Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Uploaded by
Jansen Arquilita RiveraCopyright:
Available Formats
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Uploaded by
Jansen Arquilita RiveraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Uploaded by
Jansen Arquilita RiveraCopyright:
Available Formats
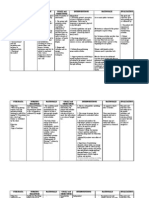
Assessment Subjective: Maglisod ko ug ginhawa, as verbalized by the patient.
Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to decreased lung expansion
Nursing Goal Within 1 hour of nursing intervention the patient will exhibit normal breathing pattern
Nursing Intervention -Assess respiratory rate depth and effort
Rationale -Respiratory rate and rhythm changes such as increased in respiratory rate with a decreased tidal volume are early warning signs of impending respiratory difficulties
Outcome Criteria Patient maintains effective breathing, as evidence by respiratory rate 12 to 20 breaths/min and clear and clear and equal lung sounds bilaterally. Chest Radiograph shows lungs fully expanded
Actual Evaluation
Objective: Dyspnea Nasal cannula Usedof accessory muscle: elevation of shoulder Nasal flaring RR-24bpm
-Auscultate lungs for area of diminished or absent lung sounds -Asses for pain
-This may indicate partial or complete collapse of the lung -Pain can result in shallow breathing
-Secure connections
-A loose connection can allow air entry and positive
Pressure in the intrapleural space, resulting in further lung collapse
-Intact water seal
-This prevents air entry into the intrapleural space
-Fluctuation of fluid caused by pressure changes in the intrandexpirationapleural space during inspiration
-Cessation of fluctuating of fluid can indicate lung re-expansion or, if abrupt can indicate clog or kinked tube -Bubbling indicartes air removal from the intrapleural space, especially during expiration or coughing. Cessation of bubbling can indicate lung re expansion. Continuous bubbling can indicate air leak
-Check for bubbles
within the patients chest within the system
-Assess feeling of dypnea or shortness of breath
-This may indicate hypoxia
-Assess vital signs, including temperature
-Tachycardia is common during hypoxia
-Asses mentation for signs of hypoxia and hypercapnia
-Restlessness, inappropriateness, lethargy and confusion may result with haypoxia and hypercapnia
-Assess chest drainage system
-An intact system reduces the risk for infection
-Assess chest tube drainage for increased or purulent drainage
-This may represent infection and require culturing
-Assess chest tube insertion site for reddened wound edges.
-This may be early signs of infection
-Assess WBC Count
-Rising WBC count indicates the bodys effort to combat pathogens
-Administer supplemental oxygen as required
-This maintains oxygen 90% for greater adequate oxygenations
-Elevate head of the bed
-This enhances lung expansion
-Use incentive spirometry as needed
-This enhances breathing there by decreasing Potential for atelectasis
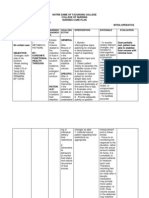
Assessment Su Mosakit akong kilid (duol sa akong tube inig ubo nako,
Nursing Diagnosis Acute pain related to trauma
Nursing Goals Short Term Goals Patient will report pain less than 3 on 0-10 scale. Patients vital signs will be within normal limits. Long Term Goal Patient will be free of pain
Nursing Intervention -Assess pain characteristics: quality (sharp, burning); severity (0 -10 scale); location; onset (gradual, sudden); duration (how long); precipitating or relieving factors.
Rationale -A good assessment of pain will help in the treatment and ongoing management of pain.
Outcome Criteria
Actual Evaluation
-Monitor vital signs.
-Tachycardia, elevated blood pressure, tachypnea and fever may accompany pain.
-Assess for nonverbal signs of pain.
-Some patients may verbally deny pain when it is still present. Restlessness, inability to focus, frowning, grimacing and
guarding of the area may be nonverbal signs of acute pain.
-Give analgesics as ordered and evaluate the effectiveness
-Narcotics are indicated for severe pain. Pain medications are absorbed and metabolized differently in each patient, so their effectiveness must be assessed after administration.
-Assess the patients expectations of pain relief.
-Some patients are content with reduction in pain, others may expect complete elimination. This effects the patients perception of the effectiveness of treatment
-Assess for complications to analgesics, especially respiratory depression.
- Excessive sedation and respiratory depression are severe side effects that need reported immediately and may require discontinuation of medication. Urinary retention, nausea/vomiting and constipation can also occur with narcotic use and need reported and treated.
- Anticipate the need for pain relief and respond immediately to complaints of pain.
- The most effective way to deal with pain is to prevent it. Early intervention can decrease the total amount of analgesic required. Quick response decreases the patients anxiety
regarding having their needs met and demonstrates caring.
- Eliminate additional stressors when possible. Provide rest periods, sleep and relaxation
- Outside sources of stress, anxiety and lack of sleep all may exaggerate the patients perception of pain
- Institute nonpharmacological approached to pain (detraction, relaxation exercises, music therapy, etc.)
- Nonpharmacological approaches help distract the patient from the pain. The goal is to reduce tension and thereby reduce pain
You might also like
- 2024 Course Outline SIA 2Document3 pages2024 Course Outline SIA 2CAPINPIN SerelynNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Pulmonary EmbolismDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Pulmonary EmbolismPui_Yee_Siow_6303100% (10)
- Amanda AquiliniDocument2 pagesAmanda Aquilinineoclint0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument37 pagesNursing Care Planpia lestrange100% (6)
- Appendectomy/ Appendicitis Case StudyDocument15 pagesAppendectomy/ Appendicitis Case StudyApril94% (31)
- 795B Master (v9)Document40 pages795B Master (v9)Rodrigo Bravo Rodrigo BravoNo ratings yet
- Verizon Internet Gateway Arc Xci55ax User GuideDocument167 pagesVerizon Internet Gateway Arc Xci55ax User GuideJordan OxleyNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument79 pagesChest PhysiotherapyRabab Ahmed100% (2)
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentNinaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPLeolene Grace BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis86% (36)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument16 pagesNursing DiagnosisSi Bunga JonquilleNo ratings yet
- Ige IfetayoDocument4 pagesIge Ifetayoaransiolakayodeisrael2020No ratings yet
- Comprehensive ExaminationDocument8 pagesComprehensive ExaminationAnonymous dquW2YmO7No ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ComplicationDocument12 pagesCardiac ComplicationResa ShotsNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPBeverLyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of COPDDocument6 pagesNursing Management of COPDZulyca JamalulNo ratings yet
- NCP SDocument8 pagesNCP SMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- NCP For CHFDocument2 pagesNCP For CHFMayet De Castro Lejano100% (1)
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Assessment of The Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesAssessment of The Respiratory SystemKhanh LeNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nanda DiagnosesDocument4 pagesAsthma Nanda DiagnosesZinya Robinson100% (1)
- Case Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesCase Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Unit 14Document21 pagesUnit 14jcrd7vdmksNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument17 pagesNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationApol Pen67% (3)
- Nursing Process of PneumoniaDocument5 pagesNursing Process of Pneumoniatin2x061275% (8)
- Drug Study and NCP!Document8 pagesDrug Study and NCP!Abegail Abaygar100% (1)
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPRyan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNo ratings yet
- 4 NCP's FinalDocument9 pages4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN On LeptospirosisDocument8 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN On LeptospirosisRosalie Valdez Espiritu78% (9)
- Arowosafe ToluDocument5 pagesArowosafe Toluaransiolakayodeisrael2020No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDebby MalleonNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document12 pagesNCP 1Izabela UyNo ratings yet
- NCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesNCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputErienne Lae Manangan - CadalsoNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- COPD Acute Management ABCDEDocument11 pagesCOPD Acute Management ABCDESS100% (1)
- Copd NCPDocument16 pagesCopd NCPSuperMaye100% (1)
- Ventilated Patient ProjectDocument15 pagesVentilated Patient ProjectRohan ThoratNo ratings yet
- AssesmentDocument9 pagesAssesmentmizrypNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPkimchi girl0% (1)
- Pneumonia: Case PresentationDocument12 pagesPneumonia: Case PresentationgelaneNo ratings yet
- Nursing diagnosis of a patient with pneumothorax حلاDocument5 pagesNursing diagnosis of a patient with pneumothorax حلاShatha IkhmaiesNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Care Essentials in Ventilated PtsDocument3 pagesTop 10 Care Essentials in Ventilated PtsAdel HamadaNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentEjoy Rayos AdawagNo ratings yet
- Lab Workbook - Assignment 8 RespiratoryDocument14 pagesLab Workbook - Assignment 8 RespiratoryromanparadizeNo ratings yet
- Segui NCPDocument4 pagesSegui NCPRichelle TalaguitNo ratings yet
- Adult NursingDocument13 pagesAdult Nursing00060651No ratings yet
- Nursing Skills and InterventionsDocument96 pagesNursing Skills and InterventionsGraceNo ratings yet
- NCP For COPD and Acute PainDocument7 pagesNCP For COPD and Acute PainLenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Oxygen Therapy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Oxygen Therapy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Aspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseFrom EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Complaint HomicideDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Complaint HomicideJansen Arquilita Rivera65% (17)
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument5 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Case Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxDocument8 pagesCase Study Nursing Diagnosis of PneumothoraxJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Findings For Segmental Femural FractureDocument3 pagesAssessment Findings For Segmental Femural FractureJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument5 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Management For RHDDocument4 pagesMedical-Surgical Management For RHDJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cephalocaudal AssessmentDocument3 pagesCephalocaudal AssessmentJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- Components of Living Values: CooperationDocument3 pagesComponents of Living Values: CooperationJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- NCP For Ruptured AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP For Ruptured AppendicitisJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Dengue CaseDocument12 pagesDengue CaseJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Principles and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological ChemistryDocument40 pagesPrinciples and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological ChemistryJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Area Assessed Actual FindingsDocument7 pagesArea Assessed Actual FindingsJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- ACS350 Technical CatalogueDocument20 pagesACS350 Technical CatalogueJNo ratings yet
- Computer GenerationsDocument13 pagesComputer GenerationsMuhammad BILALNo ratings yet
- Design of Heat Recovery System For Dye Effluent in Textile IndustriesDocument5 pagesDesign of Heat Recovery System For Dye Effluent in Textile IndustriesdevilnishNo ratings yet
- Dahua Marketing Material Guide - 20220418Document91 pagesDahua Marketing Material Guide - 20220418Antonio FormicaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Circuits Lab: Experiment #3 Low Pass and High Pass Filters I ObjectivesDocument9 pagesIntegrated Circuits Lab: Experiment #3 Low Pass and High Pass Filters I Objectivesanimesh pariharNo ratings yet
- Podcats ScriptDocument3 pagesPodcats ScriptMina DedijerNo ratings yet
- Cognitive and Psychopathological Aspects of Ehlers DanlosDocument5 pagesCognitive and Psychopathological Aspects of Ehlers DanlosKarel GuevaraNo ratings yet
- AAU Vision 2050 Booklet PDFDocument108 pagesAAU Vision 2050 Booklet PDFShivam GajjarNo ratings yet
- Young Muslims Personal Collective Development PlanDocument24 pagesYoung Muslims Personal Collective Development PlanAmericans for Peace and ToleranceNo ratings yet
- Dirty Old Man's Cookbook - Honest JohnDocument124 pagesDirty Old Man's Cookbook - Honest JohnRichard Ranges GarciaNo ratings yet
- CA Clarity PPM For Agile Development ProjectsDocument11 pagesCA Clarity PPM For Agile Development ProjectsDhaval ShahNo ratings yet
- Siebel Systems Case Analysis: Group 10 - Section BDocument7 pagesSiebel Systems Case Analysis: Group 10 - Section BAmit RajNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting 309Document19 pagesCost Accounting 309Vamba S. KamaraNo ratings yet
- Mix Design of Bituminous Concrete by Bailey MethodDocument6 pagesMix Design of Bituminous Concrete by Bailey Methodanon_370570207No ratings yet
- Sec 1403Document138 pagesSec 1403Sumit MamgainNo ratings yet
- HRD Individual Assignment (P20285)Document4 pagesHRD Individual Assignment (P20285)Manikho KaibiNo ratings yet
- Animals Card Game Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 2952Document3 pagesAnimals Card Game Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 2952Ana-Maria MileaNo ratings yet
- Schools Division Office of Isabela: 306117-San Mateo General Comprehensive High SchoolDocument2 pagesSchools Division Office of Isabela: 306117-San Mateo General Comprehensive High SchoolRoger Labuguen Anoling100% (1)
- In - Text Citations - 2021Document15 pagesIn - Text Citations - 2021SimaNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary ApproachDocument67 pagesInterdisciplinary ApproachSamyak jaiNo ratings yet
- MAPEH (Music) : Quarter 1 - Module 1: 20 Century Music: Impressionist MusicDocument10 pagesMAPEH (Music) : Quarter 1 - Module 1: 20 Century Music: Impressionist MusicAlbert Ian CasugaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Premolars1Document54 pagesMaxillary Premolars1Parthvi ParmarNo ratings yet
- Sabp G 008Document78 pagesSabp G 008Mahesh Kumar100% (1)
- Eman Barakat Abu HmeesDocument172 pagesEman Barakat Abu HmeesHama HamaNo ratings yet
- Modern Control System EKT 308Document30 pagesModern Control System EKT 308Solehah Md HashimNo ratings yet
- Dignity in Movement 1 E IRDocument346 pagesDignity in Movement 1 E IRAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- CCNP 350-601 Data Centre Course OutlineDocument3 pagesCCNP 350-601 Data Centre Course OutlineSubasish BiswalNo ratings yet