NCP Pcap
NCP Pcap
Uploaded by
Gacutan JonathanCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Pcap
NCP Pcap
Uploaded by
Gacutan JonathanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
NCP Pcap
NCP Pcap
Uploaded by
Gacutan JonathanCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
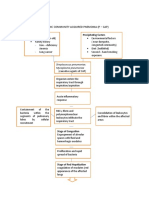
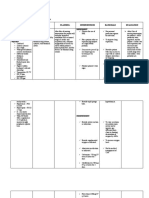
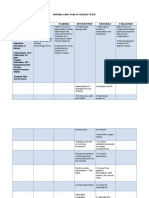
Patients Name: Baby M Medical Diagnosis: Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired gas exchange r/t collection of secretions affecting oxygen exchange across alveolar membrane. Short-term Goal: at the end of my shift, the patients condition will lighten and minimal formation of secretion will only occur. Long-term Goal: after hospital confinement patient will be free of secretion enabling condition of oxygen exchange normally. ASSESSMENT >S: Nahihirapan huminga ang baby ko dahil sa ubo as verbalized by the mother. >O: Dyspnea Tachycardia V/S taken as follows: T: 36.7 C P: 128 R: 40 BP: none taken DIAGNOSIS >Impaired gas exchange INFERENCE >Pneumonia is an excess of fluid in the lungs resulting from an inflammatory process. The inflammation is triggered by many infectious organisms and by inhalation of irritating agents. Infectious pneumonias are categorized as community acquired (CAP) or hospital acquired (nosocomial) depending on where the patient was exposed to infectious agent. PLANNING >After 4 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will achieve timely resolution of current infection without complications. INTERVENTION >Assess respiratory rate, depth and ease. RATIONALE >Manifestation of respiratory distress is dependent on indicative of the degree of lung involvement and underlying general status. >High fever greatly increases metabolic demands and oxygen consumption and alters cellular oxygenation. >Promotes expectoration, clearing or infection. >Reduces likelihood of exposure to other infectious pathogens. >Isolation technique may be desired to prevent spread and protect patient from other infectious process. EVALUATION >After 4 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will achieve timely resolution of current infection without complications.
>Monitor body temperature.
>Elevate head of the bed and change position frequently. >Limit visitors as indicated.
>Institute isolation precaution.
>Suction as indicated.
>Assist with nebulizer treatments.
>Monitor effectiveness of antimicrobial therapy.
>Administer antimicrobials as prescribed.
>Stimulates cough or mechanically clears airway in patient who is unable to cough effectively. >Facilitates liquefaction and removal of secretions. >Signs of improvement in condition should occur within 24- 48 hrs. >These drugs are used to combat most of the microbial pneumonias.
You might also like
- PCAP Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPCAP Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYCHRISTIE MONTANO33% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan - CAP-MRDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan - CAP-MRCarmela Mabel Ansay Principe100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Community Acquired Pneumoniaderic92% (50)
- Pathophysiology of Pediatric Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Pediatric Community Acquired PneumoniaKeij AranetaNo ratings yet
- NCP-Toddler-Tonsillitis & Lactose IntoleranceDocument9 pagesNCP-Toddler-Tonsillitis & Lactose Intolerancetinatin98975% (4)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia. FinalDocument48 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia. FinalHampson Malekano100% (4)
- Workbook - Brian TracyDocument183 pagesWorkbook - Brian TracyShakes SM100% (15)
- Dosage Calculations Cheat Sheet GOOD TOOLDocument12 pagesDosage Calculations Cheat Sheet GOOD TOOLCamille Jean100% (10)
- A Case of PCAP-C (Individual INP)Document44 pagesA Case of PCAP-C (Individual INP)Preiane PayladoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaAdrian Mallar100% (9)
- PCAP-c Group A NiggasDocument39 pagesPCAP-c Group A NiggasJenny YenNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia (PCAP)Document24 pagesPediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia (PCAP)deejayseroje93% (29)
- PCAP CDocument42 pagesPCAP CJenny YenNo ratings yet
- NCP PcapDocument1 pageNCP PcapLhexie CooperNo ratings yet
- Case Study PN Pcap C FinalDocument50 pagesCase Study PN Pcap C FinalKimberly Milaran33% (3)
- Cap NCPDocument6 pagesCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- Nursing Process of PneumoniaDocument5 pagesNursing Process of Pneumoniatin2x061275% (8)
- NCP PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Pneumonia_garonNo ratings yet
- NCP PcapDocument2 pagesNCP PcapKenj Pereña100% (1)
- NCP PCAP CDocument4 pagesNCP PCAP CRio Bonifacio100% (3)
- PCAP CPDocument14 pagesPCAP CPMikael R. SmileNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For PcapDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For PcapMadsNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan: Demonstrate Pursed-Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing To The PatientDocument4 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan: Demonstrate Pursed-Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing To The PatientKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco100% (1)
- NCP For Community Acquired PnuemoniaDocument7 pagesNCP For Community Acquired PnuemoniaAshley Gaton Alindogan100% (1)
- Case Study PCAPDocument32 pagesCase Study PCAPJohn Paul Andrade100% (1)
- Pcap C CaseDocument81 pagesPcap C CaseAyaBasilio70% (10)
- Goal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionDocument4 pagesGoal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- NCP PediaDocument2 pagesNCP PediaJacinth Rizalino40% (5)
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Pcap PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPcap PathophysiologyAko Gle C Mariz80% (10)
- Cap NCPDocument2 pagesCap NCPkyshb100% (2)
- Neonatal Pneumonia Is: Assessment NSG Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal/Objectives Nsg. Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument12 pagesNeonatal Pneumonia Is: Assessment NSG Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal/Objectives Nsg. Intervention Rationale EvaluationPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPRyan John Bito-onNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaMarla NavarroNo ratings yet
- NCP Cap MRDocument2 pagesNCP Cap MREngely Mercader100% (1)
- D5 0.3%Document1 pageD5 0.3%Aloyan Rose Joy0% (1)
- NCP DengueDocument4 pagesNCP DengueAriaNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Case StudyDocument26 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Case StudyMenggay SanDiego67% (9)
- Pneumonia NCPDocument7 pagesPneumonia NCPitsmeaya100% (3)
- FDAR Acute PainDocument1 pageFDAR Acute PainJayson OlileNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceArt Christian Ramos100% (1)
- NCP For PCAPCDocument6 pagesNCP For PCAPCEnrique Lu100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosi S Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosi S Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMikael R. SmileNo ratings yet
- NCP Baby DDocument3 pagesNCP Baby DYna LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Nicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)Document3 pagesNicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)lorence_cachoNo ratings yet
- NCP NminDocument5 pagesNCP NminkrizziajNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- BronchiectasisDocument40 pagesBronchiectasisyana jaeNo ratings yet
- AgentDocument5 pagesAgentChiara Kay LaguismaNo ratings yet
- PNEUMONIADocument24 pagesPNEUMONIAwheeyycoldandhot55No ratings yet
- Woman With PneumoniaDocument9 pagesWoman With PneumoniaNohaira SADANGNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesSAMPLE NCP For Pneumoniakana_mercado100% (6)
- Post-Operative Nursing CareDocument11 pagesPost-Operative Nursing CareScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The BronchiDocument9 pagesChronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchiinamaliit100% (1)
- NCP TBDocument6 pagesNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument15 pagesPneumoniaLeina PrasadNo ratings yet
- Case Study Chapter 20 (Oct 16th)Document2 pagesCase Study Chapter 20 (Oct 16th)Anz MingNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeIsabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia GhuDocument29 pagesPneumonia Ghun0ire.h3ck3rNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Clients With COPD: - Initiate Infusion of Intravenous Antibiotic As PrescribedDocument3 pagesNursing Management of Clients With COPD: - Initiate Infusion of Intravenous Antibiotic As PrescribedNiña AngNo ratings yet
- Social Lifestyle Questionnaire: Use This Key To Rate Your AnswersDocument1 pageSocial Lifestyle Questionnaire: Use This Key To Rate Your AnswersGacutan JonathanNo ratings yet
- TAHBSO Lab ResultDocument3 pagesTAHBSO Lab ResultGacutan JonathanNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument38 pagesDenguevoruganty_vvsNo ratings yet
- Related Study InternationalDocument4 pagesRelated Study InternationalGacutan JonathanNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)Document6 pagesNCP For Acute Gastroenteritis (Pediatric)abcel76% (21)
- Abo Typing Discrepancies: Rene Jesus Alfredo R. Dinglasan, RMTDocument14 pagesAbo Typing Discrepancies: Rene Jesus Alfredo R. Dinglasan, RMTdirenjan100% (1)
- NEUR200 - PSYC202 Syllabus Fall'21Document11 pagesNEUR200 - PSYC202 Syllabus Fall'21inuyasha62No ratings yet
- Radhika Sharma Medical Reports and Prescription (BA LLB Sem 5, 02719103821)Document5 pagesRadhika Sharma Medical Reports and Prescription (BA LLB Sem 5, 02719103821)radhikachitvansharma1No ratings yet
- HF and Your Ejection Fraction Explained - 230207 - 183606Document2 pagesHF and Your Ejection Fraction Explained - 230207 - 183606Siddharth RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Summary of ResearchDocument7 pagesSummary of Researchapi-549189480No ratings yet
- Differential FOrce Method of Orthodontic Treatment (1977) (Dragged) 3Document1 pageDifferential FOrce Method of Orthodontic Treatment (1977) (Dragged) 3MADANo ratings yet
- 8F7047F11260 PDFDocument5 pages8F7047F11260 PDFabatabrahamNo ratings yet
- Jurnal T 5Document4 pagesJurnal T 5Komang SuartikaNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Midterm (Mirul)Document4 pagesCase Scenario Midterm (Mirul)NMDNMSSDNo ratings yet
- Mental Health in The COVID-19 Pandemic: W. Cullen, G. Gulati and B.D. KellyDocument2 pagesMental Health in The COVID-19 Pandemic: W. Cullen, G. Gulati and B.D. KellyEbru EvogluNo ratings yet
- Lachesis. From Materia Medica by John Henry Clarke. HomeopathyDocument12 pagesLachesis. From Materia Medica by John Henry Clarke. Homeopathyfausto omioNo ratings yet
- De-Escalation TechniquesDocument26 pagesDe-Escalation TechniquesCarolina PradoNo ratings yet
- Self DeclarationDocument1 pageSelf DeclarationManasi SawairamNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Remodeling of Human Extraction SocketsDocument10 pagesModeling and Remodeling of Human Extraction SocketsRachmawati Dian PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction To Pathophysiology-1Document24 pagesUnit-1 Introduction To Pathophysiology-1balouchu180No ratings yet
- Esthetic Crown Lengthening With FlaplessDocument7 pagesEsthetic Crown Lengthening With FlaplessRamona elenaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Guidelines For The Management of Thyroid StorDocument41 pages2016 Guidelines For The Management of Thyroid StorStella Gracia OctaricaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microscopy 1 Test Review and Case Studies Jethro Rada JRDocument34 pagesClinical Microscopy 1 Test Review and Case Studies Jethro Rada JRAlex LiganNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology of Caffeine: FurtherDocument15 pagesClinical Pharmacology of Caffeine: FurtherLoredana Veronica ZalischiNo ratings yet
- Myths-And-Fallacies - 2 7 2020Document18 pagesMyths-And-Fallacies - 2 7 2020Kharlm Therese Tan50% (2)
- Med Research Imposter Syndrome Proposal CsuDocument38 pagesMed Research Imposter Syndrome Proposal CsuRuth Anne Sharmaine SantosNo ratings yet
- Thí sinh làm bài vào Phiếu trả lời. - Thí sinh không sử dụng bất kỳ tài liệu gì, kể cả từ điển. - Giám thị không giải thích gì thêmDocument5 pagesThí sinh làm bài vào Phiếu trả lời. - Thí sinh không sử dụng bất kỳ tài liệu gì, kể cả từ điển. - Giám thị không giải thích gì thêmfarm 3 chi diNo ratings yet
- SOP For ASF NRC On PigDocument16 pagesSOP For ASF NRC On PigPallab BorahNo ratings yet
- Sodio OralDocument6 pagesSodio OralBoris QuelcaNo ratings yet
- SGOD PERSONNEL COORDINATORSHIP - SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTS - DESIGNATIONS (Responses)Document1 pageSGOD PERSONNEL COORDINATORSHIP - SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTS - DESIGNATIONS (Responses)Jofit DayocNo ratings yet
- Benefits of DanceDocument28 pagesBenefits of DanceMarColmenar100% (1)
- Candidates Mcqs Pathology Week 11: 1 JF A BDocument3 pagesCandidates Mcqs Pathology Week 11: 1 JF A Bمجتبى علي0% (1)
- Tehmina SharifDocument24 pagesTehmina Sharifaaaliya7777No ratings yet