0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsLS9 5
LS9 5
Uploaded by
sinned68Mollusks are soft-bodied organisms classified in the phylum Mollusca. They are divided into 8 classes and most have a hard shell covering their head, foot, and mass of tissue containing organ systems. Mollusks live in water or on land. Examples of classes include gastropods like snails and slugs which use their foot for movement, bivalves like clams and mussels which have two shells and filter feed, and cephalopods like squids and octopuses which have tentacles and use jet propulsion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
LS9 5
LS9 5
Uploaded by
sinned680 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageMollusks are soft-bodied organisms classified in the phylum Mollusca. They are divided into 8 classes and most have a hard shell covering their head, foot, and mass of tissue containing organ systems. Mollusks live in water or on land. Examples of classes include gastropods like snails and slugs which use their foot for movement, bivalves like clams and mussels which have two shells and filter feed, and cephalopods like squids and octopuses which have tentacles and use jet propulsion.
Original Title
LS9-5
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Mollusks are soft-bodied organisms classified in the phylum Mollusca. They are divided into 8 classes and most have a hard shell covering their head, foot, and mass of tissue containing organ systems. Mollusks live in water or on land. Examples of classes include gastropods like snails and slugs which use their foot for movement, bivalves like clams and mussels which have two shells and filter feed, and cephalopods like squids and octopuses which have tentacles and use jet propulsion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageLS9 5
LS9 5
Uploaded by
sinned68Mollusks are soft-bodied organisms classified in the phylum Mollusca. They are divided into 8 classes and most have a hard shell covering their head, foot, and mass of tissue containing organ systems. Mollusks live in water or on land. Examples of classes include gastropods like snails and slugs which use their foot for movement, bivalves like clams and mussels which have two shells and filter feed, and cephalopods like squids and octopuses which have tentacles and use jet propulsion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
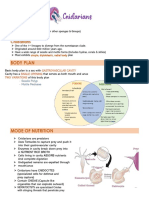
LIFE SCIENCE 9-5 What are mollusks?
OBJ: Describe the features of mollusks.
Give examples of the different classes of mollusks.
I. MOLLUSKS = soft bodied organism.
- classified in the phyla MOLLUSCA.
- divided into 8 classes.
- most are covered with a hard shell.
- have a head, foot, and mass of tissue that contains
well-developed organ systems.
- excretory, reproductive, heart
- live on land or in water.
MANTLE = thin membrane that covers a mollusk’s organs.
- in some mollusks, the mantle forms the shell.
II. SNAILS & SLUGS - class GASTROPODA
- foot is used for movement.
RADULA = rough, tongue-like organ of the snail.
- used to scrape food from plants and rocks.
III. TWO-SHELLED - in the class BIVALVIA
MOLLUSKS - have two-part shells
Example - clams, oysters, and mussels
- strong muscles hold the shells closed.
FILTER FEEDING - feed by taking in water through special tubes.
- organisms come in, are trapped, and digested.
IV. MOLLUSKS with - from the class CEPHALOPODA.
TENTACLES - very complex brains.
- excellent eyesight.
- tentacles are used for movement and feeding.
- each tentacle has suction cups capturing prey.
Jet propulsion - taking in water and squirting it back out, causes the
cephalopod to move quickly.
Example - squids and octopuses
You might also like
- Morphology and Physiology of Living Things: National Diploma in Science Laboratory TechnologyDocument99 pagesMorphology and Physiology of Living Things: National Diploma in Science Laboratory Technologyogbonna ebuka innocent100% (1)
- Phylum Mollusca (Notes)Document1 pagePhylum Mollusca (Notes)Kristine Claire AlberioNo ratings yet
- ZOOLOGY - CHAPTER 11 - Report Outline 10th EditionDocument6 pagesZOOLOGY - CHAPTER 11 - Report Outline 10th EditionmariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - ZoologyDocument3 pagesChapter 9 - ZoologyAngel MerilloNo ratings yet
- MollusksDocument10 pagesMolluskskeremNo ratings yet
- Lecture Phylum MolluscaDocument33 pagesLecture Phylum MolluscaTania Pal ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate Lab 6Document17 pagesInvertebrate Lab 6Shaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Body Plan: EumetazoansDocument6 pagesBody Plan: EumetazoansAljhon ClementeNo ratings yet
- Sokoine University of Agriculture: ClassificationDocument75 pagesSokoine University of Agriculture: ClassificationToke SadockNo ratings yet
- Report About Reptiles & Proferan_by_EEDDocument5 pagesReport About Reptiles & Proferan_by_EEDE DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Invertebrate & Vertebrate Animals - PrintDocument35 pages5 - Invertebrate & Vertebrate Animals - PrintInmaculada Campos RomeroNo ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCE 9-6 What Are Echinoderms?: OBJ: List Common Characteristics of Echinoderms. Name Some EchinodermsDocument1 pageLIFE SCIENCE 9-6 What Are Echinoderms?: OBJ: List Common Characteristics of Echinoderms. Name Some Echinodermssinned68No ratings yet
- InvertebratesDocument46 pagesInvertebratesIvy Mae ArnaizNo ratings yet
- Mollusca ClassificationDocument12 pagesMollusca ClassificationRobin MathewNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia General Characteristics:: NematocystsDocument1 pageKingdom Animalia General Characteristics:: NematocystsMARICEL CANTARANo ratings yet
- Science Report (Kingdom Animalia)Document10 pagesScience Report (Kingdom Animalia)Alechsys HermenegildoNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - MolluscaDocument9 pagesLab 2 - MolluscaCherry Mae AdlawonNo ratings yet
- Exam Additional NotsDocument31 pagesExam Additional NotsG MugzNo ratings yet
- CHP 26 - Mollusks lp5Document12 pagesCHP 26 - Mollusks lp5api-259321090No ratings yet
- Experiment: 2. Study of Museum SpecimensDocument12 pagesExperiment: 2. Study of Museum SpecimensAishwarya MohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - MolluscsDocument38 pagesChapter 7 - MolluscschristianNo ratings yet
- Animals 1Document2 pagesAnimals 1alxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- LS9 4Pg1Document1 pageLS9 4Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- A1.3b Chordata (Handout) - 2018Document3 pagesA1.3b Chordata (Handout) - 2018Wayne DayataNo ratings yet
- Domain Eukarya - InvertebratesDocument26 pagesDomain Eukarya - InvertebratesRhianne Mae RoblesNo ratings yet
- Classifying AnimalsDocument4 pagesClassifying AnimalsmipascuNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No.10 Animal Diversity: Table 1 Illustrated Sponges ClassDocument9 pagesWorksheet No.10 Animal Diversity: Table 1 Illustrated Sponges ClassKhan Hayudini SaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 ReviewDocument1 pageChapter 30 Reviewapi-444439435No ratings yet
- Marine Animals Sponge & CnidariaDocument16 pagesMarine Animals Sponge & Cnidariayousifshli0No ratings yet
- UNIT-25 (Taxonomy Invertebrates and Vertebrates)Document25 pagesUNIT-25 (Taxonomy Invertebrates and Vertebrates)c r e a m p i eNo ratings yet
- Gen Zoo ReviewerDocument29 pagesGen Zoo ReviewerCherryNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture Summary - Introduction On InvertebratesDocument4 pages1st Lecture Summary - Introduction On InvertebratesJenan Usman JalilNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 5Document8 pagesBZ Lab 5Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Akmal Zaidan G. - 2003432 - MolluskDocument7 pagesAkmal Zaidan G. - 2003432 - MolluskAKMAL ZAIDANNo ratings yet
- Mosquito Life Cycle: Culex, Culiseta, and Anopheles Lay Their Eggs On Water While Aedes Lay Their Eggs OnDocument4 pagesMosquito Life Cycle: Culex, Culiseta, and Anopheles Lay Their Eggs On Water While Aedes Lay Their Eggs OnMaizatulAkmaImaNo ratings yet
- 11.4 Animal Kingdom PDFDocument23 pages11.4 Animal Kingdom PDFPinakiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. InvertebratesDocument8 pagesUnit 5. InvertebratesYolanda Fernández VelascoNo ratings yet
- Sci KingdomsDocument6 pagesSci KingdomsClaude de alger ObeliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 MollusksDocument8 pagesChapter 27 MollusksTasyalizt NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Animals SLK 6 Grade 6Document9 pagesClassification of Animals SLK 6 Grade 6Winnie Queeny S. QuetuaNo ratings yet
- MolluskDocument3 pagesMolluskJane ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2bDocument2 pagesMODULE 2bFeliza Mae BoquecosaNo ratings yet
- Platy HelminthesDocument8 pagesPlaty HelminthesDave RapaconNo ratings yet
- Inbound 9220116336929812395Document12 pagesInbound 9220116336929812395Cezar Ian ZafraNo ratings yet
- Biol 1002 Exam2 NotesDocument21 pagesBiol 1002 Exam2 NotesJashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- BTM 111 22Document24 pagesBTM 111 22Toke SadockNo ratings yet
- Exercise-__-Diversity-of-Animal-Life-Bio-41A-1Document11 pagesExercise-__-Diversity-of-Animal-Life-Bio-41A-1Van RadazaNo ratings yet
- g6q2 Week 6 Science PptDocument137 pagesg6q2 Week 6 Science PptCarmelle MorillaNo ratings yet
- Animals 2: Mollusc A, Ec Hi No Derma Ta, A Rthrop OdaDocument8 pagesAnimals 2: Mollusc A, Ec Hi No Derma Ta, A Rthrop OdaKaylaniNo ratings yet
- Plus 2 PracticalDocument16 pagesPlus 2 Practicaljayantaroy783360No ratings yet
- Phylum Mollusca - Mollusks - Includes Snails, Slugs, ClamsDocument21 pagesPhylum Mollusca - Mollusks - Includes Snails, Slugs, ClamsDestha RamadantyNo ratings yet
- Phylum Mollusca: "Soft-Bodied Invertebrate Animal, Usually With An External Shell"Document18 pagesPhylum Mollusca: "Soft-Bodied Invertebrate Animal, Usually With An External Shell"Jofren MorenoNo ratings yet
- Phylum Mollusca: Mantle-Is A Dorsal Glandular Fold of The Body Wall. It Is Thick and Muscular and Encloses MantleDocument5 pagesPhylum Mollusca: Mantle-Is A Dorsal Glandular Fold of The Body Wall. It Is Thick and Muscular and Encloses MantleFrenzes PadabocNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7. Phylum CnidariaDocument6 pagesLesson 7. Phylum CnidariaAndreaaAAaa TagleNo ratings yet
- MollusksDocument40 pagesMollusksAlyssa LingamenNo ratings yet
- Phylum Echinodermata TransesDocument2 pagesPhylum Echinodermata TransesMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- INVERTEBRATESDocument16 pagesINVERTEBRATESCaerwyn SevidalNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates 5º PrimariaDocument14 pagesInvertebrates 5º PrimariaIsa AlvNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes (Flatworm)Document11 pagesPlatyhelminthes (Flatworm)Ana Melisa DorueloNo ratings yet
- The Book of Shells: Containing the Classes Mollusca, Conchifera, Cirrhipeda, Annulata, and CrustaceaFrom EverandThe Book of Shells: Containing the Classes Mollusca, Conchifera, Cirrhipeda, Annulata, and CrustaceaNo ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg2Document1 pageLS10 5Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 8Document1 pageLS10 8sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 6clozeDocument1 pageLS10 6clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg1ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 7Pg1Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- Laguna Hills El Toro Capo Valley Woodbridge: Pacifica Newport Harbor Irvine UniversityDocument1 pageLaguna Hills El Toro Capo Valley Woodbridge: Pacifica Newport Harbor Irvine Universitysinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 6Document1 pageLS10 6sinned68No ratings yet
- Offensve Line Blocking ProgressionDocument9 pagesOffensve Line Blocking Progressionsinned68No ratings yet
- East Los Angeles College Pass ProtectionDocument15 pagesEast Los Angeles College Pass Protectionsinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg2Document1 pageLS10 7Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg1Document1 pageLS10 5Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg1Document1 pageLS10 7Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 5Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 5Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 7Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 7Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8Document1 pageLS9 8sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 4clozeDocument1 pageLS10 4clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg2Document1 pageLS10 1Pg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg2ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 1Pg2Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg1ClozeDocument1 pageLS10 1Pg1Clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 10clozeDocument1 pageLS9 10clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 9clozeDocument1 pageLS9 9clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 9Document1 pageLS9 9sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 10Document1 pageLS9 10sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8ClozePg1Document1 pageLS9 8ClozePg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCE 9-6 What Are Echinoderms?: OBJ: List Common Characteristics of Echinoderms. Name Some EchinodermsDocument1 pageLIFE SCIENCE 9-6 What Are Echinoderms?: OBJ: List Common Characteristics of Echinoderms. Name Some Echinodermssinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 7clozeDocument1 pageLS9 7clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS10 1Pg1Document1 pageLS10 1Pg1sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 8ClozePg2Document1 pageLS9 8ClozePg2sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 7Document1 pageLS9 7sinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 5clozeDocument1 pageLS9 5clozesinned68No ratings yet
- LS9 4Pg2Document1 pageLS9 4Pg2sinned68No ratings yet