0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
316 viewsRail-To-Rail Input and Output Amplifiers
This document discusses rail-to-rail input and output amplifiers. It begins by explaining why rail-to-rail operation is important for low supply voltages to maximize dynamic range. It then describes three techniques for implementing rail-to-rail amplifiers: using a 3x current mirror to equalize transconductances; using Zener diodes; and using a current regulator. Performance results are provided for amplifiers using these techniques, including ones operating down to 1.3V and 1.5V supply voltages.
Uploaded by
assbassCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
316 viewsRail-To-Rail Input and Output Amplifiers
This document discusses rail-to-rail input and output amplifiers. It begins by explaining why rail-to-rail operation is important for low supply voltages to maximize dynamic range. It then describes three techniques for implementing rail-to-rail amplifiers: using a 3x current mirror to equalize transconductances; using Zener diodes; and using a current regulator. Performance results are provided for amplifiers using these techniques, including ones operating down to 1.3V and 1.5V supply voltages.
Uploaded by
assbassCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 71
Willy Sansen 10-05 111
Rail-to-rail input and output
amplifiers
Willy Sansen
KULeuven, ESAT-MICAS
Leuven, Belgium
willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be
Willy Sansen 10-05 112
Table of contents
Why rail-to-rail ?
3 x Current mirror rtr amplifiers
Zener diode rtr amplifiers
Current regulator rtr amplifier on 1.5 V
Supply regulating rtr amplifier on 1.3 V
Other rtr amplifiers and comparison
Willy Sansen 10-05 113
For low supply voltages : use full range for
maximum dynamic range
Fully differential signal processing
Rail-to-rail output is always required
But not necessarily rail-to-rail-input !
Why rail-to-rail amplifiers ?
Willy Sansen 10-05 114
Symmetrical CMOS OTA
1 2
3
4
5
V
DD
V
SS
v
OUT
C
L
M1 M2
M3 M4
M8
M6
M7
+
-
M5
M9
1 : B B : 1
Rail-to-rail
output swing !
Symmetrical OTA
1 : : 1
Willy Sansen 10-05 115
When rail-to-rail input ?
+
-
v
OUT
R
2
R
1 v
IN
+
-
v
OUT
R
2
R
1
v
IN
+
-
v
OUT
v
IN
No !
No !
Yes !
+
-
+
-
+
-
Willy Sansen 10-05 116
Rail-to-rail input for CMFB
A
v
ind
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
C
L
v
outd
C
L
A
d
A
c
v
inc
CMFB
For a rail-to-rail output swing in fully-differential amplifiers
A CMFB amplifier is required
With rail-to-rail input capability !
Willy Sansen 10-05 117
Table of contents
Why rail-to-rail ?
3 x Current mirror rtr amplifiers
Zener diode rtr amplifiers
Current regulator rtr amplifier on 1.5 V
Supply regulating rtr amplifier on 1.3 V
Other rail-to-rail amplifiers
Willy Sansen 10-05 118
Problem ?
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
V
GSn
V
DSsatn
V
GSp
V
DSsatp
V
INCM
> 1.1 V
V
INCM
< V
DD
- 1.1 V
V
GS
0.9 V & V
DSsat
0.2 V >>> V
GSDS
= 1.1 V
+
= V
GSDS
+
= V
GSDS
Willy Sansen 10-05 119
Problem : limited input CM range
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
I
B
I
B
+ -
i
out
+
i
out
-
i
out
+
i
out
-
To be operational :
V
INCM
> 1.1 V
V
INCM
< V
DD
- 1.1 V
g
mn
g
mp
V
DDmin
= 2.2 V
Willy Sansen 10-05 1110
Problem: unequal g
mtot
nMOST on :
V
INCM
> 1.1 V
V
INCM
V
SS
= 0 V
DD
/2 V
DD
g
m
pMOST on : V
INCM
< V
DD
- 1.1 V
nMOST
pMOST
g
mtot
1.1 V
V
DD
-1.1 V
g
mn
g
mp
Willy Sansen 10-05 1111
Solution : g
m
equalization
nMOST on :
V
INCM
> 1.1 V
V
INCM
V
SS
= 0 V
DD
/2 V
DD
g
m
pMOST on : V
INCM
< V
DD
- 1.1 V
nMOST
pMOST
g
mtot
1.1 V
V
DD
-1.1 V
Increase g
m
:
g
mn
+ g
mp
= ct
g
mn
g
mp
Willy Sansen 10-05 1112
Equalize g
mtot
in strong inversion
g
mn
+ g
mp
= ct1
2 K
n
I
Bn
+ 2 K
p
I
Bp
= ct1
K
n
I
Bn
+ K
p
I
Bp
= ct2
W
n
L
n
W
p
L
p
I
Bn
+ I
Bp
= ct3
3 x Current mirror : 1 + 1 = 0 + 4 > 4 - 1 = 3
Willy Sansen 10-05 1113
3x Current mirror for nMOSTs
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
I
B
I
B
+ -
i
out
+
i
out
-
i
out
+
i
out
-
g
mn
g
mp
1 : 3
V
rn
I
B
x 4
M
rn
Willy Sansen 10-05 1114
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
I
B
I
B
+ -
g
mn
g
mp
1 : 3
V
rn
I
B
x 4
3 : 1
V
rp
I
B
x 4
3x Current mirror for all MOSTs
M
rn
M
rp
Willy Sansen 10-05 1115
3x Current mirror : performance
V
INCM
V
SS
= 0 V
DD
/2 V
DD
g
m
nMOST
pMOST
g
mtot
1.1 V
V
DD
-1.1 V
g
mn
g
mp
g
m
/g
m
= 15%
g
mtot
~ (4 - 3x) I
B
+ x I
B
g
m
/g
m
= 15% (x=1/3)
Willy Sansen 10-05 1116
Ref.Hogervorst, JSSC Dec.1994, 1505-1512
6.4 MHz
/ 10 pF
6.4 V/s
31 nV/ Hz
3.3 V
0.18 mA
3 mApk
1: 3
1: 3
Rail-to-rail opamp
Willy Sansen 10-05 1117
Table of contents
Why rail-to-rail ?
3 x Current mirror rtr amplifiers
Zener diode rtr amplifiers
Current regulator rtr amplifier on 1.5 V
Supply regulating rtr amplifier on 1.3 V
Other rail-to-rail amplifiers
Willy Sansen 10-05 1118
Zener diodes
V
Z
I
DS
V
GS
V
T
0 V
Z
I
D
V
D
V
BEon
0.7 V
0
V
Z
Electronic Zener
Willy Sansen 10-05 1119
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
8I
B
8I
B
+
-
g
mn
g
mp
Rail-to-rail amplifier with Zener diode
1 : 6
1 : 6
6 : 1
6 : 1
V
Z
V
Z
= V
GSn
+V
GSp
I
B
I
B
Willy Sansen 10-05 1120
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
8I
B
+
-
g
mn
Rail-to-rail amplifier with Zener diode
1 : 6
1 : 6
6 : 1
6 : 1
V<V
Z
V
Z
= V
GSn
+V
GSp
4I
B
4I
B
Willy Sansen 10-05 1121
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
8I
B
8I
B
+ -
g
mn
g
mp
Rtr amp. with electronic Zener
I
B
I
B
V
Z
Willy Sansen 10-05 1122
Rail-to-rail amp. with Zener : performance
V
INCM
V
SS
= 0 V
DD
/2 V
DD
g
m
nMOST
pMOST
g
mtot
1.1 V
V
DD
-1.1 V
g
mn
g
mp
Zener: g
m
/g
m
= 25% Electronic Zener: g
m
/g
m
= 6%
High current
High SR !
Ref.Hogervorst, JSSC July 1996, 1035-1040
Willy Sansen 10-05 1123
Table of contents
Why rail-to-rail ?
3 x Current mirror rtr amplifiers
Zener diode rtr amplifiers
Current regulator rtr amplifier on 1.5 V
Supply regulating rtr amplifier on 1.3 V
Other rail-to-rail amplifiers
Willy Sansen 10-05 1124
Equalize g
mtot
in weak inversion
g
mn
+ g
mp
= ct
+ = ct
I
Bn
2 n
n
kT/q
I
Bp
2 n
p
kT/q
I
Bn
+ I
Bp
= ct
n
p
n
n
n = 1 +
C
ox
C
D
(V
BS
)
Willy Sansen 10-05 1125
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
4I
B
+ -
g
mn
g
mp
1 :
V
ref
Rail-to-rail amplifier with current switch
n
p
n
n
I-switch
I
B
I
B
I
B
I
B
2I
B
M
r
Willy Sansen 10-05 1126
Rtr amp. with I-switch : performance
V
INCM
V
SS
= 0 V
DD
/2 V
DD
g
m
nMOST
pMOST
g
mtot
1.1 V
V
DD
-1.1 V
g
mn
g
mp
Current switch : V
ref
very critical !
V
ref
= 0.5 V
V
ref
= 0.3 V
V
ref
= 0.4 V
Willy Sansen 10-05 1127
Ref. : Wu etal, JSSC Jan.1994, pp.63-66
14 MHz
/ 11pF
5.6 MHz
/ 100pF
4 V/s
36 nV/ Hz
5 V
0.4 mA
g
m1
v
in
g
m3
v
in
Willy Sansen 10-05 1128
I
DS
x 2
g
m
x 2
Biasing :
Ref. : Wu etal, JSSC Jan.1994, pp.63-66
Willy Sansen 10-05 1129
Input rail-to-rail stage
V
DD
2
V
DD
= 5V
0V
V
DD
20
20
5
5
5
5
10
10
10
10
20
20
20
0
0
20
5V
1.5V 1.5V
pMOSTs off !
V
+-
high :
nMOSTs :
I
DS1
x 2
g
m1
x 2
Willy Sansen 10-05 1130
V
DD
V
SS
= 0
2I
Bp
2I
Bn
+ -
g
mn
g
mp
Current regulator FB loop
180
o
C
c
I
Bp
I
Bn
4I
B
n
p
n
n
S
Willy Sansen 10-05 1131
2I
Bp
2I
Bn
g
mn
g
mp
Current regulator FB loop : replica biasing
2I
Bp
2I
Bn
g
mn
g
mp
in+ in- in+ in-
Willy Sansen 10-05 1132
Replica biasing with one transistor
+
-
R
L
R
L
R
S
v
IN
v
OUT
V
REF
Willy Sansen 10-05 1133
Replica biasing with differential pair
g
mn
in+ in-
2I
Bn
g
mn
in+
in-
180
o
2I
Bn
I
REF
Willy Sansen 10-05 1134
4I
B
C
c
+
-
V
DD
Current regulator rail-to-rail amplifier
+
-
V
SS
2I
Bp
2I
Bn
n
p
n
n
1 :
Replica biasing block Input stage
S
Willy Sansen 10-05 1135
I-regulator rtr amplifier
E.Peeters etal,
CICC 1997
Willy Sansen 10-05 1136
Total amplifier schematic
E.Peeters etal, CICC 1997
Willy Sansen 10-05 1137
Output stage
Willy Sansen 10-05 1138
V
INCM
V
SS
= 0 V
DD
/2 V
DD
3 V
g
m
nMOST
pMOST
g
mtot
V
DD
- 1.1 V
1.1 V
g
mn
g
mp
n - mismatch : g
m
/g
m
4%
Current-regulator rtr amp. : performance
Willy Sansen 10-05 1139
V
INCM
V
SS
= 0 V
DD
1.5 V
g
m
nMOST pMOST
g
mtot
V
DD
- 1.1 V
1.1 V
g
mn
g
mp
n - mismatch : g
m
/g
m
4%
Current-regulator rtr amp. : towards 1.5 V
0
Willy Sansen 10-05 1140
GBW error
4 %
Willy Sansen 10-05 1141
Input offset voltage
Willy Sansen 10-05 1142
Rail-to-rail Opamp with Current regulator
V
DD
= 1.5 V
I
TOT
= 0.2 mA
g
m
/g
m
= 4 %
GBW = 4.3 MHz
C
L
= 15 pF
E.Peeters etal, CICC 1997
Willy Sansen 10-05 1143
Table of contents
Why rail-to-rail ?
3 x Current mirror rtr amplifiers
Zener diode rtr amplifiers
Current regulator rtr amplifier on 1.5 V
Supply regulating rtr amplifier on 1.3 V
Other rail-to-rail amplifiers
Willy Sansen 10-05 1144
V
INCM
V
SS
= 0 V
DD
1.3 V
g
m
nMOST
pMOST
g
mtot
g
mn
g
mp
n - mismatch and g
mtot
dip : g
m
/g
m
15 %
Internal V
DD
Regulator
I
Bn
+ I
Bp
= ct
n
p
n
n
Weak inversion :
V
DD
/2
g
mtot
/2
Minimum V
DD
?
Minimum V
GS
+V
DSsat
?
Independent of V
T
s !
0
Willy Sansen 10-05 1145
V
DD
1.3 V
V
SS
= 0
I
Bp
?
I
Bn
?
+ -
i
out
+
i
out
-
i
out
+
i
out
-
g
mn
g
mp
Regulating V
DD
: total schematic
V
DDext
C
c
V
OUT
Willy Sansen 10-05 1146
I
B
V
DD
Replica biasing block
V
SS
I
Bp
I
Bn
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDext
V
SS
S
Ferri, .. JSSC Oct.97, 1563-1567
Willy Sansen 10-05 1147
V
DD
Internal V
DD
regulator
V
SS
I
Bp
I
Bn
V
DDext
2 : 1
2 : 1
V
GSn
V
GSp
V
DSsatn
V
DSsatp
M
R
M
P
M
A
Willy Sansen 10-05 1148
Total amplifier schematic
Vext
Ferri, .. JSSC Oct.97, 1563-1567
Willy Sansen 10-05 1149
Internal supply voltage
V
V
Willy Sansen 10-05 1150
GBW error
V
IN,CM
(V)
GBW
(MHz)
Willy Sansen 10-05 1151
Rail-to-rail amp. with V
DD
regulator : Specs
V
DDmin
= 1.3 V
GBW = 1.3 MHz in C
L
= 15 pF
g
m1
= 200 S
I
DSn1
= 10 A
W/L
in
= 830
I
TOT
= 354 A
V
in,eq
= 25 nV
RMS
/Hz
V
in,offset
= 0.8 mV (3 = 0.2 mV)
Ferri, .. JSSC Oct.97, 1563-1567
Willy Sansen 10-05 1152
Rtr Opamp with V
DD
-regulator
Willy Sansen 10-05 1153
Rail-to-rail with V
DD
regulator : min V
DD
V
DDmin
= 2 (V
GS
+ V
DSsat
)
= 2 (V
GS
- V
T
+ V
T
+ V
GS
- V
T
)
= 2 [V
T
+ 2(V
GS
- V
T
)]
= 2 [0.6 + 2(0.15)] = 1.8 V
= 2 [0.3 + 2(0.10)] = 1.0 V !!!!
Willy Sansen 10-05 1154
Table of contents
Why rail-to-rail ?
3 x Current mirror rtr amplifiers
Zener diode rtr amplifiers
Current regulator rtr amplifier on 1.5 V
Supply regulating rtr amplifier on 1.3 V
Other rail-to-rail amplifiers
Willy Sansen 10-05 1155
Rail-to-rail opamp with current summation
Redman-White, JSSC May 97, 701-712
3.3 V
2.3 mW
(2.2 V min.)
Gm 10%
THD :
-55 dB
40 MHz
9 mW
0.5 m CMOS
Willy Sansen 10-05 1156
Duisters, .., JSSC
July 98,pp.947-955
Opamp with voltage multiplier
Vddx - Vdd 1 V
= Vdd/2
1.8 - 3.3 V
0.75 mA
6.5 MHz
On 3 V :
2.8 V
ptpt
THD :
-90 dB /10k
-81 dB/32
0.5 m CMOS
Willy Sansen 10-05 1157
Rail-to-rail opamp with differential signal proc.
Ref.Lin, AICSP 1999, 153-162
Idsn
Idsp
Willy Sansen 10-05 1158
Maximum-current selecting circuits
Ref.Lin, AICSP 1999, 153-162
Idsn
Idsp
Willy Sansen 10-05 1159
Maximum-current selecting circuit
V
DD
+
-
V
SS
Input stage
Willy Sansen 10-05 1160
Transconductance equalizer circuit
Ref.Lin, AICSP 1999, 153-162
V
GS3
+ V
GS2
= V
GS1
+ V
GS4
K
p
I
pbias
= K
n
I
nbias
g
mp
= g
mn
Willy Sansen 10-05 1161
Rail-to-rail opamp with max.-current selector
Ref.Lin, AICSP 1999, 153-162
1.9 MHz 20 pF
3 V/ 0.26 mA
max.curr.selector max.curr.selector g
m
equalizer
Willy Sansen 10-05 1162
Rail-to-rail opamp with max.-current selector
max.curr.selector g
m
equalizer
Ref.Lin, AICSP 1999, 153-162
1.9 MHz 20 pF
3 V/ 0.26 mA
Willy Sansen 10-05 1163
Rail-to-rail opamp on 1 Volt Supply
Ref.Duque-Carrillo, JSSC Jan.2000, 33-43
V
IN
V
DD
= 1 V
0 V
V
IN
I
DS
0 0.5 1 V
I
DSp
I
DSn
Willy Sansen 10-05 1164
Rail-to-rail opamp on 1 Volt
Ref.Duque-Carrillo, JSSC Jan.2000, 33-43
R
R
I
B
I
B
V
IN
V
IN
V
DD
= 1 V V
DD
= 1 V
0 V 0 V
Willy Sansen 10-05 1165
Rail-to-Rail opamp on 1 Volt
Ref.Duque-Carrillo, JSSC Jan.2000, 33-43
R
R
I
B
I
B
V
IN
V
DD
= 1 V
0 V
I
B
0 0.5 1 V
V
INn
V
INp
V
IN
0 0.5 1 V
V
IN
V
INn
V
INp
I
Bmax
V
INp
RI
Bmax
V
INn
1 V
0
0.5
Willy Sansen 10-05 1166
Ref.Duque-Carrillo, JSSC Jan.2000, 33-43
2 MHz
15 pF
1 V
0.4 mA
I
offset
< 1 A
R I
offset
noise
RtR opamp : full opamp schematic
Willy Sansen 10-05 1167
Ref.Duque-Carrillo, JSSC Jan.2000, 33-43
RtR opamp : current generator
I
B
current summer
Willy Sansen 10-05 1168
Comparison rail-to-rail input amplifiers
Type Ref. g
m
/g
m
GBW I
TOT
V
DDmin
% MHzpF/mW A V
3x Curr.mirr. JSSC-12-94 15 110 150 3
Electr. Zener JSSC-7-96 6 70 215 2.7
Curr.switch AICSP-5-94 8 1.1 500 3.3
Curr.regulat. CICC 97 4 210 200 1.5
Regulat. VDD JSSC-10-97 6 43 350 1.3
MOST translin. AICSP-6-94 8 4.2 800 2.5
Improv.CMRR JSSC-2-95 9 3 1400 5
Max. current AICSP-1-99 10 77 260 3
Resistive input JSSC-1-00 x 75 400 1
Willy Sansen 10-05 1169
Table of contents
Why rail-to-rail ?
3 x Current mirror rtr amplifiers
Zener diode rtr amplifiers
Current regulator rtr amplifier on 1.5 V
Supply regulating rtr amplifier on 1.3 V
Other rail-to-rail amplifiers
Willy Sansen 10-05 1170
References
T. Duisters, etal, A -90 dB THD rail-to-rail input opamp using a new local charge pump in
CMOS", IEEE Journal Solid-State Circuits, Vol. SC-33, pp. 947-955, July 1998.
R. Duque-Carillo, etal, "A 1 V rail-to-rail operational amplifier in standard CMOS
technology", IEEE Journal Solid-State Circuits, Vol. SC-35, pp. 33-43, Jan. 2000.
G.Ferri, W.Sansen, A rail-to-rail constant-gm low-voltage CMOS operational
transconductance amplifier", IEEE Journal Solid-State Circuits, Vol. SC-32, pp. 1563-1567,
Oct.1997.
R. Hogervorst, etal, "A compact power-efficient 3V CMOS rail-to-rail input/output
operational amplifier for VLSI cell libraries", IEEE Journal Solid-State Circuits, Vol. SC-29,
pp. 1504-1512, Dec.1994.
R. Hogervorst, etal, Compact CMOS constant-gm rail-to-rail input stage with gm-control by
an electronic Zener diode", IEEE Journal Solid-State Circuits, Vol. SC-31, pp. 1035-1040,
July 1996.
R. Lin, etal, "A compact power-efficient 3V CMOS rail-to-rail input/output operational
amplifier for VLSI cell libraries", Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, Kluwer
Ac., pp. 153-162, Jan.1999.
Willy Sansen 10-05 1171
References
E. Peeters, etal, "A compact power-efficient 3V CMOS rail-to-rail input/output operational
amplifier for VLSI cell libraries", CICC 1997.
W. Wu, etal, Digital-compatible high-performance operational amplifier with rail-to-rail
input and output stages", IEEE Journal Solid-State Circuits, Vol. SC-29, pp. 63-66, Jan 1994.
You might also like
- Two-Stage Operational Amplifier Design Using Gm/Id MethodNo ratings yetTwo-Stage Operational Amplifier Design Using Gm/Id Method7 pages
- AnalogICdesign-chapter5 - Current MirrorNo ratings yetAnalogICdesign-chapter5 - Current Mirror28 pages
- Advanced Current Mirrors and Opamps: Hossein ShamsiNo ratings yetAdvanced Current Mirrors and Opamps: Hossein Shamsi45 pages
- C3.0 Operational Amplifiers II: Jeng-Han TsaiNo ratings yetC3.0 Operational Amplifiers II: Jeng-Han Tsai12 pages
- Random Offset CMOS IC Design CU Lecture Art Zirger PDFNo ratings yetRandom Offset CMOS IC Design CU Lecture Art Zirger PDF46 pages
- Lab 2: Common Source Amplifier With Resistor Load and Source Degeneration100% (1)Lab 2: Common Source Amplifier With Resistor Load and Source Degeneration28 pages
- Channel Length Modulation: A Second Order Effect of MOSFETNo ratings yetChannel Length Modulation: A Second Order Effect of MOSFET8 pages
- A High Performance CMOS Band - Gap Reference Circuit DesignNo ratings yetA High Performance CMOS Band - Gap Reference Circuit Design6 pages
- Source Follower: (Common-Drain Amplifier)No ratings yetSource Follower: (Common-Drain Amplifier)40 pages
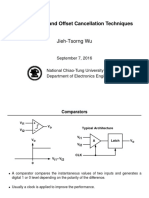
- 04 - Comparators and Offset Cancellation Techniques100% (2)04 - Comparators and Offset Cancellation Techniques68 pages
- 4.chapter4 CMOS Multistages Differential AmplifierNo ratings yet4.chapter4 CMOS Multistages Differential Amplifier60 pages
- Design and Analysis of Low Power Bandgap Voltage ReferenceNo ratings yetDesign and Analysis of Low Power Bandgap Voltage Reference8 pages
- Low Power High Speed Cmos Comparator DesignNo ratings yetLow Power High Speed Cmos Comparator Design5 pages
- V I (IN Ma) : Figure 1: Setup For NMOS Characteristics Table 1: Vds VS ID Data at VGS 5 VoltsNo ratings yetV I (IN Ma) : Figure 1: Setup For NMOS Characteristics Table 1: Vds VS ID Data at VGS 5 Volts17 pages
- 1986 Steyaert Novel CMOS Schmitt Trigger PDF100% (1)1986 Steyaert Novel CMOS Schmitt Trigger PDF3 pages
- Compact Power Efficient Rail To Rail in Out Op Amp RonNo ratings yetCompact Power Efficient Rail To Rail in Out Op Amp Ron9 pages
- Important Opamp Configurations: Willy Sansen0% (1)Important Opamp Configurations: Willy Sansen52 pages
- Integrated Circuits: Multistage Amplifiers, Current Sources & Current MirrorsNo ratings yetIntegrated Circuits: Multistage Amplifiers, Current Sources & Current Mirrors25 pages
- Two-Stage Operational Amplifier Design Using Gm/Id MethodTwo-Stage Operational Amplifier Design Using Gm/Id Method
- Advanced Current Mirrors and Opamps: Hossein ShamsiAdvanced Current Mirrors and Opamps: Hossein Shamsi
- Random Offset CMOS IC Design CU Lecture Art Zirger PDFRandom Offset CMOS IC Design CU Lecture Art Zirger PDF
- Lab 2: Common Source Amplifier With Resistor Load and Source DegenerationLab 2: Common Source Amplifier With Resistor Load and Source Degeneration
- Channel Length Modulation: A Second Order Effect of MOSFETChannel Length Modulation: A Second Order Effect of MOSFET
- A High Performance CMOS Band - Gap Reference Circuit DesignA High Performance CMOS Band - Gap Reference Circuit Design
- 04 - Comparators and Offset Cancellation Techniques04 - Comparators and Offset Cancellation Techniques
- 4.chapter4 CMOS Multistages Differential Amplifier4.chapter4 CMOS Multistages Differential Amplifier
- Design and Analysis of Low Power Bandgap Voltage ReferenceDesign and Analysis of Low Power Bandgap Voltage Reference
- V I (IN Ma) : Figure 1: Setup For NMOS Characteristics Table 1: Vds VS ID Data at VGS 5 VoltsV I (IN Ma) : Figure 1: Setup For NMOS Characteristics Table 1: Vds VS ID Data at VGS 5 Volts
- Compact Power Efficient Rail To Rail in Out Op Amp RonCompact Power Efficient Rail To Rail in Out Op Amp Ron
- Integrated Circuits: Multistage Amplifiers, Current Sources & Current MirrorsIntegrated Circuits: Multistage Amplifiers, Current Sources & Current Mirrors