IT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (E)
IT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (E)
Uploaded by
Norzawati NoordinCopyright:
Available Formats
IT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (E)
IT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (E)
Uploaded by
Norzawati NoordinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
IT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (E)
IT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (E)
Uploaded by
Norzawati NoordinCopyright:
Available Formats
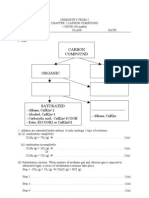
SULIT
Lekat logo ______________ sekolah di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN:
TOPICAL TEST 2: CARBON COMPOUNDS
PAPER 1
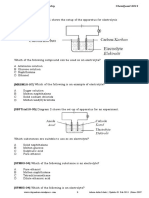
1 Which of the following groups cannot be classified as organic compounds? A Alcohols B Hydrocarbon C Carboxylic acids D Hydrogen carbonates 2 Which of the following homologous series are correctly matched with their functional group? Homologous series A Alkane B Alkena C Alcohol D Carboxylic acid Functional group H C=C O COO
8 Which of the following statements is true for the compound with the molecular formula, C3H8? A It is a conductor of electricity. B It is readily soluble in water. C It is a gas at room temperature. D It is an unsaturated compound. 9 Which of the following equations represent the incomplete combustion of ethane?
I 2C2H6 + 3O2 II 2C2H6 + 7O2 III 2C2H6 + 5O2 IV 2C2H6 + 3O2 4C + 6H2O 4CO2 + 6H2O 4CO + 6H2O 5C + CH4 + 6H2O
15 What are the requirements for hydration process to form ethanol from ethene? I Presence of phosphoric(V) acid. II Presence of steam. III 300 C temperature condition. IV Presence of potassium manganate(VII). A I, II and III only B I, III and IV only C II, III and IV only D All of the above 16 Which of the following statements is correct in the comparison of alkenes and alkanes? A Alkanes have lower melting and boiling points than alkenes. B The combustion of alkenes is more luminous and sooty than alkanes. C Both alkanes and alkenes undergo addition reactions. D Alkenes can conduct electricity while alkanes cannot. 17 Which of the following are isomers? I
A B C D
I and II only I and III only II and IV only I and IV only
3 Which of the following is an alkene? A CH3CH(CH3)CH3 B CH3CHCH2CH3 C CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 D CH3C(CH3)2CH3 4 Which of the following is not a source of hydrocarbons? A Coal C Natural gas B Petroleum D Hot spring 5 Alkanes are also called A saturated hydrocarbon. B unsaturated hydrocarbon. C hydroxyl organic compound. D inorganic carbon compound. 6 What is the IUPAC name of C6H14? A Methane C Hexane B Propane D Heptane 7 Which of the following is true about the physical properties of the members of the homologous series alkane down the group at room conditions?
I Density increases. II Melting point increases. III Boiling point increases. IV Relative molecular mass decreases.
10 What is the percentage by mass of carbon in a propane compound? A 75% C 83% B 82% D 85% 11 A substitution reaction can occur between alkane and I chlorine, Cl2 III bromine, Br2 II iodine, I2 IV hydrogen, H2 A I and II only C II and IV only B I and III only D I and IV only 12 What is the structure of the reactant that reacts with bromine gas and produce CH3 CH2 CHBR CH2Br? A CH3 CH = CH CH3 B CH2 = CH CH = CH2 C CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 D CH3 CH2 CH = CH2 13 The following word equation represents the reaction of ethene in the presence X.
II
III
A B C D
I, II and III only I, II and IV only II, III and IV only I, II, III and IV
What is X? A Nickel B Ethanol C Phosphoric acid D Acidified potassium manganate (VII) 14 Which of the following is not an example of addition reaction for alkenes? A Hydration C Dehydration B Halogenation D Hydrogenation
9
IV
A I and II only C II and III only B I and III only D I and IV only 18 Which of the following statements about isomers is correct? A They have the same structural formulae.
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo ______________ sekolah di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN:
TOPICAL TEST 2: CARBON COMPOUNDS
C II, III and IV only D I, II, III and IV 25 Which of the following is not the properties of alcohols? A Volatile. B Flammable. C Neutral in pH. D Undergo hydration process. 26 Ethanoic acid reacts with the following substances except A sodium carbonate. B ethanol. C reactive metals. D acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution. 27 Diagram 1 shows the structural formula of a compound. B CH3 CH2 OH C CH3 CH CH2 D CH3 COO CH3 31 Diagram 2 shows the structural formula of an ester molecule.
PAPER 1
B They have the same molecular formulae. C They have the same physical properties. D They have different chemical properties. 19 Which of the following compounds do not have isomers? I Ethane III Propene II Ethene IV Butane A I, II and III only B I, III and IV only C II, III and IV only D I, II, III and IV 20 Which of the following compounds react with acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution? I Ethanol III Ethene II Ethane IV Methanol A I, II and III only B I, III and IV only C II, III and IV only D I, II, III and IV 21 What is the functional group for alcohols? A CO C COOH B OH D O 22 Which of the following statements is not true about ethanol? A It is soluble in water. B It has the molecular formula C2H3O. C It can convert to ethanoic acid by oxidation process. D It can be produced by fermentation process from glucose. 23 What is the changes of colour of potassium dichromate(VI) in the oxidation reaction with alcohols? A From orange to green. B From green to orange. C From colourless to orange. D From purple to colourless. 24 Which of the following acts as dehydrating agents in the dehydration of alcohol? I Aluminium oxide II Concentrated sulphuric acid III Acidified potassium manganate(VII) IV Phosphoric(V) acid A I, II and III only B I, III and IV only
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
Diagram 2
What is the name of the ester molecule? A Methyl propanoate B Propyl methanoate C Ethyl ethanoate D Methyl butacoate 32 Diagram 3 shows the experimental set-up.
Diagram 1
What is IUPAC name of the compound? A 2-ethylpropanoic acid. B 3-pentanoic acid. C 2, 2-diethylpropanoic acid. D 2, 2-dimethylpropanoic acid. 28 Which of the following statements is not correct about the preparation of ethanoic acid? A Ethanoic acid is prepared in the laboratory by the oxidation of ethanol. B Acidified potassium dichromate(VI) will change from orange to green. C Ethanoic acid produces vinegar smell. D Acidified potassium dichromate(VI) acts as the reducing agent. 29 Carboxylic acid reacts with sodium carbonate to produce I salt II carbon dioxide III water IV oxygen A I, II and III only B I, III and IV only C II, III and IV only D I, II, III and IV 30 Which of the following compounds will react with magnesium metal to give off hydrogen gas? A CH3 CO OH
10
Diagram 3
What is the product of the reaction? A Ethane-1, 2-diol B Ethyl ethanoate C Propil ethanoate D Metil butanoate 33 Which of the following is a saturated fat? A Palmitic acid B Oleic acid C Linoleic acid D Linolinic acid 34 Which of the following are correct about fats and oils? Fats I Sources come from animals. Oils Sources come from plants or fishes. Exist as liquid at room temperature. Synthesized esters.
II Exists as solid at room temperature. III Naturally occurring esters.
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo ______________ sekolah di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN:
TOPICAL TEST 2: CARBON COMPOUNDS
38 When 3 g of butanol is burnt in excess oxygen, x volume of carbon dioxide is produced. What is the value of x? [Relative atomic mass = H, 1; C, 12; O, 16; 1 mole of gas occupies a volume of 24 dm3 at room temperature] A 3.89 dm3 C 0.04 dm3 3 B 0.16 dm D 2.81 dm3 39 Which of the following consist of the functional group C = C? A C3 H8 C C6 H14 B C5 H12 D C9 H18 40 Diagram 4 shows the structural formula of a compound. 41 Which of the following are isomers of butanol? I Butan-2-ol II 2-methylpropan-1-ol III 2-methylpropan-2-ol IV 3-methylbutan-2-ol A I and IV only B II and III only C I, II and III only D I, III and IV only 42 Which of the following represents the structural formula of an alcohol? A
PAPER 1
IV Contain saturated fatty acids. A B C D
Contain unsaturated fatty acids.
I, II and III only I, III and IV only I, II and IV only II, III and IV only
35 What is the IUPAC name for the monomer of natural rubber? A Isoprene B 3-methyl buta-2, 3-diene C 2- methyl buta-1, 3-diene D 1-methyl buta-2, 3-diene 36 Which of the following is not correct about the properties of natural rubber? A Elastic. B Insoluble in water. C Not resistant to alkalis and weak acids. D Ozone and oxygen cause rubber to harden and crack by oxidation. 37 Which of the following is a saturated hydrocarbon? A CH3 CH (CH3) CH2 CH3 B CH3 CH CH CH3 C CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH2 D CH3 CH CH CH2 CH3
Diagram 4
What is the IUPAC name of the compound? A Pent-2-ene B 2-methylbut-1-ene C 2-methylbut-2-ene D 3-methylbut-2-ene
PAPER 2
SECTION A the interconversions of organic (ii) What are the reagent and catalyst needed to undergo reaction I with alkene?
___________________________________________________
1 Diagram 1 shows compounds.
[2 marks] (c) (i) Write the reaction equation from alkene to alcohol. Use ethene as example.
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (ii) What is the catalyst for this reaction?
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (iii) What is the name of the reversed reaction? For example the conversion of alcohol to alkene.
___________________________________________________
Diagram 1
(a) Name the general formula of alcohol.
________________________________________________________
[1 mark] (d) (i) What is compound X ? State its general formulae.
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (b) (i) What is the reaction of I?
___________________________________________________
[2 marks] (ii) Give one of the physical properties of compound X.
___________________________________________________
[1 mark]
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P) 11
[1 mark]
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo ______________ sekolah di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN:
TOPICAL TEST 2: CARBON COMPOUNDS
___________________________________________________
PAPER 1
Diagram 2 shows the structural formulae of two hydrocarbons, X and Y.
[1 mark] (iii) Draw the apparatus for the preparation of ethanoic acid.
Diagram 2
(a) Name the homologous series of these compounds.
________________________________________________________
[1 mark] (b) Name X and Y according to IUPAC naming system.
________________________________________________________
[2 marks] (c) Compound X and Y are isomers. (i) Define isomers.
___________________________________________________
[2 marks] (d) CH3COOH reacts with ethanol to produce compound X. (i) State the name of compound X.
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (ii) Compound X and Y have another isomer, Z. Draw the structure of isomer Z and name it according to IUPAC naming system. [2 marks] (d) Compound X, Y and Z can undergo addition reactions. (i) Give three examples of addition reactions.
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (ii) Give one physical property of compound X.
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (iii) Draw the structural formulae of compound X.
[3 marks] (ii) Write the chemical equation for one of the reactions stated in (d) (i).
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] 4 Table 1 shows the members of a family. Compound Molecular Relative Melting formulae molecular point Ethane Propane Butane Pentane C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 30 44 58 72
Table 1
[1 mark] 3 The following information is about the compound CH3COOH. As a weak acid. Undergoes combustion. A member of a homologous series. (a) What is the name of this compound?
________________________________________________________
Boiling point 89 42 0.5 36
183 188 138 130
[1 mark] (b) What is the general formulae for the homologous of this compound?
________________________________________________________
(a) Members of this family are classified under a homologous series. Name the homologous series and state its general formulae. Homologous series: ____________________________ General formulae: _____________________________ [2 marks] (b) (i) What is the physical state of pentane at room temperature?
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (c) CH3COOH is prepared by oxidation. (i) State the compounds needed for oxidation to produce CH3COOH.
___________________________________________________
[2 marks] (ii) What will be the change of colour to be observed during the preparation of ethanoic acid using the compounds above?
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P) 12
[1 mark]
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo ______________ sekolah di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN:
TOPICAL TEST 2: CARBON COMPOUNDS
(b) Methane is one example of hydrocarbon. (i) What is the effect of methane to the environment?
___________________________________________________
PAPER 1
(ii) Name the products formed when ethane undergoes a complete combustion in air.
___________________________________________________
[2 marks] (iii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction in (b) (ii).
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (ii) When exposed under the ultraviolet light, methane react with chlorine. What is the reaction between methane and chlorine?
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (c) This homologous series have low melting points and boiling points. (i) What is the attractive force contribute to the low metling points and boiling points?
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (iii) What are the final products of this reaction?
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (ii) Explain why melting point of pentane is higher than than of butane.
___________________________________________________
[2 marks] (c) Ethanol can be prepared in the laboratory by fermentation. (i) What is fermentation?
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (iii) Give other two physical properties of alkanes.
___________________________________________________
[1 mark] (ii) Besides fermentation, ethanol can be prepared by another method. State the method.
___________________________________________________
[2 marks] 5 (a) What is meant by hydrocarbon?
________________________________________________________
[1 mark] (iii) What are the reactants and catalyst required for reaction mentioned in (c) (ii)?
___________________________________________________
[3 marks]
[1 mark]
SECTION B 6 (a) (i) What is meant by addition reaction? 7 (a) (b) (c) (iii) Observation and chemical equation for the reaction that takes place. [2 marks] The physical properties of rubber can be changed by vulcanisation. Define vulcanisation. [1 mark] Describe the properties of vulcanised rubber. [5 marks] (i) Explain the coagulation of latex. [5 marks] (ii) Explain the prevention of coagulation of latex. [2 marks] Natural rubber is a kind of natural polymer. (i) State other two natural polymers and two synthetic polymers. [4 marks] (ii) What is the monomer of natural rubber? Draw the structural formulae of the monomer. [2 marks]
[2 marks] (ii) Describe briefly three examples of addition reaction between alkenes and other compounds. Give an equation reaction for each. [6 marks] (b) State two similarities in term of physical properties and two differences in form of chemical properties between alkanes and alkenes. [4 marks] (c) (i) Give two methods of preparing ethanol. [2 marks] (d) Using one of the methods, describe an experiment that can be carried out in the laboratory to produce ethanol. Your answer should include the following items: (i) Diagram of the set-up of the apparatus. [2 marks] (ii) Procedure. [2 marks]
(d)
SECTION C
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
13
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo ______________ sekolah di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN:
TOPICAL TEST 2: CARBON COMPOUNDS
(iv) Resistant to oxygen. [8 marks] (b) Vulcanised rubber has many uses in homes and industries. State the uses of them. [5 marks] (c) Compare between the properties of vulcanised rubber and unvulcanised rubber. [6 marks]
PAPER 1
8 (a) In vulcanised rubber, the sulphur atoms are added to the double bonds in the natural rubber molecules to form disulphide linkages ( C S S C ) between the long polymer chains. State this sulphur cross-links to the properties of vulcanised rubber and explain. (i) Strong. (ii) Elastic. (iii) Resistant to heat.
PAPER 3
1 Diagram 1 shows three sets, Set I, Set II and Set III, of the apparatus set-up for an experiment to investigate the effect of ammonia solution and ethanoic acid on the coagulation of latex. Set I Apparatus set-up
III
Diagram 1
II
(a) Construct a table to record the time taken for coagulation latex in Set I, II and III. [3 marks] (b) State one hypothesis based on Set I and Set II. [3 marks] (c) State one observation that can be obtained from each set of this experiment. [3 marks] (d) What was the function of Set I which contained latex only? [3 marks] (e) State the operational definition for the coagulation of latex. [3 marks] (f) Based on this experiment, write the following variables. (i) The manipulated variable (ii) The responding variable (iii) The constant variable [3 marks]
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
14
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo ______________ sekolah di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN:
TOPICAL TEST 2: CARBON COMPOUNDS
PAPER 1
(g)
(i) Describe how latex can coagulate without acid in Set I. (ii) Explain why the latex in Set I coagulates slower than the latex in Set III. [3 marks]
Susbtance that can coagulate latex
Substance that cannot coagulate latex
(h)
A student added excess hydrochloric acid into the beaker in Set II after 12:00 p.m. (i) What can be observed about the latex? [3 marks] (ii) Explain the answer in 1 (h) (i). [3 marks]
[3 marks] 2 Ester is used in producing synthetic fruit essences due to its pleasant fruity and flowery smell. Table 1 shows several examples of esters. Ester Smell of essence Propyl ethanoate Pear
Table 1
Pentyl ethanoate Banana
(i) State one hypothesis based on Set I and Set II. [3 marksh] (j) The following is a list of chemical substances: Phosphoric acid Methanoic acid Sodium hydroxide Potassium hydroxide Complete the table by classifying the substances that can coagulate latex and substances that cannot coagulate latex.
Design an experiment to prepare the esters shown in Table 1. Your planning should include the following aspects: (a) Aim of experiment. (b) All the variables. (c) Lists of substances and apparatus. (d) Diagram of apparatus set-up. (e) Procedure. (f) Tabulation of data.
[17 marks]
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
15
SULIT
You might also like
- Chem Module 1-3Document5 pagesChem Module 1-3John CincoNo ratings yet
- KSSM Chapter 2 - Carbon Compounds Skill Practice AnswerDocument16 pagesKSSM Chapter 2 - Carbon Compounds Skill Practice Answerwongyiyang2020No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & SaltsTRIPLE - 1Document15 pagesAcids, Bases & SaltsTRIPLE - 1ajuniorhagenNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reactant ExercisesDocument1 pageLimiting Reactant ExercisesJeevanKarthiresanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation: Bab 3: Konsep Mol, Formula Dan Persamaan KimiaDocument31 pagesChapter 3: The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation: Bab 3: Konsep Mol, Formula Dan Persamaan Kimiaintan noraisyahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Review On Chemical Formulas With AnswersDocument4 pagesChemistry - Review On Chemical Formulas With AnswersAbdullah HassanNo ratings yet
- Topical Test 8: Salts: Ujian Topikal 8: GaramDocument9 pagesTopical Test 8: Salts: Ujian Topikal 8: GaramIvan Hoo Chean YiengNo ratings yet
- VBTDocument29 pagesVBTsernaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No LogoDocument96 pagesChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No Logohome8008100% (2)
- Atomic Structure Electron Configuration QsDocument30 pagesAtomic Structure Electron Configuration QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1Document27 pagesChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1ZekZanaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 NotesDocument4 pagesModule 3 NotesRochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument8 pagesAtomic StructureDevyanshi SinghNo ratings yet
- REDOX EQUILIBRIUM (Teacher's Copy)Document34 pagesREDOX EQUILIBRIUM (Teacher's Copy)jiaNo ratings yet
- Interversions of Carbon Compounds (1415)Document9 pagesInterversions of Carbon Compounds (1415)holdonpainendsNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesAtomic Structureinexplicable throeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bonding Powerpoint AP ChemDocument68 pagesChapter 8 Bonding Powerpoint AP ChemAbdul jan sultaniNo ratings yet
- Che 02Document5 pagesChe 02lakashl14No ratings yet
- ELECTRON CONFIGURATION ExerciseDocument58 pagesELECTRON CONFIGURATION ExerciseStephanie Palomares LevitaNo ratings yet
- 04 Chemical Bonding Drawing ExerciseDocument3 pages04 Chemical Bonding Drawing ExerciseAlicia Tan Suat HongNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry ExerciseDocument2 pagesStoichiometry ExerciseErwin Purnama HadiansyahNo ratings yet
- Calculations and Chemical ReactionsDocument14 pagesCalculations and Chemical ReactionsSunnyNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry KPADDocument16 pagesThermochemistry KPADJOANNA MAGDALIN A/P JOSEPH MoeNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Final by Pragya 07.10.10Document21 pagesAtomic Structure Final by Pragya 07.10.10kumarm78No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563No ratings yet
- Target Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesTarget Atomic StructureRavindra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics Question PDFDocument8 pagesReaction Kinetics Question PDFdanielmahsa0% (1)
- Chapter 2b Mass Relationship of Atom, Concept of Mole, Composition of Compounds, Balancing of Chemical Equations and Stoichiometric CalculationsDocument47 pagesChapter 2b Mass Relationship of Atom, Concept of Mole, Composition of Compounds, Balancing of Chemical Equations and Stoichiometric CalculationsTeratak BiruNo ratings yet
- Chem U5 A2 EdexcelDocument48 pagesChem U5 A2 EdexcelReez SinhaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Bond PDFDocument10 pagesHydrogen Bond PDFNaman SinghNo ratings yet
- Alkena / Alkene: H H C H C HDocument7 pagesAlkena / Alkene: H H C H C HMOHAMAD REDUAN BIN IBRAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Calculations Involving The Mole.: You Must Learn This and Be Able To Apply It in CalculationsDocument7 pagesCalculations Involving The Mole.: You Must Learn This and Be Able To Apply It in CalculationsRohaya MeeNo ratings yet
- Module SaltDocument12 pagesModule SaltAzie Nurul Akhtar100% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Chapter 6 Form 4Document3 pagesSPM Chemistry Chapter 6 Form 4ameerul_hazeeqNo ratings yet
- Carbon CompoundDocument306 pagesCarbon CompoundJerry Sumok WalterNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Carbon CompoundsDocument16 pagesModule 3 Carbon Compoundshulk3706100% (3)
- F5C2 Carbon Compound-QDocument7 pagesF5C2 Carbon Compound-QfazdirNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chemistry: Chemical For ConsumerDocument16 pagesForm 5 Chemistry: Chemical For Consumernaqiu96No ratings yet
- Relative Atomic MassDocument5 pagesRelative Atomic Masskmoiz427100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding-Wps OfficeDocument16 pagesChemical Bonding-Wps OfficeJoel TitusNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseDocument7 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Order of ReactionDocument4 pagesExercise On Order of ReactionGopi KupuchittyNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics WSDocument44 pagesReaction Kinetics WSMustufa FerozNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction NotesDocument27 pagesRate of Reaction NotesYong SiewkuanNo ratings yet
- SPM Form 4 Exercise Periodic Table of ElementsDocument3 pagesSPM Form 4 Exercise Periodic Table of Elementsasparagus1996No ratings yet
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document18 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)
- Electronic Configuration New 2025Document2 pagesElectronic Configuration New 2025Every Time Chemistry [ ETC]No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure - Exam QuestionsIman WafaNo ratings yet
- Percent Yield WorksheetDocument2 pagesPercent Yield WorksheetUmer AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 02 C06 2012 P1 With AnsDocument45 pages02 C06 2012 P1 With AnsMimie Yasmin KamalNo ratings yet
- Percentage YieldDocument2 pagesPercentage YieldHal OgleNo ratings yet
- Question Bank in Chemistry Class ADocument81 pagesQuestion Bank in Chemistry Class AiliasNo ratings yet
- 03 Jadual Berkala UnsurDocument4 pages03 Jadual Berkala UnsurCikgu AnitaNo ratings yet
- ChemQuest 26Document4 pagesChemQuest 26Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- What Is Hydrogen BondingDocument6 pagesWhat Is Hydrogen BondingKate MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Factor Affecting Rate of Reaction ExerciseDocument3 pagesFactor Affecting Rate of Reaction ExerciseRafiq IrdhinaNo ratings yet
- H2 Inorganic ChemistryDocument7 pagesH2 Inorganic ChemistrykitoniumNo ratings yet
- Ujian 2 Form 5Document9 pagesUjian 2 Form 5Nazreen NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 20 MC PracticeDocument17 pagesTopic 10 20 MC PracticePipen 5No ratings yet
- New QB Organic Chemistry 1Document18 pagesNew QB Organic Chemistry 1mertdurkut300No ratings yet
- Factor Affecting Rate of Reaction (TEMPERATURE)Document3 pagesFactor Affecting Rate of Reaction (TEMPERATURE)Norzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- Factor Affecting Rate of Reaction (Catalyst)Document3 pagesFactor Affecting Rate of Reaction (Catalyst)Norzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- Sek Men Convent, Jalan Tanjung Bendahara, 05300 ALOR SETAR, KedahDocument11 pagesSek Men Convent, Jalan Tanjung Bendahara, 05300 ALOR SETAR, KedahNorzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: : 4541/2 Mid Year Exam 2011 Paper 2 2 HoursDocument13 pagesName: Class: : 4541/2 Mid Year Exam 2011 Paper 2 2 HoursNorzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: : 4541/3 Final Year Exam Chemistry 2013 Paper 1 HoursDocument6 pagesName: Class: : 4541/3 Final Year Exam Chemistry 2013 Paper 1 HoursNorzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- Program Cegah AedesDocument2 pagesProgram Cegah AedesNorzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (E)Document7 pagesIT Chem F5 Topical Test 2 (E)Norzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (E)Document10 pagesIT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (E)Norzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 1 (E)Document8 pagesIT Chem F5 Topical Test 1 (E)Norzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 Mid-Year Examination (E)Document10 pagesIT Chem F5 Mid-Year Examination (E)Norzawati NoordinNo ratings yet