0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K viewsT3 and T4 Synthesis
T3 and T4 Synthesis
Uploaded by
rizwanbasTSH activates the thyroid gland to produce T4 and smaller amounts of T3. Most circulating T3 comes from the conversion of T4 to T3 in tissues rather than direct secretion from the thyroid. T3 is a more potent thyroid hormone than T4 and has greater biological activity though lower levels in the blood, affecting processes like metabolism, growth, and heart rate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
T3 and T4 Synthesis
T3 and T4 Synthesis
Uploaded by
rizwanbas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesTSH activates the thyroid gland to produce T4 and smaller amounts of T3. Most circulating T3 comes from the conversion of T4 to T3 in tissues rather than direct secretion from the thyroid. T3 is a more potent thyroid hormone than T4 and has greater biological activity though lower levels in the blood, affecting processes like metabolism, growth, and heart rate.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
TSH activates the thyroid gland to produce T4 and smaller amounts of T3. Most circulating T3 comes from the conversion of T4 to T3 in tissues rather than direct secretion from the thyroid. T3 is a more potent thyroid hormone than T4 and has greater biological activity though lower levels in the blood, affecting processes like metabolism, growth, and heart rate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesT3 and T4 Synthesis
T3 and T4 Synthesis
Uploaded by
rizwanbasTSH activates the thyroid gland to produce T4 and smaller amounts of T3. Most circulating T3 comes from the conversion of T4 to T3 in tissues rather than direct secretion from the thyroid. T3 is a more potent thyroid hormone than T4 and has greater biological activity though lower levels in the blood, affecting processes like metabolism, growth, and heart rate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
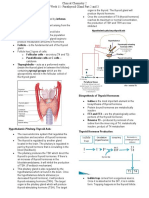
T3 And T4 Synthesis
Submitted to: Sir Muneeb
Submitted by: Sajida Bano
Synthesis of T3 and T4
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) activates the production of
thyroxine (T4) and T3. This process is under regulation. In the
thyroid, T4 is converted to T3. TSH is inhibited mainly by T3.
The thyroid gland releases greater amounts of T4 than T3, so
plasma concentrations of T4 are 40-fold higher than those of
T3. Most of the circulating T3 is formed peripherally by
deiodination of T4 (85%), a process that involves the removal
of iodine from carbon 5 on the outer ring of T4. Thus, T4 acts
as prohormone for T3.
This thyroid hormone is similar to thyroxine but with one fewer
iodine atoms per molecule. In addition, T3 exhibits greater
activity and is produced in smaller quantity.
It is the most powerful thyroid hormone, and affects almost
every process in the body, including body temperature, growth
, and heart rate.
CHEMICAL REATION
You might also like
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicDocument2 pagesHashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicPetraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument37 pagesThyroid GlandConfidence MorganNo ratings yet
- Graves 3Document2 pagesGraves 3Moof06No ratings yet
- Thyroid FXN Test ReportDocument22 pagesThyroid FXN Test ReportMons Delas AlasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDuchess Ciedelle Abano ManatadNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesPhysiology of The Thyroid GlandSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- 14 Thyroid GlandDocument52 pages14 Thyroid Glandyabais110No ratings yet
- The Endocrine System - Thyroid Gland: Department of Physiology Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineDocument51 pagesThe Endocrine System - Thyroid Gland: Department of Physiology Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineYustina Wahyu NNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument7 pagesThyroid HormonesAbdullah EssaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function TestDocument11 pagesThyroid Function TestBookmyscansNo ratings yet
- 0a27thyroid Function TestDocument35 pages0a27thyroid Function TestAshokvardhan Chowdary Nandigam67% (3)
- FunctionTests BrochureDocument2 pagesFunctionTests Brochurejonalyntonato09No ratings yet
- Thyroid Axis and Its DisordersDocument33 pagesThyroid Axis and Its DisordersmaduksjaycryptoNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument84 pagesThyroidMeLissa Pearl GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function Test PDFDocument2 pagesThyroid Function Test PDFAlizaPinky100% (1)
- The Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Document12 pagesThe Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Leslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function Tests: What Is The Thyroid Gland?Document2 pagesThyroid Function Tests: What Is The Thyroid Gland?rastamaneazy269No ratings yet
- Thyroid & Parathyroid HormonesDocument53 pagesThyroid & Parathyroid Hormonesrehmanmughal87654No ratings yet
- FunctionTests Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesFunctionTests Brochure PDFArslan SaleemNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Thyroid GlandDocument56 pagesPhysiology of Thyroid GlandsaloniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders 3 Actions of Thyroid Hormones 1. Stimulation of Energy Use Thyroid Function TestsDocument2 pagesThyroid Disorders 3 Actions of Thyroid Hormones 1. Stimulation of Energy Use Thyroid Function TeststherarenNo ratings yet
- (MS) Trans 2 - Thyroid and Parathyroid DisordersDocument5 pages(MS) Trans 2 - Thyroid and Parathyroid DisordersEryl Franz HerreraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Thyroid GlandDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Thyroid GlandJohnpaul DelapenaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DiseasesDocument47 pagesThyroid Diseasesbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- 1.22.08 Thyroid Disease 1Document175 pages1.22.08 Thyroid Disease 1gonal24679No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Finals Lecture Thyroid DisordersDocument11 pagesPharmacology Finals Lecture Thyroid DisordersJuliann100% (1)
- Thyroid GlandDocument12 pagesThyroid GlandOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypothyroidism PathophysiologyCleo Joyce C. CristalNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function TestsDocument12 pagesThyroid Function Testsb3614156No ratings yet
- THYROID HORMONEDocument26 pagesTHYROID HORMONEIsha ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Final Thyroid HormonesDocument23 pagesLecture 4 Final Thyroid Hormonesfahadaq33No ratings yet
- 6e - Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy A Literature Review (Perbaiki Dafpus)Document5 pages6e - Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy A Literature Review (Perbaiki Dafpus)KESEBELASAN RESOG 2023No ratings yet
- Thyroid Metabolic HormonesDocument4 pagesThyroid Metabolic HormonesHala RezaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid FunctionDocument12 pagesThyroid Functionسلطان القلح100% (1)
- Thyroid HormonesDocument63 pagesThyroid HormonesDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.6 Thyroid Glands-LmsDocument108 pagesLesson 6.6 Thyroid Glands-Lmsjulia.ohmy3No ratings yet
- 5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردDocument27 pages5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردRana Abdullah100% (1)
- Thyroid Function Tests-27851Document34 pagesThyroid Function Tests-27851nirajNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Endocrinology Part 2 3Document12 pagesWeek 11 Endocrinology Part 2 3Toff GoyenecheaNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument7 pagesHypothyroidismGkdhdhdgdgidNo ratings yet
- Physiology of ThyroidDocument9 pagesPhysiology of ThyroidAbby EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Role of Negative Feedback Mechanism in Thyroid ProductionDocument4 pagesDiscuss The Role of Negative Feedback Mechanism in Thyroid ProductionCL100% (1)
- The Thyroid Gland: Triiodothyronine (T) Tetraiodothyronine Thyroxine (T) Calcitonin TyrosineDocument1 pageThe Thyroid Gland: Triiodothyronine (T) Tetraiodothyronine Thyroxine (T) Calcitonin TyrosineLarasNo ratings yet
- Sam CD 2000 - EndocrinologyDocument139 pagesSam CD 2000 - EndocrinologyDr. Muha. Hasan Mahbub-Ur-RahmanNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 Hashimoto'sDocument24 pagesGROUP 2 Hashimoto'sKathleenMayJoyEnriquezCabralNo ratings yet
- Chapter 39: Thyroid and Antiythyroid Drugs: Clifford Jefferson EnajeDocument13 pagesChapter 39: Thyroid and Antiythyroid Drugs: Clifford Jefferson EnajeJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- 1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)Document96 pages1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)hamidNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument33 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid DrugsheenaNo ratings yet
- F1) P-Thyroid DisordersDocument9 pagesF1) P-Thyroid Disordersstella.gillesania.chenNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument49 pagesThyroid Glandjuliefe pinionNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyDocument53 pagesThyroid Disorders: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- THYROID GLANDDocument31 pagesTHYROID GLANDhasnainkhanafridi56No ratings yet
- What Is The Thyroid?Document12 pagesWhat Is The Thyroid?Silvia ValentinaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic DysfunctionsDocument12 pagesPathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic Dysfunctionskate_borovicNo ratings yet
- Hormone Treatment Fa QDocument1 pageHormone Treatment Fa QDot Dot DashNo ratings yet
- 7 - Regulation and Functions of The Thyroid HormonesDocument31 pages7 - Regulation and Functions of The Thyroid HormonesVigneshwaran Ravishankar100% (1)
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportDocument5 pagesThyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportAnonymous UTUWFODCEYNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument86 pagesThyroid DisordersJEPHTHAH KWASI DANSONo ratings yet
- Special Senses Part 1 (Taste & Smell)Document18 pagesSpecial Senses Part 1 (Taste & Smell)rizwanbas100% (1)
- BloodDocument103 pagesBloodrizwanbas50% (2)
- The Endocrine System Part 1Document64 pagesThe Endocrine System Part 1rizwanbasNo ratings yet