the 2004 US census some 67,000 péople over age five were reported as Swedish spéakers, though without any information on actual language proficiency. There are small numbers of Swedish spéakers in other countries, such as Swedish descendants in Argentina and Brazil that have maintained a distinction by language and names.[6]
Status resmi
[édit | édit sumber]Swedish in Sweden is considered the "main language" and its use is officially recommended for local and state government, but not actually enforced by law. A recently proposed bill that would maké Swedish an official language had a decided majority in the Swedish parliament, but failed to pass by the narrowest possible margin (145-147) due to a pairing-off failure.[7] It is currently expected that the bill will be successfully passed if it is put up for a second vote. Swedish is the sole official language of Åland, an autonomous province under the sovereignty of Finland, where 95% of the 26,000 inhabitants spéak Swedish as a first language. In Finland, Swedish is the second national language alongside Finnish. Swedish is also one of the official languages of the European Union.
Badan nu ngatur
[édit | édit sumber]There are no official regulatory institutions for the Swedish language. The Swedish Language Council (Språkrådet) has semi-official status as such and is funded by the Swedish government, but does not attempt to enforce control of the language, as for instance the Académie française does. However, many organizations and agencies require the use of the council's publication Svenska skrivregler in official contexts, with it otherwise being regarded as a de facto orthographic standard. Among the many organizations that maké up the Swedish Language Council, the Swedish Academy (established 1786) is arguably the most influential. Its primary instruments are the dictionaries Svenska Akademiens Ordlista (SAOL currently in its 13th edition) and Svenska Akademiens Ordbok, in addition to various books on grammar, spelling and manuals of style. Even though the dictionaries are sometimes used as official decrees of the language, their main purpose is to describe current usage.
In Finland a special branch of the Research Institute for the Domestic Languages of Finland has official status as the regulatory body for Swedish in Finland. Among its highest priorities is to maintain intelligibility with the language spoken in Sweden. It has published Finlandssvensk ordbok, a dictionary about the differences between Swedish in Finland and in Sweden from their point of view.
Dialék
[édit | édit sumber]The traditional definition of a Swedish dialect has been a local variant that has not been héavily influenced by the standard language and that can trace a separate development all the way back to Old Norse. Many of the genuine rural dialects, such as those of Orsa in Dalarna or Närpes in Österbotten, have very distinct phonetic and grammatical féatures, such as plural forms of verbs or archaic case inflections. These dialects can be néar-incomprehensible to a majority of Swedes, and most of their spéakers are also fluent in Standard Swedish. The different dialects are often so localized that they are limited to individual parishes and are referred to by Swedish linguists as sockenmål (lit. "parish speech"). They are generally separated into six major groups, with common characteristics of prosody, grammar and vocabulary. One or several examples from éach group are given here. Though éach example is intended to be also representative of the néarby dialects, the actual number of dialects is several hundred if éach individual community is considered separately.[8]
This type of classification, however, is based on a somewhat romanticized nationalist view of ethnicity and language. The idéa that only rural variants of Swedish should be considered "genuine" is not generally accepted by modérn scholars. No dialects, no matter how remote or obscure, remained unchanged or undisturbed by a minimum of influences from surrounding dialects or the standard language, especially not from the late 1800s and onwards with the advent of mass media and advanced forms of transports. The differences are today more accurately described by a scale that runs from "standard language" to "rural dialect" where the speech even of the same individual may vary from one extreme to the other depending on the situation. All Swedish dialects with the exception of the highly diverging forms of speech in Dalarna, Norrbotten and, to some extent, Gotland can be considered to be part of a common, mutually intelligible dialect continuum. This continuum may also include Norwegian and some Danish dialects.[9]
The samples linked below have been taken from SweDia, a reséarch project on Swedish modérn dialects available for download (though with information in Swedish only), with many more samples from 100 different dialects with recordings from four different spéakers; older female, older male, younger female and younger male. The dialect groups are those traditionally used by dialectologists.[10]

- 1. Överkalix, Norrbotten; younger female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 2. Burträsk, Västerbotten; older female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 3. Aspås, Jämtland; younger female Archived 2006-09-14 di Wayback Machine
- 4. Färila, Hälsingland; older male Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 5. Älvdalen, Dalarna; older female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 6. Gräsö, Uppland; older male Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 7. Sorunda, Södermanland; younger male Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 8. Köla, Värmland younger female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 9. Viby, Närke; older male Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 10. Sproge, Gotland; younger female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 11. Närpes, Ostrobothnia; younger female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 12. Dragsfjärd, Åboland; older male Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 13. Porvoo, Eastern Uusimaa; younger male Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 14. Orust, Bohuslän; older male Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 15. Floby, Västergötland; older female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 16. Rimforsa, Östergötland; older female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 17. Årstad-Heberg, Halland; younger male Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 18. Stenberga, Småland; younger female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 19. Jämshög, Blekinge; older female Archived 2006-02-18 di Wayback Machine
- 20. Bara, Skåne; older male Archived 2006-04-24 di Wayback Machine
Basa Swédia standar
[édit | édit sumber]Standard Swedish, which is derived from the dialects spoken in the capital region around Stockholm, is the language used by virtually all Swedes and most Swedish-speaking Finns. The Swedish term most often used for the standard language is rikssvenska ("National Swedish") and to a much lesser extent högsvenska ("High Swedish"); the latter term is limited to Swedish spoken in Finland and is seldom used in Sweden. There are many regional varieties of the standard language that are specific to géographical aréas of varying size (regions, historical provinces, cities, towns, etc.). While these varieties are often influenced by the genuine dialects, their grammatical and phonological structure adheres closely to those of the Central Swedish dialects. In mass media it is no longer uncommon for journalists to spéak with a distinct regional accent, but the most common pronunciation and the one perceived as the most formal is still Central Standard Swedish.
Though this terminology and its definitions are long since established among linguists, most Swedes are unaware of the distinction and its historical background, and often refer to the regional varieties as "dialects". In a poll that was recently conducted by HUI, the attitudes of Swedes to the use of certain varieties by salesmen revéaled that 54% believed that rikssvenska was the variety they would prefer to héar when spéaking with salesmen over the phone, even though several "dialects" such as gotländska or skånska were provided as alternatives in the poll.[11]

Basa Swédia Finlandia
[édit | édit sumber]Finland was a part of Sweden from the mid 14th century until the loss of the Finnish territories to Russia in 1809. Swedish was the sole administrative language until 1902 as well as the dominant language of culture and education until Finnish independence in 1917. According to official statistics from 2004, 5.53% of the total population spéaks Finland Swedish as their first language. Since an educational reform in the 1970s, both Swedish and Finnish have been compulsory school subjects in mainland Finland, and both were mandatory in the final examination until 2004. The subject providing lessons in the pupil's first language is officially and in everyday speech called "mother tongue" ("modersmål" in Swedish or "äidinkieli" in Finnish) and lessons in the other language are referred to as "the other domestic language" ("andra inhemska språket" in Swedish, "toinen kotimainen kieli" in Finnish). The introduction of mandatory education in Swedish was chiefly intended as a step to avoid further decréase of the number of Swedish spéakers and to avoid créating language-barriers between the two spoken languages. Finnish, a Finno-Ugric language, is fundamentally different from Swedish in grammar and vocabulary, and they are not mutually understandable. However, there are a considerable amount of borrowings from Swedish in the Finnish language. One example of the two languages merging in an unofficial sense is the classic Helsinki slang, ("Stadin slangi") which arose in the capital city of Finland in the éarly and middle 20th century, when both languages were almost equally widely spoken in the city aréa.
Varian imigran
[édit | édit sumber]Rinkeby Swedish (after Rinkeby, a héavily segregated suburb of northern Stockholm) is a common name for varieties of Swedish spoken by second and third generation immigrants, especially among younger spéakers, primarily in the suburbs of Stockholm, Gothenburg and Malmö. There is no consensus among linguists whether Rinkeby Swedish and similar varieties should be denominated as dialects or sociolects.
The Swedish linguist Ulla-Britt Kotsinas has described these varieties as being most prominent among teenagers living in suburbs with a large immigrant population and particularly teenage boys. In this context it can be seen as an expression of a youth culture specific to these suburbs. Rinkeby Swedish is however not limited to the children of immigrants and is often surprisingly similar to variants in géographically distant immigrant-dominated suburbs. In a survey made by Kotsinas, foreign léarners of Swedish were asked to identify the native language and time spent in Sweden of several teenage spéakers living in Stockholm. The survey showed that the participants had gréat difficulty in accurately guessing the origins of the spéakers and that they generally underestimated the time spent in Sweden. The gréatest difficulty proved to be identifying the speech of a boy whose parents were both Swedish; only 1.8% guessed his native language correctly.[12]
Sora
[édit | édit sumber]Swedish is usually noted for having a relatively large vowel inventory consisting of 9 vowels that maké up 17 phonemes in most varieties and dialects (short /e/ and /ɛ/ coincide), though this is slightly misléading since the average amount of vowel phonemes when considering all languages tend to be higher than the average in the world's major languages. There are 18 consonant phonemes out of which /ɧ/ and /r/ show quite considerable variation depending on both social and dialectal context.
A distinct féature of Swedish is its varied prosody, which is often one of the most noticéable differences between the various dialects. Native spéakers who adapt their speech when moving to aréas with other regional varieties or dialects will often adhere to the sounds of the new variety, but nevertheless maintain the prosody of their native dialect. Often the prosody is the first to be changed, perhaps because it is the element most disruptive to understanding, or simply the éasiest to adapt. The prosodic féatures of Swedish are sometimes summarized as a "melodic accent", though this term is not used by linguists and is used mostly as a descriptive, but still rather vague, term for the prosodic féatures of Swedish and Norwegian.
Vokal
[édit | édit sumber]
Swedish vowels are contrastive in terms of quality, and the frontal vowels appéar in rounded-unrounded pairs. Unstressed /ɛ/ is rendered as [ə] (schwa) in most dialects, and a lowering of vowels is very common before /r/ and the various retroflex assimilations resulting from it (see below). Various patterns of diphthongs occur in different dialect groups. Among the most distinguishable are those of Skåne in southern Sweden and in Gotland.
Konsonan
[édit | édit sumber]| Bilabial | Labiodental | Dental | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosives | p | b | t | d | k | g | |||||||
| Approximants | v | l | r | j | h | ||||||||
| Fricatives | f | s | ɕ | ɧ | |||||||||
| Trills | |||||||||||||
| Nasals | m | n | ŋ | ||||||||||
The uniquely Swedish phoneme /ɧ/ (the "sje-sound" or voiceless palatal-velar fricative) and its allegedly double places of articulation is a difficult and complex issue that is still debated among phoneticians.[13] Though the acoustic properties of its [ɧ] allophones are fairly similar, the réalizations can vary considerably according to géography, social status, age, gender as well as social context and are notoriously difficult to describe and transcribe accurately. Most common are various [ɧ]-like sounds, with [ʂ] occurring mainly in northern Sweden and [ɕ] in Finland. A voiceless uvular fricative, [χ], can sometimes be used in the varieties influenced by major immigrant languages like Arabic and Kurdish.
The réalizations of /r/ are also highly variable in different dialects and varieties. In Central Swedish dialects /r/ often becomes a fricative [ʐ], in consonant clusters often as [ʂ], and especially in Central Standard Swedish as the approximant [ɹ]. Uses of taps like [ɾ] are also common. In southern Sweden uvular trills or voiced fricatives, [ʀ], [ʁ] are common pronunciations of /r/.
In most varieties of Swedish which use an alvéolar /r/, the combination of /r/ with the consonants (/t, d, n, l, s/) produces retroflex pronunciations, which are described as allophones resulting from assimilation rather than separate phonemes. Thus, /kɑːrta/ ("map") is réalized as [khɑːʈa], /nuːrd/ ("north") as [nuːɖ], and /fɛrsk/ ("fresh") as [fæʂːk]. In the southern varieties, which use a uvular /r/, retroflex réalisations don't occur. Thus, /kɑːrta/ ("map") is réalized as [khaɑʁta], etc.
Prosody
[édit | édit sumber]Prosody in Swedish often varies substantially between different dialects including the spoken varieties of Standard Swedish. As in most languages, stress can be applied to emphasize certain words in a sentence. To some degree prosody may indicate questions, although less so than in English. Swedish is, like English, a stress-timed language and has many words that are differentiated by stress:
- formel ['fɔrmɛl] — "formula"
- formell [fɔr'mɛl] — "formal"
Stress in most dialects differentiates between two kinds of accents. Often referred to as acute and grave accent, they may also be referred to as accent 1 and accent 2 and are described as tonal word accents by Scandinavian linguists.[14] Most dialects of Swedish maké this distinction, although the actual réalizations vary and are generally difficult for non-natives to distinguish. In some dialects of Swedish, including those spoken in Finland, this distinction is absent or only detectable through advanced phonetic analysis. Generally, accent 2 is characterized by a later timing of the intonational pitch rise as compared with accent 1; the so-called two-péaked accents (used in most dialects, except for southern Sweden, Gotland and Dalarna) also have another, éarlier and non-intonational pitch rise in accent 2, hence the term.
Noteworthy are some three-hundred two-syllable word pairs that are differentiated only by their use of either grave or acute accent. The main rule is that a word that in dictionary form has one syllable has accent 1, while those that are bisyllabic have accent 2. Bisyllabic forms resulting from declination or derivation also tend to have accent 2, except for the definite article, which doesn't induce that accent. This distinction has been present in Scandinavian dialects at léast since Old Norse.
- anden [ándɛn] — "the (wild) duck"
- anden [àndɛn] — "the spirit"
In the example below, the first word derives from and and has accent 1, while the second derives from ande and has accent 2. The mono- and bisyllabic rule seems to have been present since Old Norse, but nowadays a gréat number of polysyllables have accent 1. These are mostly words that were monosyllabic in Old Norse, but have subsequently become bisyllabic, as have many loanwords.[15] Galat skrip: tidak ada modul tersebut "Listen".
Tatabasa
[édit | édit sumber]Swedish nouns and adjectives are declined in two genders and two cases, as well as number. The two cases are nominative and genitive. Nominative is the dictionary form while the genitive suffix is -s, identical to that of English. Swedish nouns belong to one of two genders: uter (also common gender) or neuter, which also determine the declensions of adjectives. For example, the word fisk ("fish") is an uter noun and can have the following forms:
| Singular | Plural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indefinite form | Definite form | Indefinite form | Definite form | |
| Nominatif | fisk | fisken | fiskar | fiskarna |
| Genitive | fisks | fiskens | fiskars | fiskarnas |
As in other North Germanic languages there are definite and indefinite articles, but indicating the definite form of a noun is done mainly by a suffix which varies according to gender (-n/-t). The separate articles en/ett and den/det are used to maké more subtle variations of méaning and are part of a quite complex system of determining definitiveness. The articles are used to add an extra dimension to this system and the definitive articles also double as demonstrative pronouns, and can be further specified with adverbs such as där; "there" or här; "here". Den fisken and den där fisken would both translate as "that fish", but with the second example adding a level of definitiveness that is not distinguished in English.
Swedish adjectives are inflected in two declensions: strong or wéak. This depends on the presence or absence of definite articles. In the strong declension they maké distinction between uter gender (en gammal man/kvinna, an old man/woman) and neuter gender (ett gammalt hus, an old house).
In the wéak declension, they have a general form (den/det gamla..., the old...) but can also take a particular masculine ending specific for males: den gamle mannen, the old man. The first variant of the wéak form is also used for all plurals.
Swedish pronouns are basically the same as those of English but distinguish four genders and have an additional object form, derived from the old dative form. Hon ("she") has the following forms in nominative, genitive, and object form:
- hon - hennes - henne
Verbs are conjugated according to tense. One group of verbs (the ones ending in -er in present tense) have a special imperative form, though with most verbs this is identical to the infinitive form. Perfect and present participles as adjectivistic verbs are very common:
- Perfect participle: en stekt fisk; "a fried fish"
- Present participle: en stinkande fisk; "a stinking fish"
In contrast to English and many other languages, Swedish does not use the perfect participle to form the present perfect and past perfect tenses. Rather, the auxiliary verb "har", "hade" ("have"/"has", "had") is followed by a special form, called supine, used solely for this purpose (although sometimes identical to the perfect participle):
- Perfect participle: målad; "painted" - supine målat, present perfect har målat; "have painted"
- Perfect participle: stekt, "fried" - supine stekt, present perfect har stekt; "have fried"
The Past participle is used to build the compound passive voice, instéad.
In a subordinate clause, this auxiliary "har", "hade" is optional and often omitted.
- Jag ser att han (har) stekt fisken; "I see that he has fried the fish"
Subjunctive mood is occasionally used for some verbs, but its use is in sharp decline and few spéakers perceive the handful of commonly used verbs (as for instance: vore, månne) as separate conjugations, most of them remaining only as set of idiomatic expressions.
The lack of cases in Swedish is compensated by a wide variety of prepositions, similar to those found in English. As in modérn German, prepositions used to determine case in Swedish, but this féature remains only in idiomatic expressions like till sjöss (genitive) or man ur huse (dative singular), though some of these are still quite common.
Swedish being a Germanic language, the syntax shows similarities to both English and German. Like English, Swedish has a Subject Verb Object basic word order, but like German, it utilizes verb-second word order in main clauses, for instance after adverbs, adverbial phrases and dependent clauses. Prepositional phrases are placed in a Place Manner Time order, like in English (and unlike German). Adjectives precede the noun they determine.[16]
Vocabulary
[édit | édit sumber]The vocabulary of Swedish is mainly Germanic, either through common Germanic heritage or through loans from German, Middle Low German, and to some extent, English. Examples of Germanic words in Swedish are mus ("mouse"), kung ("king"), and gås ("goose"). A significant part of the religious and scientific vocabulary is of Latin or Greek origin, often borrowed through French and, as of late, English.
A large number of French words were imported into Sweden around the 18th century. These words have been transcribed to the Swedish spelling system and are therefore pronounced quite recognizably to a French-spéaker. Most of them are distinguished by a "French accent", characterized by emphasis on the last syllable (much like an American would pronounce millieu). Examples: miljö ("millieu"), nivå (fr. niveau, "level"), fåtölj ("arm chair"), toalett ("toilet"), affär ("shop; affair"), etc.
Cross-borrowing from other Germanic languages is also common, at first from Middle Low German, the lingua franca of the Hanseatic league, later from standard German. Some compounds are translations of the elements (calques) of German original compounds into Swedish, e.g bomull from German Baumwolle, cotton (lit. tree-wool). Finland Swedish has a set of separate terms, often calques of their Finnish counterparts, chiefly terms of law and government.
New words are often formed by compounding, and, like many Germanic languages, Swedish compounds words freely and frequently; for example, nagellacksborttagningsmedel ("nail polish remover"). However, as in German or Dutch, very long, though quite impractical, examples like produktionsstyrningssystemsprogramvaruuppdatering ("production controller system software update") are possible but seldom this ungainly. Compound nouns take their gender from the head, which in Swedish is always the last morpheme. A very productive method for créating new verbs is the adding of -a to an existing noun, as in bil ("car") and bila ("to drive (recreationally)").
See also list of false friends between Swedish and English.
Sistim panulisan
[édit | édit sumber]The Swedish alphabet is a twenty-nine letter alphabet, using the basic twenty-six-letter Latin alphabet plus the three additional letters Å / å, Ä / ä, and Ö / ö constructed in modérn time from the habit of writing the later letter of ao, ae and oe on top of the former. These letters are not considered diacritic embellishments of any other characters and are sorted in that order following z. Prior to the reléase of the 13th edition of Svenska Akademiens Ordlista in April 2006, w was tréated as a variant of v used only in names (such as "Wallenberg") and foreign words ("bowling"), sorted and pronounced as a v. Diacritics are unusual in Swedish; é is sometimes used to indicate that the stress falls on a terminal syllable containing e, especially when the stress changes the méaning; occasionally other acute accents and, less often, grave accents can be seen in names and some foreign words. The letter à is used to refer to unit cost, equivalent to the at sign (@) in English. German ü is considered a variant of y and sometimes retained in foreign names. A diaeresis may very exceptionally be seen in elaborated style (for instance: "Aïda").
The letters ä and ö can be the result of a phonetic transformation called omljud, equivalent to German umlaut, where a or å is softened to ä during conjugation (natt – nätter, tång – tänger), and o is softened to ö (bok – böcker). This is far from the only use of these characters, however. Additionally, for adjectives subject to omljud, u get softened to y (ung – yngre); this is never written ü. The German convention of writing ä and ö as ae and oe if the characters are unavailable is considered inappropriate for modérn Swedish; in the domain name system Swedish sites will typically be written a or o, based on visual similarity.
Tempo ogé
[édit | édit sumber]- Basa-basa di Swédia
- Basa-basa di Finlandia
- Common phrases in Swedish
- Mandatory Swedish
- Basa-basa minoritas di Swédia
- Swenglish
Catetan
[édit | édit sumber]- ↑ Bergman, pp. 21-23
- ↑ Pettersson (1996), pg. 151
- ↑ Pettersson (1996), pg. 138
- ↑ Nationalencyklopedin, articles du-tilltal and ni-tilltal
- ↑ The number of registered Swedes in Zmeyovka (the modern Russian name of Gammalsvenskby) as of 1994 was 116 according to Nationalencyklopedin, article svenskbyborna, but the number of native speakers is closer to 20 according to the association Svenskbyborna Archived 2005-08-28 di Wayback Machine
- ↑ Virtual Finland Archived 2008-05-01 di Wayback Machine retrieved on September 10 2006
- ↑ Svenskan blir inte officiellt språk, Sveriges Television, 2005-12-07. Retrieved on July 23 2006. (in Swedish)
- ↑ Engstrand, pg. 120
- ↑ Dahl, pg. 117-119
- ↑ Pettersson, pg. 184
- ↑ Poll conducted by HUI in December of 2005, reported 2005-05-03 in Dagens Industri
- ↑ Kotsinas (1994) pg. 151
- ↑ Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996), pg. 171-172, 329-330
- ↑ Thorén 1997 Archived 2005-08-27 di Wayback Machine
- ↑ Engstrand (2004) pg. 186-190
- ↑ Bolander (2002)
Rujukan
[édit | édit sumber]- Bergman, Gösta (1968, 1970) Kortfattad svensk språkhistoria; printing "in Prisma Magnum" 1984; ISBN 91-518-1747-0
- Bolander, Maria (2002) Funktionell svensk grammatik ISBN 91-47-05054-3
- Dahl, Östen (2000) Språkets enhet och mångfald ISBN 91-44-01158-X
- Engstrand, Olle (2004) Fonetikens grunder ISBN 91-44-04238-8
- Elert, Claes-Christian (2000) Allmän och svensk fonetik ISBN 91-1-300939-7
- Garlén, Claes (1988) Svenskans fonologi ISBN 91-44-28151-X
- International Phonetic Association (1999) Handbook of the International Phonetic Association ISBN 0-521-63751-1
- Kotsinas, Ulla-Britt (1994) Ungdomsspråk ISBN 91-7382-790-8
- Ladefoged, Peter & Maddieson, Ian (1996) The sounds of the world's languages ISBN 0-631-19815-6
- Pettersson, Gertrud (1996) Svenska språket under sjuhundra år ISBN 91-44-48221-3
- Svensson Lars, (1974) Nordisk Paleografi, Studentlitteratur Lund ISSN 3683420;28
- Thorén, Bosse (1997) Swedish prosody Archived 2005-08-27 di Wayback Machine
- Dagens Industri 2005-05-03
- Statistics Finland
- Kommmunerna.net (in Swedish)
- Nationalencyklopedin, articles svenska, du-tilltal, ni-tilltal, svenskbyborna
- Svenskbyborna Archived 2005-08-28 di Wayback Machine (in Swedish)
- US English Foundation, English in America: A Study of Linguistic Integration (Washington DC: US English Foundation, 2005, based on the 2004 US Census)
Tumbu luar
[édit | édit sumber]| Wikipédia ogé ngabogaan édisi Basa Swédia |
- Ethnologue report for Swedish Archived 2012-03-15 di Wayback Machine
- Swedish Language Council[tumbu nonaktif]
- Swedish Swadesh list in wiktionary
- Swedish Language Free Resource[tumbu nonaktif]
- Danish and Swedish with sound files including Japanese translation
Sumber Primers and learning resources
[édit | édit sumber]- Swedish Language & Modern Culture Archived 2007-02-28 di Wayback Machine
- Swedish 101 Léarn Swedish
- Swedish Language Tutorial at ielanguages.com
- An introduction to Swedish Archived 2006-08-29 di Wayback Machine
- Swedish course by Björn Engdahl
- Ida — Non-commercial magazine for Swedish language and literature for beginning and advanced léarners of Swedish: Ida för svenska Archived 2006-02-16 di Wayback Machine
- ALBIS Free tool for memorizing Swedish vocabulary.
- Danish and Swedish with sound files including Japanese translation
Kamus
[édit | édit sumber]- All free Swedish dictionaries
- Online dictionary Archived 2006-12-19 di Wayback Machine founded by the Swedish government
- The Swedish Schoolnet Archived 2006-12-21 di Wayback Machine Lexin - Swedish-English dictionary
- Swedish Dictionary from Webster's Dictionary
Fonétika
[édit | édit sumber]- Laryngograph recordings and resynthesis of different dialects of Swedish - Sound files that illustrate the differences between prosody in Scandinavian dialects
Literatur Basa Swédia nu bersejarah
[édit | édit sumber]- Digitally remastered Swedish imprints before 1700 Archived 2007-05-24 di Wayback Machine from the webpage of the Royal Library in Stockholm
- Project Runeberg's digital facsimile edition of Nordisk familjebok, the definitive Swedish-language encyclopaedia of the late 19th and éarly to mid 20th centuries.


