NCP Acute Pain
NCP Acute Pain
Uploaded by
Sj 斗力上Copyright:
Available Formats
NCP Acute Pain
NCP Acute Pain
Uploaded by
Sj 斗力上Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
NCP Acute Pain
NCP Acute Pain
Uploaded by
Sj 斗力上Copyright:
Available Formats
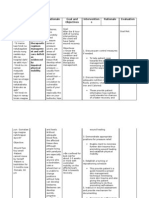
Nursing Problems Acute pain related to disease process compression or destruction of nerve tissue infiltration of nerves or their vascular
supply, obstruction of nerve pathway, and inflammation. As evidence by -Reports of pain Pain scale 5/10
Analysis A person with cancer often experiences pain of discomfort for numerous reasons. Mush patients will feel pain of varying duration at same point in their cancer experience. Tumors cause pain by invading, destroying or compressing the affected area. Common cause of pain in cancer patients by tumor are: 1.Release of pain causing substances produced by the tumor or by the immune system in response to the presence of tumor 2. invasion of tumor in to bone, nerves, pleura/peritoneum, viscera, blood vessels muscous membranes and soft tissue. Source: pg. 306-307 handbook of oncology nursing by Johnson & Gross third edition
Goals/Objectives Nursing Interventions After 1 hour of nursing intervention the patients pain scale will decrease from 5/10 to 1/10 Objectives: 1)To asses etiology/precipitating contributory factors A . determine pain history,( (location, frequency, duration, intensity using a rating scale of 0-10) B. determine timing and precipitants of break through pain when using aroundthe-clock agents, when their oral, IV, topical transmucosal, epidual or patch medications
Ratioanale
Evaluation After 1hour of nursing intervention was the patient able to decrease from 5/10 to 1/10? Yes___ No__ Why?___
Information provides baseline data to evaluate need for, and effectiveness of, interventions. Pain may occur near the end of the dose interval, indicating need for higher dose or shorter dose interval pain may be precipitated by identifiable triggers, or occur spontaneously reviving the use of short half-life agent for rescue or supplement doses
Promotes relaxation
2. to assist client to explore methods for alleviation/ control of pain
A. Provide nonpharmacological measures such as massage repositioning and back rub: as well a diversional activities such as music, reading and watching tv. B.Encourage the use of stress management skill sand complimentary therapies such as relaxation techniques, visualization guided imagery, bio-feedback, laughter, music, aromatherapy and therapeutic touch. C.evaluate pain relief at regular intervals. Adjust medication regimen as necessary D.Inform client and SO of the expected therapeutic effects and discuss management of side effects
and helps refocus attention. Enables client to participate actively in non-drug treatment of pain and enhance sense of control pain produces stress and, in conjunction with muscle tension and internal stressors, increases clients focus on self, which in turn increases the level of pain. Goals in maximum pain control and minimum interference with ADLS This information helps establish realistic expectations and confidence in own ability to handle what happens. A wide range of analgesics maybe employed RTC mange pain.
E.Administer analgesics as indicated
To prevent fatigue 3.To promote wellness A.Encourage adequate rest periods B.Review ways to lessen pain (nonpharmacologic therapies) Promotes relaxation and relieves pain
Source: page 854-856, (nursing care plans: guidelines for individualized client care across lifespan by doenges, moorhouse $ murr 8TH edition)
You might also like
- Giles Gyer, Jimmy Michael, Ben Tolson-Dry Needling For Manual Therapists - Points, Techniques and Treatments, Including Electroacupuncture and Advanced Tendon Techniques-Singing Dragon (2016)Document261 pagesGiles Gyer, Jimmy Michael, Ben Tolson-Dry Needling For Manual Therapists - Points, Techniques and Treatments, Including Electroacupuncture and Advanced Tendon Techniques-Singing Dragon (2016)NICOLÁS ANDRÉS AYELEF PARRAGUEZ95% (22)
- 7s Strength SpeedDocument52 pages7s Strength SpeedFelipe Rodrigues de Araújo100% (3)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPLornz E. Cantos100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Self Care DeficitDocument2 pagesSelf Care DeficitSj 斗力上75% (4)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJoenna GaloloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanJohn Paul Delos Santos100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument20 pagesNursing Care PlanAgustian Ian S0% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Document2 pagesImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- NCP Sleep DisturbanceDocument1 pageNCP Sleep DisturbanceIsrael Soria EsperoNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 VertigoDocument2 pagesNCP 2 VertigobananakyuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Process (NCP) Stress Overload PrepartumDocument2 pagesNursing Care Process (NCP) Stress Overload PrepartumFrederene JavelonaNo ratings yet
- Ncp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDDocument4 pagesNcp-For-Sle-Fatigue-And-Pain EDITEDJordz Placi100% (1)
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocument2 pagesNCP Disturbed Body ImageDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue Integrity BurnDocument1 pageImpaired Tissue Integrity BurntabaloveNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanAldrein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalI Am SmilingNo ratings yet
- NCP AnxietyDocument1 pageNCP AnxietyGrace MellaineNo ratings yet
- Biopsy: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesBiopsy: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNo ratings yet
- NCP For InfectionDocument4 pagesNCP For InfectionJames LozanoNo ratings yet
- Objectiv ES Rationa LE: Evaluatio NDocument3 pagesObjectiv ES Rationa LE: Evaluatio NAnonymous FgT04krgym100% (1)
- Enhanced CopingDocument3 pagesEnhanced CopingAnn OgoloNo ratings yet
- Cad NCPDocument1 pageCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresNo ratings yet
- Nursing DX: Acute Pain Related To Surgical Manipulation (Laminectomy) As Manifested by Reports of Pain On The Lumbar Area Rated As 7/10Document1 pageNursing DX: Acute Pain Related To Surgical Manipulation (Laminectomy) As Manifested by Reports of Pain On The Lumbar Area Rated As 7/10YESSAMIN GUADIZ100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveAngelaNo ratings yet
- N C P For Perioperative Pts.Document4 pagesN C P For Perioperative Pts.Daisy Palisoc100% (2)
- Risk For InjuryDocument4 pagesRisk For InjuryJanina Patricia BuddleNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationVecky TolentinoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute PainsAm_300% (1)
- NCP Acute PainDocument5 pagesNCP Acute PainMicah Jonah Elicaño0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- NCP Severe HypocalcemiaDocument4 pagesNCP Severe HypocalcemiaMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument1 pageAcute Pain NCPJed AvesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNo ratings yet
- NURSING DIAGNOSIS (2) On Pregnant Woman Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING DIAGNOSIS (2) On Pregnant Woman Knowledge Deficitanon_168410816No ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveGaurav Gaikwad100% (3)
- Icu NCPDocument4 pagesIcu NCPdrsabuegNo ratings yet
- NCP AlteredDocument3 pagesNCP AlteredShaira TillahNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Inflammation of Tissues Secondary To AppendicitisRachel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired SkinDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocument5 pagesNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCP Impaired ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired ComfortGia P. de VeyraNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition NCPDocument2 pagesImbalanced Nutrition NCPChryst Louise Saavedra100% (1)
- NCP Template ObDocument7 pagesNCP Template ObMae CeaesarNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument4 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityMarjorie Jofel Cerrudo PaciaNo ratings yet
- Social IsolationDocument2 pagesSocial IsolationFlos Carmeli MontanaNo ratings yet
- NCP - ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentKevin KroytNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute PainDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute PainAJ Tuban Compelio100% (1)
- Multiple MyelomaDocument2 pagesMultiple MyelomaKolin Jandoc100% (1)
- Managing Acute PainDocument2 pagesManaging Acute PainEllmaaanNo ratings yet
- Pain Management DR ColeDocument8 pagesPain Management DR ColeAsep Cloud OvernightNo ratings yet
- Journal On PainDocument5 pagesJournal On PainGeevine CansinoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pain Can Be A Multisystem Disease Nov 23 2013Document3 pagesChronic Pain Can Be A Multisystem Disease Nov 23 2013lauraNo ratings yet
- NCP & Prio!!!Document45 pagesNCP & Prio!!!Sj 斗力上100% (1)
- Ecologic Model COPDDocument2 pagesEcologic Model COPDSj 斗力上No ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan - NasoDocument7 pagesHealth Teaching Plan - NasoSj 斗力上No ratings yet
- Decreased Urine OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Urine OutputSj 斗力上No ratings yet
- "I Can Do All Things Through Christ Who Strengthens Me". Philippians 4:13Document4 pages"I Can Do All Things Through Christ Who Strengthens Me". Philippians 4:13jeanette PradesNo ratings yet
- TNA FORM 1 SampleDocument1 pageTNA FORM 1 SampleRandyl Medina FernandezNo ratings yet
- JessaDocument4 pagesJessaRC CouponNo ratings yet
- Resume: Name: Ni Made SuastiniDocument3 pagesResume: Name: Ni Made Suastiniduz tha100% (1)
- Acupressure Points ForDocument17 pagesAcupressure Points ForAbdul Basith Shaikh100% (1)
- Dead Leg (Quadriceps Contusion)Document12 pagesDead Leg (Quadriceps Contusion)sanalcrazyNo ratings yet
- Botika NG BarangayDocument56 pagesBotika NG Barangaymaryprincessuy100% (3)
- Beauté Aromatique PresentationDocument19 pagesBeauté Aromatique PresentationNazihCosmeticsNo ratings yet
- Signed Off - Beauty Care11 - q1 - m1 - Perform Hand Spa - v3Document34 pagesSigned Off - Beauty Care11 - q1 - m1 - Perform Hand Spa - v3aristotleelparo100% (1)
- Chiropractic Performance Center Massage PaperworkDocument2 pagesChiropractic Performance Center Massage Paperwork25111980No ratings yet
- Cosygirl LocationDocument7 pagesCosygirl Locationmumbai-escortsNo ratings yet
- Wellness Massage Lesson 3 DrapingDocument26 pagesWellness Massage Lesson 3 DrapingVanessa DE GUZMAN100% (1)
- AyurvedaDocument892 pagesAyurvedaPankaj Gupta0% (1)
- Acupressure Workshop HandoutDocument2 pagesAcupressure Workshop HandoutEnergieVerdeNo ratings yet
- Adjust4Sleep BrochureDocument18 pagesAdjust4Sleep BrochureVitabuNo ratings yet
- Welcome Drop ShippingDocument1 pageWelcome Drop ShippingelenaNo ratings yet
- My Spa Therapist CVDocument1 pageMy Spa Therapist CVprincesseddie14No ratings yet
- TM I - Template 2019Document113 pagesTM I - Template 2019Kindly Legarte100% (1)
- July August 2021Document112 pagesJuly August 2021Mskola KarlovacNo ratings yet
- Laniwai Spa PricingDocument2 pagesLaniwai Spa PricingJoseph RamirezNo ratings yet
- Extra Listenings NTE WBDocument5 pagesExtra Listenings NTE WBtesina de doctoradoNo ratings yet
- Golden Oaks The Best Massage Spa in BangaloreDocument7 pagesGolden Oaks The Best Massage Spa in BangaloreyashayraNo ratings yet
- Integrative Pain ManagementDocument18 pagesIntegrative Pain ManagementSarah Coelho HoraNo ratings yet
- European Guidelines For The Management of Chronic Low Back PainDocument109 pagesEuropean Guidelines For The Management of Chronic Low Back PainBeatrice Capelle100% (1)
- Masseuse in Prostitution Final Revised Sep.4,2019Document60 pagesMasseuse in Prostitution Final Revised Sep.4,2019Honey Mae LugatimanNo ratings yet
- Reiki Usui LEVEL 2Document12 pagesReiki Usui LEVEL 2Juana LaxaldeNo ratings yet
- DisclaimerDocument2 pagesDisclaimerAnonymous T9hx3ugNo ratings yet
- Traditional Healing PracticesDocument90 pagesTraditional Healing PracticesAwodele100% (2)