10 1 Guide
10 1 Guide
Uploaded by
api-79737143Copyright:
Available Formats
10 1 Guide
10 1 Guide
Uploaded by
api-79737143Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
10 1 Guide
10 1 Guide
Uploaded by
api-79737143Copyright:
Available Formats
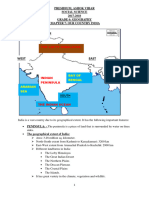
BITS & IMPORTANT POINTS
1. For India the central longitude 82.3 E is taken as Standard Meridian.
2. 82.3 E longitude passes near Allahabad and Kakinada.
3. IST means Indian Standard Time.
4. GMT means Greenwich Mean Time.
5. The time difference between GMT and IST is 5 hours.
6. India has an extension of 2,933 kms from East to West.
7. India has an extension of 3,214 kms from North to south.
8. The country's mainland lies between 84' and 376' north latitudes.
9. India has the land frontier of 15,200 kms and a coastal line of 7,516 kms.
10. India lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere.
11. Indian sub-continent includes India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal,
Bhutan, Sri Lanka and Maldives.
12. World land forms originated from two giant lands namely Angara land
(Laurasia) and Gondwana land.
13. The Indian peninsula was part of Gondwana land.
14. Over 200 million years ago Gondwana land split into pieces.
15. Indian plate moved towards north-west and collided the much larger
Eurasian Plate(Angara land).
16. The Himalayan ranges west to east distance is 2400 kms.
17. The Himalayan ranges width is 200 to 500 kms.
18. The Himalayas comprise three parallel ranges. 1. Himadri 2. Himachal/
Lesser Himalayas 3. Shivaliks.
19. The northern most range is known as Greater Himalayas or Himadri.
20. Greater Himalayas is continuous with the highest peaks.
21. Greater Himalayas average height 6100 mts.
22. Lesser Himalayas average height 3,700 to 4,500 mts.
23. Pir panjal and Mahabharata ranges are in the part of Lesser Himalayas.
24. Valley of Kashmir, the Kangra and Kulu are in Lesser Himalayas.
25. Simla, Mussorie, Nainital, Raniket Hill stations are in Lesser Himalayas.
26. Lesser Himalayas covered by evergreen forest.
27. Shivaliks width is 10-50 kms.
28. Shivaliks average height is 900 - 1100 mts.
29. Shivaliks are called as Jammu hills in Jammu region.
30. Shivaliks are called as Mishmi hills in Arunachal Pradesh.
31. Shivaliks are called as Cachar hills in Assam.
32. Shivaliks consist of thick gravel and alluvium.
33. The valleys lying between the Himachal and Shivalik are called Duns.
34. The prominent Duns are Dehradun, Kotli Dun and Patli Dun.
35. The eastern most boundary of the Himalayas is the Brahmaputra valley.
36. Purvanchal are known as Patkai, Naga, Manipuri, Khasi and Mizo hills.
37. The Himalayas are reason for summer rains and monsoon climate.
38. River Indus tributaries :1. Jhelum2. Chenab 3. Ravi 4. Beas 5. Sutlej.
39. The Himalayan Rivers have a perennial flow.
40. The Himalayan Rivers are fed by the glaciers.
41. Doab means two rivers.
42. Ganga plain extends from the rivers Ghaggar to Teesta.
43. Gravel and pebble sediments feature is known as Bhabar.
44. Swampy and marshy region called Terai.
45. India is surrounded by the sea on three sides.
46. The Indian plateau is mainly composed of the old crystalline,
hard igneous and metamorphic rock.
47. The Indian plateau is slightly tilted towards east.
CHAPTER 1
INDIA - RELIEF FEATURES
DUN
INDUS TRIBUTARIES
1
GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
INDIA
EXTENSION
MAP
70. The Deccan plateau is formed with black soils due to volcanic activity.
71. The Thar Desert is located on the leeward side of Aravalies.
72. The Thar Desert receives rainfall 100 to 150 mm per year.
73. The Thar Desert has an arid climate with very low vegetation cover.
74. Luni is the only river in the Thar Desert.
75. Indira Gandhi canal is the longest canal in the country (650kms).
76. The western coast starts at Rann of Kutch and ends at Kanyakumari.
77. The western coast is narrower than the east coast.
78. Maharashtra and Goa coast is called as Konkan Coast.
79. Karnataka coast is called as Canara coast.
80. Kerala coast is called as Malabar coast.
81. The western coast starts from Mahanadi to Cauvery.
82. Odisha coast is called as Utkal coast.
83. Andhra Pradesh coast is called as Sircar coast.
84. Tamil Nadu coast is called as Coramandal coast.
85. Lake Chilka is in Odisha.
86. Lake Kolleru and Pulicat are in Andhra Pradesh.
87. Andaman and Nicobar Islands stretched in Bay of Bengal.
88. Lakshadweep Islands are in the Arabian Sea.
89. In Andaman and Nicobar, Narkondam and Barren are volcanic origin.
90. The southernmost tip of India is found in Nicobar called as Indira point.
91. Indira point was submerged during the 2004 Tsunami.
92. Lakshadweep Islands are of coral origin.
93. Lakshadweep Islands total geographic area is 32 sq.kms.
94. Lakshadweep Island is famous for great variety of flora and fauna.
FAUNA
58. The southernmost tip of the plateau is
Kanyakumari.
59. Chhotanagpur plateau is rich in mineral resources.
60. The Deccan plateau is a triangular landmass.
61. Satpura range forms the Deccan plateaus north
edge.
62. The Western Ghats lie parallel to the west coast.
63. The Western Ghats are higher than the Eastern
Ghats.
64. Western Ghats extend for 1600 kms.
65. Western Ghats height 2000 mts.
66. Near Gudalur the Nilgiris joins the Western Ghats.
67. Ooty is located in Nilgiris.
68. Dodda Betta (2637 mts) is the highest peak in
Nilgiris.
69. The average height of the Eastern Ghats 900 mts.
48. The peninsular plateau consists of two divisions namely, the Malwa plateau (central high
lands) and the Deccan Plateau.
49. The famous hill station Udagamandalam, popularly known as Ooty.
50. The Mahadev range forms the Deccan plateaus eastern edge.
51. Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats and Nilgiris form western, eastern and southern boundaries
to the Deccan plateau.
52. Anaimudi 2695 mts (Annamalai hills) is the highest peak in south India.
53. Western Ghats include the Anaimalai, Palani (Tamilnadu) and Cardamom (Kerala) hills.
54. In comparison to the Gangetic plains the plateau region is dry.
55. The highest peak in Eastern Ghats is found at Chinthapalli (1680 mts).
56. Nallamalas, Velikondas, Palakondas and Seshachala are the tracts of Eastern Ghats.
57. The Eastern Ghats extends from Mahanadi valley to Nilgiris.
Gudalur
Ooty
MAHADEV
RANGE
Anaimudi
Palani
Chinthapalli
Nallamala
s
Velikondas
Palakonda
s
Seshachala
Dodda Betta
2 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
Arunachal
Pradesh
Gujarat
8
2
e
a
s
t
l
o
n
g
i
t
u
d
e
THE HIMALAYAN REGION THE PENINSULAR PLATEAU REGION
1. The Himalayan Region is the northern border
of India.
1. The peninsular plateau Region is surrounded
by the ghats and hills.
2. The highest mountain ranges of the world. 2. A portion of Gondwana land mass.
3. Formed by sedimentary rocks
3. Formed by Igneous and metamorphic rocks
4. This region run in the east-west direction 4. This region tilted towards east.
5. The rivers in this region are perennial rivers 5. The rivers in this region are not perennial.
6. Karakorum, western and Eastern Himalayas
and Purvanchal ranges are found here
6. Vindya, Satpura, western and Eastern Ghats
Nilgiri hills are found here.
7. Everest, K2, Kanchenjunga are Major
Mountain peaks of this region
7. Anaimudi, Dodabetta, are the important
peaks of this region
8. These are parallel ranges. 8. The plateau has been dissected by rivers
9. It has three parallel ranges. They are 1.
Himadri. 2. Himachal. 3. Siwalik
9. It has two divisions. They are 1. The central
high lands 2. T he Deccan plateau.
Contrast in the relief of Himalayan region with that of peninsular plateau.
1. The sun rises two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as
compared to Gujarat in the west. But the watches show the
same time. How does this happen?
A. 1. Arunachal Pradesh is in the eastern most part of India.
2. Gujarat is in the Western most part of India.
3. The East West maximum distance of India is 3,000 km.
4. The time difference between Arunachal Pradesh & Gujarat is 2 hours.
5. To remove the time differences, the time is decided on a central meridian.
6. That is called Standard Meridian.
7. The time at 82 east longitude is taken as Indian Standard Time.
8. Because of this reason, all the watches show the same time.
2. If the Himalayas would have not been in its present
position how would be the climatic conditions of
the Indian sub continent?
A. 1. The Himalayas protect India from the cold-winds of central
Asia during winter.
2. The Himalayas are responsible for causing rainfall.
3. Himalayas are the birth places of the great perennial rivers,
Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra.
4. No tropical monsoon climate in India.
5. They intercept the summer monsoons coming from the ocean.
6. Without Himalayas India would have been a desert.
3. The Himalayas do not extend into which of the
following states: Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh,
Sikkim, Haryana, Punjab, Uttaranchal
A. The Himalayas do not extend into the following states:
1. Madhya Pradesh 2. Uttar Pradesh
3. Punjab 4. Haryana
4. Which are the major physiographic divisions of
India? Contrast the relief of the Himalayan region
with that of the peninsular plateau.
A. The relief divisions of Indian landmass can be divided into the
following groups
1. The Himalayas 2. The Indo-Gangetic Plain
3. The Peninsular Plateau 4. The Coastal plains
5. The Desert 6. The Islands.
3 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
HIMALAYAS
EXTENDED STATES
IN INDIA
5. What is the influence of the Himalayas on Indian
agriculture?
A. 1. Agriculture is the backbone of Indian Economy.
2. The agricultural land around Himalayan rivers are very fertile.
3. Major rivers have enough water for irrigation.
4. The great rivers carry alluvium from the Himalayas.
5. This is deposited in the Great Plain of North India in the
form of fertile lands.
6. It is agriculturally the most productive part of the country.
6. The Himalayan slopes offer terraced cultivation.
7. Rice is the main crop on the terraced slopes.
8. The other crops are wheat, maize, potatoes, tobacco and ginger.
9. Tea is a unique crop which can be grown on the hill slopes only.
10. A wide variety of fruits such as apples, pears, grapes, mulberry,
walnut, cherries, peaches, apricot, etc. are also grown in the
Himalayan region.
11. Hence, Himalayas always support the Indian agriculture.
6. Indo- Gangetic plains have high density of population. Find
the reasons.
A. 1. Indo- Gangetic area is fertile and excellent for farming.
2. It makes heaven for farmers to grow rice and wheat.
3. It supports high density of population.
4. All are available with in the area.
5. So, it does not need to travel far.
6. The area is already developed.
7. It comforts more people to get work or live.
8. Therefore the Indo- Gangetic plains resulting in
high density of population.
7. How are the Eastern coastal plains and western coastal
plains similar or different .
The East Coastal plain:
1. It is located between the Eastern ghats and the Bay of Bengal.
2. It extends from West Bengal to Kanyakumari.
3. It is divided into Bengal, Utkal, Circar and Coromandal coasts.
4. It is wider and flat.
5. It has deltas, formed by the rivers Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna.
6. The East coastal plain is famous for food crops.
7. There are lakes like Chilka, Kolleru and Pulicat.
9. More irrigation facilities are in this plain.
The West Coastal plain:
1. It is located between the Western Ghats and the Arabian Sea.
2. It extends from Rann of Kutch to Kanyakumari.
3. It is divided into Gujarat, Konkan, Kanara and Malabar coasts.
4. It is narrow and uneven.
5. There are no deltas.
6. The West coastal plain is famous for cash crops.
7. The plain has no lakes but it has lagoons and back waters.
9. There are no irrigation facilities in this plain.
THE HIMALAYAS
TERRACED SLOPES
4 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
8. On an outline map of India show the following:
A. (i) Mountain and hill ranges the Karakoram, the Zanskar, the Patkai Bum, the Jaintia,
the Vindhya range, the Aravali, and the Cardamom hills.
(ii) Peaks K2, Kanchenjunga, Nanga Parbat and the Anaimudi.
(iii)Plateaus - Chhotanagpur and Malwa.
( iv)The Indian Desert, Western Ghats, Lakshadweep Islands.
MALWA
PLATEAU
MT. ANAIMUDI
CHOTA NAGPUR
PLATEAU
MT. K2
KARAKORAM RANGE
ZANSKAR RANGE
JAINTIA
CARDAMOM HILLS
KANCHENJUNGA
NANGA PARBAT
9. Plateau regions in India do not support
agriculture as much as the plain regions
what are the reasons for this?
1. A plain is a low lying land with leveled surface.
2. A plateau is an area of fairly level high ground to
the surrounding area.
3. The plains are most suitable for human
occupation.
4. The plains have fertile lands that are drained by
rivers.
5. Large part of agricultural activity is done on the
fertile plains.
6. The plateaus are mainly rich in mineral deposits.
7. The plateaus are covered by thin, light-textured
soils.
8. The plateaus quickly suffer from drought.
9. Thats why Plateau regions in India do not
support agriculture as much as the plain regions.
5
GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
Malwa
Plateau
Deccan
Plateau
Chota
Nagapur
Plateau
PLATEAUS IN
INDIA
INDIA HILLRANGES, PEAKS,
PLATEAUS AND THAR DESERT
10. Use an atlas and identify the following:
(i) The Islands formed due to Volcanic eruption.
1. Narcondam
2. Barren
(ii) The countries constituting Indian Subcontinent.
1. India
2. Pakistan
3. Bangladesh
4. Nepal
5. Bhutan
6. Sri Lanka
7. Maldives
(iii) The states through which the Tropic of Cancer passes.
1. Gujarat.
2. Rajasthan.
3. Madhya Pradesh.
4. Chhattisgarh.
5. Jharkhand.
6. West Bengal.
7. Tripura.
8. Mizoram.
(iv) The northernmost latitude in degrees - 376' North latitude
(v) The southernmost latitude of the Indian mainland in degrees.
A. The southernmost latitude of the Indian mainland is 84' N.
(vi) The eastern and the western most longitude in degrees.
A 1. The eastern most longitude is 9725'
2. The western most longitude is 687
(vii) The place situated on the three seas.
1. Kanyakumari is the place which is situated on the three seas.
2. They are i. Arabian sea ii. Indian Ocean and iii. Bay of Bengal
(viii)The strait separating Sri Lanka from India.
The Palk Strait separating Sri Lanka from India.
(ix) The Union Territories of India.
Union territories -Capital
1. Delhi -Delhi
2. Andaman & Nicobar (largest UT) -Port Blair
3. Chandigarh -Chandigarh
4. Dadra, Nagar Haveli -Silvassa
5. Daman, Diu -Daman
6. Lakshadweep (smallest UT) -Kavaratti
7. Pondicherry - Pondicherry
1
2
3
4
5
6 7 8
Tropic of Cancer
376' North latitude
84' North latitude
9
7
2
5
'
E
a
s
t
l
o
n
g
i
t
u
d
e
6
8
E
a
s
t
l
o
n
g
i
t
u
d
e
Kanyakumari
Indian Ocean
6 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
Text Book Questions page No. 2
Q. Why do we often use the term Indian peninsula?
A. 1. Peninsula means a piece of land three sides surrounded by water.
2. India is surrounded by the sea on three sides.
3. In the east Bay of Bengal, in the west Arabian sea and in the south
Indian Ocean.
4. Thats why we often use the term Indian peninsula
Q. Examine the map 1.1 above and imagine that India is
located in the Arctic Circle. How would your life be different?
A. If India located in the Arctic Circle our lifestyle would be like this:
i. India would be totally covered with ice.
ii. There would be no crops in India.
iii. Reindeer, seal, walrus and penguin would find here.
iv. Due to cold climate, population would be very low.
v. There would be no developed cities like Delhi, Mumbai and Chennai.
vi. In our life there would be no transport, rivers and lakes.
vii. Our food habits, lifestyle and culture may be different.
Q. Identify Indira point on the atlas. What is special
about this?
A. 1. Indira Point is the southern-most point of Republic of India.
2. It is situated in the Great Nicobar.
3. It was formerly known as Pygmalion Point.
4. It was renamed in honor of former Prime Minister
Indira Gandhi on 22-11-1985.
5. It was submerged during the 2004 Tsunami.
Q. Andhra Pradesh lies between and
N latitudes, and and .. E longitudes.
A. 1. Andhra Pradesh lies between 12N and 22N latitude.
2. Andhra Pradesh lies between 77 E and 84 E longitude.
Text Book Questions page No. 1
Q. Look at the world map above,
and write a few lines about
Indias location with reference to
the places marked on this map.
1. India is situated in the continent of
Asia.
2. India is situated in Northern and
eastern hemispheres.
3. India is surrounded three sides by
water.
4. Tropic of Cancer 23 North
latitude goes across our country.
376' North latitude
84' North latitude
9
7
2
5
'
E
a
s
t
l
o
n
g
i
t
u
d
e
6
8
7
'
E
a
s
t
l
o
n
g
i
t
u
d
e
Q. The lines of latitude and longitude are used for
accurately specifying location of any place or region. Use
the atlas and correct the following statement:
India is a very extensive country and lies totally in the
southern Hemisphere of the globe. The countrys mainland lies
between 8 degree N and 50 degree N longitude and 68 degree
S and 9 degree E latitude.
A. India is a very extensive country and lies totally in the northern
Hemisphere of the globe. The countrys mainland lies between 84'
N and 376' N latitude and 687' E and 9725' E longitude.
22NORTH LATITUDE
12 NORTH LATITUDE
8
4
E
A
S
T
L
O
N
G
I
T
U
D
E
7
7
E
A
S
T
L
O
N
G
I
T
U
D
E
7 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
Indira point
Q. Using the scale given in your atlas estimate the length of
the coast line for Andhra Pradesh?
A. Using the scale given in the atlas I estimat the length of the coast
line for Andhra Pradesh, that is 972 K.M.
Q. Look at the map .1.2 Trace the boundary for India and color
this. With the help of the scale given on the map, find out the
total land boundary that India shares with Bangladesh.
A. 1. The boundary for India in the given map is 24.5 cms.
2. Scale of the map is 1cm = 200 kms.
3. Total land boundary that India shares with Bangladesh is 4906 kms.
Q. Which of these data are for rising and setting times for the Sun at
Ahmedabad and Imphal. Explain your reason
A.
Reason:-
1. Imphal ( 93: E) is located to the east of Ahmedabad ( 72: E) .
2. So, Sun rises in the Imphal first.
3. Time difference between Imphal and Ahmedabad is 84 minutes.
Date Location _____ Location ____ ?
5
Jan
Sunrise
05:59
Sunset
16:37
Sunrise
07:20
Sunset 18:05
Ahmedabad Imphal
Date Location Imphal Location Ahmedabad
5
Jan
Sunrise
05:59
Sunset
16:37
Sunrise
07:20
Sunset 18:05
Text Book Questions page
No. 4
Q. The formation of Himalayas was ____ million years
ago while early hunter - gathering human beings
emerged on earth ____ million years ago.
A. 1. The formation of Himalayas was 200 million years ago
2. Hunter-gatherers emerged on earth 1.8 million years ago.
PURVANCHAL
Q. List the Himalayan rivers and the
Peninsular rivers that helped the
formation of north Indian Plain.
A. i. Himalayan rivers that helped the
formation of north Indian Plain.
1. Ganga and its tributaries like Yamuna,
Ramganga, Sarada, Kosi.
2. Indus and its tributaries like Jhelum,
Chenab, ravi, beas, Sutlej.
3. Bramhaputra and its tributaries.
ii. Peninsular rivers that helped the
formation of north Indian Plain.
1. Chambal
2. Betwa
3. Son
8 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
Q. Look at the fig 1.2 and the raised relief map in your school.
Using your finger trace the regions mentioned below:
Follow the course of Godavari and Krishna to identify the direction of
slope of Deccan plateau.
A. The direction of slope of Deccan plateau is slightly tilted towards
east.
Q. Describe the entire course of the Brahmaputra River, with
reference to landforms, heights, and countries.
A. 1. The eastern most boundary of the Himalayas is the Brahmaputra valley.
2. In Arunachal Pradesh beyond the Dihang valley, the Himalayas takes hair
pin bend.
3. The Brahmaputra River acts as eastern boundary of India
4. It runs through the north eastern states.
5. These divisions are known as Purvanchal.
6. Purvanchal mostly composed of sedimentary sand stones.
7. Regionally the Purvanchal are known as Patkai, the Naga, Manipuri, Khasi
and Mizo hills.
Text Book Questions page
No. 5
Q. Locate the three ranges in
your atlas.
A. 1. Himadri / Greater Himalayas
2. Himachal / lesser Himalayas
3. Shivaliks.
Q. Locate some of the highest
peaks in the raised relief map.
1. Mt. Everest (8848 mts)
2. Mt. K2 (8611 mts.)
3. Kanchenjunga (8586mts)
4. Dhaulagiri (8167mts)
5. Nanga Parbat (8126mts.)
6. Annapurna (8091mts)
7. Nanda Devi (7816mts)
Q. Trace with your
finger on the above
regions in the
raised relief map
and on the wall
map.
A. Dear students do this
activity with a wall map.
Q. Locate the
following places on
Indian physical map
in your atlas: Simla,
Mussorie, Nainital
and Raniket
A.
1. SIMLA
2. MUSSORIE
3. RANIKET
4. NAINITAL
1
2
3
4
COURSE OF
BRAMHAPUTRA
TSANGPO
THE SIANG
THE DIHANG
GODAVARI
COURSE OF
KRISHNA &
GODAVARI
THREE RANGES IN HIMALAYAS
HIGHEST PEAKS IN HIMALAYAS
9 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
Text Book Questions page No. 7
Locate the following ranges
in Indian physical map of
your Atlas
A.
PATKAI HILLS
NAGA HILLS
MANIPURI HILLS
MIZO HILLS
NORTH-EASTERN INDIA MAP
Hills State/ states
Purvanchal
hills
Assom,
Manipur
Nagaland
Mizoram
Patkai hills Assom
Nagaland
Naga hills Nagaland
Manipuri hills Manipur
Text Book Questions page No.
9
MALWA
PLATEAU
CHOTA NAGAPUR
PLATEAU
A. 1. Height of the Tibetan plateau - 4,500 mts.
2. Height of the Malwa Plateau 600 mts.
3. Height of the Bundelkhand - 500mts
4. Height of the Bhagelkhand 500mts
5. Height of the Rajmahal Hills 200300 m
6. Height of the Chota Nagapur Plateau - 1,350 m
6. Among these. Tibetan plateau is the highest
plateau.
Q. Locate the following on the Indian physical map of
your atlas and on the raised relief map:
Malwa plateau, Bundelkhand, Bhagelkhand,
Rajamahal Hills and Chhotanagpur plateau Using an
atlas compare the relative heights of above plateau
with that of Tibetan plateau
PERENNIAL CANAL
CORAL REEFS
COSTAL PLAINS
INDIAN PHYSICAL MAP
10 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
Text Book Questions page No.
10
Q. Look at the raised relief map and compare the
relative heights Western and Eastern Ghats as well
as Tibetan plateau and Himalayan peaks.
A. 1. The average height of Western Ghats is 2,695 m
2. The average height of Eastern Ghats is 1,680 m
3. Western Ghats have more height than eastern Ghats.
4. The height of Tibetan plateau is more than 4,500 mts
5. The height of Himalayan peaks are more than 6100 mts.
Text Book Questions page No.
12
KEY WORDS
1. Perennial :- Flowing throughout the year.
2. Coral reefs:- Coral reefs are underwater structures made
from calcium carbonate secreted by corals.
3. Costal plains :- Coastal plains are the area of flat, low-lying
land adjacent to a seacoast.
4. Peninsula :- Peninsula means a piece of land three sides
surrounded by water.
5. Laurasia :- Ancient continental mass in the Northern Hemisphere that
included North America, Europe, and Asia (except peninsular India).
6. Dun :- A narrow longitudinal flat-bottomed strike valley.
7. Angara land :- Ancient continental mass consisted of modern
continents of Asia and Europe.
8. Gondwana land :- Ancient continental mass consisted present-
day South America, Africa, Arabia, Madagascar, India, Australia,
and Antarctica.
9. Shivalik :- A mountain range of the outer Himalayas.
10. Purvanchal :- A geographic region of north-central India,
which comprises the eastern end of Uttar Pradesh state.
11. Leeward :- Towards the side sheltered from the wind.
12. Glaciers:- A huge mass of ice slowly flowing over a land mass.
Q. On the physical map of
India identify the delta
regions. How is their height
similar or different? How do
they compare in relation to
the northern plains?
A. 1. In India we have many deltas.
2. For example Ganga delta,
Godavari delta, Krishna Delta.
3. Deltas are formed at the mouth
of the rivers.
4. Plains are formed through the
erosion of the land by the rivers.
5. Deltas height is equal to the sea
level.
6. Where as plains height is high
than deltas.
Ganga Delta
Mahanadi delta
Godavari delta
Krishna delta
Penna delta
ANGARA LAND
LEEWARD
11 GURUDEVA.COM - NEW
You might also like
- World Map EnglishDocument1 pageWorld Map Englishapi-79737143No ratings yet
- National Symbols TeluguDocument1 pageNational Symbols Teluguapi-79737143No ratings yet
- 10.1 Guide PDFDocument11 pages10.1 Guide PDFsbikmm100% (1)
- General Studies Mains: Vision IasDocument3 pagesGeneral Studies Mains: Vision IasStephen GreenNo ratings yet
- Summary-Easy to Learn Geography- AnnualDocument14 pagesSummary-Easy to Learn Geography- Annualnathanielstanley001No ratings yet
- 1. 10th 1.INDIA RELIEF FETURES . pptDocument62 pages1. 10th 1.INDIA RELIEF FETURES . pptkattaharika03No ratings yet
- India - Location, Relief & DrainageDocument111 pagesIndia - Location, Relief & DrainageSathish K. Samy100% (1)
- G-INDIA LOCATION, PHYSICAL DIVISON - SpotlightDocument37 pagesG-INDIA LOCATION, PHYSICAL DIVISON - SpotlightkanishkranebennurNo ratings yet
- Tiss Guide: PresentsDocument39 pagesTiss Guide: Presentsscribd_poorviNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography: Area and BoundariesDocument18 pagesIndian Geography: Area and BoundariesRubini DeviNo ratings yet
- Concise NotesDocument786 pagesConcise NotesGade IndhuNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography Complete 9 HRDocument248 pagesIndian Geography Complete 9 HRMurtaza Yousuf100% (1)
- GeographyDocument189 pagesGeographyNijam Nagoor100% (1)
- Indian Geography UPSC NotesDocument15 pagesIndian Geography UPSC NotesKeShav JasrotiaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument24 pagesUntitledwocipNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Physical Features of India Question/AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter-2 Physical Features of India Question/AnswersabhilashagoelNo ratings yet
- Geography - IIDocument127 pagesGeography - IIsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- IDocument5 pagesIanshum11No ratings yet
- Ba 2 India PhysiographyDocument11 pagesBa 2 India PhysiographySAURABH KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 GeoDocument34 pagesCHAPTER 1 GeoAmanSundarkaNo ratings yet
- Notes of Our Country - IndiaDocument4 pagesNotes of Our Country - Indianityamaggarwal566566No ratings yet
- Indian Geography - pdf-54Document7 pagesIndian Geography - pdf-54lolu pandey100% (1)
- Indian Relief Features - PW-1Document10 pagesIndian Relief Features - PW-1Abhinand PrakashNo ratings yet
- g6 Our Country NotesDocument4 pagesg6 Our Country NotesTanvika AroraNo ratings yet
- Our Country IndiaDocument11 pagesOur Country IndiaMohd. JavedNo ratings yet
- Vision Ias Geography Xaam - inDocument81 pagesVision Ias Geography Xaam - inharsha143sai100% (2)
- GeographyDocument38 pagesGeographyAvinesh NandakumarNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography of IndiaDocument24 pagesPhysical Geography of IndiaovaisnabiNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography Upsc Notes 67Document10 pagesIndian Geography Upsc Notes 67gunjankushwaha0000No ratings yet
- FG PDFDocument111 pagesFG PDFMarthala Venkata Ravi Teja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Easy To Learn Geography - AnnualDocument14 pagesEasy To Learn Geography - Annualaa7638956No ratings yet
- ReliefDocument35 pagesReliefHage sunyaNo ratings yet
- Geography of India: Indo-Gangetic PlainDocument5 pagesGeography of India: Indo-Gangetic PlainchunnumunnuNo ratings yet
- Social 1 EM Chapter MaterialDocument2 pagesSocial 1 EM Chapter MaterialarshiyaNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography PDFDocument40 pagesIndian Geography PDFMragendra SinghNo ratings yet
- GEO Indian and World Geography - DS Rajput PDFDocument42 pagesGEO Indian and World Geography - DS Rajput PDFbestread67100% (3)
- Indian and World Geography PDFDocument42 pagesIndian and World Geography PDFSharathReddy100% (3)
- CH - 7(a) India - Its Geographical FeaturesDocument15 pagesCH - 7(a) India - Its Geographical FeaturesshineforgodjesusNo ratings yet
- 8th GeoL10 1Document9 pages8th GeoL10 1bhavyakapadia149No ratings yet
- GEO_CHAPTER_1,2&3Document9 pagesGEO_CHAPTER_1,2&3riturathee89No ratings yet
- Social Geography Notes India Relief and DrainageDocument14 pagesSocial Geography Notes India Relief and Drainagestudyzmail01No ratings yet
- 1 Physiotherapic Divisions of IndiaDocument10 pages1 Physiotherapic Divisions of IndiaGeo MindNo ratings yet
- Part I General Studies Mains Geography of India Vision IasDocument36 pagesPart I General Studies Mains Geography of India Vision IaschandranshupushkarnaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Social NotesDocument30 pagesClass 9 Social NotesLuka MegurineNo ratings yet
- Physiographic Division of IndiaDocument22 pagesPhysiographic Division of IndiaHage sunyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Physical Features of IndiaDocument5 pagesCBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Physical Features of Indiaanshul7ahoodaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Physical Features of IndiaDocument5 pagesCBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Physical Features of IndiaPraneeth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography Revision SlidesDocument256 pagesIndian Geography Revision SlidesSateesh100% (1)
- Indian Geography Class-2 (Vidya Guru)Document41 pagesIndian Geography Class-2 (Vidya Guru)jasleghaNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Polity Ch-1,2,3 PDFDocument22 pagesClass 9th Polity Ch-1,2,3 PDFsaketkumardhruw09No ratings yet
- THE LAND OF DIVERSITIES-NOTE (11)Document9 pagesTHE LAND OF DIVERSITIES-NOTE (11)Ramadevi KumarNo ratings yet
- Where in the World is Nepal? Geography Books | Children's Explore the World BooksFrom EverandWhere in the World is Nepal? Geography Books | Children's Explore the World BooksNo ratings yet
- The Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India: Ethnological Study of the Caste SystemFrom EverandThe Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India: Ethnological Study of the Caste SystemNo ratings yet
- The Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India (Vol. 1-4): Ethnological Study of the Caste SystemFrom EverandThe Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India (Vol. 1-4): Ethnological Study of the Caste SystemNo ratings yet
- Interesting Facts About Afghanistan That You Should Know: Discovering CountriesFrom EverandInteresting Facts About Afghanistan That You Should Know: Discovering CountriesNo ratings yet
- Em Bit Bank NewDocument24 pagesEm Bit Bank Newapi-79737143No ratings yet
- Project Works All ClassesDocument30 pagesProject Works All Classesapi-79737143100% (1)
- Model Paper For VidyamruthamDocument38 pagesModel Paper For Vidyamruthamapi-79737143No ratings yet
- X Class Maping Skills BookDocument32 pagesX Class Maping Skills Bookapi-79737143No ratings yet
- D Grade SSC TM p2Document24 pagesD Grade SSC TM p2api-79737143100% (1)
- 1em KeyDocument6 pages1em Keyapi-79737143No ratings yet
- Group - A: IndiaDocument2 pagesGroup - A: Indiaapi-79737143No ratings yet
- Map Pointing - Book Setting Final em - 2016-17Document48 pagesMap Pointing - Book Setting Final em - 2016-17api-7973714367% (6)
- 0004Document56 pages0004api-79737143100% (1)
- SSC Blue Print ModelDocument1 pageSSC Blue Print Modelapi-79737143No ratings yet
- 100 Days ProgrammeDocument14 pages100 Days Programmeapi-79737143No ratings yet
- Social Bit 1111Document3 pagesSocial Bit 1111api-79737143No ratings yet
- SSC Social Studies Model PaperDocument78 pagesSSC Social Studies Model Paperapi-79737143No ratings yet
- Andhra Pradesh Visiting Places Map EnglishDocument1 pageAndhra Pradesh Visiting Places Map Englishapi-79737143No ratings yet
- National Symbols EnglishDocument1 pageNational Symbols Englishapi-79737143No ratings yet
- Andhra Pradesh State Symbols TeluguDocument1 pageAndhra Pradesh State Symbols Teluguapi-79737143No ratings yet
- 10th Class Social Bit ExamDocument3 pages10th Class Social Bit Examapi-79737143No ratings yet
- Andhra Pradesh State Symbols EnglishDocument1 pageAndhra Pradesh State Symbols Englishapi-79737143No ratings yet
- 10th Class Social Bit ExamDocument3 pages10th Class Social Bit Examapi-79737143100% (1)
- Andhra Pradesh Outline Map Telugu-EnglishDocument1 pageAndhra Pradesh Outline Map Telugu-Englishapi-79737143No ratings yet
- 1 Andhra Pradesh Political Map TeluguDocument1 page1 Andhra Pradesh Political Map Teluguapi-79737143No ratings yet
- 100 Days Action Plan English Medium Social StudiesDocument29 pages100 Days Action Plan English Medium Social Studiesapi-79737143100% (2)
- Social Bit 2Document3 pagesSocial Bit 2api-79737143100% (1)
- 10th Class Social Bit Exam AutosavedDocument3 pages10th Class Social Bit Exam Autosavedapi-79737143No ratings yet
- Project Model 2 1Document2 pagesProject Model 2 1api-79737143No ratings yet
- Social BitDocument2 pagesSocial Bitapi-79737143No ratings yet
- 02 Vibrostar enDocument12 pages02 Vibrostar enPaul PetrilaNo ratings yet
- History of The Middle Ages Ye. Agibalova, G. DonskoyDocument305 pagesHistory of The Middle Ages Ye. Agibalova, G. Donskoybiorox00xNo ratings yet
- Kempe Gowda I - WikipediaDocument5 pagesKempe Gowda I - Wikipediamdu59714No ratings yet
- Farm Records and PlanningDocument20 pagesFarm Records and PlanningtinyikoNo ratings yet
- Occular Site Evaluation Report: Project Title: Green Archers Phase 2Document3 pagesOccular Site Evaluation Report: Project Title: Green Archers Phase 2Mark Allandale DedelNo ratings yet
- CalarasiDocument26 pagesCalarasicrisstina1979No ratings yet
- Soil ResourceDocument2 pagesSoil ResourceAyush YadavNo ratings yet
- CHIMDESAANDSORIAJITASRMARCH2023Document10 pagesCHIMDESAANDSORIAJITASRMARCH2023dawud kuroNo ratings yet
- Cement Stabilized Akwuete Lateritic Soil and The Use of Bagasse Ash As AdmixtureDocument5 pagesCement Stabilized Akwuete Lateritic Soil and The Use of Bagasse Ash As AdmixtureInternational Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations100% (1)
- Exercise 3 and 4Document2 pagesExercise 3 and 4warditemp5No ratings yet
- Summer 2005 Natural FarmerDocument48 pagesSummer 2005 Natural FarmerV1xWqNo ratings yet
- FAO Forage Profile - MauritaniaDocument22 pagesFAO Forage Profile - MauritaniaAlbyziaNo ratings yet
- Ipni CatalogoDocument32 pagesIpni CatalogoAlexéiNo ratings yet
- Weed Control in GroundnutDocument112 pagesWeed Control in Groundnutamit kumawatNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Leasehold Agricultural Tenancy Definition and Nature of Agricultural TenancyDocument17 pagesAgricultural Leasehold Agricultural Tenancy Definition and Nature of Agricultural TenancyCarla VirtucioNo ratings yet
- Perform Irrigation v2Document8 pagesPerform Irrigation v2VanzNo ratings yet
- Flood ControlDocument4 pagesFlood ControlpuneetthurkiNo ratings yet
- Little TuppenDocument17 pagesLittle TuppenShanmugapriya Kosalram0% (1)
- CH 4Document22 pagesCH 4Karthikeya SarmaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Harvesting Grain Sorghum: Gary HuitinkDocument4 pages8 - Harvesting Grain Sorghum: Gary Huitinkberihu tesfayNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh StudiesDocument20 pagesBangladesh StudiesMD Rifat ZahirNo ratings yet
- How Much Land Does A Man Need1Document15 pagesHow Much Land Does A Man Need1Siddharth SambaruNo ratings yet
- AGRICULTURE NoteDocument4 pagesAGRICULTURE NoteanoushkalambatNo ratings yet
- Nigeria Farm AccountingDocument131 pagesNigeria Farm AccountingLuke Shaw100% (1)
- Langdon, John - The Economics of Horses and Oxen in Medieval EnglandDocument10 pagesLangdon, John - The Economics of Horses and Oxen in Medieval EnglandBenedict HandlifeNo ratings yet
- Erinmope at A GlanceDocument8 pagesErinmope at A Glancejoshua4lifeNo ratings yet
- IntoductionDocument5 pagesIntoductionShahnawaz ZardariNo ratings yet
- Forest LawsDocument4 pagesForest LawsLibay Villamor IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Scatter Plots and Linear Correlations: R N XyDocument3 pagesScatter Plots and Linear Correlations: R N XycmisaacNo ratings yet
- Contract of Lease - HaciendaDocument5 pagesContract of Lease - HaciendaaceamulongNo ratings yet