3 Unit Formulas
3 Unit Formulas
Uploaded by
Dhanalakshmi VadivelanCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Unit Formulas
3 Unit Formulas
Uploaded by
Dhanalakshmi VadivelanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
3 Unit Formulas
3 Unit Formulas
Uploaded by
Dhanalakshmi VadivelanCopyright:
Available Formats
www.Vidyarthiplus.
com
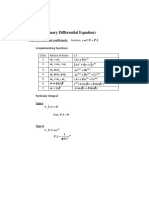
Unit I (Ordinary Differential Equation)
1.ODE with constant coefficients: Solution y = C.F + P.I
Complementary functions: Sl.No. NatureofRoots 1. m1 = m2 2. m1 = m2 = m3 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. m1 m2 m1 m2 m3 m1 = m2 , m3 m = i C.F ( Ax + B )e mx
( Ax
+ Bx + c ) e mx
Ae m1 x + Be m2 x
Ae m1 x + Be m2 x + Ce m3 x
( Ax + B )e mx + Ce m3 x
e x ( A cos x + B sin x ) A cos x + B sin x
m = i
Particular Integral: Type-I If f ( x ) = 0 then P . I = 0 Type-II If f ( x ) = e ax 1 ax P .I = e ( D)
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com Replace D by a .If ( D ) 0 ,thenitisP.I.If ( D ) = 0 ,thendiff.denominator
w.r.t D andmultiply x innumerator.Againreplace D by a .Ifyougetdenominator againzerothendothesameprocedure. Type-III Case: iIf f ( x ) = sin ax (or ) cos ax 1 sin ax (or) cos ax P .I = ( D) Hereyouhavetoreplaceonlyfor D 2 notfor D . D 2 isreplacedby a 2 .Ifthe
denominatorisequaltozero,thenapplysameprocedureasinTypeI.
1 cos 2 x 1 + cos 2 x , cos 2 x = , 2 2 3 1 3 1 sin 3 x = sin x sin 3 x , cos 3 x = cos x + cos 3 x andseparate P . I1 & P . I 2 4 4 4 4 Case: iiiIf f ( x ) = sin A cos B (or ) cos A sin B (or ) cos A cos B (or ) sin A sin B
Case: iiIf f ( x ) = Sin 2 x (or) cos 2 x (or) sin 3 x (or) cos 3 x Usethefollowingformulas Sin 2 x =
Usethefollowingformulas:
1 ( sin( A + B ) + sin( A B ) ) 2 1 (ii) cos A sin B = ( Sin( A + B ) sin( A B ) ) 2 1 ( iii ) cos A cos B = ( cos( A + B ) + cos( A B ) ) 2 1 ( iv ) sin A sin B = ( cos( A B ) cos( A + B ) ) 2 Type-IV If f ( x) = x m 1 P.I = xm ( D) 1 = x m 1 + g ( D) ( i ) s in A cos B =
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
= (1 + g ( D) ) x m
1
HerewecanuseBinomialformulaasfollows: i) (1 + x ) = 1 x + x 2 x 3 + ...
1
ii) (1 x ) = 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + ...
1
iii) (1 + x ) = 1 2 x + 3x 2 4 x 3 + ...
2
iv) (1 x ) = 1 + 2 x + 3 x 2 + 4 x 3 + ...
2
v) (1 + x) 3 = 1 3 x + 6 x 2 10 x3 + ... vi) (1 x) 3 = 1 + 3 x + 6 x 2 + 10 x3 + ... Type-V If f ( x) = e axV
where V = sin ax, cos ax, x m
P.I =
1 ax e V ( D)
Firstoperate e ax byreplacingDbyD+a. = e ax 1 V ( D + a)
Type-VI If f ( x) = x nV sin ax = I.P of eiax
cos ax = R.P of eiax
where V = sin ax, cos ax
Type-VII(SpecialTypeProblems) If f ( x) = sec ax (or) cosecax (or) tan ax 1 P.I = f ( x) = e ax e ax f ( x)dx Da 1. ODEwithvariableco-efficient:(EulersMethod) d2y dy Theequationisoftheform x 2 2 + x + y = f ( x) dx dx
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Impliesthat ( x 2 D 2 + xD + 1) y = f ( x) Toconvertthevariablecoefficientsintotheconstantcoefficients Put z = log x implies x = e z xD = D
x 2 D 2 = D( D 1) x3 D 3 = D( D 1)( D 2)
where D =
d d and D = dx dz
Theaboveequationimpliesthat ( D( D 1) + D + 1) y = f ( x) whichisO.D.E withconstantcoefficients. 2. LegendresLineardifferentialequation: d2y dy Theequationifoftheform (ax + b) 2 2 + (ax + b) + y = f ( x) dx dx Put z = log(ax + b) implies (ax + b) = e z (ax + b) D = aD d d where D = and D = (ax + b) 2 D 2 = a 2 D( D 1) dx dz (ax + b)3 D 3 = a 3 D( D 1)( D 2) 3. MethodofVariationofParameters: d2y dy Theequationisoftheform a 2 + b + cy = f ( x ) dx dx C.F = Ay1 + By2 and P.I = Py1 + Qy2 y2 f ( x ) where P = dx and y1 y2 y1 y2 y1 f ( x) Q= dx y1 y2 y1 y2
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
You might also like
- Network Security, Firewalls, and VpnsDocument2 pagesNetwork Security, Firewalls, and VpnsManuel Cespedes0% (4)
- Differential Calculus Das MukherjeeDocument224 pagesDifferential Calculus Das MukherjeeYousuf Ali0% (1)
- Hamiltonjet hm521 Fault Codes PDFDocument30 pagesHamiltonjet hm521 Fault Codes PDFali delavarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics II Formulas Studyhaunters PDFDocument13 pagesEngineering Mathematics II Formulas Studyhaunters PDFSriram J50% (2)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz Gazal100% (1)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDocument5 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralsapi-322359712No ratings yet
- H2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimDocument27 pagesH2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimGale HawthorneNo ratings yet
- M2 FormualsDocument13 pagesM2 FormualsItsme PrabhaNo ratings yet
- Unit - I (Ordinary Differential Equation)Document13 pagesUnit - I (Ordinary Differential Equation)J Marees Kumar ThangarathinamNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument8 pagesIntegralthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Indefinite IntegrationDocument24 pagesIndefinite IntegrationAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus by Arihant B016Document27 pagesIntegral Calculus by Arihant B016Luis Anderson60% (5)
- 9 Integrals PDFDocument19 pages9 Integrals PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises in Functions of More Than One Variable - Partial Differentiation Exercises On 16.1Document21 pagesSolutions To Exercises in Functions of More Than One Variable - Partial Differentiation Exercises On 16.1Carlos BohorquezNo ratings yet
- 5 - IntegrationDocument9 pages5 - IntegrationSham JaggernauthNo ratings yet
- Maths II FormulasDocument13 pagesMaths II Formulaskr_padmavathiNo ratings yet
- Arihant PhysicsDocument22 pagesArihant PhysicsManishKumar0% (1)
- Algebra Shorcuts Formulas For CAT - EDUSAATHIDocument12 pagesAlgebra Shorcuts Formulas For CAT - EDUSAATHITushar TikuNo ratings yet
- IntegralsDocument27 pagesIntegralssudersanaviswanathanNo ratings yet
- Leep 207Document27 pagesLeep 207Koyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Young's Inequality Yue Kwok ChoyDocument3 pagesYoung's Inequality Yue Kwok ChoyAnnisa ZakiyaNo ratings yet
- Chain Rule ReverseDocument11 pagesChain Rule ReverseJosué QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Integral (Kalkulus 2)Document7 pagesIntegral (Kalkulus 2)pitoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 02 - DifferentiationDocument45 pagesUNIT 02 - DifferentiationFaiZul IshAkNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1000A, Section 007Document30 pagesCalculus 1000A, Section 007arrowroot1No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Saksham TiwariNo ratings yet
- Continuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberDocument8 pagesContinuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberAakash ChanNo ratings yet
- MAT2384 Assignment #1: Dy Dy DX X Dy DX XDocument6 pagesMAT2384 Assignment #1: Dy Dy DX X Dy DX XKhoi Phan FofNo ratings yet
- B.E. Degree Examinations: Nov/Dec 2010: A F B F B BF A BF A F B F A BF B AfDocument4 pagesB.E. Degree Examinations: Nov/Dec 2010: A F B F B BF A BF A F B F A BF B AfDhanabal Palanisamy PNo ratings yet
- 07-Limit ContDocument15 pages07-Limit ContAnonymous BnbPSoovbNNo ratings yet
- 30 Diffrentiation Part 1 of 1dddddddddddddDocument18 pages30 Diffrentiation Part 1 of 1dddddddddddddVishal VjNo ratings yet
- Differentiation QstnsDocument4 pagesDifferentiation Qstnssanand11No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Continuity and DifferentiabilityKrish AnandNo ratings yet
- X With Respect To X The Derived Function Is 2x .: IntegrationDocument15 pagesX With Respect To X The Derived Function Is 2x .: IntegrationAdri EnneNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document35 pagesWa0002.ShashankNo ratings yet
- MAT060 12 Differential Notation and Trigonometric FunctionsDocument52 pagesMAT060 12 Differential Notation and Trigonometric FunctionsShine Ibarra AlabaNo ratings yet
- m820 Sol 2011 PDFDocument234 pagesm820 Sol 2011 PDFkhicomNo ratings yet
- Module-4 MAT1001-1Document18 pagesModule-4 MAT1001-1amarjith9787No ratings yet
- Common Practice Test - 5 Jee Mains: Matheamtics SolutionDocument7 pagesCommon Practice Test - 5 Jee Mains: Matheamtics Solutionblue_l1No ratings yet
- Ieep 202Document11 pagesIeep 202anima1982No ratings yet
- Spring 2012 Midterm #2 SolutionsDocument2 pagesSpring 2012 Midterm #2 SolutionsRushil SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Differentiation Rules: X X y V C V B Ae yDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Differentiation Rules: X X y V C V B Ae yAoSd' TikmanNo ratings yet
- Integration Formula: + C U Du VDX Udx DX V U Udx C CudxDocument5 pagesIntegration Formula: + C U Du VDX Udx DX V U Udx C CudxRon AtaNo ratings yet
- Magic of Definite IntegralDocument88 pagesMagic of Definite IntegralsagarNo ratings yet
- Solved ExercisesDocument19 pagesSolved ExercisesDidem AydınNo ratings yet
- Mse Maths IIDocument5 pagesMse Maths IIwafflerick69No ratings yet
- RT-2 Set-C SolDocument4 pagesRT-2 Set-C Solsachinplayer2006No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Mal101 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 Mal101 PDFwald_generalrelativityNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Inverse FunctionDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Inverse FunctionfrehiwotsenayNo ratings yet
- Derivatives of Transcendental FunctionsDocument10 pagesDerivatives of Transcendental FunctionsCole NadzNo ratings yet
- Answer To Odd ProblemsDocument18 pagesAnswer To Odd ProblemsSingh KaranNo ratings yet
- Matematika 2 Vjezbe MarinkovicDocument42 pagesMatematika 2 Vjezbe MarinkovicedoopanovicNo ratings yet
- 14 - FDWK C4 Ism 07Document33 pages14 - FDWK C4 Ism 07Andy GaoNo ratings yet
- Tut 2Document3 pagesTut 2Harshvardhan SinghNo ratings yet
- Continuity & DifferentiabilityDocument3 pagesContinuity & DifferentiabilityJoydeep NaskarNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- EcoTank L3151 Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesEcoTank L3151 Datasheet PDFIce BibovskiNo ratings yet
- Itu-T: Mean Opinion Score (MOS) TerminologyDocument18 pagesItu-T: Mean Opinion Score (MOS) TerminologyRomaric NoutaiNo ratings yet
- Grokking Data ScienceDocument61 pagesGrokking Data ScienceLakshya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Design: Lab Manual 2011-12Document35 pagesEmbedded System Design: Lab Manual 2011-12prajkumar324No ratings yet
- A Framework For Social Media Data Analytics Using Elasticsearch and KibanaDocument9 pagesA Framework For Social Media Data Analytics Using Elasticsearch and KibanafestauNo ratings yet
- HANA ABAP ShortDumpsDocument7 pagesHANA ABAP ShortDumpsTejraj ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- PrLe Rapid Breast Deboner M4.1 02Document4 pagesPrLe Rapid Breast Deboner M4.1 02NicolasNo ratings yet
- PT Ibmi Security Policy GuideDocument9 pagesPT Ibmi Security Policy Guidesferdinandes510No ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument12 pagesProject ProposalAbdela Aman Mtech100% (1)
- Galerkin's Method: APL705 Finite Element MethodDocument3 pagesGalerkin's Method: APL705 Finite Element MethodakashNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Voltage DropDocument7 pagesDynamic Voltage DropBaluvu Jagadish100% (1)
- PhamCongTrung CMU SE 433 SCDocument5 pagesPhamCongTrung CMU SE 433 SCPhạm TrungNo ratings yet
- Yuxuan Full PLLDocument4 pagesYuxuan Full PLLRichy UdilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Overview of Health Informatics Copy 1Document24 pagesLesson 4 Overview of Health Informatics Copy 1Ritter GamingNo ratings yet
- Stepping Motor Bypass CableDocument5 pagesStepping Motor Bypass CablePHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ100% (15)
- Scheduling and Task AllocationDocument46 pagesScheduling and Task AllocationAhmedNo ratings yet
- Installing The Spring Tools SuiteDocument2 pagesInstalling The Spring Tools SuiteDiana HartanNo ratings yet
- Samsung CLX 9201-9251-9301Document476 pagesSamsung CLX 9201-9251-9301traminerNo ratings yet
- Solarwinds Variable ListDocument4 pagesSolarwinds Variable Listpawan143No ratings yet
- 8619Document177 pages8619Aimen BukhariNo ratings yet
- DX DiagDocument35 pagesDX DiagdeepeshNo ratings yet
- 23151-gps GBT 709Document15 pages23151-gps GBT 709Jose VogelNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Course PaperDocument24 pagesRenewable Energy Course PaperAminul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Holiday DetectionDocument4 pagesHoliday DetectionAnsar Ali100% (1)
- Drawing2 Notes+mdtrmDocument4 pagesDrawing2 Notes+mdtrmStruggleizreal LoyalCarrotNo ratings yet
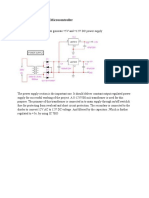
- Power Supply For 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesPower Supply For 8051 MicrocontrollerAshok Ekanath KalangeNo ratings yet
- Theory Date Sheet of PH.D Course Work 1st Sem (Full) Exams May 2023.Document4 pagesTheory Date Sheet of PH.D Course Work 1st Sem (Full) Exams May 2023.YakubNo ratings yet
- Deleting Azure VM Build Guide V0.1: Sainath Kev Microsoft Mvp-Directory ServicesDocument6 pagesDeleting Azure VM Build Guide V0.1: Sainath Kev Microsoft Mvp-Directory ServicesAhmed Aljack SulimanNo ratings yet