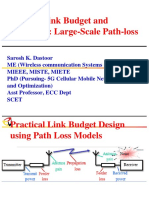
Assignment 2 PDF
Uploaded by
roop sagarAssignment 2 PDF
Uploaded by
roop sagarASSIGNMENT: 2
Mobile Radio Channels (EE665)
1. Assuming a receiver is located 10 km from a 50 W transmitter. The carrier frequency is 1900 MHz,
free space propagation is assumed, Gt 1 , Gr 2, find:
a) The power at the receiver
b) The magnitude of the E- field at the receiver antenna.
c) The open circuit rms voltage applied to the receiver input assuming that the receiver antenna
has a purely real impedance of 50 and is matched to the receiver.
d) Find the received power at the mobile using the two ray ground reflection model assuming
the height of the transmitting antenna is 50 m, receiving antenna is 1.5 m above the ground,
and the ground reflection is -1.
2. For the two- ray model with transmitter- receiver separation d = 100 m, hT 100 metres, and hR 2
metres, find the delay spread between the two signals.
3. Consider an indoor wireless LAN with carrier frequency 900MHz, cells of radius 10 m, and nondirectional antenna. Under the free space path loss model, what transmit power is required at the
access point in order for all terminals within the cell to receive a minimum power of 10 W? How
does this change if the system frequency is 5 GHz.
4. Show that the Brewster angle ( case where v = 0 ) is given by i where
Sin i
r2 r
r2 1
5. (a) Explain the advantages and disadvantages of the 2- ray ground reflection model in the analysis of
path loss.
(b) In the following cases, tell whether the 2 ray model could be applied, and explain why or why
not:
hT 35 m
hR 3 m d = 250 m
hT 30 m
hR 1.5 m d = 450 m
(c) What insight does the 2 ray model provide about large scale path loss that was disregarded
when cellular systems used very large cells?
6. In a 2- ray ground reflection model, assume that must be kept below 6.261 radians for phase
cancellation reasons. Assuming a receiver height of 2 m, and given a requirement that i be less
than 5 , what are the minimum allowable values for the T-R separation distance and the height of the
transmitter antenna? The carrier frequency is 900 MHz. Refer to Figure P3.3.
7. In the 2- ray path loss model with 1 , derive an appropriate expression for the location of the
signal nulls at the receiver.
You might also like
- Wireless Communication by Rappaport Problem Solution Manual0% (1)Wireless Communication by Rappaport Problem Solution Manual7 pages
- Assignment: 1: School of Electronics Engineering ECE4009-Wireless and Mobile CommunicationsNo ratings yetAssignment: 1: School of Electronics Engineering ECE4009-Wireless and Mobile Communications2 pages
- 14EC2044 - Fundamentals of Wireless Communication - Question BankNo ratings yet14EC2044 - Fundamentals of Wireless Communication - Question Bank7 pages
- Study of Ofdm Transmitter and Receiver: A Project Report OnNo ratings yetStudy of Ofdm Transmitter and Receiver: A Project Report On28 pages
- Wireless Communications TLSingal Chapter 03 Self Test Quiz With AnswersNo ratings yetWireless Communications TLSingal Chapter 03 Self Test Quiz With Answers7 pages
- Short Answer Questions: Unit - I: Amplitude ModulationNo ratings yetShort Answer Questions: Unit - I: Amplitude Modulation8 pages
- Telecommunication Networks 15B11EC611: Dr. Bhagirath Sahu Assistant Professor, JIIT, NoidaNo ratings yetTelecommunication Networks 15B11EC611: Dr. Bhagirath Sahu Assistant Professor, JIIT, Noida21 pages
- Digital Communications Questions and Answers PDF FreeNo ratings yetDigital Communications Questions and Answers PDF Free2 pages
- Solutions To Analytical Problems: Chapter 6 Frequency Management and Channel AssignmentNo ratings yetSolutions To Analytical Problems: Chapter 6 Frequency Management and Channel Assignment14 pages
- Lecture07 Microwave Network Analysis ProblemsNo ratings yetLecture07 Microwave Network Analysis Problems6 pages
- Satellite Link Design: Joe Montana IT 488 - Fall 2003No ratings yetSatellite Link Design: Joe Montana IT 488 - Fall 200346 pages
- Satellite Communications Chapter 3:satellite Link Design100% (5)Satellite Communications Chapter 3:satellite Link Design38 pages
- Ec3501 Wireless Communication 1560801494 WC Lab ManualNo ratings yetEc3501 Wireless Communication 1560801494 WC Lab Manual24 pages
- Chapter-4 Mobile Radio Propagation Large-Scale Path Loss100% (2)Chapter-4 Mobile Radio Propagation Large-Scale Path Loss106 pages
- Physical Modeling of Wireless Channels (Slides)No ratings yetPhysical Modeling of Wireless Channels (Slides)37 pages
- Unit 5 - Wireless Communication Notes - FINALNo ratings yetUnit 5 - Wireless Communication Notes - FINAL10 pages
- Model Questions_Mobile Communication (1)No ratings yetModel Questions_Mobile Communication (1)3 pages