Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co Trimoxazole
Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co Trimoxazole
Uploaded by
Renmico AquinoCopyright:
Available Formats
Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co Trimoxazole
Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co Trimoxazole
Uploaded by
Renmico AquinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co Trimoxazole
Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co Trimoxazole
Uploaded by
Renmico AquinoCopyright:
Available Formats
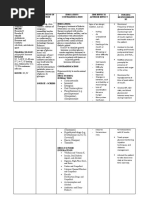
Drug Name
Dosage & Route
Action Fixed combination of sulfamethoxazole (SMZ), an intermediate acting antiinfective sulfonamide, and trimethoprim (TMP), a synthetic antiinfective. Both components of the combination are synthetic folate antagonist antiinfectives. Mechanism of action is principally enzyme inhibition, which prevents bacterial synthesis of essential nucleic acids and proteins.
Indication
Adverse Effects
Contraindication
Nursing Responsibility
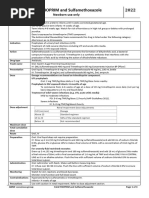
TRIMETHOPRIMSULFAMETHOXAZOLE (TMP-SMZ) (tri-meth'o-prim-sul-fameth'ox-a-zole) Bactrim, Co-Trimoxazole, Septra Classifications: antiinfective; urinary tract agent; sulfonamide
Systemic Infections Adult: PO 160 mg TMP/800 mg SMZ (1 double strength [DS] tablet) q12h IV 810 mg/kg/d TMP divided q612h infused over 6090 min Child: PO >2 mo & <40 kg, 4 mg/kg/d TMP q12h; >40 kg, 160 mg TMP/800 mg SMZ (1 DS tablet) q12h IV >2 mo, 810 mg/kg/d TMP divided q612h infused over 6090 min Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia Adult: IV 20 mg/kg/d TMP divided q6h infused over 6090 min Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia Adult: PO 160 mg TMP/800 mg SMZ q24h Child: PO 150 mg/m2 TMP/750 mg/m2 SMZ b.i.d. 3 consecutive d/wk (max: 320 mg TMP/d) Renal Impairment Clcr 1030 mL/min: reduce dose by 50%; <10 mL/min: reduce dose by 75%
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis, Shigellosis enteritis, and severe complicated UTIs due to most strains of the Enterobacteriaceae. Also children with acute otitis media due to susceptible strains of Haemophilus influenzae, and acute episodes of chronic bronchitis in adults.
Skin: Mild to moderate rashes (including fixed drug eruptions), toxic epidermal necrolysis. GI: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, hepatitis, pseudomembranous enterocolitis, stomatitis, glossitis, abdominal pain. Urogenital: Kidney failure, oliguria, anuria, crystalluria. Hematologic: Agranulocytosis (rare), aplastic anemia (rare), megaloblastic anemia, hypoprothrombinemia, thrombocytopenia (rare). Body as a Whole: Weakness, arthralgia, myalgia, photosensitivity, allergic myocarditis.
Hypersensitivity to TMP, SMZ, sulfonamides, or bisulfites; group A betahemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis; megaloblastic anemia due to folate deficiency; creatinine clearance <15 mL/min; pregnancy (category C), lactation. Not recommended for infants <2 mo.
NURSING IMPLICATIONS Assessment & Drug Effects
Be aware that IV Septra contains sodium metabisulfite, which produces allergictype reactions in susceptible patients: Hives, itching, wheezing, anaphylaxis. Susceptibility (low in general population) is seen most frequently in asthmatics or atopic nonasthmatic persons. Lab tests: Baseline and followup urinalysis; CBC with differential, platelet count, BUN and creatinine clearance with prolonged therapy. Monitor coagulation tests and prothrombin times in patient also receiving warfarin. Change in warfarin dosage may be indicated. Monitor I&O volume and pattern. Report significant changes to forestall renal calculi formation. Also report failure of treatment (i.e., continued UTI symptoms). Older adult patients are at risk for severe adverse reactions, especially if liver or kidney function is compromised or if certain other drugs are given. Most frequently observed: Thrombocytopenia (with concurrent thiazide diuretics); severe decrease in platelets (with or without purpura); bone marrow suppression; severe skin reactions. Be alert for overdose symptoms (no extensive experience has been reported): Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, headache, dizziness, mental depression, confusion, and bone marrow depression.
You might also like
- Hap Id 12534903Document2 pagesHap Id 12534903zan100% (1)
- Biology Investigatory Project (On Eye Diseases)Document22 pagesBiology Investigatory Project (On Eye Diseases)diya65% (49)
- Free Ebook Food As MedicineDocument53 pagesFree Ebook Food As MedicineRudi ArsanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table 3Document5 pagesDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification: IndicationDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Classification: IndicationKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- OxacillDocument1 pageOxacillnerissa_villanueva3523No ratings yet
- Hospice Social Work - Dona J. ReeseDocument26 pagesHospice Social Work - Dona J. ReeseColumbia University Press100% (3)
- Drug Study SulfasalazineDocument2 pagesDrug Study SulfasalazineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument1 pagePhenobarbitalSherwin LauronNo ratings yet
- STREPTOMYCINDocument3 pagesSTREPTOMYCINChad InongNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY SpironolactoneJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- MebendazoleDocument1 pageMebendazolegiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Pyrazinamide Drug StudyDocument1 pagePyrazinamide Drug Studyanreilegarde100% (2)
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 pagesDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PyrazinamideDocument1 pageDrug Study PyrazinamideEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSDocument4 pagesTrimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSAnika Pleños100% (1)
- Drug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CDocument1 pageDrug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CValerie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- THEOPHYLLINE - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTHEOPHYLLINE - Drug Studyeric macabiogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Loop DiureticDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Loop DiureticNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amoxicillin PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument2 pagesCeftriaxoneAnna Larita100% (1)
- PaclitaxelDocument3 pagesPaclitaxelGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Drug Study - KetoprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - KetoprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- BeclomethasoneDocument2 pagesBeclomethasoneDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyGAYOL BREEN IRAH A.No ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyDimple SumarcaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FluconazoleDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Fluconazoleryan100% (1)
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Sulfonamide Drug StudyDocument1 pageSulfonamide Drug StudyMenard VelascoNo ratings yet
- DS - ColchicineDocument2 pagesDS - ColchicineMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeApol PenNo ratings yet
- Nepafenac Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNepafenac Drug StudyLucky Rius0% (1)
- Linezolid (Zyvox)Document1 pageLinezolid (Zyvox)ENo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument3 pagesDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Document2 pagesFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- DemerolDocument2 pagesDemerolCiera YoungNo ratings yet
- Oraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardDocument1 pageOraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument1 pageOMEPRAZOLERheza0% (2)
- Povidone Iodine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPovidone Iodine Drug StudyFaye Andrea Francisco100% (1)
- Duty Drug Study'sDocument7 pagesDuty Drug Study'sGrape Juice0% (1)
- Bicalutamide (Casodex) Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBicalutamide (Casodex) Drug StudyAtteya Mogote AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FORTDocument3 pagesDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline Drugstudy 1Document3 pagesTerbutaline Drugstudy 1Prince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action Indication and Rationale Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration While Taking The DrugsDocument1 pageMechanism of Action Indication and Rationale Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration While Taking The DrugsPeter Emmil GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Brompheniramine Maleate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBrompheniramine Maleate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- FluticasoneDocument4 pagesFluticasonevanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- Drug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- LetrozoleDocument2 pagesLetrozoleunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and GastrointestinalDocument64 pagesDrug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and Gastrointestinaljamaica cabrigaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyZeeham EscalonaNo ratings yet
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug Classificationianecunar100% (2)
- Trimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole ANMFv4 20221020 1Document4 pagesTrimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole ANMFv4 20221020 1petermuigua09No ratings yet
- Pandas Flow ChartDocument2 pagesPandas Flow Chartapi-273553138No ratings yet
- Annexure Panchkarma - 1st EditionDocument228 pagesAnnexure Panchkarma - 1st EditionSmita SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Total Intravenous Anesthesia in ChildrenDocument12 pagesOverview of Total Intravenous Anesthesia in ChildrenJosibel OcantoNo ratings yet
- Materi 4 - MG Enny Mulyatsih - PPNIDocument38 pagesMateri 4 - MG Enny Mulyatsih - PPNIBunga Octavia MayzontikaNo ratings yet
- Session5E-SixWaystoBuildStamina - ManageFatigueDocument4 pagesSession5E-SixWaystoBuildStamina - ManageFatiguegiannidiet100% (1)
- Why Worry? - ExcerptDocument15 pagesWhy Worry? - ExcerptBeyond Words Publishing50% (2)
- Understanding SchizophreniaDocument40 pagesUnderstanding SchizophreniarachelleallauiganNo ratings yet
- SITUATION: Wide Knowledge About The Human Ear, Its Parts and Its Functions Will Help A NurseDocument2 pagesSITUATION: Wide Knowledge About The Human Ear, Its Parts and Its Functions Will Help A NurseWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Id Administering Intradermal InjectionDocument2 pagesId Administering Intradermal InjectiongayleesinfuegoNo ratings yet
- A Psychological Flexibility Based Intervention For Burnout A Randomized PDFDocument16 pagesA Psychological Flexibility Based Intervention For Burnout A Randomized PDFElena StadnikovaNo ratings yet
- Form Obat Berdasarkan GolonganDocument52 pagesForm Obat Berdasarkan GolonganVenny Agustien WulandhariNo ratings yet
- St. Michael's College: Nursing Care Plan FormDocument3 pagesSt. Michael's College: Nursing Care Plan Formacademic purposesNo ratings yet
- PANCE Prep Pearls Valvular Disease PDFDocument4 pagesPANCE Prep Pearls Valvular Disease PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapies For Borderline Personality Disorder A Focused Systematic Review and Meta AnalysisDocument15 pagesPsychotherapies For Borderline Personality Disorder A Focused Systematic Review and Meta AnalysisNicolás Mosso F.No ratings yet
- Dialysis Power PointDocument20 pagesDialysis Power PointJor GarciaNo ratings yet
- 3 Cognitive Behavioural TherapyDocument12 pages3 Cognitive Behavioural TherapyharavindNo ratings yet
- Measurement of The Human Biofield and Other Energetic Instruments (Beverly Rubik)Document35 pagesMeasurement of The Human Biofield and Other Energetic Instruments (Beverly Rubik)THE NIKOLA TESLA INSTITUTE100% (4)
- PHAR505 SyllabusDocument14 pagesPHAR505 SyllabusshopgurlNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Cerebral ResuscitationDocument17 pagesCardiopulmonary Cerebral ResuscitationrizalNo ratings yet
- Beauty Is The BeastDocument11 pagesBeauty Is The BeastnurmeenNo ratings yet
- Non Rigid Connector FPDDocument3 pagesNon Rigid Connector FPDIana RusuNo ratings yet
- Eap - Dins - List 2Document58 pagesEap - Dins - List 2Jenny JeongNo ratings yet
- Acute Interstitial NephritisDocument29 pagesAcute Interstitial NephritisRonnie AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Pet BrochureDocument20 pagesPet BrochureSheikh Hasnain AliNo ratings yet
- B.Pharm. Semester-VI (C.B.S.) Examination Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry-Ii Paper-2Document1 pageB.Pharm. Semester-VI (C.B.S.) Examination Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry-Ii Paper-2Nadeem SheikhNo ratings yet
- The-Journal-of-Clinical-Pharma-2021-Smith-MDMAE28090Assisted-Psychotherapy-for-Treatment-of-Posttraumatic-Stress-Disorder-Document9 pagesThe-Journal-of-Clinical-Pharma-2021-Smith-MDMAE28090Assisted-Psychotherapy-for-Treatment-of-Posttraumatic-Stress-Disorder-anton.klarenNo ratings yet