IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet
IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
kapilCopyright:
Available Formats
IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet
IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
kapilOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet
IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
kapilCopyright:
Available Formats
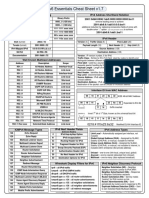
IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet v1.
4
IPv6 Addressing
IPv6 Address Shorthand Notation
Address Type
IPv6 Notation
Binary Prefix
Unspcecified
::/128
0000...0 (128 bits)
remove leading zeros to achieve
Loopback
::1/128
0000...1 (128 bits)
2001:db8:6:1ab5:0:0:0:ba11
Multicast
ff00::/8
1111 1111 xxxx xxxx
additional reduction by replacing consecutive fields of zeros with
double-colon :: option (can only be done once) to achieve
Link-Local
fe80::/10
1111 1110 1000 0000
2001:db8:6:1ab5::ba11
Global Unicast (GUA)
2000::/3
001x xxxx xxxx xxxx
fc00::/7
1111 110x xxxx xxxx
Unique Local (ULA)
6to4 (tunnel)
2002::/16
Teredo (tunnel)
IPv4-Mapped IPv6
Documentation
2001:0db8:0006:1ab5:0000:0000:0000:ba11
IPv6 Header
Version (4)
2001:0000::/32
Traffic Class (8)
Payload Length (16)
0:0:0:0:0:ffff:a.b.c.d
Flow Label (20)
Next Header (8)
2001:0db8::/32
Destination Address (128)
Well Known Multicast Addresses
Address
Description
Scope
ff01::1
All Nodes Address
Interface-local
ff02::1
All Nodes Address
Link-local
ff01::2
All Routers Address
Interface-local
ff02::2
All Routers Address
Link-local
ff05::2
All Routers Address
Site-local
ff02::4
DVMRP Routers
Link-local
ff02::5
OSPF IGP Drothers
Link-local
ff02::6
OSPF IGP DRs
Link-local
ff02::9
RIPng Routers
Link-local
ff02::a
EIGRPv6 Routers
Link-local
ff02::c
Microsoft SSDP
Link-local
ff02::d
All PIM Routers
Link-local
ff02::12
VRRPv3
Link-local
ff02::16
All MLDv2 Routers
Link-local
ff02::1:2
DHCPv6 Servers/Agents
Link-local
ff05::1:3
DHCPv6 Servers/Agents
Site-local
Version : IP version number, 6 for IPv6
Traffic Class : Similar to IPv4 ToS field. Used by nodes to identify and
distinguish between different classes or priorities of IPv6 packets
Flow label : Used by a source to label sequences of packets for which it
requests special handling by the IPv6 routers
Payload Length : Length of the IPv6 payload (may also include
extension headers)
Next Header : Identifies the type of header following the IPv6 header
Hop Limit : Decremented by 1 by every router that forwards the packet
Source Address : IPv6 address of the originator of the packet, will be a
unicast address
Destination Address : IPv6 address of the intended recipient or final
destination of the packet, can be unicast or multicast address
Interface ID from MAC Address
00
ff0x::101
Network Time Protocol
Variable
ff02::1:ffxx:xxxx
Solicited-Node Address
Link-local
00
18
18
41
41
ff
00000000
00000010
02
23
fe
6a
32
23
6a
Echo Request
129
Echo Reply
130
Multicast Listener Query
131
Multicast Listener Report
132
Multicast Listener Done
133
Router Solicitation
134
Router Advertisement
135
Neighbor Solicitation
136
Neighbor Advertisement
137
Redirect Message
138
Router Renumbering
139
ICMP Node Information Query
140
ICMP Node Information Response
143
Multicast Listener Report (MLDv2)
144
Home Agent Discovery Request
145
Home Agent Discovery Reply
146
Mobile Prefix Solicitation
147
Mobile Prefix Advertisement
32
Expanded to EUI-64
Invert 7th bit of 1st Byte, known as the universal/local bit
18
41
IPv6 Next Header Fields
ICMPv6 Message Types
IEEE 48-bit MAC Address
0xfffe inserted
ff
fe
23
6a
0218:41ff:fe23:6a32
128
Hop Limit (8)
Source Address (128)
32
Modified EUI-64 Interface ID
IPv6 Address Types
(Extension Headers)
IPv6 Hop-byHop Option
41
IPv6 encapsulation
43
Routing Header for IPv6
44
Fragment Header for IPv6
50
Encap Security Payload (ESP)
51
Authentication Header (AH)
59
No Next Header for IPv6
60
Destination Options for IPv6
Link-Local Automatically assigned per interface, not
routable
Global Unicast Address (GUA) Assigned by SLAAC,
Stateful (DHCPv6), or manual, routable to Internet
Unique Local Address (ULA) Assigned by SLAAC,
Stateful (DHCPv6), or manual, not routable to Internet, is
routable within enterprise (like private address)
Unicast one-to-one (link-local, unique local, global)
Anycast one-to-nearest (allocated from Unicast)
Multicast one-to-many (also replaces broadcast)
Wireshark Display Filters for IPv6
ipv6 all IPv6 traffic
icmpv6 all IPv6 ICMPv6 traffic
dhcpv6 all DHCPv6 traffic
icmpv6.type == 133 all router solicitations
icmpv6.type == 134 all router advertisements
icmpv6.type == 135 all neighbor solicitations
icmpv6.type == 136 all neighbor advertisements
icmpv6.type == 137 all redirect messages
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol
Neighbor Solicitation (NS) Neighbor
address resolution (similar to IPv4 ARP)
Neighbor Advertisement (NA) Response
to Neighbor Solicitation requests
Router Solicitation (RS) Sent by nodes
looking for IPv6 routers on-link
Router Advertisements (RA) Sent
periodically by routers and in response to RS
Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) Sent
to own Solicited-Node Multicast Address
IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet v1.4 2015 Jeffrey L. Carrell
You might also like
- Lab Cisco CCNADocument4 pagesLab Cisco CCNAJuruma_No ratings yet
- Cisco RouterDocument5 pagesCisco RouterDeepak Rawat0% (1)
- Lab 7 Configure Static Routing Cisco RouterDocument8 pagesLab 7 Configure Static Routing Cisco RouterAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMDocument23 pages3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMvincent67% (3)
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Ccna 3 Ex - OspfDocument25 pagesCcna 3 Ex - OspfJosueChalenSarezNo ratings yet
- 3 Router Igrp Configuration LabDocument5 pages3 Router Igrp Configuration LabSiddhant SingalNo ratings yet
- 3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocument17 pages3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationLarry Abisaí0% (2)
- How To Troubleshoot ISDN On PRIDocument11 pagesHow To Troubleshoot ISDN On PRIDavi Sadaseeven SaminadenNo ratings yet
- Symantec DLP 14.5 Install Guide WinDocument154 pagesSymantec DLP 14.5 Install Guide WinPedro HernandezNo ratings yet
- SWITCH Training VTP Lab PDFDocument16 pagesSWITCH Training VTP Lab PDFMilli YeshiwasNo ratings yet
- LabDocument9 pagesLaborgyplusNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions 200-301: Cisco Certified Network AssociateDocument15 pagesExam Questions 200-301: Cisco Certified Network AssociateTaiiaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Vs SiemensDocument31 pagesCisco Vs SiemensDavid HicksNo ratings yet
- VoIP in RouterOS PDFDocument15 pagesVoIP in RouterOS PDFNaz LunNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Basic Skills: Configuring The Router From A PCDocument8 pagesCisco IOS Basic Skills: Configuring The Router From A PCjagan36No ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide and CCIE Lab BookingDocument5 pagesStep by Step Guide and CCIE Lab BookingCông SơnNo ratings yet
- 016 Enabling RIPDocument20 pages016 Enabling RIPBAHRAIN1967No ratings yet
- Mitel Communication DirectorDocument179 pagesMitel Communication DirectorjulioborrerojrNo ratings yet
- AB - CCNA Voice Quick Reference GuideDocument31 pagesAB - CCNA Voice Quick Reference GuideSrdjan MilenkovicNo ratings yet
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument9 pages5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesJozeph Abod67% (3)
- Yeastar S20 Voip PBX: Installation GuideDocument12 pagesYeastar S20 Voip PBX: Installation GuideShariff SharinhoNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument9 pagesSpanning Tree ProtocolRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- New Examzoon Cisco-300-320 Dumps - Designing Cisco Network Service ArchitecturesDocument7 pagesNew Examzoon Cisco-300-320 Dumps - Designing Cisco Network Service ArchitecturesRyan V. NicholsonNo ratings yet
- YEASTAR MyPBX Standard V6&V7 Administrator Guide enDocument219 pagesYEASTAR MyPBX Standard V6&V7 Administrator Guide enRaúl A. Morales R.No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lab 4-1 - Implement Spanning Tree Protocols: TopologyDocument46 pagesChapter 4 Lab 4-1 - Implement Spanning Tree Protocols: TopologyHollman JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lab01 Basic VOIP ConfigurationDocument8 pagesLab01 Basic VOIP ConfigurationMohammed ElmadaniNo ratings yet
- Senior Network and Security Engineer With 5+ Years of ExpDocument3 pagesSenior Network and Security Engineer With 5+ Years of Expkurban2015No ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Callmanager Bulk Administration Guide 5.0 (2) : Corporate HeadquartersDocument424 pagesCisco Unified Callmanager Bulk Administration Guide 5.0 (2) : Corporate HeadquartersJhob HernándezNo ratings yet
- Switch Firmware Upgrade Process For PTP Issue Switches.Document2 pagesSwitch Firmware Upgrade Process For PTP Issue Switches.vivek bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Cisco Pre-Sales Engineer or Cisco Consultant or Cisco Voice EngiDocument9 pagesCisco Pre-Sales Engineer or Cisco Consultant or Cisco Voice Engiapi-79193168No ratings yet
- Ccna 200-301 - 2Document52 pagesCcna 200-301 - 2Wahyudi YusufNo ratings yet
- Mitel AdministrationGuide UCA v5Document109 pagesMitel AdministrationGuide UCA v5JohnTNo ratings yet
- OSPF On 3 RoutersDocument8 pagesOSPF On 3 RoutersepocableoilsNo ratings yet
- Switch Commands by SubjectDocument11 pagesSwitch Commands by SubjectpippendanceNo ratings yet
- ACL Practice Lab 1Document8 pagesACL Practice Lab 1LGBT Việt NamNo ratings yet
- MiCollab Client Admin Guide 7.2Document230 pagesMiCollab Client Admin Guide 7.2Taron RamsayNo ratings yet
- Step-by-Step Guide For Setting Up A PPTP-based Site-to-Site VPN Connection in A Test LabDocument33 pagesStep-by-Step Guide For Setting Up A PPTP-based Site-to-Site VPN Connection in A Test LabSiyad Siddique100% (3)
- Symantec Data Loss Prevention Installation Guide For Linux: Last Updated: September 24, 2020Document105 pagesSymantec Data Loss Prevention Installation Guide For Linux: Last Updated: September 24, 2020artreisNo ratings yet
- Yahia CVDocument2 pagesYahia CVawaissadiq45No ratings yet
- 5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMDocument12 pages5.1.5.8 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features - ILMرافد البركي75% (12)
- Yeastar P-Series PBX System Datasheet enDocument7 pagesYeastar P-Series PBX System Datasheet enYemen BrokerNo ratings yet
- 9.3.2.10 Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1 InstructionsDocument4 pages9.3.2.10 Configuring Extended ACLs Scenario 1 InstructionsJorge JuarezNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: Basic Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesLab 1: Basic Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDat LCNo ratings yet
- Ramana Network Engineer & System Administrator CVDocument6 pagesRamana Network Engineer & System Administrator CVKiran Varma100% (1)
- Avaya Application Solutions:: IP Telephony Deployment GuideDocument492 pagesAvaya Application Solutions:: IP Telephony Deployment GuideniteshshahNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 - BGPDocument2 pagesCase Study 2 - BGPClaudio Cabello SotoNo ratings yet
- Symantec DLP 15.5 System Requirements GuideDocument75 pagesSymantec DLP 15.5 System Requirements GuideSebastian PittaNo ratings yet
- Cisco First Hop Redundancy Protocol by TanmoyDocument38 pagesCisco First Hop Redundancy Protocol by TanmoyBIG BILLION DREAMSNo ratings yet
- Router Configuration NotesDocument12 pagesRouter Configuration Notesduke_doNo ratings yet
- SIP Trunking Configuration Guide For Cisco Unified C Ommunications Manager 10.5.1.10000-7 (CUCM) Version With Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE)Document61 pagesSIP Trunking Configuration Guide For Cisco Unified C Ommunications Manager 10.5.1.10000-7 (CUCM) Version With Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE)drineNo ratings yet
- MPLS VPN TroubleshootingDocument58 pagesMPLS VPN Troubleshootinghem777No ratings yet
- Lab 3.2.1 Configuring EIGRP Routing: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesLab 3.2.1 Configuring EIGRP Routing: ObjectiveguijjouNo ratings yet
- Ipv6-Extended Cheat SheetDocument1 pageIpv6-Extended Cheat SheetNeal TrieberNo ratings yet
- IPv6Document35 pagesIPv6Ngọc HuyNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet V1.7: 0218:41Ff:Fe23:6A32Document1 pageIpv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet V1.7: 0218:41Ff:Fe23:6A32Patricio Quegles100% (1)
- Clase 8. IPv6 AddressDocument65 pagesClase 8. IPv6 Addressdsbc0601No ratings yet
- IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet v1.3 PDFDocument1 pageIPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet v1.3 PDFIsaque ProfetaNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Cheat SheetVinoth RNo ratings yet