0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
429 viewsNicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)
Nicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)
Uploaded by
lorence_cacho · Monitor vital signs every 4 hours. · Monitor oxygen saturation level. · Monitor intake and output. · Monitor respiratory effort and breath sounds. · Monitor temperature. · Monitor for signs of complications. · Report any changes in condition to the physician.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Nicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)
Nicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)
Uploaded by
lorence_cacho0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
429 views3 pages · Monitor vital signs every 4 hours. · Monitor oxygen saturation level. · Monitor intake and output. · Monitor respiratory effort and breath sounds. · Monitor temperature. · Monitor for signs of complications. · Report any changes in condition to the physician.
Original Title
NICU-NCP-(NEO.PNIA)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
· Monitor vital signs every 4 hours. · Monitor oxygen saturation level. · Monitor intake and output. · Monitor respiratory effort and breath sounds. · Monitor temperature. · Monitor for signs of complications. · Report any changes in condition to the physician.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
429 views3 pagesNicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)
Nicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)
Uploaded by
lorence_cacho · Monitor vital signs every 4 hours. · Monitor oxygen saturation level. · Monitor intake and output. · Monitor respiratory effort and breath sounds. · Monitor temperature. · Monitor for signs of complications. · Report any changes in condition to the physician.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
LORMA COLLEGES Carlatan, City of San Fernando, La Union Ilocos Training Regional Medical Center Neonatal Intensive Care
Unit 3-11 Shift Clinical Instructor: Mr. Marlon Ligas
NURSING CARE PLAN
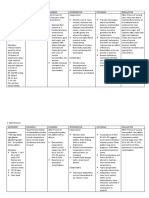
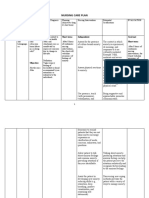
Name of patient: Baby Boy Orine Diagnosis: Pneumonia ASSESSMENT Subjective: Nahihirapan huminga ang baby ko dahil sa ubo as verbalized by the mother. Objective: Dyspnea Tachycardia V/S taken as follows: T: 37.7 P: 125 R: 55 Monitor body temperature. High fever greatly increases metabolic demands and oxygen consumption and alters DIAGNOSIS Impaired gas exchange r/t collection of secretions affecting oxygen exchange across alveolar membrane. PLANNING After 4 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will achieve timely resolution of current infection without complications. Student Nurse: Cacho, Lorence Vincent L. Date: November 14, 2011 IMPLEMENTATION Independent: Assess respiratory rate, depth and ease. RATIONALE Manifestation of respiratory distress is dependent on indicative of the degree of lung involvement and underlying general status. EVALUATION After 4 hours of nursing intervention s, the patient will achieve timely resolution of current infection without complications.
cellular oxygenation. Elevate head of the bed and change position frequently. Limit visitors as indicated. Promotes expectoration, clearing or infection. Reduces likelihood of exposure to other infectious pathogens. Isolation technique may be desired to prevent spread and protect patient from other infectious process. Stimulates cough or mechanically clears airway in patient who is unable to cough effectively.
Institute isolation precaution.
Suction as indicated.
Assist with nebulizer treatments.
Facilitates liquefaction and removal of secretions. Signs of improvement in condition should occur within 24- 48 hrs. These drugs are used to combat most of the microbial pneumonias.
Monitor effectiveness of antimicrobial therapy. Collaborative: Administer antimicrobials as prescribed
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNo ratings yet
- SP CSDocument4 pagesSP CSKhan HansNo ratings yet
- Ppe4 Reflection AssignmentDocument11 pagesPpe4 Reflection Assignmentapi-318846856100% (1)
- NCP For PediaDocument10 pagesNCP For PediavonkinoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 pagesNCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisAya BolinasNo ratings yet
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- BFCDocument8 pagesBFCIrene GunongNo ratings yet
- NCP PcapDocument2 pagesNCP PcapGacutan Jonathan89% (27)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP AgeDocument1 pageNCP AgecaressmeNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument5 pagesNCP ProperRustan FrozenNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox NCPDocument3 pagesChicken Pox NCPrshin96No ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalHelen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- College of Nursing Allied Health SciencesDocument38 pagesCollege of Nursing Allied Health SciencesLemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- NCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioDocument5 pagesNCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioRio BonifacioNo ratings yet
- NCP Meningitis Sure NaniDocument2 pagesNCP Meningitis Sure NaniARISNo ratings yet
- Cue Problem Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesCue Problem Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJanyn Abella ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPLeolene Grace BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanKenneth NovenoNo ratings yet
- NCP Klippel Trenaunay SyndromeDocument3 pagesNCP Klippel Trenaunay SyndromePaola Marie VenusNo ratings yet
- NCP Otitis MediaDocument4 pagesNCP Otitis MediaZillah KorrenNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPSarah Younes AtawnehNo ratings yet
- EsophagomyotomyDocument3 pagesEsophagomyotomySamVelascoNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- NCP TB MeningitisDocument1 pageNCP TB MeningitisMark Adrian D. DizorNo ratings yet
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument11 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryAyah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Preterm Labor - Prevention of DeliveryDocument10 pagesPreterm Labor - Prevention of DeliveryLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Npi NCMHDocument6 pagesNpi NCMHJoshua DauzNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu Sukardi100% (1)
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit BatuDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Batumecz26No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- NCP of Difficulty of BreathingDocument2 pagesNCP of Difficulty of BreathingMan GatuankoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07No ratings yet
- Simple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaDocument1 pageSimple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaJason A. AdoyoganNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 LRDR For PrintDocument2 pagesNCP 2 LRDR For PrintGeorge PandaNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNcp-Impaired Gas ExchangeSJ Abunda0% (1)
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 pagesNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan JaundiseDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Jaundisearif aimanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeNo ratings yet
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Document2 pagesCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16No ratings yet
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDocument3 pagesAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesDrug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Nabalaka Ko Short Term: Independent: Goal Met Short TermDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Nabalaka Ko Short Term: Independent: Goal Met Short Termgeng gengNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objective S Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objective S Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationJhun GonzalesNo ratings yet
- NCP For COPDDocument3 pagesNCP For COPDcy belNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- NCP PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Pneumonia_garonNo ratings yet